It turns out that people suffered from such a disease as ankylosing ( ankylosing spondylitis ) back in ancient times. Archaeological scientists came to these conclusions when studying Egyptian mummies. They discovered a human skeleton where the sacrum, pelvic bones, lumbar vertebrae and 10 thoracic vertebrae were fused into a single bone, which is extremely typical for ankylosing spondylitis.
In the mid-16th century, an attempt to describe the skeleton of a person with the same disease was made by the Italian Renaissance surgeon Realdo Colomno. But only the outstanding Russian doctor and scientist Vladimir Bekhterev at the end of the 19th century was the first to systematize the signs of spondyloarthritis. In honor of this scientist, this disease in Russia is often called ankylosing spondylitis.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a relatively rare rheumatological disease that affects about 2% of the world's population. This disease is predominantly “male”, and it is typical for young men (from 15 to 40 years). Ankylosing spondylitis is 5 times less common in women.
1
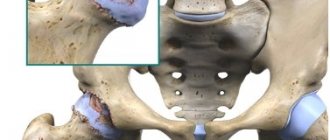
X-ray of the pelvis
2 Diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
3 Fluorography
Morbidity statistics
This is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease of connective tissue of an autoimmune nature with primary damage and deformation of joints and internal organs. Seronegative forms of arthritis are characterized by the fact that, unlike the seropositive form, rheumatoid factor (RF) - an antibody to immunoglobulin G, which transforms into a protein foreign to the body - an antigen, is not detected in the blood and joint fluid of patients. The disease code according to ICD is 10 M06.0.
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (SNRA) affects one fifth of all RA patients. The prevalence of the disease is no more than 1%. Women get sick more often.
How the disease develops
The main reason for the development of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis is a genetic factor - a family predisposition to the disease.
Therefore, if one of your close relatives suffers from this articular pathology, you need to take care and avoid exposure to various factors that can trigger the autoimmune process.
These factors include:
- stress, heavy physical and mental stress;
- any acute and chronic infections; Especially often, various types of herpes viruses are “accused” of involvement in CHRA, including the Epstein-Barr virus, which causes mononucleosis;
- traumatic lesions of the limbs;
- hypothermia;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- living in cold, damp areas.
Chondroprotectors: what are they, how to choose, how effective are they?
Joint pain at rest
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis begins when, under the influence of these factors, an autoimmune process is launched in the body, which is based on an imbalance between cytokines that support and suppress inflammation. Cytokines are information molecules that regulate physiological processes in cells. Inflammatory cytokines predominate, which is the basis for an imbalance of the immune system and a long-term inflammatory process that develops in the connective tissue.
First of all, the connective tissue of the joint cavity is affected: the synovial membrane becomes inflamed and grows, cartilage and bone tissue suffer, and joint function is impaired.
There is connective tissue in the internal organs, so they can also be damaged. With a long-term pathological process, protein metabolism is disrupted and protein-polysaccharide complexes - amyloid - are deposited in the internal organs. Amyloidosis is a serious complication that causes damage to the function of internal organs - heart, liver, kidneys, lungs.
Types of spondylitis
Depending on the causes of the disease, pathology is usually divided into:
- Specific spondylitis
. This category includes diseases caused by a specific infectious pathogen. As a rule, these are spondylitis secondary to tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea, typhoid fever, actinomycosis, brucellosis and other diseases. - Nonspecific spondylitis
.
This group of spondylitis occurs as a result of nonspecific infections. They are caused by microorganisms that are already found in the human body or are considered only conditionally pathogenic. Therefore, spondylitis
begins only after a “trigger” has been triggered - for example, injury, stress, hypothermia, hormonal imbalance.
Based on the location of the inflammatory focus, the following are distinguished:
- cervical spondylitis;
- thoracic spondylitis;
- spondylitis of the lumbar spine
.
of spondylitis also varies
- it can progress slowly, with exacerbations, quickly and rapidly (within several hours - which is typical for septic spondylitis).
Tuberculous spondylitis
Tuberculous spondylitis
(Pott's disease) most often affects the thoracic region in children and adolescents because their musculoskeletal system is still developing. Bacteria (Koch's bacillus) penetrate the vertebral body and, releasing toxins, provoke a focal necrotic process in it. Over time, tuberculous spondylitis spreads to neighboring vertebrae, leading to the formation of edema and abscesses. Patients complain of increased fatigue, insomnia, and back pain.
Tuberculous spondylitis
may debut several months or even years after infection with tuberculosis - after stress, injury or decreased immunity.
The disease is characterized by a severe course, since it affects large areas at once. Also, the difficulty of treating tuberculous spondylitis
lies in the resistance of the pathogen to most antibiotics.
Aseptic spondylitis
Kümmel-Verneuil disease, also known as aseptic spondylitis
, begins with a back injury. Usually, several months or years pass between the injury and the onset of spondylitis - often patients even forget about the initial incident. However, after the appearance of necrotic lesions in the spine, their condition begins to worsen. Due to improperly distributed load, the risk of compression fractures of the spine and inflammatory processes in the nerve roots increases.
First of all, aseptic spondylitis affects the thoracic region, in rare cases it declares itself as lumbar spondylitis
. Young men under the age of 40-45 are most susceptible to it.
Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis
also known as ankylosing spondylitis. In this disease, the body's immune cells begin to attack its own bone and cartilage tissue, destroying the structure of the joint and the ligaments surrounding it. The body tries to compensate for the loss of tissue by replacing it with bone growths (osteophytes). Ultimately, this leads to ossification and complete immobility of the affected joint.
In addition to the loss of normal motor abilities of patients with ankylosing spondylitis
I am bothered by excruciating pains that do not subside even at night. When fusion of the vertebrae in the thoracic region occurs, difficulty breathing is observed, which can cause congestion in the lungs. Symptoms of the disease intensify after physical activity or prolonged rest.
90% of patients with ankylosing spondylitis
are made up of men.
The disease makes its debut between the ages of 15 and 40 years, and early onset often precedes its unfavorable course. Among patients with ankylosing spondylitis, lumbar spondylitis
.
Symptoms
The symptoms and course of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis differ from the typical manifestations of seropositive RA. The main manifestation of the latter is the gradual damage to the small joints of the hands and feet. Seronegative arthritis presents differently.
Course of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis
First signs
The onset of the disease is usually not gradual, but acute. Suddenly there is a fever. The temperature can be either low-grade or very high, with changes and the appearance of heavy sweating throughout the day. The general condition is disturbed: weakness, malaise, headache, dizziness appear, which are characteristic of the initial stage of the disease.
Stiffness of movement in seronegative arthritis is almost never observed, but the pain syndrome is quite severe. Swelling and pain appear in the area of one large joint. Most often these are the knees, elbows or ankles. At the onset of the disease, there is a characteristic absence of small articular lesions of the hand and foot - this is a rare clinical symptom in this form of the disease.
In the lymph nodes with seronegative arthritis, the following changes occur: they become dense and painless.
Sometimes signs of damage to internal organs appear from the very beginning. If the heart is affected, this is shortness of breath and palpitations.
Obvious symptoms
Gradually, the fever gives way to normal or subfebrile temperature. After six months, the inflammatory process in seronegative arthritis becomes symmetrical due to the appearance of inflammation in several more joints. After some time, the process spreads further, inflammation may occur in the small joints of the fingers and toes - signs of polyarthritis develop. The hands and fingers take on a characteristic shape.
Joint pain increases, destructive changes quickly develop, pronounced signs of ankylosis (fusion of cartilage and bones), and impaired limb function appear. Quite often, with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis, the hip joint is affected. Erosion of the articular surfaces is insignificant, but there is a rapid proliferation of connective tissue, closure of the joint space and the formation of ankylosis.
Systemic manifestations in seronegative RA are also not long in coming: signs of damage to the heart (endocarditis), lungs (pleuritis), kidneys (nephritis), and intestines appear. The liver and spleen enlarge. By prescribing timely treatment, it is possible to achieve long-term remission during this pathology and suppress the progression of the disease. If this is not done, the disease will progress.
The most dangerous symptoms of seronegative arthritis
The most dangerous signs are:
- fever for a long time;
- multiple lesions of large and small joints;
- the appearance of severe shortness of breath at rest.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
Forecast
This disease will have to be treated throughout your life.
The prognosis worsens:
- In men.
- At early onset (before 19 years of age).
- With the development of hip arthritis and limited mobility of the spine in the first years from the onset of the disease (the first 2 years).
- If you have the HLA-B27 marker and family members suffering from the disease.
- With concomitant peripheral arthritis and local pain at the attachment sites of tendons and ligaments.
Remissions (periods of improvement) are short-lived and unstable; the disease sooner or later results in partial or complete loss of spinal mobility and varying degrees of disability.
Complications
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
If a sick person is not prescribed comprehensive treatment in a timely manner, the course of the disease may become more complicated:
- necrosis of the femoral head, which will lead to disability;
- severe damage to the cardiopulmonary system;
- amyloidosis, in which the functions of internal organs are affected.
To reduce the risk of developing severe complications with seronegative arthritis, you must follow all your doctor’s recommendations.
Stages of the disease
There are 4 stages of development of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis:
- Initial.
During the first one and a half to two months, signs of intoxication and initial damage to one large joint develop. - Early.
This is the first 12 months of the disease. Articular degenerative changes progress, the lesions become symmetrical. Signs of systemic damage appear. - Progressive.
Develops from one to two years. Irreversible damage increases in the affected areas, and damage to the small joints of the hand and foot occurs. - Launched.
After two years. Due to ankylosis, joint function is impaired and the limb becomes immobile.
Stages of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made on the basis of characteristic symptoms and is confirmed by additional examination data, which makes it possible to identify the pathological process at an early stage.
- Laboratory research:
- general blood test - signs of inflammation are revealed - accelerated ESR, increased leukocyte content; signs of anemia;
- biochemical analysis - an imbalance of serum proteins is revealed: the amount of alpha globulins decreases and the amount of gamma globulins increases; C-reactive protein (CRP) is detected in the blood - a sign of an inflammatory process;
- Immunological tests are a marker that allows you to distinguish between seronegative and seropositive types of RA:
- rheumatoid factor (antibodies to IgG) is not detected or its titers are insignificant; the presence of rheumatoid factor indicates seropositive RA;
- antibodies to cyclic citrulline-containing peptide (anti-CCP, ACCP) may be positive and then this confirms the diagnosis of seronegative arthritis; citrulline is a metabolic product that is normally completely excreted from the body; in RA, enzymes are secreted that integrate citrulline into tissue proteins and convert it into a foreign protein - antigen; The immune system produces antibodies to this antigen.
- Instrumental diagnostics:
- x-ray of joints;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI or CT are the most informative diagnostic methods;
- if necessary, arthroscopy - endoscopic examination of the affected joint.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
Prevention
Preventive measures include preventing injuries and the possibility of introducing infectious diseases into the body. This requires:
- install curbs and rugs in the bathroom,
- avoid walking in the dark,
- minimize heavy lifting and other excessive stress on the spinal column,
- avoid walking on slippery surfaces,
- wash your hands before eating,
- eat only fresh food,
- properly handle food before consumption,
- drink high-quality, preferably boiled or filtered water.
When these preventive measures are taken, the chance of contracting infectious diseases and injuring the spine, thereby causing other degenerative changes, is reduced.
Therapeutic measures
Is it possible that seronegative rheumatoid arthritis can be cured? It is impossible to cure completely, but in the treatment of seronegative forms of RA, as in the treatment of any other chronic disease, they try to achieve long-term remission. The longer it is, the higher the patient’s quality of life.
Modern treatment technologies make it possible to achieve unlimited remission. But the patient should always remember that a relapse is possible and follow the doctor’s recommendations to prevent exacerbations.
Treatment of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis should be comprehensive and include:
- compliance with the motor regime, exercise therapy;
- proper balanced nutrition;
- drug therapy;
- blood purification;
- traditional medicine prescribed by a doctor;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- orthopedic correction;
- surgery.
Treatment of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis
Regime, exercise therapy, diet
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis requires a conscious attitude to the daily routine and physical activity. Restriction of movement is necessary only during exacerbations of seronegative arthritis. As soon as the patient’s condition improves, he is prescribed physical therapy (physical therapy) complexes with a gradually increasing load. If this is not done, blood circulation will be impaired, the mobility of the limb will decrease, the risk of developing ankylosis will increase, the muscles will lose their strength and decrease in volume.
In addition to exercise therapy, during remission it is recommended to walk, swim, and ride a bike more. Traumatic movements - jumping, football, etc. - are contraindicated.
It is important to eat right; your diet should contain a sufficient amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Food should be enriched with calcium and vitamin D (cottage cheese, cheese, kefir, fish oil) - this is necessary to prevent osteoporosis.
Drug therapy and traditional medicine
Medical treatment of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis begins with the use of anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve inflammation and associated pain. Patients are prescribed medications from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These are Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, Meloxicam, etc. They are prescribed internally or in the form of external agents - gels, ointments, creams.
In severe cases of the disease, glucocorticosteroid hormones (GCS) are prescribed - Hydrocortisone, Betamethasone, Dexamethasone, etc. They are taken orally, injected or directly into the joint cavity. They can also be used externally in the form of ointments and creams. GCS perfectly relieve signs of inflammation, but have serious side effects, so they are prescribed only when indicated and in short courses for several days.
The next group of drugs is immunosuppressants - drugs that suppress excessive immune activity - Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine, Cyclophosphamide, Cyclosporine, Leflunomide. Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis often does not respond to the use of a particular drug and is more difficult to treat than seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Therefore, doctors often use combination basic therapy, using several medications at once, monitoring the patient’s condition and laboratory parameters.
The most modern drugs for suppressing the activity of seronegative arthritis are biological agents. Drugs in this group belong to biologically active substances (antibodies, cytokines) that act directly on broken parts of the immune system. These drugs include Rituximab, Tocilizumab, Abatacept. This is an effective, but quite expensive therapy that can take treatment to a higher level.
To enhance the effect of drug therapy for seronegative arthritis, the use of individually selected medications is combined with traditional medicine. This can also reduce the large drug burden on the patient's body.
Blood purification
In case of severe intoxication and a widespread process, procedures such as hemosorption and plasmapheresis, which rid the blood of toxic substances, can be used.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy is added at all stages of treatment of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Electrophoresis with NSAIDs and GCS helps eliminate inflammation and pain; magnetic and laser therapy can be used to suppress destructive processes in tissues. Physiotherapy courses speed up the recovery process and reduce the risk of complications.
Orthopedic correction
A patient with seronegative arthritis is taught to hold the affected limb in a physiologically correct position to reduce the risk of deformity. For this purpose, special devices are used to straighten the limb - orthoses. They are worn for several hours a day, removed during exercise. Orthoses help treat joint dysfunction in various forms of rheumatoid arthritis.
Surgical operations
Treatment methods for seronegative rheumatoid arthritis
It is rarely used, only if functional joint failure is diagnosed. Endoprosthesis replacement or resection of part of the joint capsule is performed. The operation helps to cure the patient even with severe lesions.
Nutrition
It may seem that arthritis of various types cannot in any way depend on the patient’s diet and there is no need to filter the patient’s menu even in severe stages. This is not true, because it is very important to prevent weight gain. The greater the patient's weight, the greater the load on the joints, which is dangerous and harmful for sick, deteriorating tissues. It is better to follow a gentle diet that includes all the necessary substances, but limit yourself in the amount of food and frequency of meals.
The diet for the patient should be gentle
Approach to treating the disease in our clinic
The Paramita clinic in Moscow practices an individual approach to the treatment of each patient. Our doctors use in their practice a combination of advanced Western and traditional, time-tested, Eastern methods of treating seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Before prescribing complex therapy, a complete examination of the patient is required. Treatment methods used:
- drug therapy – a complex of highly effective drugs is prescribed, the latest regimens and techniques are used;
- medicinal herbs – both scientific approaches to the use of herbal medicine and folk remedies are used to reduce the burden of medications;
- physiotherapy – a skillful combination of drug therapy with physiotherapy gives a quick and lasting positive effect;
- therapeutic movement - specially selected physical therapy and kinesitherapy exercises improve blood circulation and train muscles; therapeutic massage consolidates this effect;
- plasma lifting (PRP therapy) is an advanced technique for activating recovery processes using the patient’s own platelets, processed using a special technique;
- reflexology (RT - acupuncture, moxibustion with wormwood cigarettes, acupressure) - impact in various ways on active points on the surface of the human body, reflexively associated with various organs and tissues; proven over centuries, the high efficiency of RT methods allows you to completely relieve the patient from relapses of the disease, even without the use of drugs;
- Pharmacopuncture is a reflexology method in which modern effective medications are injected into acupuncture points.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Our clinic’s specialists are able to quickly achieve remission of seronegative arthritis and maintain it for a long time. Patients who follow all the doctor’s recommendations and regularly carry out anti-relapse treatment forget about their disease and lead a normal life.
Prevention of exacerbations
Prevention of exacerbations
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis is a serious disease that requires constant adherence to doctor's recommendations. To prevent relapse, you need:
- move more, do mandatory physical therapy exercises, but avoid heavy physical activity, lead a healthy lifestyle;
- avoid hypothermia, if necessary, change place of residence, profession;
- eliminate all bad habits;
- Healthy food;
- maintain the health of your body, treat concomitant diseases;
- carry out all procedures prescribed by the doctor.
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis can and should be constantly maintained in remission. Specialists from the Moscow Paramita clinic will help you cope with this difficult task and improve your quality of life.
Literature:
- Nasonov EL, Karateev DE, Balabanova RM. Rheumatoid arthritis. In the book: Rheumatology. National leadership. Ed. E.L. Nasonova, V.A. Nasonova. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media; 2008.S. 290–331
- Nasonov EL, editor. Genetically engineered biological drugs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Moscow: IMA-PRESS; 2013.
- Emery P, Breedveld FC, Dougados M, Kalden JR, Schiff MH, Smolen JS. Early referral recommendation for newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis: evidence based development of a clinical guide. Ann Rheum Dis 2002;61:4 290-297 doi:10.1136/ard.61.4.290
- Schett G, Emery P, Tanaka Y, et al. Tapering biological and conventional DMARD therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: current evidence and future directions. Ann Rheum Dis 2016l0:1-10. Doi.10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209201.
Themes
Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 04/09/2020 Date of update: 11/12/2020
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (2)
Causes of spondylitis
Spondylitis of the spine
can be called a “disease of neglected infections” - most often it occurs as a complication due to late access to a doctor for the treatment of infectious diseases.
It can be caused by both a chronic infection circulating in the body (for example, streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, actinomycosis) and an acute infectious disease (for example, typhus, gonorrhea and even tonsillitis or pyoderma). The following factors can provoke the development of spondylitis against the background of an underlying infection:
- general suppression of the immune system due to an unhealthy lifestyle or bad habits;
- hormonal changes in the body or endocrine disorders;
- psycho-emotional or physical stress;
- spinal injuries;
- the presence of a focus of chronic infection;
- severe hypothermia or overheating;
- long-term use of medications (especially glucocorticoids and cytostatics);
- genetic predisposition (indicative if there have already been cases of spondylitis in the family).