Symptoms of the disease ↑
Spondylolisthesis manifests itself in different ways, depending on the degree of its development:
first degree displacement (up to 25% of the width of the entire vertebral body) occurs very often and is not accompanied by any extraneous symptoms; the second degree of displacement (50%) is more pronounced and causes pain in the lumbar region, which is accompanied by radicular symptoms - shooting pain radiating to the lower extremities and intensifying with any load on the spine; third degree of displacement (more than 50%). It is characterized by the formation of pain with almost any minor concussion of the spine (unsuccessful descent or ascent of stairs, etc.). A spasm of the paravertebral muscle appears, as a result of which the patient’s active and passive movements are sharply reduced. The displacement of the vertebra can be felt with your hands.
Some experts also distinguish stages 4 and 5, when a vertebra “falls out” into the pelvic area.
Causes of spondylolisthesis
Vertebral displacement is a disease that most often occurs due to insufficient or, on the contrary, excessive physical activity
It is important to find the “golden mean” in physical education so as not to harm your spine
Displacement of the vertebrae can occur for many reasons
But there are other reasons, which include:
Previous injuries. If a patient has ever encountered a hernia, an advanced stage of osteochondrosis, or another disease of the musculoskeletal system, then his spine remains weakened and vulnerable to other diseases for the rest of his life. If such a person does not take enough care of his health, then the chance of vertebral displacement is quite high. Hereditary disorder of the structure of the spine or its parts. There are cases when a person from birth has this structure somewhat different from the “standard” one - individual vertebrae remain underdeveloped, the position of the entire column is not entirely normal, and the healthy configuration of the ligaments is disrupted. Temperature changes. Often the cause is hypothermia, which can occur in both winter and summer. In the cold season, it occurs due to insufficient insulation of the back, and in the warm season, due to the fact that a person can be under an air conditioner or fan for a long time, having previously been in the scorching sun. This can lead not only to displacement, but also to many other diseases of the spine. Weight lifting
It is very important to lift heavy objects correctly: you need to squat down and only then pick up the object, and not lean towards it. In this case, although the load on the spine will be exerted, it will not be so strong - the force will not work to break. Sitting for a long time
The spine needs movement, and if a person constantly sits, then his musculoskeletal system suffers greatly. In a sitting position, a load of 150-180 kg is placed on the lumbar region. The spine can withstand such pressure for some time, but not permanently. Therefore, if you have to do such work at a desk, then at least once every three hours you need a break, preferably with simple physical exercises.
Staying in a sitting position for a long time is very dangerous for the spine, especially if a person does not exercise
- Age-related changes. Older people are more likely to experience back pain: over the years, the tissues of their spine weaken and “wear off” against each other. Because of this, they experience disorders more often, and spinal displacement is no exception.
- Falls, accidents and other injuries. If a person has ever had a spinal injury due to an accident, bad move, or any other unfortunate event, then there is also a high chance that he or she may experience spondylolisthesis.
Therapeutic warming products
Don't forget about psychological reasons. The connection between psychoemotional and physical states is studied by the science of psychosomatics. Experts in this field argue that displacement of the vertebrae in the lumbar region is often caused by a feeling of insecurity or dislike for oneself, as well as “dropping out” from society. When a person is regularly under pressure from his own negative thoughts and experiences, this also affects his physical condition.
Therefore, it is important to take care of a healthy psychological atmosphere
Even an unstable mental state can cause spondylolisthesis
Treatment methods ↑
At the very initial stages of the disease, conservative treatment methods are used.
These include:
relieving pain and inflammation using medications; the use of orthopedic products that fix the spine; physiotherapy.
If all of the above methods cannot cope with the problem that has arisen or the disease has reached its final stage, then surgical intervention is resorted to.
But still, the most effective and affordable method of treating spondylolisthesis is physical therapy, which will be the rest of the story in the article.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Did you know that...
Next fact
Displacement that does not affect nerve fibers is asymptomatic, but if a nerve is pinched or the pathology progresses, then symptoms appear.
At the initial stage of development, patients do not feel pronounced signs of damage. Spontaneous pain occasionally occurs when lifting heavy objects or staying in one position for a long time.
The second stage is characterized by the appearance of aching pain when bending, turning, or physical activity.
The third degree of development is characterized by a sharp limitation of movements and severe pain. The spinal disc is greatly displaced, even completely erased, which leads to pinched nerve fibers, problems with urination and defecation.
At the fourth stage, patients complain of incessant excruciating pain in the back, joints of the arms and legs, and hips. Cramps, fatigue and severe weakness appear, knees give way, and gait changes.
General symptoms that do not indicate the presence of displacement:
- numbness of the lower back;
- loss of concentration;
- drowsiness;
- lameness;
- dizziness;
- severe back pain;
- fatigue, weakness;
- the appearance of intervertebral hernia, protrusion.
Often, against the background of spondylolisthesis, infectious diseases of the spine develop, complete or partial numbness of the limbs and lameness are observed.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor must interview the patient, collect a complete anamnesis and study the medical history. Palpation and examination are required, and only after that, the specialist will prescribe additional examinations.
These include:
- MRI or CT;
- radiography;
- spondylogram.
These procedures will allow you to accurately see the location of the vertebral displacement, the stage of progression of the lesion, and possible pinched nerve endings.
Based on the examination, the doctor prescribes an appropriate course of therapy, which includes taking medications, gymnastics, massage, and physiotherapy. In some cases, it will not be possible to do without surgical intervention.
Video: “Diagnostics of vertebral displacement in the lower back”
Want to know more about spondylolisthesis? Read the following articles:
- Surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis
- Spondylolisthesis of the lumbosacral spine
- Spondylolisthesis of the cervical spine
Why is exercise therapy necessary for successful treatment? ↑
Physical therapy cannot completely cure this pathology - it will simply help keep it under control.
The main focus of exercise therapy is strengthening the abdominal and back muscles.
Thereby:
lumbar lordosis decreases; the patient's ability to hold the torso in an upright position for a longer time appears.
According to statistics, the majority of spinal spondylolisthesis is caused by weakening of muscle groups.
When you regularly perform a certain set of exercises, the spinal column is firmly fixed in a tight muscle corset.
A set of exercises for physical therapy, as a rule, is compiled by a methodologist.
In doing so, he must take into account:
the cause of the development of the pathology; patient's age; degree of pathological changes.
Indeed, in each individual case, methodological recommendations may differ significantly.
For example, young people involved in sports and children most often suffer from isthmic or dysplastic spondylolisthesis, but older people, those over 60 years old, develop degenerative spondylolisthesis.
The most effective exercises for spondylolisthesis ↑
A set of exercises from therapeutic gymnastics
If there is pain, the doctor prescribes simpler exercises with the following parameters:
starting position - lying on your back; slow and deliberate movements that cause the least pain; small range of motion.
Spinal stretching exercises:
№ 1
Lie on your back, stretch your legs, point your toes towards you, put your hands under your head and slowly stretch your whole body.
Freeze in this position for 5-10 seconds, then relax and repeat the exercise 3-4 more times.
№ 2
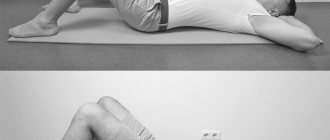
The starting position is the same - lying on your back. Bend one knee and clasp it with your hands, bringing it closer to the chest.
Freeze for a few seconds, then relax and repeat 3-5 times. Then change the knee;
№ 3
The so-called barrel - position, as in the previous exercise - lying on your back with both knees clasped.
Only now you need not to freeze, but to make several rocking movements back and forth.
In this case, the spine will be “stroked” on the floor, which can help smoothly place the slipped vertebra into place.
When severe pain subsides, you can begin to perform exercises aimed at strengthening the abdominal and back muscles in order to create a muscle corset that will support the spinal column.
The main feature of exercises to strengthen the listed muscles is their implementation in the so-called static mode, i.e. holding a certain pose without moving the body.
This is due to the fact that various rotations and bends of the body can contribute to the appearance of severe pain and even greater displacement of the vertebra.
Exercises to help strengthen your back muscles:
№ 1
Get on all fours, then slowly raise your straight leg, holding it in this position for several seconds.
Repeat 5-10 times. Do the same with the other leg.
№ 2
Lie on the floor on your stomach, place your arms along your body.
Gently lift your chest and head, holding the pose for about 3 seconds. Repeat the exercise 3 times.
№ 3
Starting position – lying on your stomach, arms extended, head slightly raised. Lower and raise your leg (very slowly).
Can be combined with lifting the opposite leg with the hand.
Repeat 10 times, then change legs;
Exercises to help strengthen your abdominal muscles:
№ 1
Lie on your back, put your hands behind your head (an easier option is to put them along your body), bend your legs 90 degrees at the knees.
Raise your chest and head to your maximum height.
Hold for 5 seconds. Lower yourself to the floor and repeat 5 more times.
№ 2
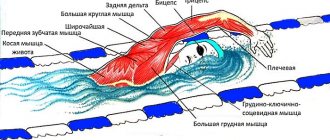
Lie on your stomach and perform an exercise that will simulate swimming in the water using the breaststroke style.
Exercises to help slightly correct a subluxated vertebra:
№ 1
One of the simplest and most effective exercises of this kind is walking on all fours.
You need to do it until you get tired of it.
It promotes the realignment of displaced vertebral bodies due to the performance of translational movements, during which the interarticular spaces widen.
№ 2
Get on all fours and relax your back. Then sharply and quickly bend and straighten the elbow joints, thereby creating a kind of shaking.
Perform the exercises for about a minute.
Repeat several times throughout the day.
Exercises to stretch the chest muscles:
№ 1
Sit down, or better yet stand up, pick up the ball and press it to your chest.
Then raise your arms up or simply squeeze the ball intensely at chest level, thereby pumping up your chest muscles.
№ 2
Sit on the floor, spread your arms to the sides. Pull your shoulders back, trying to bend them to the floor as low as possible.
In this case, the lumbar lordosis is leveled.
Other exercises:
№ 1
Get on all fours, place your hands at shoulder level. Extend your right arm and left leg forward.
Freeze in this position for 5 seconds, lower your arm and leg. Do this several times and change the arm and leg to the opposite.
№ 2
The next exercise is to sit on your heels, put a gymnastic stick on your shoulders like a yoke, bend forward, bending the hip joint, without bending your lower back.
№ 3
Next, lie on your back and perform the simple and familiar exercise “riding a bicycle.”
№ 4
The starting position is the same. Stretch your arms up.
Alternately raise your legs, trying to touch your toes.
Relax and repeat a few more times.
№ 5
Lie on your stomach, put your hands on your head. Raise your upper body (do not arch), leaving your legs and pelvis on the floor.
Hold this for a few seconds. Relax and repeat the exercise.
№ 6
Take a gymnastic stick (the distance from hand to hand is as large as possible), slowly raise your arms up and move the stick behind your back, trying not to bend your elbows.
Hold this for a few seconds, then move the stick to its original position.
№ 7
The starting position is the same. Moving the stick back to the level of the shoulder blades.
Slowly tilt your torso to a horizontal state and bend your thoracic region as much as possible.
Stay in this position for 5 seconds, move the stick forward and relax. Repeat 5-10 times.
№ 8
Place your feet shoulder-width apart and keep your back straight. Squat with your feet pressed to the floor.
Bend your knees no more than 90°. The deviation of the back is allowed when the hip joints flex.
№ 9
Get on all fours, extend your left arm forward. “Draw” a circle with it, involving the shoulder girdle in the process. Repeat about 3-4 times, then change hands.
№ 10
Stand up straight, lower your arms. Lift them up, while trying to bring your shoulder blades together.
Freeze for a few seconds and, with your back straight, stretch your arms even higher. Slowly return to the starting position.
You can perform a similar exercise, only you need to clasp your hands in front of you.
№ 11
Holding onto a support (a wall or the back of a chair), slowly swing your leg, first forward, then back.
Repeat 3-4 times, change legs.
All of the above exercises are performed slowly and with a small range of motion.
Begin to perform 3-4 repetitions, gradually increasing their number to 10-15.
Spondylolisthesis and yoga
Yoga is a whole system of psychophysical exercises aimed at restoring health, good shape and balancing the psychological aspects of a person.
By performing special exercises that strengthen the spinal muscles, there is an increase in activity, a decrease in pain and relaxation of the entire body.
But if you have spondylolisthesis, it is worth considering that most yoga exercises are contraindicated, since there is a high risk of complete displacement of the spinal disc.
When choosing yoga poses for this disease, you need to choose those in which the position of the back will be correct.
Under no circumstances should you bend backward or bend forward at the same time, combined with twisting. If you need to bend over, your back should be straight and your spine should be elongated.
Several popular yoga exercises for the spine:
№ 1
An effective “Cat” exercise aimed at stretching the spine and interarticular spaces.
Get on all fours, arch your back as if you were crawling under a bar. Straighten up, repeat 3-4 times.
№ 2
Get on all fours.
Raise your right arm and left leg at the same time, freeze for 5 seconds, relax. Repeat at least 5 times on each side.
№ 3
Position – lying on your stomach. Press your legs together, stretch your arms forward.
At the same time, slightly raise both your arms and legs, holding this position for a few seconds.
At the same time, you should watch your back - it should be straight and not bend.
№ 4
This exercise can be performed standing, sitting or lying down. Tighten your stomach until it becomes hard.
Freeze for 3 seconds and relax. Do 5-10 repetitions.
№ 5
Breathing exercise.
Take slow breaths, while inflating your stomach, then slowly exhale, drawing your stomach inward.
Do 3-4 times for 5-6 approaches.
If after starting yoga exercises you feel pain, stop immediately.
Either you are doing something wrong, or yoga is contraindicated for you at all.
How are the vertebrae connected in our spine? About
types of joints of the spinal column
you can find out from our article.
How is rehabilitation after a spinal cord injury? You will find a lot of information on this issue here.
What exercises are recommended for shoulder arthrosis? See here.
Some tips ↑
You should start doing a set of exercises with just one exercise.
If it does not cause pain, then after about 3-4 days you can try the following.
So, gradually, adding one exercise at a time, perform the entire complex every day.
You should only perform exercises that do not cause pain. If it does occur, then they are not suitable for you and you should choose others.
In order to avoid exacerbation of the disease, it is necessary to observe the correct motor mode, from which carrying heavy objects or at least their even distribution is excluded. You also need to watch your posture.
If cyclic training is necessary, then you should give preference to simple cycling, exercise bike and swimming.
Unlike other sports, they do not cause impact on the vertebrae.
Do not engage in physical therapy or yoga during an exacerbation of the disease.
Physical therapy for spondylolisthesis is not a panacea that will help completely cope with the problem, but it is still the main method of maintaining the spine in normal condition.
To do this, it is necessary to perform a set of exercises for a long time and not let the disease take its course.
Video: gymnastics for the spine
How does this happen?
With regular mechanical stress, worn out spinal discs are damaged at the cellular level. In a normal situation, they are gradually restored. But when there is a disruption in the damage-recovery processes in the tissues, degenerative processes begin to develop, which affect the structure of the tissues. Constant trauma leads to the formation of bone growths called osteophytes. Spondylosis occurs. The structure not only changes in the process, but also leads to their displacement, reducing the spaces between the bones of the ridge. The spinal canal narrows and the nerve roots are pinched.
Important! Osteochondrosis is not associated with salt deposition and is not such. This is a misconception about the disease.
If the intervertebral discs are worn out, look for a different problem.
All these processes occur for a number of reasons. The combination of several factors leads to spinal disease.
These can be either pathologies, metabolic disorders, or external factors:
These reasons are important only if they affect the abrasion of intervertebral tissues constantly or periodically. When they are present against a background of poor nutrition, insufficient or excessive exercise, or hypothermia, the development of the disease accelerates.
Treatment of lumbar vertebrae displacement
Treatment for displacement of the lumbar vertebrae can be surgical or conservative.
Conservative treatment of vertebral displacement
The principle is to treat pain caused by spinal pathology or compression of nerve roots. Conservative treatment is quite effective in many cases and includes:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Oral steroids are indicated. Physiotherapy on the affected area (thermal procedures, warming up). Manual therapy (massage). Injections of drugs into the epidural area.
Treatment is also aimed at strengthening the spinal and abdominal muscles, this is necessary in order to eliminate instability of the spinal column. If the pain is too severe and frequent, drug therapy is prescribed - non-steroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects, for example diclofenac, ibuprofen, butadione, dimexide.
Diclofenac for adults is prescribed at a dose of 25-50 mg 2-3 times a day, but the frequency of administration may vary depending on the severity of the disease. When taken externally, Diclofenac in the form of an ointment is applied to the affected area, 2-4 g 3-4 times a day. The daily dose should not exceed 2 mg/kg.
Possible gastrointestinal disorders in the form of nausea, vomiting, anorexia, stomach pain, flatulence, constipation, diarrhea, rarely - liver dysfunction; when used rectally, inflammation of the colon and bleeding are possible.
From the central nervous system, the following may be observed: dizziness, headache, agitation, insomnia, irritability, fatigue, in rare cases - paresthesia, visual disturbances, tinnitus, sleep disorders, convulsions, irritability, tremor, mental disorders, depression.
Ibuprofen for adults is prescribed at a dose of 400-600 mg 3-4 times a day. When taking it, it is necessary to keep the blood picture, the condition of the liver and kidneys under control, and if gastrointestinal disorders or epigastric pain occur, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, a blood test with determination of Hb, hematocrit, and a stool test for occult blood are indicated. To prevent the development of gastropathy, it is recommended to combine it with PgE drugs (misoprostol). Drinking alcohol is completely contraindicated during the course of treatment with Ibuprofen, and it is also necessary to refrain from all activities that require increased attention, quick mental and motor reactions.
The drug is contraindicated in cases of hypersensitivity, gastric and duodenal ulcers in the acute stage, ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcers, Crohn's disease - ulcerative colitis), "aspirin" asthma, blood clotting disorders (including hemophilia, prolongation of bleeding time , tendency to bleeding, hemorrhagic diathesis), pregnancy, lactation. Cirrhosis, hyperbilirubinemia, gastric and duodenal ulcers (history), gastritis, enteritis, colitis; liver and/or kidney failure, nephrotic syndrome; CHF, arterial hypertension; blood disease of unknown etiology, childhood (for tablet forms - up to 12 years, 6 months - for oral suspension). Children 6-12 months are prescribed only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Dimexide is prescribed for local anesthesia, in the form of a 25 - 50% solution of the drug for compresses, 100 - 150 ml 2 - 3 times a day. Dimexide is tolerated without complications, but erythema, itching, dizziness, insomnia, adynamia, dermatitis, and diarrhea may occur. In severe cases, nausea, vomiting, and bronchospasm are observed.
Dimexide is contraindicated in cases of severe cardiovascular insufficiency and atherosclerosis, angina pectoris, impaired renal and liver function, stroke, coma, pregnancy, lactation, glaucoma, cataracts. Prescribe with caution to elderly people. Contraindicated in children under 12 years of age, during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Steroid anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in particularly severe forms of the disease, these include: cortisone, hydrocortisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone, triamcinolone.
Dexamethasone is dosed depending on the complexity of the disease; the drug is prescribed both orally and in the form of injections, but strictly according to a doctor’s prescription. Before you start taking Dexamethasone, you need to do a blood test to monitor the amount of sugar and electrolytes. Dexamethasone is contraindicated in pregnant and breastfeeding women.
When taking the drug, immunity decreases, so you need to take it in combination with immunoglobulins, and also limit communication with infectious patients. It is also better not to combine Dexamethasone with other drugs - this may reduce the effectiveness of one of the drugs.
Cortisone is prescribed orally or intramuscularly (in the form of a suspension - a suspension of solid particles of the drug in a liquid). Take 0.1-0.2 g per day orally in the first days of treatment (in 3-4 doses), then the dose is gradually reduced to 0.025 g per day. The course dose is 3-4 g. The highest single dose of cortisone for adults is 0.15 g, daily dose is 0.3 g.
With long-term treatment and the use of large doses (more than 0.1 g per day), the development of obesity, hirsutism (excessive hair growth in women, manifested by the growth of a beard, mustache, etc.), acne, menstrual irregularities, osteoporosis, Itsenko-symptom complex is possible. Cushing's, mental disorders, etc. Ulcerations of the digestive tract are also possible.
Cortisone is contraindicated in severe hypertension (persistent rise in blood pressure), diabetes mellitus, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, pregnancy, stage III circulatory failure, peptic ulcer, recent surgery, syphilis, active form of tuberculosis, old age.
Also, in the non-acute phase of spondylolisthesis, alternative treatment is effective - ointments, compresses, baths.
Apply ointment based on 50 g. mustard powder, camphor, two eggs, and 20 gr. alcohol The ointment is applied to the affected area for 2 hours, then the remaining ointment is removed by wiping the affected area dry. After the procedure, the affected area should be wrapped warmly. To relieve inflammation and pain, prepare the following composition: 2 cups of honey, 2 cups of grated radish and 0.5 cups of vodka. All components are mixed well and used as a rub. You can also consume mumiyo - in the form of ointments, rubs, or orally in the form of tablets. You can buy mumiyo at a pharmacy. For spondylolisthesis, it is useful to take mint-based baths. It is better to collect mint during the flowering period, then boil it in a bucket, let it brew and pour it into the bath, you can dilute it a little with plain water. The bath should be taken before the water cools down. After the bath, you need to rub the sore spot well and put on warm underwear and wrap yourself up. Baths are contraindicated for severe heart disease, vascular disease, and mental disorders.
Physiotherapy can rightfully be considered an important component of the treatment of spondylolistosis. Physiotherapeutic treatment can be divided into two types - active and passive.
Passive treatment includes:
Massage of deep back muscles. Temperature treatment is the application of heat or cold to the affected area to improve blood circulation. Electrophoresis on the affected area for the purpose of electrical stimulation of the nerve roots. Ultrasound treatment or ultraphonotherapy helps reduce muscle spasms, cramps, swelling, stiffness and pain. Sound waves, penetrating deep muscles, create heat, which improves blood circulation and speeds up the healing process.
Active treatment includes the development of an individual set of exercises to strengthen the muscle corset, which helps maintain the spine in the correct position and also improves posture. In case of acute pain, wearing a corset is recommended, but you need to take into account that wearing a corset for a long time is contraindicated, otherwise the back muscles will begin to weaken, and this will only aggravate the course of the disease.
Surgical treatment of lumbar vertebrae displacement
An extreme measure is indicated in the absence of improvement during conservative therapy. The essence of the operation is to stabilize the spinal column and reduce compression of the nerve branches. A quite effective method of vertebral plastic surgery is when an element of the iliac crest is used for restoration, which is then attached to the overlying vertebra with special pins. If there is a manifestation of compression of the nerve roots, then an additional laminectomy is performed in order to solve the problem of vertebral displacement and compression of the spinal cord and nerve roots, and removal of the vertebral arch is indicated. Excess scar tissue that is compressing nerves and causing pain is removed. Next, the actual stabilization of the spinal column is carried out, aimed at restoring the spinal motion department.
Advice for patients with displacement of the lumbar vertebrae boils down to minimizing the load on the lumbar spine. This is the correct sleeping position, preferably on your side and with your legs pulled up; the bed should be flat, for example, with a foam mattress (6-8 centimeters thick).
During the acute period, it is necessary to ensure maximum rest for the spine - no stress, massage, physiotherapy, periodic wearing of an elastic corset is recommended. After significant relief, you can begin physical therapy, namely stretching the spinal column and strengthening the abdominal and spinal muscles.
Classification
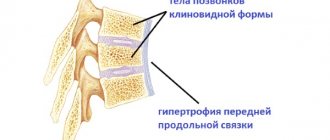
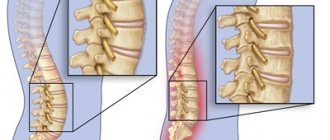
According to the degree of displacement of the underlying vertebra to the overlying vertebra, the displacement occurs by 25%, 50%, 75%, 100%.
Types of displacement: - Dysplastic Caused by a failure in the development of the sacral bone. Mostly children suffer from this type of displacement. — Spondylolysis Caused by a gradual fracture of the arch with continuous fatigue of the spine. — Degenerative The result of problems in the metabolic process in the spine. Typically, older people are at risk for this shift. — Traumatic Occurs after fractures and injuries to parts located between the joints.
In its true form, vertebral displacement occurs as a result of a congenital defect of part of the vertebral arch (spondylolysis). Usually the defect is located on both sides.
In the degenerative form, there is mainly displacement of the lumbar vertebrae or displacement of the cervical vertebrae. Due to the development of osteochondrosis, the intervertebral disc degenerates and its height decreases. At the same time, the load on the facet joints increases and spondyloarthrosis develops. The inability of a “weak” disc and an altered facet joint to support the vertebrae leads to their displacement.
With a traumatic form, in addition to the listed cervical and lumbar vertebrae, displacement of the thoracic vertebrae may occur. The thoracic spine has its own congenital rib corset, which prevents displacement of the vertebrae. When a sufficient traumatic impact force is applied to the thoracic, cervical or lumbar spine, damage occurs to the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the spine, as well as to the vertebrae themselves. As a result, depending on the location of the applied impact force, displacement of the vertebrae occurs.
With pathological displacement, we are talking about a tumor lesion of the fixing apparatus of the vertebrae.
Most often, displacements occur in the cervical and lumbar regions.
Gymnastics for displacement of the lumbar vertebrae
Gymnastics for displacement of the lumbar vertebrae is an element of the complex of conservative treatment for displacement of the vertebrae. In combination with wearing orthopedic corsets and symptomatic drug treatment, exercise therapy plays an important role.
It is impossible to completely cure the displacement of the lumbar vertebrae using a complex of exercise therapy, but it is quite possible to control the stability of the spinal column. The main task is to develop an individual set of therapeutic and gymnastic exercises aimed at strengthening the deep muscles of the back and abdominals. When the vertebrae are displaced, a decrease in the tone of the paravertebral muscles is observed, and their strengthening contributes in the best way to the formation of a muscle corset and maintaining the spinal column in the correct position.
When compiling an individual set of exercises, the doctor takes into account the degree of neglect of the disease, the degree of vertebral displacement, and the patient’s age. Degenerative changes are observed mainly in elderly people, over the age of 60. Dysplastic and isthmic displacement of the vertebrae occurs more often in childhood and in young athletes. Accordingly, this will fundamentally affect the preparation of a therapeutic set of exercises.
Degrees of displacement and their signs
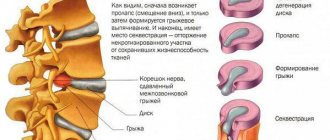
Spinal disc displacements are divided into four types according to severity, each of which has a number of specific characteristics. The process of vertebral displacement occurs gradually, the symptoms intensify as the stages change:
- Prolapse. The initial stage, when the displacement of the spinal discs does not exceed 2 mm. Prolapse is characterized by the absence of obvious symptoms: pain occurs only during sudden movements, heavy lifting, and sports activities.
- Protrusion. Now the spinal disc has shifted significantly, by 10 mm or more. Nagging pain in the spine becomes more frequent, increasing during physical activity.
- Extrusion. Displacement of the lumbar vertebrae by 50%. The subsidence of the spinal column begins due to depletion of the intervertebral discs. The third stage is characterized by severe pain attacks in the lumbar region and stiffness of movements. The progression of the disease can cause displacement of several lumbar vertebrae and damage to nerve endings.
- Sequestration. The joints of the spine are subject to irreparable distortion. The pain in the lower back becomes chronic and does not allow you to take a vertical position for a long time. The patient complains of constant fatigue, cramps, and numbness in the limbs. The gait changes and becomes uncertain. Fingers, feet, knees hurt.
Exercises for displacement of the lumbar vertebrae
Exercises for displacement of the lumbar vertebrae are developed strictly individually, taking into account the degree of progression of the disease, the nature of degenerative changes, and the age of the patient. For example, degenerative changes in the spine appear in old age, and dysplastic and isthmic changes are observed in children and young athletes. This will greatly influence the formation of an effective set of exercises.
Despite the peculiarities of the set of exercises itself, there are conditions for implementation:
You need to start performing the complex in a lying position. You can lie on your back, stomach, side, or stand on all fours. This allows you to completely unload the spine and reduce pressure in the affected area. At the early stage of the disease, exercises are aimed at relaxing the muscles of the body and limbs. Relieving spasm relieves compression of the nerve roots. In the acute stage, as well as in the subacute stage, exercises cannot be done. You should not do exercises that require tilting your torso more than 15-20 degrees. This provokes an increase in intravascular pressure, displacement of discs, stretching of fibrous tissue and muscle tissue of the lumbar region. In a state of unstable remission, these exercises are also contraindicated. Exercises aimed at stretching the spinal column give good results. This leads to an increase in the intervertebral spaces and the diameter of the intervertebral foramina, which relieves compression of the vertebral nerve roots.
To stabilize the affected area of the spine and strengthen the muscles of the body, pelvis and limbs, static exercises are acceptable. With a mild degree of damage, you can gradually give a higher load by performing isotonic exercises. This complex helps eliminate vascular hypertonicity in the affected area. In case of severe damage to the spine, isometric exercises with gradual muscle relaxation are recommended.
Displacement of the vertebrae along the entire length of the spinal column and especially its lower lumbar part can be prevented by performing simple exercise therapy complexes that strengthen the back muscles. Physical exercises in the form of exercises, yoga and special gymnastics are useful not only for prevention, but also for the treatment of pathologies such as osteochondrosis, spondylolisthesis, etc. Regular physical exercise will stop the course of the disease, excluding its progress and future operations.
Exercise therapy for displacement of the lumbar vertebrae is used in the first and second stages of the disease, when the displacement of the vertebra in relation to the underlying one does not exceed 50%. See also: displacement of the 5th lumbar vertebra.
Spondylolisthesis is a pathological progressive change in the spinal column, in which the spinal discs are displaced relative to each other. The lumbar region is often affected, less often the cervical region. The disease affects any age group, but especially physically active people with high loads on the back.
Principles of physical therapy
Despite the fact that exercises are prescribed on an individual basis, they must be performed according to certain rules that are considered common to all patients:
The first exercises should be performed while lying on your back. In some cases, exercises during which a person stands on all fours are acceptable. They relieve tension from the affected area, unload the spine and relieve pressure from it. When the disease is in the first or second stage of development, physical therapy relaxes the muscle tissue located in the back and limbs. When the spasm is relieved, the nerve roots stop being compressed. If the disease worsens or has a subacute stage, physical therapy is contraindicated. You can bend over during exercises no more than fifteen to twenty degrees. A larger inclination angle can be made only when the disease has been in remission for a long period of time. The most effective exercises are those that stretch the spine. They must be present in the exercise therapy complex.
Symptoms of spinal joint displacement
In most cases, this disease is asymptomatic, but if it is accompanied by pathologies such as osteochondrosis, hernias or disc protrusions, the following manifestations may be observed:
dizziness and headaches during physical activity; lower back pain; numbness of the lower extremities.
Degenerative spondylolisthesis occurs mainly in older people over 65 years of age. The main symptom is pain in the leg, which manifests itself during a long stay in one position or walking.
Only an experienced specialist can correctly diagnose and determine the type of spondylolisthesis.
Exercises for the spine
Any exercises that can harm the body should be avoided. The safest ones are the following, which are performed lying on your back:
Socks pulled towards you, place your hands back behind your head, try to smoothly stretch your whole body forward. Stay in this pose for 5-10 seconds, take a break, repeat 2-3 times. Arms extended parallel to the body, strain the back muscles as much as possible without stretching the spine. Hold for 10-15 seconds. Grasp the knee, smoothly pull it towards the chest, repeat 3-4 times on each leg. “Barrel”. Grasp both knees with your hands and rock back and forth. The exercise should be performed for 10-15 seconds on a mat or gymnastics mat.
This complex is ideal for relieving pain in the first stages of the disease.
Exercises for the back muscles
It is important to perform the entire complex carefully to avoid unpleasant sensations in the joints and muscles.
Torso bends. The legs are spaced to the size of the shoulders, the back is kept straight. Next, you need to lean forward, straighten your back, then repeat bending your torso in both directions. Repeat 5-10 times. Standing on all fours, extend your leg, fix it for 10 s, slowly return it to the starting position, then a short break - up to 10 s, after which you need to repeat the same movements with the other leg. Exercise "Cat" . Standing on all fours, slowly arch your back to form an arch, stay for 15 seconds, and smoothly return to the starting position. The recommended number of repetitions is 5-10 times.
Exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles
Therapeutic gymnastics classes should begin with a minimum set of exercises, gradually increasing their number and approaches.
"Plank". Lying on your stomach, rest your elbows on the floor, raise your body parallel to the floor, focus on your elbows and toes. Hold the body in this position for up to 20 seconds. “Scissors.” Lying on your back, raise your legs 10-15 cm, place your palms under your buttocks. Keep your knees straight, alternately swinging your legs, imitating the work of scissors. Perform 2 sets, rest no more than 30 seconds.
Breathing exercises to eliminate negative consequences
These exercises are widely used in yoga; when performed correctly, muscles and joints are saturated with oxygen and blood circulation improves.
In a “Turkish” pose with your legs crossed, hands on your knees, palms up. Try to relax completely, take a shallow breath, then exhale forcefully, with tension in your abdominal muscles. The sound will be similar to a suppressed cough. After this, rhythmically inhale and exhale air only through the nose. In this case, a feeling of slight tension in the abdominal muscles should appear. Lying on your back, one hand on your chest, the other at the bottom of the chest at the level of the diaphragm, breathe calmly and measuredly. You should feel how the lower chest area expands, the stomach rises, while the chest itself remains almost motionless. This exercise is ideal to complete a gymnastics cycle. It can be performed right in bed, before going to bed.
You should not expect too quick results; treatment of spondylolisthesis is a very long and labor-intensive process.
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, you should not perform too heavy exercises, and you should also stop exercising if you experience pain.
At what stage of spondylolisthesis is surgery required?
When diagnosing spondylolisthesis, surgical intervention is required in cases that cannot be treated with conservative therapy methods that have been used for at least six months.
The basis for surgery is the patient’s deteriorating health condition, which is accompanied by:
- Strong, constant, intensely increasing pain;
- An increase in neurological symptoms (radicular symptoms, spinal cord damage, etc.);
- Increasing displacement of the vertebrae.
To study X-ray of the spine - what does it show?
Surgical treatment is mandatory for grade 4-5 vertebral displacement with stable spondolisthesis. In an unstable form of the disease, surgery may be recommended already at stage 2 of the disease, if conservative methods do not give the expected result.
Also, surgical intervention is indicated for children under 14 years of age, since this disease at this age progresses very quickly and leads to severe pathologies of the spine. Therefore, wasting time in this case can cause serious harm to the child’s health.
The surgeon’s task during the operation is to restore the original position of the vertebrae and nerve endings, as well as their reliable fixation. Before surgery, the doctor must determine the degree of displacement of the vertebrae, as well as the percentage of deformation and narrowing in the intervertebral foramina.
To do this, after a preliminary examination, the following medical tests are carried out:
- Lab tests;
- A radiograph, which should contain both frontal and lateral projections with the body rotated by 45 degrees;
- Computed spiral tomography;
- Electromyography;
- Magnetic resonance examination.
The effectiveness of the operation and further rehabilitation depends on the accuracy and quality of the diagnosis of the disease.
Massage and self-massage
Massage therapy for severe pain should be performed by a professional. In this case, all the characteristics of the patient are taken into account, the number of sessions and their intensity are selected. Massage improves blood circulation in joints and tissues, reduces pain. After the condition improves or in the absence of neurological diseases, you can resort to self-massage.
Self-massage technique:
Massage of the lumbosacral region. It will be most effective after preheating. To do this, you can use warm sand or salt, warming ointments. You should start with a light warm-up of the muscles, stroking, and then move on to more intense stimulation with the pads of your thumbs, knuckles and the back of your hand. Using incoming circular movements up and down, massage the lumbar region, gradually descending to the sacral region. In a standing or sitting position, knead the spine area starting from the shoulder blades. The back is kneaded with two clasped hands or fists. Movements can be longitudinal or circular. Using point movements with your fingertips (with your right hand, massage the left side of the back, with your left hand, massage the right side) massage with medium strength until slight pain occurs. For this exercise, you will need a special orthopedic roller (if you don’t have one, you can use a two-liter bottle of water). The massage should be carried out in comfortable clothes made from natural fabrics. Gently lower yourself onto the roller with your back supported by your hands, roll the bottle along the spinal column 3-4 times.
Gradually increase the time and intensity of the massage, focusing on your sensations.