The spinal column consists of vertebrae assembled into an S-shaped structure, which ensures the musculoskeletal function of the entire skeleton.
Spine (vertebral column)
The structure of a human vertebra is both simple and complex, so further we will consider what parts it consists of and what function it performs.
Structure of a human vertebra
Spine
The spine is the main part of the human skeleton, ideally adapted to perform a supporting function. Due to its unique structure and shock-absorbing capabilities, the spine is able to distribute the load not only along its entire length, but also to other parts of the skeleton.
The spine consists of 32-33 vertebrae, assembled into a movable structure, inside of which there is a spinal cord, as well as nerve endings. Between the vertebrae there are intervertebral discs, thanks to which the spine has flexibility and mobility, and its bone parts do not touch each other.
The main part of the skeleton of the body serves as an organ of support and movement, the receptacle of the spinal cord
Thanks to the structure of the spine ideally created by nature, it is able to ensure normal human life. He is responsible for:
- creating reliable support when moving;
- proper functioning of organs;
- combining muscle and bone tissue into one system;
- protection of the spinal cord and vertebral artery.
The spine provides support for the body, being the place of attachment of muscles, and takes part in body movements
The flexibility of the spine is developed individually for everyone, and depends, first of all, on genetic predisposition, as well as on the type of human activity.
The cervical and lumbar regions have the greatest mobility, the mid-thoracic spine has minimal mobility
The spinal column is a framework for attaching muscle tissue, which in turn serves as a protective layer for it, as it takes on external mechanical influences.
Supportive corset for the spine
Drug treatment of lumbar vertebrae
Spinal diseases have periods of exacerbation, which manifest themselves in the form of acute and crippling pain in the lower back. To alleviate the condition, symptomatic drug therapy is usually prescribed, aimed at alleviating the patient's condition. What means are used:
- NSAIDs or analgesics. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help relieve inflammation and severe lower back pain. Usually, injectable forms are prescribed for use for 2-3 days, after which they switch to tablets. These drugs are not suitable for long-term use, as they have a relatively high degree of gastrotoxicity (harmful to the stomach), so people suffering from stomach ulcers or gastritis should use them with caution, using the most gentle means. Examples of trade names are Diclofenac, Movalis, Nimesil.
- Muscle relaxants. Often, back pain is associated with a pathological and painful muscle spasm that causes severe discomfort. To eliminate severe pain, you need a course of muscle relaxants. In severe situations, short-term use of tablets is ineffective, so they must be taken for at least 3-4 weeks. Examples of trade names are Baclofen, Sirdalud, Mydocalm.
- Neurotropic B vitamins. These drugs are prescribed for sciatica or lumbago, when the pain syndrome is associated with pinching of the sciatic nerve or nerve roots in the spine. B vitamins in combination, namely thiamine (B1), pyridoxine (B6), cyanocobalamin (B12), which in large doses have an analgesic effect. Medicines are used in courses - injection solutions are administered over 1-2 weeks, and then switched to tablets. Oral forms of release are taken for two months to consolidate the result. Examples of drugs are Milgamma, Neurobin, Neuromax.
- Corticosteroids. This group of drugs belongs to hormonal drugs and has a large list of side effects, so they are prescribed in difficult situations. If the patient suffers from severe pain that cannot be relieved by using NSAIDs, then a corticosteroid is administered through an intra-articular injection. An example of an effective remedy is Diprospan. Under the supervision of an ultrasound sensor, an injection solution is injected into the interarticular cavity, which has a long-lasting effect. Usually, one injection is enough to relieve symptoms of pain for a long time. If for some reason it is impossible for a patient to receive a Diprospan injection, it is recommended to carry out a novocaine blockade. This is a non-hormonal agent with a powerful anesthetic effect.
Medicines to maintain the health of the lumbar back
When the period of exacerbation has passed, doctors recommend using medications that support the patient’s health condition in order to minimize the risks of a recurrent attack. These medications include:
- Chondroprotectors. These are medications aimed at maintaining the health of cartilage tissue, successfully used in the treatment of degenerative processes associated with age-related deterioration. Most often, the use of chondroprotectors is recommended in the presence of joint diseases and the progressive development of osteochondrosis. These drugs are used as a long-term course of treatment for several months or more. First, injectable forms of release are prescribed, used for several months. Then they switch to tablets, which need to be taken for 3-6 months without a break. After which they take a short rest and then use chondroprotectors again. It is important to understand that these drugs do not reduce the risk of degenerative destruction of the vertebrae. They nourish cartilage tissue, and therefore slow down the rate of progression of osteochondrosis. The active ingredients are glucosamine and chondroitin. Examples of medicines are Dona, Chondrogard, Mukosat.
- D3 supplements, calcium. There are specific supplements with a strong evidence base used to support bone tissue at any age. In particular, such supplements are needed by people who are at risk for diseases of the musculoskeletal system - postmenopausal women, people suffering from osteoporosis and children during a period of intensive growth and development of the body. Calcium and vitamin D3 support healthy bone tissue. The first component will not be able to be absorbed normally in the intestines if the patient has cholecalciferol deficiency, so it is recommended to use combined supplements. Examples - Calcium D3 Nycomed, Calcium Citrate with D3, Calcemin Advance. It is advisable to prescribe such drugs for prevention to vulnerable segments of the population or after testing.
- Multivitamin and mineral complexes. Serve as an addition to the daily diet and are not mandatory for use. If the patient’s diet is depleted in vitamins and minerals, then the doctor may prescribe appropriate supplements in periodic courses to prevent hypovitaminosis.
Less commonly prescribed are homeopathy and antispasmodics. External agents in the form of ointments and gels are also often used.
Spinal sections
The spine is divided into five sections.
- Cervical.
- Chest.
- Lumbar.
- Sacral.
- Coccygeal
Parts of the human spine and possible diseases
Table No. 1. Structure of the vertebrae. Characteristics and functions of departments.
| Department | Number of vertebrae | Characteristic | Functions |
| 7 | The most mobile department. Has two vertebrae that are different from the rest. Atlas has no body because it is formed by only two arcs. It has the shape of a ring. The epistropheus has a process that is associated with Atlas. | Atlas is responsible for supporting the head and bending it forward. Axis (or epistropheus) helps with turning the head. |
| 12 | It is considered the least mobile department. There are direct connections to the ribs. This is achieved through the special structure of the vertebrae themselves. The connection into one whole leads to the formation of a kind of protected space for the internal organs - the chest. | Organ protection, body support. |
| 5 | It is called the working part of the spine. The lumbar vertebrae are distinguished by their massiveness and high strength. These two parameters are very important for the lower back, since the entire main load falls on it. | Maintaining the body. |
| 5 fused vertebrae | The sacrum consists of five fused vertebrae, which in turn are fused with other bones to form the pelvis. | Maintaining a vertical body position and distributing loads. |
| Coccygeal | 4-5 | They are connected tightly and firmly. The main feature of the coccyx is its small process. It is called the coccygeal horn. The coccyx itself is a rudiment. | Protecting important parts of the body, attaching some muscles and ligaments. |
Causes of spinal diseases
There are some risk factors that predispose to the development of musculoskeletal diseases, including spinal injuries:
- Maintaining a sedentary lifestyle. In modern times, there is a special term for this phenomenon – physical inactivity. In the age of technological progress, when a person began to move to his place of work using transport, daily energy consumption decreased significantly, which led to a noticeable deterioration in the quality of health. Individuals with physical inactivity often experience poor circulation, weakness, obesity and muscle atrophy. The last point is directly related to back pain with the slightest exertion, including walking and sitting.
- Excessive physical labor. If a person works in hazardous work and is forced to lift heavy weights without proper training, over time he risks developing spinal injuries. This leads to the early course of osteochondrosis, sciatica, radiculitis, and hernias. Builders, loaders, and factory workers are at risk.
- Having flat feet or scoliosis. If the spine is curved, the load on the muscles is distributed incorrectly, which leads to serious deterioration, including imbalance and functional impairment. Against the background of flat feet, there is an incorrect distribution of the load along the foot, which also negatively affects the health of the spine.
- Pregnancy. During this position, a rapid and stressful restructuring of the mother’s body occurs. The heart, blood vessels, and internal organs are severely affected, and the functional indicators of many body systems deteriorate. The spine and connective tissues also suffer, because the ligaments and tendons become very soft. The lumbar vertebrae are most at risk from disorders. Rapidly growing body weight creates additional burden, so the back muscles are heavily overloaded. The stomach protrudes forward strongly to a large size, which changes the center of gravity forward, creating additional stress on the lower back. The result is severe pain. For this reason, many women experienced severe discomfort in the vertebrae during gestation. The use of support bandages partially alleviates the condition of the pregnant woman.
- Previous spinal injuries. If a person has had falls or injuries, then injuries lead to deterioration of the back condition over time. The risks of spinal hernias after physical injury increase significantly.
- There is no proper nutrition, there is excess body weight. Overweight people have an increased risk of problems with the lumbosacral region, since it bears a significant load. Also, obese people lack a strong muscular frame, so the back cannot cope with chronic overloads, which leads to damage to the vertebrae. An unhealthy diet is poor in minerals and vitamins, which negatively affects the health of the body.
- The presence of congenital pathologies. Some intrauterine deformities contribute to the appearance of deterioration in the musculoskeletal system and vertebral bodies already in adulthood.
- Age factor. It is important to take into account that as the body ages, disorders of the musculoskeletal system arise that are associated with degenerative processes in the body.
If you experience discomfort in the spine, it is important to consult a doctor promptly. Health problems are indicated by persistent lumbar pain, a feeling of stiffness, lumbago in the feet, and numbness in the limbs. During the diagnosis, the specialist questions the patient and prescribes an MRI or X-ray. The results of such a study ensure the correct diagnosis in most cases. Then appropriate treatment is prescribed.
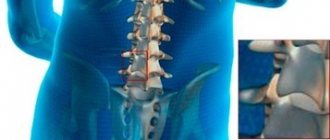
Vertebral structure
A vertebra is the main component of the spinal column.
In the center of each vertebra there is a small opening called the spinal canal. It is reserved for the spinal cord and vertebral artery. They run through the entire spine. The connection between the spinal cord and the organs and limbs of the body is achieved through nerve endings.
Schematic representation of anatomical formations located in the spinal canal
View from above. Transverse section at the level of the intervertebral disc
Basically the structure of the vertebrae is the same. Only the fused areas and a pair of vertebrae, designed to perform certain functions, differ.
A vertebra consists of the following elements:
- body;
- legs (on both sides of the body);
- spinal canal;
- articular processes (two);
- transverse processes (two);
- spinous process.
Typical vertebra
The vertebral body is located anteriorly, and the processes are located posteriorly. The latter are the connecting link between the back and the muscles. The flexibility of the spine is developed individually for everyone, and it depends, first of all, on a person’s genetics, and only then on the level of development.
Due to its shape, the vertebra ideally protects both the spinal cord and the nerves extending from it.
The spine is protected by muscles. Due to their density and location, a layer like a shell is formed. The rib cage and organs protect the spine from the front.
Muscles of the back, neck and suboccipital muscles
This vertebral structure was not chosen by nature by chance. It helps maintain the health and safety of the spine. In addition, this shape helps the vertebrae remain strong over time.
Vertebrae of various departments
The cervical vertebra has a small size and a transversely elongated shape. In its transverse processes there is a relatively large triangular foramen formed by the vertebral arch.
Cervical vertebrae
Thoracic vertebra. In its body, which is large in size, there is a round hole. There is a costal fossa on the transverse process of the thoracic vertebra. The connection between a vertebra and a rib is its main function. On the sides of the vertebra there are two more fossae - lower and upper, but they are costal.
1st (atypical) thoracic vertebra (lateral view)
5th (typical) thoracic vertebra (front view)
12th (atypical) thoracic vertebra (lateral view)
The lumbar vertebra has a bean-shaped large body. The spinous processes are located horizontally. There are small gaps between them. The spinal canal of the lumbar vertebra is relatively small.
Lumbar vertebra
Sacral vertebra. As a separate vertebra, it exists until about 25 years old, then fusion with others occurs. As a result, one bone is formed - the sacrum, which has a triangular shape, the apex of which faces down. This vertebra has a small free space allocated for the spinal canal. Fused vertebrae do not stop performing their functions. The first vertebra of this section connects the sacrum with the fifth lumbar vertebra. The apex is the fifth vertebra. It connects the sacrum and coccyx. The remaining three vertebrae form the surfaces of the pelvis: anterior, posterior and lateral.
Sacrum
Sacrum, right view
The vertebra at the coccyx is oval. It hardens late, which jeopardizes the integrity of the coccyx, since at an early age it can be damaged as a result of a blow or injury. At the first coccygeal vertebra, the body is equipped with outgrowths, which are rudiments. At the top of the first vertebra of the coccygeal region are the processes of the joints. They are called coccygeal horns. They connect to the horns located in the sacrum.
If you want to learn in more detail the structure of the human spine, and also consider what each vertebra is responsible for, you can read an article about this on our portal.
Coccyx
Features of the structure of certain vertebrae
The atlas consists of anterior and posterior arches connected together by lateral masses. It turns out that the Atlas has a ring instead of a body. There are no shoots. Atlas connects the spine and the skull thanks to the occipital bone. The lateral thickenings have two articular surfaces. The upper surface is oval, attached to the occipital bone. The lower circular surface connects to the second cervical vertebra.
First cervical vertebra (atlas)
The second cervical vertebra (axis or epistropheus) has a large process that is shaped like a tooth. This shoot is part of Atlas. This tooth is an axis. Atlas and the head rotate around her. That is why epistrophy is called axial.
Second cervical vertebra (axis)
Due to the joint functioning of the first two vertebrae, a person is able to move his head in different directions without experiencing problems.
The sixth cervical vertebra is distinguished by costal processes that are considered vestigial. It is called protruding because it has a longer spinous process than other vertebrae.
Sixth (VI) cervical vertebra, vertebra cervicalis VI; view from above
If you want to find out in more detail how many bends the human spine has, and also consider the functions of the bends, you can read an article about this on our portal.
Diagnosis of spinal diseases
Vertebrology is a modern branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of the spine.
Previously, this was done by a neurologist, and if the case was severe, then by an orthopedist. In modern medicine, this is done by doctors trained in the field of spinal pathologies.
Today's medicine provides doctors with numerous opportunities to diagnose spinal diseases and treat them. Among them, minimally invasive methods are popular, because with minimal intervention in the body, a greater result is achieved.
In vertebrology, diagnostic methods that can provide results in the form of images or other types of visualization are critical. Previously, the doctor could only order an x-ray.
Anomalies in the development of vertebral arches
There are now many more options that can provide accurate results. These include:
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- myelography;
- electroneurography;
- electromyography.
Moreover, today in medical practice, vertebrologists often use a map of segmental innervation. It allows you to associate the cause and symptoms with which vertebra is affected and which organs it is connected to.
Table No. 2. Map of segmental innervation
| Place | Connection | Cause | Symptoms |
| Cervical vertebrae | Organs of hearing and vision, speech apparatus and brain | Muscle strain | Headache |
| Seventh cervical vertebra | Thyroid | Hump at the bottom of the neck | Sudden changes in blood pressure |
| Seventh cervical vertebra and first three thoracic vertebrae | Heart | Arrhythmia, angina pectoris | Heart pain, palpitations |
| Thoracic vertebrae (fourth to eighth) | Gastrointestinal tract | Pancreatitis, ulcer, gastritis | Heaviness in the thoracic region, nausea, vomiting, flatulence |
| Thoracic vertebrae (ninth to twelfth) | urinary system | Pyelonephritis, cystitis, urolithiasis | Chest pain, discomfort when urinating, muscle aches |
| Lower lumbar region | Colon | Intestinal dysbiosis | Lower back pain |
| Upper lumbar | Genitals | Vaginitis, cervicitis (in women), urethritis, prostatitis (in men) | Feeling of discomfort and pain |
Segmental innervation of internal organs
Scheme of segmental sensory innervation of the skin
What types of diseases occur
Most often, during the examination, the following pathological conditions of the spine can be detected in the lower back:
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine. This is a degenerative change in the joints of the spine, causing damage to cartilage and bone tissue. Very often, osteochondrosis occurs as we age, since with age the intervertebral discs wear out, leading to discomfort and pain. Signs of spinal disease are stiffness, pain and burning at the site of the spinal lesion. In advanced cases, urinary incontinence and lumbago in the lower extremities occur. Over the years, pathology greatly worsens the quality of life, so treatment is necessary, requiring a comprehensive solution to the problem.
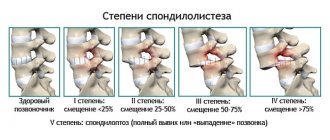
- Spondylosis. If there is too intense stress on the tailbone and lower back, then over time the height of the intervertebral discs changes downward. Spine-shaped articular processes appear on the sides of the vertebrae, which injure the cartilaginous plates and can compress areas of the spinal canal. As a result, the disease can lead to serious neurological disorders and pain. A patient with spondylosis usually complains of pain, stiffness and numbness in the lower back.
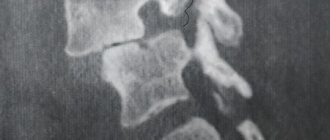
- Protrusion of the lumbar vertebrae is one of the stages of development of an intervertebral hernia. Before a true intervertebral hernia occurs, unfavorable pathological changes appear in the fibrous ring located in the intervertebral disc. When the fibrous ring is stretched with gradual leakage of the nucleus pulposus outward, protrusion is diagnosed. At this stage, you can still get rid of the protrusion non-surgically. There are techniques that allow you to correct the protrusion. Not all cases of protrusion cause symptoms, so they may not exist. Signs of the disease include pain and stiffness.
- A hernia is a more advanced form of protrusion. When a lumbar hernia occurs, serious health problems arise due to the complete protrusion of the contents of the fibrous ring into the cavity of the intervertebral disc. The condition is associated with severe discomfort and pain, often causing lumbago and a feeling of stiffness in the lower extremities. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the patient will lose his limbs and lose sensation in his toes.
- Sciatica. This is a form of radiculitis, manifested by an inflammatory process in the sciatic nerve. A patient with sciatica cannot move normally, stand or walk for a long time, and even lie down with discomfort. The patient constantly feels lumbago and pain.
Also, some patients experience arthrosis, arthritis and the consequences of lordosis. Most diseases have one common symptom - lower back pain. If discomfort persists for a long time, you should definitely visit a doctor.
Anatomy in Chinese
Several thousand years before humanity invented radiography, Chinese doctors already knew about the connection between human internal organs and the spine.
If we are based on the theory of acupuncture, then the main knowledge that we received from the ancient Chinese is knowledge about bioactive points that have a direct effect on internal organs. These points are located near the spine.
Atlas of acupuncture
Depending on the location of the pain, we can talk about the disease itself. To recover from it, you need to influence the sore point. This can be achieved using hands (massage) or various means (for example, special needles).
Acupuncture
Video – Acupuncture
The ideas of Chinese doctors of that time about the connection between internal organs and vertebrae are completely similar to the map of segmental innervation that modern doctors have.
Moreover, Chinese scientists back in ancient times came to the conclusion that emotions affect physical condition. They were able to create a system for detecting diseases based on emotions. The main emphasis is on which emotional component harms a particular organ.
Table No. 3. Chinese health card.
| Place | Organ(s) | Symptoms | Emotion as a root cause |
| Third thoracic vertebra | Lungs | Breathing disorders | Sadness |
| Fourth and fifth thoracic vertebrae | Heart | Painful sensations | Rage, aggression |
| Ninth and tenth thoracic vertebrae | Liver and gallbladder | Discomfort and pain | Anger, bile |
| Eleventh thoracic vertebra | Spleen | Performance deterioration | Doubt, oppression, depression |
| Second lumbar vertebra | Kidneys | Impaired functioning | Fear |
Modern medicine, on a scientific basis, fully confirms all the knowledge that Chinese scientists of ancient times shared with us.
What is the human spine made of? Details about its components
Natural curves of the spinal column
As everyone knows, the human, or any other spine cannot function without a strong bone base, thanks to which we are able to move without restrictions, without causing injury to ourselves. It is in order to preserve the integrity of the bone base of our body, for full movements, that the spine has physiological curves. Natural curves are those that are visible when looking at a person from the side. In the case when the bends are visible when viewed directly, they are called pathological.
Simply put, the spine has two types of curves. If the spine is turned forward, it is lordosis, and if it is turned backward, it is kyphosis. Ideally, a healthy spine must have four curves: an equal number of kyphosis and lordosis, which constantly alternate.
The structure of the vertebrae and their functions
Each vertebra has the following structure: an arch, a body and several processes.
The vertebral body has a kidney-shaped or round shape. It is the basis of the vertebra and its most massive part.
The arch, in turn, performs a certain closing function and creates the spinal canal.
Seven processes extend from each vertebra and they are located as follows:
- There are processes from the joints, four in each, which are located above and below the vertebral body. Such vertebrae perform a connecting function between adjacent vertebrae.
- Two transverse processes.
- One sharp process, which is located in the seventh vertebra, and which can be felt.
All vertebrae are simultaneously different and united by a similar structure.
How do various diseases depend on spinal injuries?
The work of the spine does not end with simply helping to maintain balance in a person when moving, ensuring free walking and combining important musculoskeletal components of the human body. It is important that the spinal cord is located in the spine, which consists of a large number of nerves, their processes and others. Each nerve of the spinal cord regulates the functioning of any organs, and that is why, in the event of damage to some part of the nerve, the work of the organ that it coordinates is correspondingly disrupted.
So, let's look at each department in more detail:
- In the cervical region there is control over the work and sensitivity of the tongue, lips, teeth, eyes, nose, forehead, blood circulation of the brain, thyroid gland and elbows. When the cervical vertebrae are damaged, the following diseases and pathological conditions may be noted: constant headaches, increased blood and arterial pressure, diseases of the nose and sinuses, throat, increased nervous excitability, memory problems, hearing impairment and bone pain.
- The thoracic region regulates the functioning of major organs, such as the kidneys, liver, intestines, mammary glands, heart and others. In case of injuries to this department, the following diagnoses can be made: problems with the functioning of the above organs (for example: gastritis, arthritis, decreased immunity, infertility, metabolic disorders, bronchitis and the like).
- The lumbar region is responsible for the large intestine, the work of the lower extremities and the organs of the reproductive system. Consequently, the following problems are possible: inflammation of sciatica, sciatica, prostatitis, constipation, appendix and others.
- The sacral region controls the functionality of the rectum and its muscles, as well as the nerves in the anus. Injuries to this department can lead to sexual disorders, hemorrhoids, pain in the sacrum and malfunction of the pelvic organs.
From the above, we can conclude that it is imperative to monitor the health of the spine and if you experience even the slightest discomfort or suspicion of problems with it, you must immediately contact a specialist.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Treatment
Physiotherapeutic devices
There are many options for spinal treatment that are performed in an inpatient setting. However, besides them, there is a simple and affordable way to improve your health - this is oriental massage. Anyone can master it and do it at home.
Oriental massage
According to Chinese tradition, bioactive points in humans are located near the above vertebrae (see table No. 2). The distance is two fingers.
At a distance of four fingers there are points where, according to Chinese doctors, destructive emotions accumulate. By walking along the entire length of the spine with just your fingertips, the massage therapist improves the functioning of the entire body.
Movements are made gently along the spine. You need to move from the highest point down.
The main rule of massage. The person receiving the massage should enjoy the process and not experience pain. If pain occurs when you press on any point, then you need to ease the pressure.
A simple massage, when performed correctly, can improve the condition of the human body. But the main thing is to get rid of the reasons that cause negative emotions. After all, they are usually the root cause of all problems.
Video – Oriental massage Yumeiho
Non-drug treatment
When a patient experiences an attack of acute pain in the vertebral area, supportive conservative treatment is recommended. What methods of preventing exacerbation of the disease help:
- Massage. Using special techniques, the massage therapist warms up the muscles and relieves tension. Local blood flow also improves, so after a course of massage the patient temporarily stops feeling pain in the lumbar vertebrae.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment. With the help of hardware technology and the use of medications, the inflammatory process is eliminated and chronic discomfort in the lower back goes away. Recommended hardware techniques are magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, shock wave therapy.
- Manual practice. This is a branch of alternative medicine that allows you to “straighten” the vertebrae to their natural position. The concept of the teaching is that if the vertebrae are in the wrong position, misalignment occurs throughout the body, which leads to back problems. Manual therapy cannot be performed if there is a large hernia.
- Physiotherapy. With the help of sports activities, it is possible to tone the muscles, which removes most of the stress from the vertebrae. As a result, the discomfort goes away almost completely. It is important to do the exercises daily. The exercise therapy complex is selected individually with an instructor, taking into account the diagnosis.
- Wearing orthopedic shoes and elastic corsets. Properly selected bandages and shoes will help relieve stress on target muscles that are not strong enough to compensate for discomfort in the vertebrae. The duration and timing of wearing should be recommended by the attending physician. Clothing models and sizes are also chosen based on recommendations.
If the situation is advanced and conservative methods of therapy do not help, surgery is required.
Theory - clinics in
Choose among the best clinics based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
Family
Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth
Moscow, st.
Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 Sevastopolskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1500
- Exercise therapy from 2700
0 Write your review
Family
Oriental Medicine Clinic "Sagan Dali"
Moscow, prosp.
Mira, 79, building 1 Rizhskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1500
- Diagnostics from 0
- Reflexology from 1000
0 Write your review
Family
Center for Chinese Medicine "TAO"
Moscow, st.
Ostozhenka, 8 building 3, 1st floor Kropotkinskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1000
- Massage from 1500
- Reflexology from 1000
0 Write your review
Show all Moscow clinics
Theory - specialists in Moscow
Choose among the best specialists based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
VertebrologistOrthopedist
Gromov Ilya Sergeevich
Moscow, st.
Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 (Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth) +7 Registration
0 Write your review
VertebrologistOrthopedist
Kudryakov Stepan Anatolievich
Moscow, st. Azovskaya, 24, building 2 POM VI/KOM 5,6,7/ET 1 (Scoliosis Treatment Center named after K. Schroth)
+7
Registry
0 Write your review
Orthopedist