This disease used to occur in one case per several tens of thousands of people, but in the modern world all the negative factors are aggravating, and a complex congenital pathology is increasingly being diagnosed - concrescence of the cervical vertebrae. Of all congenital anomalies, this is the most visible. The child, and then the adult, has practically no neck. This happens because the segments of the cervical vertebrae grow together in the baby while still in the womb. And we are not talking about aesthetics and beauty, but about deviations that negatively affect a person’s entire future life.
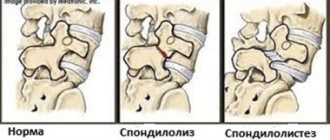
Concrescence of the cervical vertebrae
Why do vertebrae fuse?
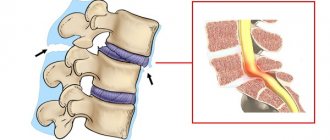
The pathology for which fusion of the vertebral segments is the main manifestation is called concrescence, and can be observed in various forms. It should be noted that in some cases, the fusion of bone bodies is a normal phenomenon, for example, with the achievement of a certain age, the pelvic vertebrae fuse, and the vertebrae of the skull become fused, and this is a physiologically based process. But concrescence of the vertebral bodies in the lower back, chest and especially the neck is an unambiguous pathology.
Why is this happening? Medicine cannot answer this question unequivocally. Only fragmentary facts are known about the disease.
- This is a congenital pathology.
- Shows up early.
- It greatly affects the child’s quality of life.
- In its complete form, when the vertebrae of the cervical zone are completely fused, it forms the basis of the most studied Klippel-Feil syndrome.
Klippel Feil syndrome
Description of the syndrome
By the way. One of the breakthroughs in the latest generation of diagnostic methods is the ability to determine pathology in the fetus while it is in the womb. Previously, it was not possible to trace the anomaly before the birth of the child.
The first reason for vertebral fusion is called a hereditary factor. But this is not the main reason, just the most obvious one. The main one is considered, although not 100% proven, a violation in intrauterine development, which occurs due to anomalies in the formation of cartilage, blood vessels and bones at the embryonic stage. That is, if the child did not receive a “bad” gene from his parents, then the cause of the anomaly was its incorrect development in the womb, which arose for reasons not fully understood by science.
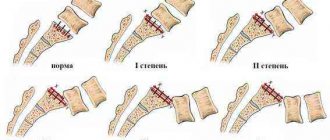
Stages of the disease
There are different stages of the anomaly. Depending on the onset (detection) of the process, four are classified.
Table. Stages of concrescence.
| Stage | Characteristic |
| Initial | It can be diagnosed between five and seven weeks of pregnancy. During this period, intervertebral discs are already forming, and the vertebral structure is clearly visible. |
| Early | Detection of pathology at 15-20 weeks of pregnancy. |
| Average | Appears and, accordingly, is detected at 25–30 weeks of age. |
| Late | An anomaly discovered after birth. |
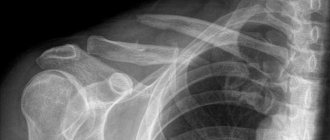
Photo of a patient with vertebral concrescence syndrome
By the way. Aggravating factors, although not proven, are suspected, which may contribute to the formation of pathology, include infections suffered by the pregnant woman, her injury, exposure of the expectant mother’s body to radioactive radiation and her poor heredity
The pathology is congenital and very rare
Types of pathology
Usually fusion of vertebral structures is congenital, but it can also be acquired in adulthood.
- Acquired concretion is the result of traumatic damage to bone tissue or cartilage.
- It can form as a result of chronic joint disease.
- Sometimes the cause is ankylosing spondylitis.
Ankylosing spondylitis - ankylosing spondylitis
Prices for massagers
If the pathology is congenital, its location in 99% of cases is the cervical area.
The vertebrae consist of their own bone body and processes extending from it. They provide mobility to the spine.
If concrescence is incomplete, only the vertebral bodies fuse, but the mobility of the processes remains.
In the full form, the processes are also fused.
Observed, depending on the location:
- fusion of the first cervical vertebral segment with the occipital bone;
- fusion of the first cervical vertebra with the second;
- capture in the process of merging the third and fourth, or connecting only them, without the participation of the first two.
Scheme of vertebral fusion
Be that as it may, a child born with concrescence is doomed to suffering and difficulties, since the fused vertebrae of the cervical area almost completely limit its mobility.
If you want to learn in more detail the causes of displacement of the thoracic vertebrae, as well as consider the causes, symptoms and treatment methods, you can read an article about this on our portal.
Risk factors, causes
The disease is associated with improper formation of the spinal column during the intrauterine development of the child. This may be due to an infection suffered by the mother, or radiation, or a mutation in the fetus, but of course, most often it is a genetic factor.
However, there is a type of acquired concrescence, which is usually provoked by two factors:
- bone injuries and damage to the cartilage of the spine, leading to fusion of the vertebrae;
- various old chronic diseases, such as ankylosing spondylitis.
Symptoms
This pathology cannot be ignored. There are different types and forms, which are expressed in a different number of vertebrae (sometimes there are not enough of them), their total or incomplete fusion. In any case, visually it immediately catches your eye.
- The cervical spine is significantly shorter than normal.
- From the back you can see that the hair growth line is located almost on the back, along the shoulder line.
- The shape of the skull is irregular.
- The glottis is significantly narrowed.
- The top of the spine has significant or complete restrictions on mobility.
- The child cannot turn or tilt his head and does not make any movements with his head.
Symptoms of pathology
These are only the first signs, and in the future, due to the narrowing of the spinal canal of ongoing degenerative-dystrophic active processes in the vertebrae, neurological disorders will progress, which will be expressed by paralysis, paresis and loss of sensitivity.
In addition to the main symptoms, patients suffering from concretion of the cervical vertebrae have concomitant birth defects.
- Scliotic deformities.
- Neck curvature.
- Curvature of the shoulder blades (one is much lower than the other).
- The scapular line is located above normal.
- Developmental disorder of the upper limbs.
- Movement in the arms and legs is impaired.
- Reduced skin sensitivity.
- Underdeveloped first finger on both or one hand.
- Changed shapes and contours of the feet.
Fusion of vertebrae is visible to the naked eye
In some cases, defects of organs located inside the body may also be detected, which are a more serious pathology than a cervical anomaly, directly affecting not only the quality, but also the life expectancy of the patient.
Important! A third of children with concrescence have severe defects of the heart and blood vessels, genitourinary and central nervous systems. They often experience involuntary friendly movements of the legs and arms, akin to deep tics, which worsen with age.
If a child is found to have fused vertebrae, this means that a complete recovery and an absolutely healthy life, despite the most modern treatment techniques, is impossible for him.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure the disease
Consequences
The disease can develop many side pathologies.
These include:
- impairment or complete loss of movement of individual limbs;
- fusion of vertebrae of different parts;
- osteochondrosis;
- violation of the development of the shoulder girdle, in which one shoulder blade stands higher than the other by about 10 centimeters;
- constant, incessant headaches, against the background of the fused first and second, or sixth and seventh vertebrae;
- diseases of the heart muscle;
- dysfunction of the digestive system, disruptions in the functioning of the respiratory organs;
- change in the appearance of the feet;
- hypoplasia;
- rachiocampsis.
All these pathologies can be either congenital or acquired, but they all must be corrected equally, depending on the complexity of the patient’s situation.
Diagnostics
This disease is diagnosed by the initial method - fluoroscopy of the cervical area. It is the x-ray that will help you see the full picture and determine the type of pathology.
There are two main types of concrescence.
The first is the fusion of two or four cervical vertebrae into a bone monolith. In this case, cleft arches and other defects of the vertebral region in the neck area are quite often recorded.
The second involves the fusion of only the first vertebra with the cranial occipital bone.
In addition to X-rays, if the diagnosis is in doubt or the case of pathology is severe, the patient is examined using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, which allows one to examine the smallest details and clearly outlines the size of the abnormal area.
Computed tomography makes it possible to see bone tissue in different projections with high clarity.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient undergoes ultrasound, radiography, MRI, rheoencephalography, genetic research, electrocardiogram
Only after an absolute comprehensive examination do doctors begin treatment planning.
Treatment methods
Concretion of spinal column fragments is treated with conservative methods. Taking medications to relieve pain. Any medications are taken for medical reasons. In addition, spinal stretching treatment is performed. During the procedures, special devices are used.
Therapeutic physical training helps restore mobility of the spinal column. Gymnastics is an important component of complex treatment that should not be ignored. Otherwise, it will continue to deform, which threatens to weaken the muscles. The set of exercises is determined by the doctor. During exercise therapy, the patient should avoid sudden movements.
Massage can be performed by health care workers or loved ones. For example, if a child is sick, the session can be conducted by the parents after consulting a doctor. When blocking the second and third vertebrae in the neck, it is necessary to wear special devices (Schanz corset).
Acupuncture, massage of internal organs, manual therapy of the spine. In advanced cases, surgical intervention cannot be avoided, which does not guarantee complete physical recovery. As a rule, surgery helps eliminate only cosmetic defects.
Traction is an effective method of therapy
How is concrescence treated?
The difficulty is that at the current stage of development of medicine there is not a single treatment option that would lead to a tangible improvement in the patient’s condition. Conservative therapy is used to relieve pain and minimize the effect of a congenital orthopedic anomaly on the entire body.
Important! It is impossible to cure concrescence completely, no matter at what stage it is detected, and no matter what area of fusion the vertebrae have. Through persistent exposure to procedures and exercises, you can only achieve a reduction in the severity of the symptoms of the disease.
Table. Methods used to treat concrescence.
| Method | Characteristic |
| Symptomatic treatment aimed at relieving pain involves taking analgesics in most cases and anti-inflammatory drugs in some particular situations. |
| Wearing a special orthopedic collar | The Shants collar or corset is prescribed to children during the period of active growth. Wearing it helps maintain existing neck mobility without increasing spinal blockage. |
| This orthopedic procedure also has a supporting effect and is used until bone growth stops, in order to somewhat stretch the spinal row and make it more flexible, as well as to reduce the manifestations of concomitant scoliosis. |
| The main emphasis in conservative therapy is on exercise therapy. A special complex that children with pathology do constantly helps maintain joint mobility. |
| Methods of manual influence for diagnosing pathology and maintaining it in a non-progressive form. |
| It can be done even for newborns, including parents who can do it after completing a special training course. Maintains level of mobility. Helps prevent secondary pathologies. |
| Increases blood flow to pathological areas, relieving paravertebral tension. |
| Plays the same role as acupuncture. |
| In rare cases, cosmetic surgery is performed, which, however, does not have a significant physiological effect. Indications for surgery may be constant pain that is not relieved by anabolic steroids. Some painful fragments are removed, but this does not change the physiological picture. Implants that can replace fused vertebrae with separate ones while preserving their functions have not yet been invented. |
About the benefits of exercise therapy
Therapeutic gymnastic exercises during concrescence are an integral part of the patient’s life almost from infancy. Only regular physical exercise helps to constantly develop the upper cervical region and maintain the level of mobility in it.
Classes are held daily
Important! Without gymnastics, and this has been proven by many years of medical practice, degenerative destruction progresses, immobility increases, muscle contracture appears, spinal deformity increases, and accompanying secondary pathologies appear.
Fitballs and medicine balls for fitness
Exercise therapy is especially effective for those who have only fused the occipital vertebra with the first cervical vertebra.
Examples of exercises.
- Sitting on a stool or standing, tilt your head to one side, to the other, back and forth. The pace is as calm as possible, no sudden movements or extreme efforts. Of course, the patient will not be able to fully tilt, and it is not necessary, the possible is enough.
Head turns
Head tilts to the sides
Head tilts forward and backward - In the same position, attempt to rotate your head on different sides. If the form of the pathology is severe, start the amplitude with a small one, gradually expanding.
- Lying on the floor, on your back, raise your head, lifting it off the floor, and try to hold it for ten seconds.
- Roll over onto your stomach and do the same - raise your head, lifting your chin off the floor and stretching the back of your head up.
- While standing, move your shoulders both up, then both down.
Raise your shoulders as high as possible and hold them in this position for 10 seconds. Relax your shoulders and take a deep breath
Concrescence (fusion) of the thoracic vertebrae
Acquired concrescence of the thoracic vertebrae can be observed in people suffering from scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis of the 2nd and 3rd degrees. The displacement leads to partial fusion of the thoracic vertebrae, which further distorts the spinal column.
Incomplete fusion of the thoracic vertebrae is usually observed in the left or right lateral projection. If this clinical sign is detected, surgery is indicated to remove bone growths and restore mobility. Then a course of rehabilitation treatment and posture correction using manual therapy methods is carried out.
Signs of this pathology:
- impaired mobility in the thoracic spine;
- constant dull pain in the back and chest;
- restriction of rib movements when taking a deep breath;
- feeling of lack of air;
- muscle weakness in the upper limbs.
Diagnosis is carried out using an x-ray image, which shows complete closure of the intervertebral spaces and partial or complete fusion of bone tissue.
Clinical prognosis
From a functional point of view, the prognosis cannot be favorable, since limited mobility remains with the person for life. In addition, with age, secondary pathologies usually appear, which aggravate neurotic symptoms.
The prognosis is considered extremely unfavorable if the concretion is accompanied by diseases or pathological conditions of the heart and blood vessels, kidneys, blood vessels and other internal organs and systems
Over the years, the condition of patients suffering from concrescence becomes worse. When they stop growing, the process of intervertebral disc degeneration begins almost immediately.
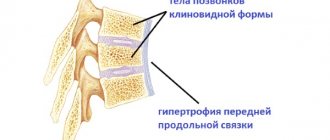
Degenerative changes in the discs
As for preventive measures, they do not exist. Since the disease is congenital, it cannot be prevented by any specific preventive measures. The only thing that prenatal diagnosticians recommend is to undergo a genetic test to determine the risks of hereditary pathologies, especially if one of your relatives has a history of concretion of the cervical spine.
Video - Gitt technique for patients with concretion of the cervical vertebrae
Concrescence (fusion) of the lumbar vertebrae
Partial fusion of the lumbar vertebrae in an adult is always associated with degeneration of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc. This could be a sequestration of a hernia, surgery, a traumatic breach of integrity, a compression fracture, etc.
Concrescence of the lumbar vertebrae has a significant impact on the process of distributing the shock-absorbing load on the spinal column. If any of the intervertebral discs is damaged or missing, then an increased load is placed on the neighboring ones. They quickly collapse and secondary fusion of the lumbar vertebrae occurs until it completely loses its physiological mobility.
Even partial fusion of the lumbar vertebrae entails serious consequences:
- disruption of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and pelvis (constipation, diarrhea, urinary incontinence or urinary retention, erectile dysfunction or infertility);
- paresthesia and impaired skin sensitivity in the lumbar region, sacrum, anterior abdominal wall and lower extremities;
- muscle weakness and impaired tone of the vascular wall, which entails disruption of the valvular system of the venous bed and the development of thrombophlebitis;
- disruption of muscle innervation and partial dystrophy.
The gradual fusion of the sacral vertebrae by the age of 25 is considered a completely physiological process.
Other diseases - clinics in
Choose among the best clinics based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
Family
Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth
Moscow, st.
Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 Sevastopolskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1500
- Exercise therapy from 2700
0 Write your review
Family
Oriental Medicine Clinic "Sagan Dali"
Moscow, prosp.
Mira, 79, building 1 Rizhskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1500
- Diagnostics from 0
- Reflexology from 1000
0 Write your review
Family
Center for Chinese Medicine "TAO"
Moscow, st.
Ostozhenka, 8 building 3, 1st floor Kropotkinskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1000
- Massage from 1500
- Reflexology from 1000
0 Write your review
Show all Moscow clinics
Other diseases - specialists in Moscow
Choose among the best specialists based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
VertebrologistOrthopedist
Gromov Ilya Sergeevich
Moscow, st.
Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 (Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth) +7 Registration
0 Write your review
VertebrologistOrthopedist
Kudryakov Stepan Anatolievich
Moscow, st. Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 (Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth)
+7
Registry
0 Write your review
Orthopedist