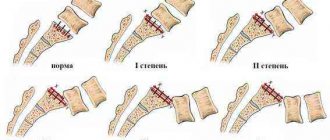
Sclerosis of the endplates is a chronic process that is not an independent disease, it is only one of the signs of the so-called degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the spine (DDPP) and is one of the indicators of a violation of the structure (its compaction) in the intervertebral space, or rather, above and below intervertebral discs. If symptoms of neurological pathology are detected, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct detailed diagnostics to verify the diagnosis and carry out therapy. The clinic is equipped with the most modern diagnostic equipment, which allows us to accurately identify the cause of endplate sclerosis.
Through the endplates, nutrition of the intervertebral discs occurs, as well as the removal of metabolic products from them. But when these plates become denser, all metabolic processes in the intervertebral space are disrupted. This symptom develops gradually and over a long period of time; often at the initial stage, the patient learns about his illness only during preventive examinations and examinations of the spine. Over time, as the disease progresses, pain and limited movement in the spine appear.
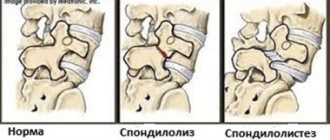
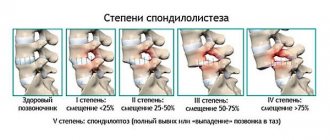
This disease of the spine today is very widely diagnosed both in old age and earlier.
Causes of endplate sclerosis:
- natural age-related changes;
- genetic predisposition;
- as a consequence of other spinal deformities (scoliosis, osteochondrosis, etc.);
- heavy loads on the spine (lifting weights);
- weakening of the muscles along the spinal column;
- spending a long time in a static position (sedentary activity);
- due to the occurrence of intervertebral hernias, which put pressure on the discs and vertebrae;
- the presence of an inflammatory process between the vertebrae;
- spinal injuries.
What is the disease?
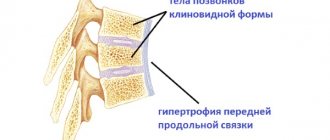
Sclerosis of the endplates of the cervical vertebrae is considered a process in which an increase in tissue density in the endplates is diagnosed. In mature patients, thinning of the end plates and deterioration of blood circulation in them are observed.
Features of the disease
When the vertebrae thicken, osteophytes form, which put pressure on the intervertebral disc. The compaction leads to pinching of nerve endings and the development of inflammation in the spine. Patients report pain in the back and an increase in neurological symptoms.
Diagnostics
Damage to the endplates can only be proven by conducting an instrumental examination. Classic methods are used for this:
- CT scan shows the condition of the vertebrae, the presence of bone growths. It is relevant when recognizing advanced forms of the disease; sometimes contrast is introduced to determine the degree of vascular damage. Read more about CT→
- MRI – reveals degenerative-dystrophic changes in osteochondrosis. Shows how much the joint space between the vertebrae has decreased. Read more about MRI→
- Densitometry is a special test to determine bone density. Usually prescribed to elderly patients.
For subchondral sclerosis of the cervical spine, duplex scanning of the brain vessels is performed to determine the degree of circulatory disturbance. The basis for its passage is neurological symptoms, visual and hearing disorders.
Causes
Sclerosis of the vertebrae occurs due to disruption of their blood supply, which leads to the growth and compaction of connective tissue. The most common cause of the disease is considered to be inflammation of the spine in the area of destruction of the intervertebral disc. The progression of the pathological process contributes to the formation of bone growths - osteophytes, which injure the surrounding soft tissues and aggravate the course of the disease.
Osteophytes with sclerosis grow along the edges of the vertebrae and in the area of the facet joints
Spinal sclerosis appears due to the following reasons:
- back injuries;
- osteochondrosis;
- congenital or acquired underdevelopment of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the spinal column;
- multiple sclerosis;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- poor nutrition;
- characteristics of labor activity (miners, builders);
- professional sports (dancers, football players, wrestlers);
- endocrine pathology (obesity, diabetes mellitus);
- age after 55 years;
- genetic predisposition.
Scattered foci of sclerosis in the bone tissue of the vertebrae are a secondary reaction to the influence of a damaging factor. In most cases, the cause of the pathological process is osteochondrosis. Its progression leads to the appearance of protrusions and hernial protrusions, which causes compression of the nerve roots and causes neurological symptoms.
Subchondral osteosclerosis develops under the influence of various provoking factors. The occurrence of pathology is observed with premature aging of the plates. A common cause of the disease is genetic predisposition. People whose close relatives have suffered from the disease are at risk. Osteosclerosis can damage the cervical or spinal region due to bruises.
Which doctor should I contact?
At the initial stage, there is no pain or stiffness. The person does not seek medical help, attributing rare discomfort to ordinary fatigue. But it is at this stage that conservative treatment with chondroprotectors is most effective. If your neck or lower back ache from time to time, or your elbow or knee creaks, then you should make an appointment with a doctor.
The patient cannot independently determine the presence of sclerosis or find out what disease has begun to develop. Even the doctor makes a diagnosis based on test data. Therefore, it is advisable to make an appointment with a therapist. A general practitioner has all the diagnostic skills.
He will order an X-ray examination, and after studying the results, he will refer the patient to a doctor of a narrow specialization:
- rheumatologist for gout, gouty, rheumatoid, infectious, reactive arthritis;
- to a traumatologist for injuries to the musculoskeletal system;
- orthopedist for deforming osteoarthritis;
- vertebrologist or neurologist for osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia.
These doctors will carry out a number of additional diagnostic measures and then begin treatment. Other specialists will also be involved in the therapy. For example, with osteochondrosis caused by diabetes mellitus, the participation of an endocrinologist is required in treatment.
Clinical picture
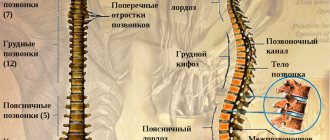
Clinical manifestations of spinal sclerosis primarily depend on the disease that led to sclerotic processes in bone tissue. Depending on the location of the pathology, sclerosis of the cervical, lumbar and thoracic spine is distinguished. In severe cases, the entire spinal column is affected, which leads to a worse prognosis of the disease.
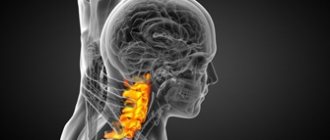
Symptoms of damage to the cervical spine:
- pain in the neck, aggravated by turning and tilting the head;
- imbalance;
- numbness of the upper extremities;
- memory impairment;
- headaches of varying degrees of intensity, dizziness;
- paresthesia of the fingers (tingling sensation, burning sensation, “crawling sensations”);
- decreased hearing and visual acuity.
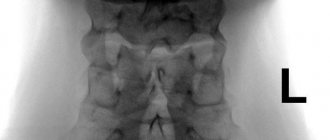
Subchondral sclerosis is detected by radiography and tomography
Symptoms of damage to the lumbar spine:
- pain in the lumbar region, aggravated by bending the body;
- pain syndrome extends to the lower extremities;
- numbness of the legs, paresthesia in the feet (burning, tingling of the fingers);
- disruption of the pelvic organs (constipation, urinary incontinence).
As a result of the pathology, a protective muscle spasm occurs in the area of inflammation, which aggravates pain in the back. The pain syndrome intensifies with the formation of osteophytes, which injure soft tissues and irritate nerve endings. In severe clinical cases, intense pain can be eliminated after surgery to remove it.
Dangerous consequences and complications
If a person is found to have damage to the subchondral layer, then an inflammatory or destructive-degenerative disease has already begun to develop in his body. In the absence of medical intervention, it will spread to healthy areas of the spine and nearby joints.
Further cell destruction can lead to the following complications:
- spontaneous hemarthrosis - sudden hemorrhage inside the joint cavity;
- ankylosis - complete or partial lack of mobility in a joint or part of the spine;
- osteonecrosis of peri-cartilaginous tissues;
- subluxations of joints or vertebrae.
The muscles, ligaments, and tendons gradually weaken. The production of synovial fluid, which acts as a shock absorber, decreases. And due to the weakening of local immunity, infectious processes will increasingly develop: bacterial synovitis, bursitis, tendinitis, tendovaginitis. At the last stage of arthrosis, a person has difficulty caring for himself in everyday life, loses professional skills, and becomes deeply disabled.
Symptoms
The pathology is characterized by mild symptoms, so the patient cannot determine it independently in the early stages of the disease. Often the symptoms of the disease are confused with manifestations of osteochondrosis. A child or adult patient complains of pain that is moderate or pronounced. The pain may radiate to the knee joint or foot. Some patients claim that their neck hurts.
Development of sclerosis
Patients report a tingling sensation in the lower back. Another symptom of the disease is numbness of the surface of the affected area. A sign of the disease is difficulty breathing, as pressure is placed on the thoracic region. With pathology, patients' coordination of movements changes. It is accompanied by difficulty in lumbar flexion.
Symptomatic manifestations
In most cases, it is determined at later stages of development, and therefore, complete recovery from this disease is impossible, but by carefully studying all the signs and consulting a doctor in time, you can prevent the progression of the disease.
- A characteristic symptom is dull or sharp pain when trying to turn, tilt or tilt the head. In later stages, if the patient has not consulted a doctor and has not completed the course of necessary therapy, the pain becomes more acute and over time, the ability to turn or tilt the head is completely lost, that is, the joint loses its ability to function.
- You can also observe symptoms such as: numbness of the extremities, both upper and lower, the patient often feels dizzy, there is ringing and noise in the ears, coordination of movements is impaired, and the patient begins to hear and see poorly.
Treatment of sclerosis
Diagnostic measures require an examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis by the doctor, which will allow him to establish a preliminary diagnosis. The doctor examines the patient's body and palpates the vertebrae, appendix and bones. To confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to:
- X-rays. Provides the ability to identify formations on the vertebrae and determine bone problems.
- Densiometry. A diagnostic procedure is recommended to determine the level of compaction.
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging. Allows you to determine the nature of changes in the spine and nearby tissues.
- Electroneuromyography. The procedure determines how much nerve fibers conduct impulses. Thanks to manipulation, the degree of compaction is determined.
In accordance with the person’s well-being and the characteristics of other pathologies, a treatment regimen is selected. Patients are prescribed drug therapy:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Celecoxib, Diclofenac, Nimesulide);
- chondroprotectors, which improve the condition of intervertebral discs;
- painkillers (Ketorola, Ketanova);
- muscle relaxants to combat muscle spasms (Mydocalma, Sirdaluda).
If drug therapy is ineffective, it is recommended to sclerose the vessels, which improves blood circulation, so the pathology will compact the tissue less intensively. To improve the patient's condition, daily physical therapy is recommended. Exercises are selected by the doctor in accordance with the severity of the pathology.
Treatment of sclerosis should be comprehensive, which will reduce the degree of its progression.
Subchondral sclerosis is a radiological sign of diseases affecting the spinal column. To detect it, the following instrumental examination methods are prescribed:
- radiography of the spine in direct and lateral projection;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging;
- densitometry (determining the density of vertebral bone tissue).
Additionally, laboratory diagnostics are prescribed - a general and biochemical blood test to identify inflammatory and metabolic disorders.
Pilates and yoga classes prevent the progression of vertebral sclerosis
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is a conservative treatment method using cold, which is prescribed for diseases of the musculoskeletal system, especially the spine.
Due to short-term exposure to extremely low temperatures, regeneration work begins in all systems of the body.
The course gives several positive effects that last up to six months:
- long-lasting analgesic effect;
- elimination of inflammation and spasms;
- reducing the load on the heart;
- increased blood supply to internal organs.
Preventive actions
Everyone knows that any disease is best prevented than treated. An integral part of both treatment and preventive measures to prevent spinal sclerosis is proper nutrition.
It is necessary to eat foods enriched with vitamins and microelements that help normalize metabolism and blood circulation. Such products include:
- seafood;
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- lean meats, consumed only boiled.
In addition, you should definitely stop using alcohol and tobacco products. In addition to nutrition, special attention should be paid to maintaining an active lifestyle. Very helpful:
- sign up for the pool;
- start doing yoga;
- spend more time outdoors, walking;
- do physical exercise.
All exercises performed should begin with moderate loads and increase them gradually.