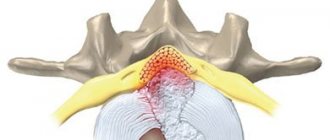
Lordosis is usually understood as a physiological or pathological curvature of the spinal column, the convexity of which is directed anteriorly. The disease is manifested by pain in the back and impaired posture of a person.
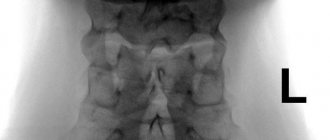
Diagnostics is carried out on the basis of an initial examination of the patient, as well as the results of radiography.
Treatment of lordosis is predominantly conservative, however, in various situations, radical methods (surgical intervention of varying degrees of complexity) can be used.
What is spinal lordosis?
Lordosis is a physiological or pathological curvature of the spinal column in the anteroposterior direction with a characteristic convexity that faces predominantly anteriorly.
Physiological lordosis of the spine forms in the first year of a person’s life, while the pathological type of the disease can form at any age, being the result of a congenital or acquired pathology.
In advanced cases, the patient may experience difficulty and serious disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Symptoms of lordosis are the following::
- protruding belly , pelvis tilted back, knees turned in opposite directions;
- stretched muscles in the lumbar region , constant aching pain, which noticeably intensifies and becomes almost unbearable from standing for a long time;
- lowering of the abdominal organs , which provokes disturbances in their functioning;
- rapid fatigue , deterioration of night sleep, pain in any attempts to straighten the back, as a result of which the patient cannot take a position on his stomach while sleeping.
In case of pathological curvature of the spine, it is necessary to consult an orthopedist or surgeon. If there is a suspicion of lordosis, a person should first perform a self-diagnosis technique . To do this, you need to press your back against the wall so that your shoulder blades, buttocks and heels touch it at the same time.
Then you need to try to stick your hand into the gap between your lower back and the wall. Difficulty in this action will be a positive sign indicating the absence of this pathology.
If the hand passes freely, especially against the backdrop of pain in the spinal column, it is necessary to see a doctor as soon as possible with suspicion of developing lordosis.
A surgeon or traumatologist can most accurately make this diagnosis . As a rule, the doctor makes a conclusion based on a general examination, studying the medical history, and assessing the range of motion and muscle strength. Neurological status is also assessed. The most accurate diagnostic method in this case is radiography.
For existing somatic or neurological symptoms, methods are also used:
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography;
- electroneuromyography.
If there is a suspicion of the development of inflammatory processes or tumors, the doctor may prescribe additional laboratory methods.
Causes of lordosis
Among the main causes of primary type lordosis, it is customary to distinguish pathological processes, including:
- congenital and acquired malformations;
- neoplasms and inflammatory foci in the vertebral area;
- spasms;
- spinal injuries.
The causes of secondary type lordosis are considered to be factors such as:
- loss of joint mobility;
- congenital hip dislocation;
- pathologies of the musculoskeletal system of a systemic nature;
- spastic paresis of the lower extremities;
- pregnancy.
It is also important to note that among the additional factors predisposing to pathology, which may be the causes of lordosis, it is also customary to name:
- poor posture;
- excess body weight, with localization of adipose tissue on the abdomen;
- a sharp growth spurt during childhood and adolescence.
Regardless of the causes of lordosis and its type, the center of gravity of the human body with the presence of pathology is shifted predominantly forward.
Types of spinal lordosis
Traumatology and orthopedics determines several current classifications of curvature of the spinal column of the presented type, according to several criteria. Let's look at the most common of them.
By location:
- cervical lordosis;
- lumbar lordosis.
Due to the occurrence:
- primary – developing against the background of various kinds of pathological processes localized directly in the tissues of the spinal column;
- secondary – having a compensatory nature and arising as a result of attempts to maintain balance.
By form:
- physiological;
- excessive pathological (hyperlordosis);
- straightening (hypolordosis).
If possible, give the spine a natural position:
- unfixed – the patient’s conscious effort allows him to straighten his back;
- partially fixed – limited change in the existing angle is possible;
- fixed – returning to the natural position is impossible.
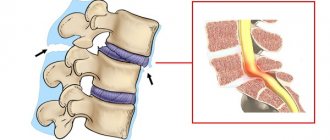
Normal spinal curves
The spine of a healthy adult has 2 kyphosis (bend, convex back) - thoracic and sacral, and 2 lordoses (bend, convex forward) - cervical and lumbar. In a newborn, there are practically no curvatures of the spinal column: there is only mild kyphosis in the sacrococcygeal region, which formed while in the fetal position. When the child begins to hold his head, cervical lordosis forms.
At 4–6 months, the child makes attempts to sit up, which leads to the formation of a bend in the thoracic region. The last to form is the anterior curve in the lumbar region. This happens closer to the year when the child learns to hold the body in an upright position and begins to walk. In a small child, all the curves are very unstable, a clear expression is formed only at 6–7 years, and the curves acquire their final shape by the age of 20.
Symptoms of lordosis
The key manifestation of cervical or lumbar lordosis, as well as other forms of this disease, is a change in a person’s posture, accompanied by increased fatigue and pain localized in the affected part of the spine.
Other symptoms include:
- excessive head tilt;
- a large gap between any part of the spine and a hard surface in the “lying” position;
- limited ability to perform simple motor actions;
- pain and discomfort;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- disruption of internal organs.
Consequences
The lack of timely treatment for the diagnosis of lordosis leads to a significant weakening of the spinal ligaments and growing muscle tension. All this leads to severe pain and constant spasms.
At the same time, the condition of the spine itself deteriorates, which manifests itself in the form:
- erasure of intervertebral discs;
- increased mobility of the vertebrae;
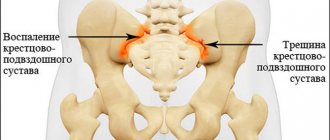
- inflammation of the iliopsoas muscle;
- development of deforming arthrosis in the joints of the spine;
- increasing the risk of developing intervertebral hernias.
Due to negative changes occurring in the body, cardiovascular pathologies, breathing problems, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract may appear.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis and treatment of lordosis is carried out by highly specialized specialists: orthopedists and vertebrologists. The diagnosis is made based on the collected medical history, as well as the results of the examination and radiography.
During a visual examination, the doctor assesses the naturalness of the patient’s body position, the characteristics of his posture, and also conducts a number of specific tests in order to establish the type of pathology and the presence of accompanying neurological disorders.
X-ray is a key research method that allows you to confirm or refute the presence of a pathological process. In order to obtain the most effective results, an X-ray of the spine is used in several projections (direct/lateral).
To determine the degree of lordosis, an X-ray is taken in a situation of maximum extension/flexion of the back, in parallel with which an assessment of the mobility of the spine in various planes is carried out.
Treatment of lordosis
The course of treatment is determined with the participation of treating specialists, namely a vertebrologist and an orthopedist. In order to achieve the most successful result, the therapy is comprehensive, and constant supervision by a specialist is preferable throughout all stages of its implementation.
The treatment program may include activities such as:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- manual therapy and medical massage;
- wearing corsets and specialized bandages;
- drug therapy;
- kinesio taping;
- therapeutic physical education (therapeutic physical education);
- surgical intervention.
All procedures used are aimed at relieving pain, relieving inflammatory processes and, of course, uniformly distributing the load on the parts of the spinal column.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapeutic treatment methods are widely applicable in eliminating lordosis, but are used exclusively in combination with other interventions.
The most important methods of physiotherapy are exposure to the affected area with ultrasound and microcurrents. A particularly beneficial effect is observed when exposed to electrophoresis and cryoprocedures.
Massage
The use of massage is permissible only after consultation with the attending physician.
The main massage techniques are stroking and vibration. The first days the procedure involves only these techniques, and only in the second week light superficial squeezing, rubbing and kneading techniques are added.
The average session duration should not exceed 20 minutes. It is important to work along the spine. It is recommended to use massage in courses of 15 sessions, alternating procedures every other day.
Wearing a corset and bandages
The use of a special corset is especially important in the treatment of lumbar lordosis, which allows you to maintain the optimal condition of the spinal column and strengthen the muscular frame.
Wearing a corset and other supporting structures is permissible only if prescribed by a doctor. The length of the product is determined by the existing angle of curvature and the characteristics of the clinical course of the disease.
Corsets are a means of treatment, and bandages are an auxiliary solution that allows for complete treatment.
Treatment of lordosis with medications
Drug therapy is an integral part of complex treatment. Properly selected drugs make it possible to stop the inflammatory process and completely relieve the patient’s pain.
As part of therapy, the following groups of drugs are used:
- anti-inflammatory;
- muscle relaxants;
- analgesics;
- vitamin and mineral complex;
- chondroprotectors.
A particularly important category of drugs are chondroprotectors, which promote the regeneration of cartilage tissue and maintain its optimal condition. Among them, the drug “Artracam” is considered to be the most effective.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention belongs to the category of radical treatment methods, the prescription of which is used in a situation where the functioning of internal organs and systems is disrupted, and the disease is not amenable to conservative treatment.
The key task of doctors is surgery to correct the curvature of the spinal column with its further fixation in an optimally comfortable position.
Surgical intervention is used extremely rarely, since it eliminates only the consequences, and not the cause of the development of the disease. In rare cases, the only correct solution is to replace the damaged vertebra with an implant, which makes it possible to restore the mobility of the spinal region.
As a result of the surgical intervention, there is a long recovery period, which requires close supervision of the attending physician and reaches one and a half years.
Therapeutic physical education (PT) in the treatment of lordosis
Clinical studies conducted in 2021 proved the effectiveness of gymnastic exercises for back curvature.
Exercise therapy occupies a special place in the complex treatment of spinal pathologies. It is through the systematic implementation of a set of exercises selected by the attending physician that patients have the opportunity to prevent the development of changes in the functioning of internal organs.
Gymnastic exercises are selected in accordance with the existing curvature, as well as taking into account the general health of the patient and his level of physical fitness.
It is best to do exercise therapy in a calm environment, under the close supervision of a specialist. Swimming or going to the gym will help increase the effectiveness of gymnastics.
Will they be called up to serve in the RF Armed Forces with this pathology?
In accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 123 of February 25, 2003:
- If there are no complaints during examination, the category “A” is assigned, and he is fit for military service.
- If during inspection the bend is quite pronounced , category “B” is assigned, which means suitability with some restrictions.
- When a significant deformity of the spinal column is detected , it becomes category “B”, in which the conscript is transferred to the reserve.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis for the development of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system can always be different, however, it remains predominantly favorable. The development of pathological processes proceeds quite slowly, which makes it possible to diagnose them and treat them before the development of critical complications.
Failure to contact your doctor in a timely manner, as well as a complete refusal or partial deviation from the established treatment plan can cause various types of complications.
The progression of the curvature leads not only to an increase in visually noticeable signs of the disorder, but also to increased discomfort and pain, which is caused by the destruction of cartilage tissue.
In a situation where the thoracic spine is affected and the chest is subject to deformation, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs may develop. In advanced cases, the functioning of the diaphragm is disrupted, which reduces lung capacity.
Prevention of lordosis
Prevention is a set of measures that is an opportunity available to every person to prevent the development of a disease.
Among the preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of pathological curvature of the spine, it is customary to highlight the following:
- developing the habit of constant posture control;
- dosage of physical activity;
- adherence to the principles of proper nutrition;
- strengthening and maintaining an optimal level of immunity;
- limiting the load on the spine, avoiding heavy physical work;
- wearing exclusively correct orthopedic shoes;
- use of high-quality mattresses and pillows for night rest;
- preventive intake of a vitamin-mineral complex (after consultation and clarification of the course of treatment with the attending physician);
- systematic planned visits to highly specialized specialists;
- timely treatment of various types of diseases and injuries.
Accurate diagnosis and quality treatment are the main priorities in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Remember about preventive measures and do not bring illnesses to a critical state.
What is the risk of the disease?
A straightened lower back not only changes the gait, but also causes an acute disruption in the normal blood supply. This in turn leads to increased fatigue, sleep problems, severe headaches, weakness and stress. Possible consequences of deformation may be:
- Degenerative processes in the spine.
- Difficulty in moving and performing simple physical actions.
- Decreased sensitivity of the lower extremities.
- Instability of intervertebral discs.
- Development of arthrosis in the knees.
- Frequent constipation, intestinal diseases.
- Inflammatory processes in the vertebrae.
- Neurological disorders.
- Lameness.
Therefore, timely diagnosis is extremely important to determine a plan to combat the problem, as well as monitoring the dynamics of treatment by a doctor. This will minimize risks and restore freedom of movement to the person.
Preventive recommendations
Treatment at home using traditional methods and without consulting a doctor is unacceptable. This in most cases causes serious complications. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you must seek help from specialists. To avoid this unpleasant disease, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Try to always keep your back straight and watch your posture while working at the computer.
- Lead an active lifestyle, choose suitable sports for yourself.
- Constantly do exercises and abdominal exercises, strengthening the back muscles.
- Treat any infections or inflammatory processes in the body in a timely manner.
- If you need to stay in an uncomfortable position for a long time due to professional activities, take periodic breaks.
- Plan your day, taking time for proper rest.
Preventive measures should begin from the birth of a person and be observed throughout life, only in this case the measures will be quite effective. Particular attention is paid not only to exercise, but also to a balanced diet and body weight control.
The smoothness of the natural curve in the lumbar region is a pathological condition that cannot be ignored. When the first symptoms appear, namely pain, constant tension and visual changes in posture, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will prescribe a comprehensive treatment that will relieve unpleasant symptoms and restore normal back mobility.