Vertebral spondylosis is characterized by the appearance of osteophytes, which put pressure on nerve endings and limit mobility. It is accompanied by severe pain that prevents a person from living and working. In some cases, the patient cannot even care for himself and requires nursing care. Many people with progressive spondylosis are interested in whether they will be given a disability group. Let's look into this issue.
What is spondylosis
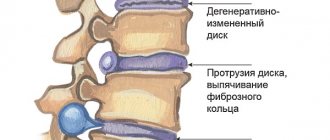
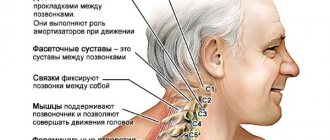
This pathology is classified as chronic, since in most cases the growth of bone tissue occurs gradually. Formations occur on segments of the spine in response to degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs. Osteophytes perform a protective function - they are necessary to increase the contact area between the vertebrae.
If the intervertebral discs are healthy, then formations do not appear on them. Otherwise, bone growth occurs, which is called osteochondrosis or spondylosis. With osteochondrosis, growths on the spine have a beak-like shape, and with spondylosis, curved marginal growths appear that prevent rupture of the intervertebral disc or its displacement.
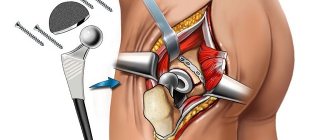
Indications for spinal surgery with metal structures
Various metal structures are widely used in neurosurgery to stabilize a specific area of the spine. They are needed in many situations, including:
- injuries (dislocations, fractures);
- degenerative-dystrophic processes;
- congenital and acquired spinal defects, including scoliotic deformity;
- spinal neoplasms;
- pronounced vertebral listhesis;
- formation of false joints;
- unsuccessful spinal surgery.
All this negatively affects the quality of life and motor abilities of a person. Stabilizing metal structures can eliminate instability of the vertebrae and bring their position closer to normal.
Spinal surgeries using metal structures are prescribed in extreme cases when conservative treatment is unsuccessful. The installed structures are made of high-strength, biologically inert metals, therefore, as a rule, they are installed once and remain in the patient’s body forever. Only in isolated cases is it necessary to remove the metal structure due to the need for re-operation on a fixed spinal motion segment or the occurrence of unforeseen complications.
Symptoms of the disease
It is by the location of the foci of pain that doctors determine which part of the spine was affected by spondylosis:
- with sacral, sacralgia is observed (localized in the coccyx);
- if the disease affects several parts of the spine at once, then doctors diagnose sciatica;
- with lumbar or chest pain, lumbodynia can be observed (discomfort is noticed in the back, buttocks, legs and perineum);
- cervical is characterized by cervicalgia.
It cannot be said that one type of spondylosis is more dangerous than the other, because if any part of the spine is affected, you can get a disability group. Cervical is complicated by the fact that it disrupts the nutrition of the brain; chest often gives complications to the heart, kidneys or stomach; with lumbar pain, a person eventually becomes unable to serve his own needs.
In addition to pain, people often experience sensory disturbances in the limbs and back. They experience the following symptoms:
- pain in the legs when they are extended at the hip joint;
- discomfort in the back when tilting the head;
- increased pain when staying in one position for a long time, during physical activity or coughing;
- when lifting one leg, discomfort occurs in the other;
- when the leg is raised, moving the foot causes pain;
- standing, lifting your leg causes pain in the hip.
Chiropractors often use these symptoms to diagnose spondylosis. If these simple movements cause pain in you, then it is necessary to treat the disease without waiting for it to progress. After all, untreated spondylosis can lead to disability.
Types of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine
Based on diagnostic information, the doctor determines what type of pathology a particular patient has:
- Degenerative. The cartilaginous part of the vertebrae has a flat shape. This characteristic is directly related to its loss of elasticity.
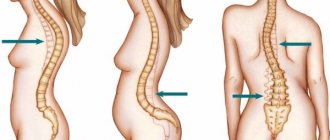
- Deforming. The size and shape of the vertebrae changes. The phenomena provoke the formation of bone growths, which, as they progress, displace cartilage. This is an irreversible process. To confirm the diagnosis, an x-ray examination is performed.
- Ankylosing. The spine becomes deformed and loses elasticity. The disorder is typical for young people and mainly affects men.
- Polysegmental. The pathology is characterized by development simultaneously in several areas of the spinal column.
The type of spondyloarthrosis is not determined until diagnostic results are obtained, since the first 3 forms are similar in clinical manifestations.
For what reasons does the disease occur?
Many people are at risk of disability due to spondylosis. Risk factors are:
- physical inactivity;
- pathologies and injuries of the spine;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- change in metabolic rate;
- inflammatory processes and a number of infectious diseases;
- static overload of the spine;
- elderly age.
Most often, doctors include people with obesity, diabetes, and acromegaly in the risk group. With diabetes, it is easier to become disabled, since in combination with spondylosis this pathology can seriously worsen a person’s quality of life.
Static overloads occur when lifting weights incorrectly - with a sharp jerk upward (often the cause of lumbosacral spondylosis), or when there is excessive stress on the spine due to prolonged carrying of loads or during training. It is important to find a middle ground in physical activity, since sedentary work and physical inactivity also have a detrimental effect on the condition of the spine.
Forms of spondylosis
The assignment of a disability group directly depends on the form in which the disease occurs:
- The most unfavorable is the lightning variety. With it, the disease immediately begins to manifest itself acutely, and the symptoms intensify in a fairly short period of time.
- A rapidly progressing disease is characterized by frequent exacerbations. It develops rapidly and not much time passes from the appearance of the first symptoms to complete limitation of mobility.
- Moderately progressive pathology occurs with periodic exacerbations.
- The slowly progressing form has a blurred clinical picture. In this case, spondylosis affects the spine unnoticed and several years may pass before constant pain appears.
The faster spondylosis develops, the more acutely it manifests itself. Accordingly, it is easiest for people with a fulminant or rapidly progressive form to obtain a disability group. They, as a rule, very quickly lose the ability to care for themselves and suffer from severe pain. They most often require surgical intervention, after which a course of rehabilitation is required. If body functions are fully restored after treatment, then the disability group can be removed.
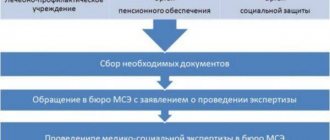
How are disability groups assigned?
Disability can only be obtained when the disease reaches a certain stage. In the absence of proper treatment, progression of spondylosis is inevitable.
- At the first stage, the patient cannot receive a disability group. Despite the fact that osteophytes are already beginning to form on the vertebrae, they do not interfere too much with a person’s life. The mobility of the spine is limited, but not completely. In the photographs you can see that the growths have not yet left the perimeter of the vertebrae.
- Due to impaired mobility of the spine at the second stage, the patient has the right to qualify for the third disability group. To do this, he will need to pass a commission. She will give a conclusion on the assignment of disability if, on x-rays, the growths have left the vertebrae.
- The third stage is the most severe; a second or first disability group may be assigned to it. The choice of group depends on the degree of vertebral fusion and the location of the disease. In photographs, osteophytes resemble staples. There is also a narrowing of the intervertebral canals. Vertebrae may be shortened.
Staples on the spine can form in different parts. In some cases, the fusion is so strong that a person cannot independently perform basic movements, then the first disability group is assigned. Otherwise, at the first stage, it’s time to apply for the second group. Disability is assigned by decision of a medical council.
Treatment of lumbar spondyloarthrosis
Treatment of the disease involves the administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Diclofenac, Voltaren, Indomethacin. Drugs in this series reduce pain and partially restore motor activity. The duration of the effect depends on the type, stage of pathology, and individual sensitivity of the patient.
No less important drugs are chondroprotectors. Glucosamine and Chondroitin sulfate act on cartilage tissue, relieve the symptoms of the disease in question, which allows:
- reduce the frequency of exacerbations to a minimum;
- normalize mobility by relieving pain and stiffness in the back;
- stop the process of destruction of cartilage tissue of the spinal column;
- prevent involvement of healthy vertebrae in the inflammatory-degenerative process.
These chondroprotectors are known for their positive tolerability profile. Medicines are safe for health.
Additionally, hormone therapy is carried out to stop the inflammatory process. More often, Dexamethasone is prescribed in small dosages or Prednisolone - according to the scheme. Prescribing vitamins allows you to normalize blood flow to tissues and improve metabolic processes. The doctor recommends administering B1, B2, B6, B12 - they are most effective in this case.
Local application of medicinal gels and ointments is aimed at reducing back pain, which allows you to fully relax.
The doctor prescribes dietary nutrition, active therapeutic exercises, and systematic visits to massage. The patient needs orthotics - the use of a fixing belt or corset. If the specialist does not see any contraindications to this, then the option of acupuncture is considered. Physiotherapeutic procedures will help consolidate the positive result.
Shock wave therapy treatment
The use of shock wave therapy to eliminate spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine makes it possible to reduce the static-dynamic load on it. The advantage of the technique is the normalization of blood circulation, which allows the active substances of drugs to be directed to the site of pathology. The procedure helps achieve a therapeutic effect.
The second advantage of the technique is the ability to reduce pain, relieve stiffness, and restore mobility.
The third positive point is a reduction in the consumption of medications. Pain and other unpleasant symptoms recede, and the need to administer analgesics is eliminated on its own.
The method has a small list of contraindications, which increases the chance of undergoing the procedure.