If health problems are identified that lead to restrictions and difficulties with communication, self-care, work, etc., a citizen may receive a disability group. To do this, you must have an ITU conclusion. In particular, people with scoliotic disease, that is, with curvature of the spine (depending on the severity of the problem), have a chance to gain a special status and associated privileges. We will talk about cases of disability registration against the background of this illness, as well as other nuances within the framework of the topic.
Disability due to scoliosis: to whom and in what cases is it issued?
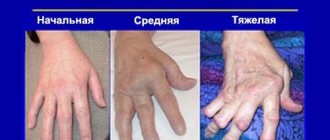
Let us immediately note that the assignment of a group for scoliosis during the course of the ITU is quite rare. The fact is that scoliotic disease at stages 2 and 1 practically does not manifest itself in the form of symptoms.
But in stages 3 and 4, there is a sharp deterioration in the condition, normal life and normal functioning are lost. And this can already serve as the basis for establishing a disability group.
As experts note, the appropriate status should be assigned if:
— scoliosis is accompanied by severe pain;
— the anomaly affected other organs;
— the progression of the problem is obvious;
— rehabilitation provoked complications;
— severe degrees of scoliotic disease were recorded, that is, 3 or 4;
— the opportunity to carry out professional duties is lost;
- the patient needs constant help from other people.
Important
! The commission members may not appoint a group during the first examination, so it is worth submitting the documents again after some time.
What is scoliosis?
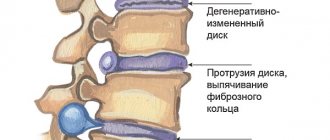
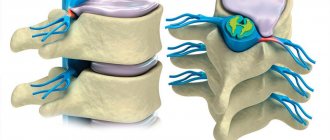
Scoliosis is a serious deformity of the vertebrae. Such curvature manifests itself in most cases in the frontal plane, after which deterioration begins and the disease can move to the saginal plane. Gradually, the bending of the affected vertebrae increases and can be complicated by kyphosis and other associated disorders of the musculoskeletal system .
Scoliosis may be accompanied by complications such as kyphosis and lordosis
Violation leads to visible and dangerous deformation of the thoracic region and pelvis, and the functioning of the lungs, heart and reproductive system is disrupted.
In more than 80% of cases, the true cause of the pathology is unknown . All factors that are now called as provoking scoliosis are conditional and do not always trigger the disease. Most often, curvature of the spine begins during the period of active growth of the patient, which can occur between the ages of 3 and 6 years and during the period of maturation.
Injuries, metabolic processes in the body, congenital pathologies, lack of minerals, constant stoop, and weakness of the thoracic and lumbar muscles can affect the health of the spine.
Attention! Some patients experience so-called infantile scoliosis. It is diagnosed before the age of one year and is associated with the currently inadequate development of the musculoskeletal system. In the absence of other diseases of the spine and chest, as well as congenital and intrauterine pathologies, the curvature goes away on its own.
What disability groups can be obtained for scoliosis?
Taking into account the well-being and restrictions present in the subject, a specific group is given for MSE.
3 group
For a citizen with scoliosis, when assigning a “working” group, the following criteria will be taken into account:
- pathological phenomena are aggravated;
— the disease continues to develop;
— the spinal trunk is immobilized;
- severe pain in the back;
- there is respiratory failure;
— the functioning of the central sensory system is disrupted.
Important
! Despite the problems described, a person must retain the ability to work and self-care.
2nd group
This category is assigned if the expert commission has identified:
- presence of sharp exacerbations of scoliosis;
— failures in the central sensory system;
— 4 or 3 degrees of scoliotic disease;
- periodic respiratory failure;
- decline in performance and loss of previous functions;
— the need to provide constant assistance (here is control, etc.);
— the need for special technical means to normalize traffic, etc.
1 group
Finally, this degree of restrictions is assigned in extremely difficult cases when diagnosing:
— 4 stages of scoliosis;
- paralysis of arms and legs;
— loss of self-care skills;
- constant need for help;
- intolerance to even small loads.
Danger and consequences of the disease
- intense pain and discomfort in the affected area,
- disruption of the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract,
- muscle spasms,
- numbness of the lower extremities,
- dysfunction of internal organs and vital systems.
The most serious consequence of scoliosis is paralysis of the lower extremities, leading to complete immobility of a person. Curvature of the spine affects the functions of the reproductive system, provoking chronic inflammatory processes in the genital organs (in especially severe cases, infertility).
Prolonged compression of nerve endings during scoliosis leads to compression of the vertebral artery. A number of patients experience thinking disorders. Curvature of the spine in adolescents can lead to severe psychological trauma (provokes isolation and feelings of inferiority).
Specifics of assigning disability for scoliosis to children
According to experts, in relation to children, we can talk about establishing the status if an X-ray of the spine shows obvious abnormalities, as well as if the column deviates by 10-20 degrees.
Against this background, a child’s disability is given taking into account certain nuances, namely: - group 3 - during exacerbations of the disease in children no more than 1-2 times a year, despite all this, there is no strong and sharp pain in the spine;
- Group 2 - if the disease manifests itself in the form of exacerbations up to 3 times a year;
— Group 1 — the main joints and the spinal column practically do not move, so the patient needs to be constantly cared for.
Important
! The attending pediatrician has the right to refer children and their parents to the ITU commission.
When can I get it?
A person suffering from scoliosis may become disabled for certain reasons:
- due to his illness, he cannot work at his previous workplace;
- respiratory failure of any degree develops. Typically, insufficiency and disability are diagnosed with scoliosis of degrees 3 and 4;
- neurological symptoms have arisen that border on pain; other methods of treating scoliosis did not give the desired result;
- after the operation, complications appeared that did not lead the disease to positive dynamics;
- the disease began to progress. In this case, the patient can receive the status of “disabled person” only if he proves that he was given treatment that did not give the desired result, the disease began to progress and worsen his general health;
- the functioning of internal organs is disrupted;
- if the patient has pronounced problems with the gastrointestinal tract and needs the help of a specialist.
Thus, if the patient does not achieve results from the treatment, his health condition becomes unstable, then he has the right to collect the required package of documents and receive the status of “disabled person”. But we should not forget that the medical commission, when making its decision, must carefully study the patient’s medical record. This will help them make sure that the patients have taken all possible methods to get rid of the disease, but there was no effect.
What disability group is assigned to a person with grade 3 scoliosis?
In order for a patient to be assigned a disability, the medical commission must accurately check the patient’s condition:
- The third degree of disability is assigned to persons with 3–4 degrees of scoliosis, which is rapidly developing. Also, with scoliosis of the fourth degree and if the patient has a disability, he becomes a stage 4 disabled person. Additionally, the patient is bothered by pain in the chest and spine, he loses sensitivity of the skin, often seeks help from a specialist, his limbs and skin become numb, breathing problems of 1st and 2nd degree appear, and mobility in the vertebral body is impaired. At the same time, a person can engage in work that does not require heavy physical work and serve himself.
- The second degree of disability is assigned to patients with grade 3–4 scoliosis, which is progressive and associated with neurological disorders. His respiratory activity is also impaired, even in the presence of remission, and respiratory impairment reaches degree 3. Additionally, the patient experiences severe pain when performing minor physical activity, for example, walking. At the same time, there is no sensitivity in the skin and in the limbs, the person is not able to perform minimal physical actions at home, it is difficult for him to move, he can move with the help of crutches, a stick, a stroller and other means of transportation, the person can serve himself, but only to a minimum extent.
- The first disability group is assigned to a patient with scoliosis in extreme cases. This occurs in cases where the patient has stage 4 spinal damage and has complete or high degree paralysis. At the same time, due to the curvature of the patient, some part of the spinal cord is affected; in order to perform minimal self-care skills, he requires the help of an outsider; such a person cannot work under any circumstances.
Remember! If a patient has grade 3 scoliosis, then he constantly needs to visit a doctor and strictly follow all the rules prescribed by him. Such a patient may be assigned a disability even when there are no typical symptoms of the disease, but the patient says that he is bothered by severe pain and his health is noticeably getting worse. The main thing is that all changes and illnesses that happen to him are recorded in his medical statement.
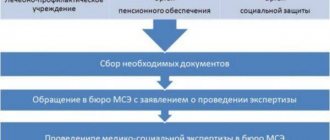
Step-by-step scheme for obtaining disability for scoliosis
1
. First of all, the applicant for the group prepares and submits to the ITU Bureau a package of documents, which includes:
— passport of the subject (plus copies of the main pages);
— application form 088/у-06;
— SNILS;
— referral for medical and social examination;
— certificate about the conditions and nature of the work (for workers);
— a copy of the work book certified by a personnel employee;
- characteristics from an educational institution (for children and students);
— originals and copies of extracts, certificates, conclusions confirming the disease;
— IPR and conclusion from the previous examination (if the commission is repeated).
2
. Also, before the ITU, a citizen is required to be examined and take tests. For example, you will need the following results:
— ECG;
- myelography;
- spirometry;
— visual inspection;
- blood, urine and other general tests.
Important
! Often, X-rays or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are prescribed directly for MSE. The second method is preferable, as it makes it possible to examine the structure of the spine in detail.
3
. As soon as the bureau receives the necessary documentation, a medical examination will be scheduled starting from that day and within a month. In addition to the person being examined, three specialists are present during the examination. But the involvement of a third-party expert who has the same rights as the other members of the commission (can ask questions, vote, etc.) is not excluded.
The inspection process is recorded in a protocol where important information is indicated. Based on the latter, a patient with scoliosis is denied or assigned a disability group. If the decision is positive, the disabled person receives an act, a certificate of his status and an IPR with recommendations.
Important! According to the new rules, a difficult condition or living in a hard-to-reach area allows a citizen to be examined in absentia. Then the expert commission makes its decision based only on the documents.
Forecast
Non-surgical treatments slow or prevent the progression of scoliosis. Decisive for the success of therapy are early initiation and consistent implementation of the doctor’s recommendations. The greater the curvature, the more likely it is that scoliosis will persist into adulthood.
Severe curvature remains even after growth has been completed. Untimely therapy can lead to long-term and serious consequences: restrictions on spinal mobility and dorsalgia. If the favorable time for surgery is missed, worsening scoliosis sometimes leads to serious impairment of heart and lung function.
Sports and physical activity, as they are commonly used to prevent back pain, strengthen the back muscles. S-shaped scoliosis often requires additional special physiotherapeutic exercises, the success of which depends on proper implementation. Parental motivation is as important for this as brace therapy. Family and friends should encourage and strengthen the self-esteem of children and adolescents with disabilities. Many children throw the corset because they feel discomfort
It is necessary to explain to the child the importance of wearing it
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/tbvuoFX23_8
Permanent disability due to scoliosis
Special status is assigned to a person for life if:
- several years from the date of establishment of incapacity;
- four years since the disabled person was assigned group 2;
- six years from the date of assignment of group 2 to a disabled child.
Plus, the category is left indefinitely when scoliosis is declared incurable or no improvement is observed within 5 years.
However, even a permanent group in all the cases presented does not cancel the patient’s obligation to be periodically examined and send the obtained data to the ITU bureau. As a rule, inspections are repeated every year or two.
Important
! Pensioners can receive an unlimited group immediately.
How long is disability granted?
Disability is issued for different periods of time depending on the group. Then you need to undergo re-examination. I disability group - you need to undergo re-examination once every 2 years; II and III disability groups - you need to undergo re-examination once a year.
Permanent disability is established for the following categories:
- disabled people of groups I and II - women over 55 years old, men over 60 years old;
- military personnel and disabled people of the Great Patriotic War who suffered during hostilities and were assigned disability groups I and II;
- disabled people with severe diseases: absence of limbs, vision, hearing, acute forms of neurological diseases, etc.;
- disabled people of groups I and II with a disability for more than 5 years, if every year they were hospitalized, which did not bring a positive result in treatment.;
- disabled people of group III with a disability for more than 7 years, if every year they were hospitalized, which did not bring a positive result in treatment;
- disabled people of groups I and II whose health status and degree of disability have not changed for more than 15 years.
The procedure for obtaining disability in Russia involves many diagnostic procedures. Therefore, a person must prepare himself to undergo numerous examinations and tests. You need to tune in to a positive result and remember that with the assignment of a disability group, it becomes possible to make your work easier and receive help from the state in the form of financial benefits and benefits.
Previous For disabled people The difference between the second and third disability groups Next For disabled people What disability group is given for oncology of different stages
To solve your problem RIGHT NOW get a FREE consultation:
8 (Moscow) (St. Petersburg) 8 (800) 350-84-13 ext. 536 (all of Russia)
Is disability removed after surgery?
For the most part, the disease in question is not eliminated through surgery. The operation alleviates the patient’s condition, but does not restore the full function of the spine. This means that usually people who have undergone surgery remain disabled.
Be that as it may, after such treatment, a second MSE is required. If an operation or other situation contributed to the cancellation of the status, you can challenge the experts’ decision. To do this, you need to submit a request to the same bureau where the examination took place.
Next, a new examination is scheduled. If, as a result of this, results that are not satisfactory to the citizen are obtained, he should file a complaint with the ITU federal commission.
Important
! The final authority for resolving such disputes is the court, for which it is important to prepare. Ideally, it would not hurt to contact a lawyer specializing in disability cases, as well as be examined by independent specialists, provide convincing evidence of health limitations, etc.
Necessary examinations to determine disability
When registering disability, the ITU commission first examines the medical history:
- outpatient card;
- extracts from hospitals and dispensaries;
- change in the nature of the patient's complaints.
Data from objective, instrumental and laboratory studies are taken into account:
- urine and blood tests;
- X-ray of the spine in projections (lateral, direct);
- computed tomography of the spine;
- spinal myelography;
- MRI of the spine;
- consultations with specialists (cardiologist, neurologist, pulmonologist, therapist, etc.).
MSE for scoliosis
Causes
Scoliosis can develop due to many reasons. The most common types of the disease include:
- Idiopathic scoliosis
The disease usually reaches its peak when the spine is still developing. Progression becomes milder as the patient reaches adulthood, but symptoms often become more severe as the curvature gradually increases over the years.
- Degenerative scoliosis
When scoliosis develops in adulthood, it is often the result of decreased bone density and muscle strength.
Also, the cause of curvature of the spine can be congenital defects of bone tissue, various pathologies, rapid growth and muscle failure, and asymmetry of loads on the spine.
Deciding on Disability
Obtaining disability is impossible without passing a medical and social examination. It is within her competence:
- conducting examinations of applicants to determine the degree of disability for which they may qualify;
- determining whether the ability to work is completely lost or only reduced;
- study of statistics on disability in this disease, as well as the expected symptomatic picture during its further course;
- determining the patient’s needs for social protection, guided by the medical documents provided to them.
Medical and social examination
On the territory of the Russian Federation, it is impossible to obtain disability without going through the ITU.