16 September 2020
36213
0
4.1 out of 5
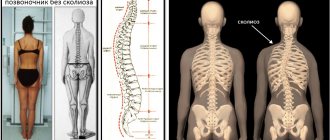
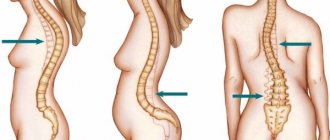
S-shaped scoliosis is the second most severe type of spinal curvature in the direct projection. It is characterized by the formation of two differently directed bending arcs, one of which is the main one, and the second is compensatory, i.e., formed in response to the formation of the first. Thus, S-shaped scoliosis differs from C-shaped scoliosis, in which the main curve is located in the thoracic spine. In an effort to restore stability and the vertical axis of the body, compensatory mechanisms are activated, resulting in the formation of a second arch with a bend in the opposite direction.
The pathology develops slowly, without pronounced symptoms, so it is most often discovered during a preventive medical examination. At the same time, S-shaped scoliosis can cause significant harm to the body and cause displacement of internal organs, which will be accompanied by severe pain and the inability to remain in an upright position for a long time. Therefore, the disease must be detected as early as possible and measures taken immediately to eliminate it.
Most often, S-shaped scoliosis is found in children and adolescents 8-16 years old and in older people who already had minor spinal deformities.
Reasons for development
The main reason for the development of S-shaped scoliosis is genetic predisposition. And its formation can be determined by a lot of different factors, each of which boils down to the fact that too much or uneven load is placed on the spine. Therefore, with the initial formation of a scoliotic arch in the lumbar region as a result of the action of compensatory mechanisms, over time a second arch will form in the thoracic spine or even invade the cervical spine.
Such processes pose a rather serious threat, as they entail a change in the position of all surrounding anatomical structures, including the ribs. Therefore, if left untreated, S-shaped scoliosis can easily provoke disturbances in the functioning of the heart, lungs and other internal organs, as well as a decrease in the quality of blood circulation. And if, as a result of curvature of the spine, the spinal roots passing through the natural openings of the vertebrae are also pinched, this will also lead to the addition of radicular syndrome. It is manifested by severe pain, disturbances in sensitivity and mobility of the corresponding parts of the body, as well as disruption of the innervation of certain organs, which will also lead to the development of unfavorable organic changes in them.
Most often, pathology occurs in children and adolescents precisely because the spine continues to form until about 20 years of age, i.e., until this age it remains quite plastic. Therefore, various types of influences can lead to its curvature, which in itself is initially completely asymptomatic.
So, the main reasons for the development of S-shaped scoliosis are the same factors, in particular:
- lack of habit of keeping your back straight when walking and working at a desk, computer, etc.;
- low level of physical activity, which leads to weakness of the muscle corset and lack of adequate support for the spine;
- lifting and carrying heavy objects;
- carrying a bag or school backpack on one shoulder.
Still, the main reason for the development of scoliosis at school age is the improper organization of the workplace, i.e., the height of the table and chair does not correspond to the height of the child.
However, S-shaped scoliosis can also develop in adults. More often, the pathology is diagnosed in older people who have had a slight curvature of the spine since adolescence. Since with age, degenerative changes inevitably occur in the intervertebral discs that separate the vertebrae, they become thinner and can no longer cope with the load. This is usually aggravated by a decrease in the tone of the back muscles, which leads to the existing scoliosis progressing and developing into an S-shape.
At the same time, the risk of spinal deformity increases in the presence of predisposing factors, which include:
- The need to remain in one position for a long time, for example, sitting at a table. Static positions negatively affect the functioning of the entire body, provoking the development of stagnation, but the spine suffers no less from them, especially if a person does not monitor his posture.
- Overweight and obesity. Every extra kilogram negatively affects the condition of the spine, increasing the load on it when moving, standing or sitting. At the same time, the type of obesity, i.e. the most problematic areas in which the bulk of adipose tissue accumulates, determines which part of the spine will suffer the most.
- Incorrect selection of intensity of power loads. Often the cause of the development of S-shaped scoliosis is not only a sedentary lifestyle, which results in a weakening of the muscle corset and a decrease in the quality of support for the spine, as well as obesity, but also excessive strength exercises. If the training regimen is incorrectly selected, especially those involving heavy lifting, the load will fall only on a certain muscle group, which will create the preconditions for spinal curvature.
- Getting a spinal injury. Compression fractures, whiplash injuries and other types of injuries to the spine are fraught with its deformation, especially if the patient neglects the need to wear an orthopedic bandage or corset. In such situations, the injured spine does not receive the support it needs, and due to a gentle lifestyle and the inevitable decrease in muscle tone, it becomes completely unprotected and begins to bend.
Risk factors
The exact reasons leading to the development of grade 3 scoliosis are not known for certain. However, there are a number of precipitating factors that have been found in patients with this diagnosis. These include the following:
- rapid growth processes in childhood and adolescence;
- endocrine disorders;
- incorrect posture;
- ossification of bones in old age;
- orthopedic diseases;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- progressive scoliosis 2 degrees;
- spinal injuries;
- past polio;
- Cerebral palsy, rickets;
- metabolic disorders.
Women during menopause are at risk. Due to decreased estrogen production, bone mass decreases.
No ads 1
Degrees and symptoms of S-shaped scoliosis
Scoliosis develops and progresses slowly. Therefore, it is easy to distinguish 4 stages in its course:
- At the 1st stage, the angle of curvature does not exceed 10°. In this case, only one arch can be detected, since the second one still remains completely invisible, although initial compensatory changes in the part of the spine adjacent to the affected one are already occurring. This is the most favorable stage of disease development from the point of view of conservative treatment, but also the most difficult to diagnose, since the patient does not notice any disturbances in his well-being, and it is still impossible to outwardly notice a deviation from the norm.
- At the 2nd stage, the bend increases to 10-25°, which is already accompanied by the formation of the 2nd arc, although it is still extremely difficult to detect it visually. At this stage, the first arch attracts attention to a greater extent, so the patient’s tendency to slouch, as well as a mild asymmetry of the shoulder blades, can already be noticed. This can only be noticed when the torso is tilted forward.
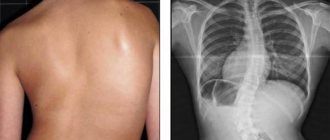
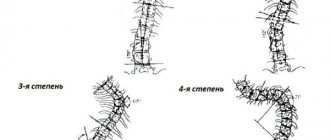
- At the 3rd stage, the degree of curvature of the first arch reaches 25-50°, and the second can already increase to 25°. At this stage, significant asymmetry in the chest and the formation of a noticeable hump in the ribs are easily detected. In this case, S-shaped scoliosis is already considered advanced and is difficult to treat conservatively. Therefore, in most situations, patients are recommended to undergo surgery. After all, the formation of two pronounced arches leads to progressive disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, among which the heart and blood vessels suffer the most, since the curvature of the spine provokes circulatory disorders in the small circle.
- At the 4th stage, the inclination of the main arc already noticeably exceeds 50°. At this stage, external changes are no longer just noticeable, but striking. Severe deformation of the spine provokes changes in position and disturbances in the functioning of almost all internal organs, and also significantly limits the patient’s mobility and leaves him practically no chance to remain in an upright position for a long time. As a result, patients with stage 4 S-shaped scoliosis often become disabled. If surgery is not performed at this stage, the result will be multiple organ failure.
Thus, when changes occur only in the vertebrae and adjacent tissues, it is impossible to detect S-shaped scoliosis without the use of instrumental diagnostic methods. In such situations, one can only suspect something is wrong based on the results of x-rays. An orthopedist or neurologist is able to notice external signs of deformation only when the bend of the main arch reaches 7-10°.
Therefore, it is important not to neglect preventive examinations, and also to independently monitor the condition of the spine of a child or elderly relatives. Warning signs that it’s time to see a doctor are the following:
- stooping, which is accompanied by the fact that a person not only hunches over, but also involuntarily stretches his neck forward, and also keeps his head down while walking;
- asymmetry of the position of the blades;
- the presence of slight muscle tightening in the ribs on one side.
Subsequently, as the degree of spinal curvature progresses, other manifestations of the disease appear:
- asymmetry of shoulder position;
- pelvic distortion;
- change in gait;
- the formation of a hump in the area of the ribs, shifted to one side or another;
- compaction and increase in the formed muscle shaft;
- increased fatigue after physical activity;
- aching dull pain in the side, resulting from muscle spasms.
When the degree of curvature increases to 40° or more, negative changes occur in the chest and circulatory organs. Since spinal deformation leads to a change in the position of the muscles and a decrease in the supporting function of the spine, this can provoke compression of the blood vessels. The consequence of such changes will be a violation of blood circulation, and therefore the course of metabolic processes.
Since the formation of a scoliotic arch in the thoracic spine is associated with a decrease in the chest, this, with an increase in the angle of curvature, provokes a change in the position of the lungs and heart, resulting in the occurrence of shortness of breath and arrhythmia, i.e., heart rhythm disturbances. Over time, these symptoms are accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys.
What not to do?
With third degree scoliosis, any running is prohibited. Circular or twisting movements should also be avoided. This is especially true for exercises in an upright position of the body, as they exert a strong axial load.
Experts do not recommend outdoor games. Football involves fast running and is a dangerous sport. Volleyball involves sudden movements.
Asymmetrical movements can further worsen scoliosis. This is why rhythmic gymnastics and acrobatics are contraindicated. Somersaults and jumps are also contraindicated. One-arm rows and presses are prohibited.
No ads 3
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of S-shaped scoliosis is the task of an orthopedist. The doctor will initially collect anamnesis, i.e. data about the patient’s lifestyle, the nature of existing health complaints, and then conduct an examination. Initially, he will examine the patient’s back, and then be sure to ask him to lean forward as much as possible so that his fingertips reach his toes or at least strive for this position. In this position, changes in the spine are best visible.
Thanks to this simple test, you can already detect changes characteristic of S-shaped scoliosis of the 2nd degree:
- the position of one shoulder is higher than the other;
- formation of a hump in the spine;
- the presence of spaces between the ribs, their incomplete retraction;
- approaching the costal arch closer to the spine;
- asymmetrical arrangement of the blades;
- asymmetrical position of the waist triangles;
- shortening of legs or arms.
Also, S-shaped scoliosis is characterized by a decrease in muscle tone, in particular the abdominal muscles.
To confirm the diagnosis and accurately determine the degree of scoliosis, an X-ray examination of the spine in several projections is prescribed. Thanks to the obtained images, it is possible to make accurate measurements and calculate the angle of curvature of each arch, which will allow you to make the correct diagnosis, as well as understand whether you can try to correct the situation using conservative methods or whether surgical intervention is already required.
If necessary, the doctor may also recommend a CT or MRI. These are more modern and expensive research methods, but with their help you can collect maximum information about all the anatomical structures that form the spine and detect the slightest pathological changes in them.
Elderly patients may additionally be prescribed densitometry, i.e., an examination designed to determine bone density. This is important for detecting osteoporosis and determining the risk of developing complications associated with it.
Massage and manual therapy: differences and similarities of effects
Both methods are carried out directly by the hands of specialists. During the massage, the doctor provides a reflex effect. Muscle tissue is subjected to various mechanical vibrations: vibration, kneading, stroking, effleurage, rubbing.
Manual therapy is a more complex procedure. All movements used are aimed at returning the spinal segments to their original physiological position. The technique begins directly with warm-up movements. This allows you to relieve tension in the muscle tissue, which reduces the pain of the procedure and ensures the desired treatment result. After warming up, the therapy session involves stretching, twisting movements, as well as kneading deep tissues that are in a stagnant state.
For scoliosis, manual therapy is carried out extremely carefully. The doctor must clearly understand the features of the anatomical structure of the spine and have reinforced practical skills in the technique. Generally, additional specialization in neurology and orthopedics is required for the internist.
Even the most competent massage is unable to eliminate spinal diseases. Manual treatment provides a therapeutic effect for many years to come. This way you can successfully get rid of the conditions that scoliosis causes by affecting your overall well-being:
- periodically a tingling sensation in the area of the heart muscle;
- constant dizziness and severe pain associated with changes in the position of the vertebrae;
- unpleasant sensations from possible displacement of the internal organs of the heart, stomach, lung.
Attention!!! The duration of the massage effect on the back area is 20-40 minutes. The manual procedure involves up to 2 hours of using various therapeutic movements.
Treatment of S-shaped scoliosis
The nature of what treatment will be prescribed to the patient directly depends on the degree of S-shaped scoliosis that was detected. Conservative methods, including drug therapy, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, manual therapy and lifestyle changes, are effective only in the initial stages of scoliosis development. In case of 3rd or 4th degree, the only way out of the situation is to perform an operation.
But in some cases, surgical intervention is also prescribed for stage 2 S-shaped scoliosis. Most often in such situations it is required for children who have a tendency to rapidly progress the disease and have additional hemivertebrae or fusion of ribs. Surgery may also be prescribed in the early stages of S-shaped scoliosis if it:
- caused the development of cardiac or respiratory failure;
- causes severe compression of blood vessels or spinal roots;
- carries a high risk of spinal cord injury.
Thus, for each patient, treatment is developed strictly on an individual basis, taking into account not only his age, but also the presence of concomitant diseases, the risk of developing complications of S-shaped scoliosis and other factors.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is far from the main method of treating S-shaped scoliosis. It can only temporarily improve the patient’s condition, as well as increase the effectiveness of other measures taken, but in no way affects the nature of the disease and is not able to restore the normal anatomy of the spine.
Therefore, as part of drug treatment, patients are mainly prescribed only muscle relaxants and anti-inflammatory drugs. The first ones are designed to reduce the tone of overly tense muscles, i.e., relieve spasm. This will reduce the severity of pain and reduce the risk of injury.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are indicated for faster resolution of the inflammatory process, which invariably occurs with spinal deformity. This also helps to reduce pain, both due to the mild analgesic effect of the most drugs in this group, and due to the reduction in the intensity of inflammation. While taking anti-inflammatory drugs, there is an additional decrease in soft tissue swelling.
Sometimes patients are additionally prescribed thyroid hormones. This is only possible with a comprehensive examination and the absence of concomitant diseases, metabolic disorders and other changes in which hormonal therapy can cause more harm than good. In S-shaped scoliosis, thyroid hormones are prescribed to increase bone plasticity, which will allow the normal position of the spine to be restored more quickly and effectively through other components of conservative therapy.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are designed to increase the effectiveness of other therapeutic interventions. As a rule, when treating S-shaped scoliosis, the following are prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound therapy.
Thanks to gentle physical effects, it is possible to increase blood circulation, increase metabolic rate, normalize muscle tone and have a general strengthening effect on the body. In most cases, for S-shaped scoliosis, courses of procedures of 8-15 sessions are prescribed, performed at a certain interval.
Sometimes patients may be offered traction therapy, i.e., spinal traction. The procedure is carried out using a special apparatus and involves carefully stretching the body in opposite directions along the central axis, which helps to normalize the position of the vertebrae and eliminate pathological bends of the ridge.
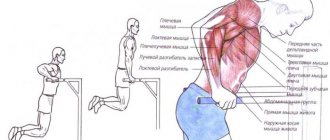
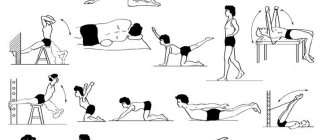
Exercise therapy
Physical therapy is one of the main methods of conservative treatment of S-shaped scoliosis. It involves daily performance of a special set of exercises, which is developed for each patient individually in accordance with the severity of his disease, level of physical fitness and age. The shape of the S-shaped scoliosis is also taken into account, or more precisely, in which direction the main arch is formed. It is recommended to conduct the first classes under the guidance of a specialist, and only after you have fully mastered the program and methods of performing each exercise, you can start practicing at home on your own.
The goals of exercise therapy are:
- strengthening the muscle corset, which can create adequate support for the spine;
- improved posture;
- activation of blood circulation and metabolic processes;
- correction of spinal deformity.
In addition to daily exercise therapy, patients are recommended to take up swimming, certain types of dancing, or some other sports disciplines that help strengthen all muscle groups of the upper half of the body.
Classes begin with light loads and a small number of repetitions. As the muscles strengthen, the load is increased, reaching the optimal level. Exercises on the Swedish wall have a good effect on the condition of the spine: hanging, pull-ups, etc.
Manual therapy
With S-shaped scoliosis, all patients, provided there are no contraindications, are prescribed manual therapy. It involves a deep massage, which not only works the back muscles, but also has a positive effect on the spine and restores the correct position of the vertebrae. A chiropractor can tone overly relaxed muscles and at the same time eliminate muscle spasms on the opposite side, which very often accompanies S-shaped scoliosis. Thanks to manual therapy sessions, it is often possible to release pinched nerve roots and blood vessels, which has a beneficial effect on a person’s well-being.
But the method cannot be used when:
- acute infectious diseases;
- skin rashes in the affected area;
- severe pathologies of the cardiovascular system, etc.
Lifestyle correction
When diagnosing S-shaped scoliosis, it is very important to create conditions so that the pathology does not worsen. Therefore, patients are recommended:
- provide a balanced diet;
- devote sufficient time to rational physical activity;
- watch your posture;
- avoid maintaining a static body position for a long time (when performing sedentary work, you must take regular breaks, get up and move, not forgetting about your posture);
- do not lift heavy objects;
- change the mattress to an orthopedic one;
- Avoid making sharp body turns.
Patients are often prescribed to wear orthopedic bandages or corsets. For mild forms of S-shaped scoliosis, soft bandages are sufficient, but for curvature of 3, not to mention 4 degrees, you will need to individually make and constantly wear a hard corset. Such designs are designed to reduce the load on the spine and minimize the risk of further curvature.
Rehabilitation period
After surgical treatment, the patient returns to normal life. You can get up and walk the next day after surgery. The rehabilitation period is shortened to 6 months in adolescents, since their spinal column quickly recovers. In adults, it lasts about a year and requires regular gymnastics and exercise therapy. Most people who have surgery to correct scoliotic deformity quickly adapt to their new lifestyle. Minor restrictions in flexibility do not interfere with their daily activities and do not cause any discomfort.
Spinal curvature in children - types
Several classifications of such deformation are known. Depending on the period of manifestation of the disorder, spinal curvature in children can be as follows:
- infantile (diagnosed in children under 3 years of age);
- juvenile (manifests at the age of 3-10 years);
- adolescence or youth (10-20 years).
There are such types of spinal curvature:
- lordosis;
- scoliosis;
- kyphosis.
Scoliosis is a lateral deformity of the spine. Depending on the nature of the curvature, the following types of illness occur:
- C-shaped
is the most common type of violation. With such scoliosis, only one arc of curvature is observed. - S-shaped
- the spinal column is deformed in two different sections. In this case, the curvature develops on both sides. Externally, this violation is similar to the Latin letter “s”. - Z-shaped
is the most severe type of pathology. Three arcs of curvature are formed.
According to etiology, scoliosis is divided into congenital or acquired. In the first case, violations arise due to deviations in the intrauterine development of the baby. In this case, the provoking factors are considered to be the bad habits of the expectant mother, an unbalanced diet during pregnancy and infectious diseases suffered during this period. Depending on the causes of origin, acquired scoliosis can be differentiated as follows:
- habitual (provoked by poor posture);
- rachitic (occurs due to rickets);
- post-traumatic (diagnosed after injuries);
- static (develops with different leg lengths);
- cicatricial (appears after a burn or surgery);
- paralytic (occurs against the background of polio and other diseases that affect muscle tissue and the nervous system of the body).
Kyphosis
is a disorder in which deformation of the spine occurs in the sagittal plane. There are several types of this pathology:
- postural – a disease that is caused by poor posture and weakening of the muscle frame;
- post-traumatic (more often provoked by compression fractures of the vertebrae);
- congenital (the appearance of such a disorder is directly related to anomalies of intrauterine development);
- tuberculosis - a disorder provoked by the action of mycobacteria;
- paralytic (the problem occurs as a result of paralysis of the muscles surrounding the spinal column);
- Scheuermann-Mau disease (considered a genetic pathology);
- total - a disorder affecting the entire spine.
Lordosis
– deformation of the column, in which the bend is directed convexly forward. This type of violation is of the following types:
- primary - a change that occurs against the background of excess weight, incorrect posture, tumors and spasms of the spinal muscles;
- secondary – lordosis, provoked by damage to the musculoskeletal system of the column.