The scapula is a flat, wide bone that is located freely in the thickness of the muscles along the back surface of the chest. Between the shoulder blade and the rib cage there are bursae to reduce friction during movement. If clicking sounds, crunching and other sound phenomena occur during movements, doctors talk about “clicking scapula” syndrome. This is a fairly rare disease. Sound phenomena appear with morphological changes in the soft tissues (inflammation, scarring, swelling) between the scapula and the chest.
Anatomy
The bones of the shoulder girdle include the humerus, clavicle and scapula. Two large muscles originate on the inner surface of the scapula. These are the subscapularis and anterior scalene muscles. The subscapularis muscle attaches to the humerus near the shoulder joint, and the anterior scalene muscle attaches to the ribs on the lateral surface of the chest.
The synovial bursa is a sac filled with a viscous viscous fluid (synovium) located between the rubbing surfaces. The bursae are located between the subscapularis and anterior scalene muscles, as well as between the anterior scalene muscle and the rib cage. Inflammation of the bursa is called bursitis. This disease can manifest itself as pain, as well as sound phenomena (crackling, clicking, etc.).
Symptoms
- A crunch in the shoulder blade when rotating the shoulder is the main symptom.
- Quite significant pain, and it increases greatly with movement, unpleasant discomfort during physical exertion.
- Swelling, redness.
- Impaired motor activity.
- Manifestation of high temperature, often a state of fever.
Experts point out that if at least one of the listed symptoms develops during rotational movements, you definitely need to undergo an examination in order to begin timely treatment, which will help eliminate the occurrence of other, more serious pathologies.
Causes
Bursitis in most cases is an “overload” disease, when, as a result of excessive tension or prolonged microtrauma, inflammation of soft tissues, including the synovial bursa, develops.
“Snapping blade” syndrome is an occupational disease of baseball players, as well as construction workers (painters, plasterers). Another cause of the disease is atrophy of the periscapular muscles as a result of prolonged inactivity or nutritional depletion. As a result, the scapula is more tightly adjacent to the ribs that form the chest wall. Friction increases and inflammation of the bursae may develop.
After improperly healed fractures of the scapula or ribs, the congruence of the articular surfaces of the scapula and chest is disrupted. This leads to increased friction during movement and can also cause the development of snapping scapula syndrome.
Sound phenomena can also occur in the presence of Luschka tubercles, which are anamolies of the development of the scapula. They are bony outgrowths located near the upper edge of the scapula. Additional synovial bursae often form underneath them, which can become inflamed and cause bursitis.
Snapping scapula syndrome
Sevmassage » Articles
The bones of the shoulder girdle include the humerus, clavicle and scapula.
Two large muscles originate on the inner surface of the scapula. These are the subscapularis and anterior scalene muscles. The subscapularis muscle attaches to the humerus near the shoulder joint, and the anterior scalene muscle attaches to the ribs on the lateral surface of the chest.
The synovial bursa is a sac filled with a viscous viscous fluid (synovium) located between the rubbing surfaces. The bursae are located between the subscapularis and anterior scalene muscles, as well as between the anterior scalene muscle and the rib cage. Inflammation of the bursa is called bursitis. This disease can manifest itself as pain, as well as sound phenomena (crackling, clicking, etc.).
Causes:
Bursitis in most cases is an “overload” disease, when, as a result of excessive tension or prolonged microtrauma, inflammation of soft tissues, including the synovial bursa, develops. “Snapping blade” syndrome is an occupational disease of baseball players, as well as construction workers (painters, plasterers).
Another cause of the disease is atrophy of the periscapular muscles as a result of prolonged inactivity or nutritional depletion. As a result, the scapula is more tightly adjacent to the ribs that form the chest wall. Friction increases and inflammation of the bursae may develop.
After improperly healed fractures of the scapula or ribs, the congruence of the articular surfaces of the scapula and chest is disrupted. This leads to increased friction during movement and can also cause the development of snapping scapula syndrome.
Sound phenomena can also occur in the presence of Luschka tubercles, these are outgrowths located near the upper edge of the scapula. Under them, additional joint capsules very often form, in which inflammation can develop, which are anamolies of the development of the scapula. They are bony outgrowths located near the upper edge of the scapula. Additional synovial bursae often form underneath them, which can become inflamed and cause bursitis.
Symptoms of a snapping blade
Sound phenomena, such as crunching or clicking when moving the hand, can only be felt by the patient, or can be heard at a distance of several meters. In some cases, movements in the scapula may be accompanied not only by sound phenomena, but also by pain, but in many patients there is no pain at all. Palpation of the scapula area is often painful.
Diagnosis
During the examination, the doctor will ask you about how long ago your symptoms began and whether you have had similar complaints in the past. A question will be asked about your profession, about playing sports. A history of scapula or rib fractures is important.
Next, palpation of the scapula and auscultation (listening) during movements are carried out.
To clarify the diagnosis, a chest x-ray may be prescribed, which reveals developmental anomalies, improperly healed fractures of the ribs and scapula. To clarify the diagnosis, a computed tomography may be prescribed, which produces a detailed image of the bones in a 3D projection. If bursitis is suspected, magnetic resonance imaging provides the most valuable diagnostic information.
Treatment
Conservative treatment
In most cases, treatment begins with conservative therapy. For pain and bursitis, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen are indicated. Hardware physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, laser therapy, electroanalgesia) is prescribed. If symptoms persist, topical injection of steroids into the area of the inflamed bursa may be suggested. Steroids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that suppress local swelling and inflammation. Outside the acute stage or during a long-term course, massage and (or) physical therapy and exercises are prescribed to help increase the strength and stability of the shoulder.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated only if conservative treatment is ineffective with severe clinical symptoms of bursitis, accompanied by pain. The operation consists of resection (removal) of the medial angle of the scapula along with the underlying synovial bursa.
Previous entry ADIPOCYTE - THE CRADLE OF CELLULITE
Next entry VASCULAR GYMNASTICS FOR THE TREATMENT OF HEADACHES AND HYPERTENSION
Diagnosis
During the examination, the doctor will ask you about how long ago your symptoms began and whether you have had similar complaints in the past. A question will be asked about your profession, about playing sports. A history of scapula or rib fractures is important.
Next, palpation of the scapula and auscultation (listening) during movements are carried out.
To clarify the diagnosis, a chest x-ray may be prescribed, which reveals developmental anomalies, improperly healed fractures of the ribs and scapula. To clarify the diagnosis, a computed tomography may be prescribed, which produces a detailed image of the bones in a 3D projection. If bursitis is suspected, magnetic resonance imaging provides the most valuable diagnostic information.
Symptom manifestation
A crunch in the shoulder blade when rotating the shoulder is a syndrome of various pathologies and diseases. The cause is joint injuries, neurological pathologies, and degenerative changes. To accurately determine the basis for the development of the disease, a complete examination must be performed.
The problem is determined not only by the unpleasant sound, but also by inflammatory processes that form in the joint capsules. When rotating movements occur, pain occurs. Most often, such pathologies develop due to severe overload, certain bruises and injuries. Diseases of internal organs can provoke certain changes and pathologies.
This can be not only the process of inflammation, but also degenerative changes in the tendon. Moreover, the muscle-tendon junction is often affected. The sliding of the joints becomes less soft, which in any case provokes swelling, tissue damage, and the occurrence of other pathologies.
Diseases can occur in an acute form, then the manifestation of extraneous sounds and pain will be more pronounced. There may be a chronic form that develops gradually, and in the initial stages the symptoms are minimally expressive.
Treatment
Conservative treatment
In most cases, treatment begins with conservative therapy.
For pain and the presence of bursitis, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are indicated. Hardware physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, laser therapy, electroanalgesia) is prescribed. If symptoms persist, topical injection of steroids into the area of the inflamed bursa may be suggested. Steroids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that suppress local swelling and inflammation. The most modern and effective is a course of shock wave therapy.
Causes
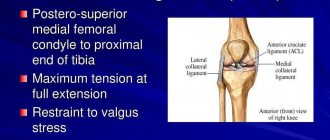
- Joint instability as a result of the formation of serious physical loads. The glenohumeral joint is subjected to very significant pressure, this provokes inflammatory processes and certain destruction of cartilage tissue.
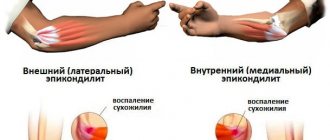
- Certain injuries . At the same time, it must be said that the manifestation of unpleasant sensations and discomfort, extraneous sounds is formed in the absence of competent treatment after bruises, dislocations, certain fractures and punctures.
- Arthritis . These are inflammatory processes that form as a result of joint damage. It is combined with a fairly strong manifestation of pain, restrictions on motor function are created, and an extraneous sound occurs.
- Osteochondrosis – affects the cervical spine. The disease is reflected by pain, activity is limited. The degree of manifestation of the disease will depend on how much the nerve endings are damaged under the influence.
- Arthrosis . In this case, the pathology is based on limited mobility of the limbs due to their damage, which consists of the proliferation of osteophytes. A crunch is formed during rotational movements.
- Salt deposits . A very common reason that causes a lot of trouble. Various factors can provoke such a disorder: poor nutrition, poor mobility, obesity, and kidney failure.
- Tendinitis and bursitis . These are inflammatory processes that affect the tendons. The pathology is provoked by infections, rheumatic diseases, and excessive physical stress.
Such negative consequences can be caused by infectious diseases, inflammation processes, changes with age, heredity, poor nutrition, and disturbances in metabolic processes.