Spondyloarthrosis is a well-known and common disease of the lumbar spine. Mostly, pathology of the lumbosacral region develops in people over 50-55 years of age, but sometimes it occurs in people who engage in heavy physical labor, have difficulty losing weight, or have suffered a spinal column injury.
Spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine affects the joints connecting the vertebrae. Of all the varieties, this disease is considered quite safe, but only at the beginning of its development. Subsequent progression of the pathology leads to problems with movement and can cause numbness in certain areas of the lumbar region and other complications.
Causes of spondyloarthrosis
The main cause of spondyloarthrosis in the lumbar region is aging. The facet joints in the spine wear down and weaken, leading to symptoms of osteoarthritis.
The disease can be caused by a number of other reasons:
- injuries, sprains of joints in the lumbar region;
- the process of destruction of intervertebral discs, the distance between them decreases, the risk of osteophytes increases;
- extension (backward movement of the torso) creates high pressure on the joint, which can also deform it;
- serious injury to the spine and, in particular, the lumbar region can cause spondyloarthrosis;
- congenital predisposition, inheritance of the disease from one of the parents or distant relatives can be the cause of spondyloarthrosis;
- constant stress on the spine, carrying heavy objects or playing strength sports.
All these reasons can become provocateurs of the disease.
Sets of exercises for various spondyloarthrosis and their detailed description
The exercise therapy program for spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine, as well as for any other type, is prescribed exclusively individually; it must be tailored to the needs of a particular patient. However, there is a general set of exercises, which include:
- This exercise is suitable either for warming up or for completely completing a set of procedures. The patient needs to lie on the floor or on a mat, straighten up completely, and then take deep breaths and exhales, repeat this for at least 5 minutes. You need to inhale quickly, but exhale as slowly as possible.
- You need to hang on a horizontal bar or any other crossbar and just hang there for a short amount of time. If this does not cause difficulties, you can additionally pull your legs towards your stomach. This exercise is included in the exercise therapy cycle for spinal spondyloarthrosis; it effectively fights pain and helps avoid further progression of the disease.
- You should lie on your back, relax your body, and then gradually begin to pull your knees towards your chin. It is best if you can still reach your knees to the desired part of the body. This strengthens the spinal column and is part of the exercise therapy complex for thoracic spondyloarthrosis.
- This technique is only the second type of the previous one, which has the same effect. Here you need to kneel down, focus on your hands, try to relax them and gradually lower yourself to the floor. This should be done so that in the end only the chest and chin touch it.
- You should lie on your back and then raise your head so that the angle is at least 45 degrees. Helping yourself with your hands or in any other way is prohibited; this technique is often used in exercise therapy for cervical spondyloarthrosis.
- You need to put your hands behind your head and begin to raise your legs one by one so that you get a right angle. Each leg must be fixed in the maximum accessible position for a period of at least 10 seconds. You should change legs several times and only then complete the procedure.
- You need to lie on your back again, but now start turning the “bicycle”, familiar to many from school days. The exercise should be repeated at least 2 times, each time for 10 seconds, give yourself a short break and start doing it again.
It is important to note that many exercises have a number of contraindications in case of exacerbation of spondyloarthrosis, and therefore, even before using them, it is strongly recommended to consult a specialist.
Symptomatic manifestations
Symptomatic signs will occur depending on which element of the spine in the lumbar region has been damaged. The aggressiveness and frequency of symptoms is also influenced by the condition of the nerve endings in the affected area.
Symptoms are intermittent, variable, and range from mild to severe. The patient may have the following manifestations of spondyloarthrosis:
- Pain in the lower back is a common symptom. Discomfort extends to the ischial region and may affect the lower limbs;
- frequent muscle spasms, leading to the need to change position;
- limited mobility, the patient cannot straighten up or tilt the body to the side, in some cases, occupying a vertical position causes a lot of difficulties;
- lack of previous coordination of movements, the patient may stumble;
- sitting causes less pain than lying;
- curvature of the spine in the lumbar region, the occurrence of lordosis;
- the presence of stenosis-like symptoms;
- stiff sensations, especially after a long sleep or being immobile, the back is constantly tense;
- pain after physical activity or carrying heavy objects;
- increased swelling in the area of degenerated facet joints.
The symptoms cannot be called specific. Most diseases associated with damage to the spinal column have similar symptoms.
Class Rules
In order not to harm your body when performing physical therapy exercises, you should adhere to medical recommendations. They are very simple:
- Instead of universal complexes, you need to use an individually developed program. It is compiled taking into account age, weight, diagnosis and other factors.
- At the beginning of classes, each exercise is repeated 3-4 times, gradually increasing the number of repetitions to 20. This must be done over several days.
- For classes, wear comfortable clothes and shoes. All movements are performed slowly and smoothly, without sharp turns and very carefully.
- Exercises are performed daily. If you feel unwell, reduce the load without interrupting regular exercise. They refuse gymnastics only if there are serious contraindications.
- During classes and immediately after them, they pay attention to their well-being. To notice the body's reaction to new exercises or loads, it is advisable to keep notes.
- It is very good if therapeutic exercises are combined with massage.
- Examinations are carried out regularly. This is necessary to track the dynamics of improvements and load correction.
- Instead of universal complexes, you need to use an individually developed program. It is compiled taking into account age, weight, diagnosis and other factors.
- At the beginning of classes, each exercise is repeated 3-4 times, gradually increasing the number of repetitions to 20. This must be done over several days.
- For classes, wear comfortable clothes and shoes. All movements are performed slowly and smoothly, without sharp turns and very carefully.
- Exercises are performed daily. If you feel unwell, reduce the load without interrupting regular exercise. They refuse gymnastics only if there are serious contraindications.
- During classes and immediately after them, they pay attention to their well-being. To notice the body's reaction to new exercises or loads, it is advisable to keep notes.
- It is very good if therapeutic exercises are combined with massage.
- Examinations are carried out regularly. This is necessary to track the dynamics of improvements and load correction.
It is better to distribute the loads throughout the day. It is best that classes last 2-3 times a day for 20 minutes. If this is not possible, then the duration of one lesson should not exceed 45 minutes. Don’t forget about posture and proper breathing: inhale through your nose, exhale through your mouth.
Physical activity during the day is not a reason to cancel classes; on the contrary, exercise will help relieve muscle tension and pain if it occurs.
Diagnostics
If pain or discomfort in the back continues for more than 14 days and becomes chronic, you need to visit the hospital for diagnosis.
The diagnostic stage is divided into two parts: anamnesis collection and instrumental examination. The first part is needed by the doctor in order to have an idea of what he will encounter, the second is to draw up a clinical picture.
The patient’s medical history is fully studied, presenting symptoms, aggressiveness and frequency of pain are collected. It is important for the doctor to know when negative signs first appeared in order to rule out inappropriate diseases.
The specialist will study not only the patient, but also his family. Spondyloarthrosis is a pathology transmitted hereditarily, not necessarily from parents. More distant relatives could have back problems.
The oral interview is followed by a visual inspection. The doctor assesses the patient’s current condition, studies nerve conduction and joint mobility. The examination does not make it possible to establish an accurate diagnosis, but it makes it possible to exclude extraneous diseases.
Additional recommendations
There is also a list of general recommendations that should be followed to improve your health, including:
- If the disease has reached a severe stage, it is strongly recommended to give up any physical exercise. Such patients are deliberately prescribed more gentle complexes.
- During the set of exercises, pain should not arise, let alone intensify, and therefore, if such symptoms occur, the course should be completed immediately and immediately contact a specialist.
- The complex should be performed every day, preferably at the same time. Classes in the morning are considered optimal.
- If you want to perform exercises 2 times a day, they should be divided into 2 complexes, but in no case should you increase the load sharply several times. This needs to be done gradually.
Thus, if you follow all the recommendations of doctors, you can improve your own health without unnecessary difficulties.
Top ↑
Instrumental diagnostics
After an oral interview and physical examination, the turn of instrumental diagnostics follows. The following methods are used for studying:
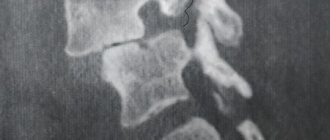
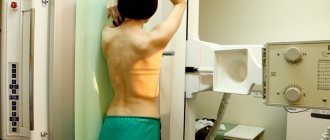
- X-ray. Allows you to determine the presence of damage to the spinal column, the presence of malignant neoplasms - osteophytes. If there is an injury, the doctor will assess its extent and take immediate action.
- PAT. A complete bone scan to exclude possible inflammatory reactions, malignant tumors and infectious diseases.
- CT. It is necessary to assess the condition of the spinal canal and surrounding structures.
- MRI. Allows you to see the morphological picture of the spinal cord, assess the condition of the nerve endings, vertebrae and the spinal column itself.
All these measures are optional. PET, CT and MRI are auxiliary instrumental diagnostics that are needed to create a true clinical picture. Symptoms of lumbosacral spondyloarthrosis are very similar to other diseases, so the doctor must be sure that he is making the correct diagnosis.
Cervical region
Spondyloarthrosis of the cervical spine is expressed by dull pain in the neck and back of the head. Turning the head and moving the neck becomes impossible. Gradually, the pain moves to the area of the shoulder blades and shoulders, as a result of which the functions of the organs of vision and hearing, as well as balance, are disrupted. Pressure drops are observed. In the later stages of the disease, complete immobilization of the joints of the cervical vertebrae is possible.
Treatment of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine
Therapy for spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral region simultaneously sets several goals:
- eliminating negative symptoms, reducing the aggressiveness of pain and stiffness in the affected area of the back;
- slowing down the process of pathological destruction or modification of joints and bones.
Doctors prefer to use conservative methods without direct intervention from specialists. But if the symptoms worsen, pathological processes continue to develop, doctors have no other choice.
But, in most cases, only conservative therapy is sufficient to treat spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral region. Here are some of the most popular methods:
- Therapeutic physical education (therapeutic physical education). A series of exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles in the lumbar region. If you train the muscle structure, the stability of the spine will increase and the load on it will decrease.
- Reducing body weight. Obesity is one of the causes of the development of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral region. Large body weight loads the spine 3-4 times more than usual. This problem can be dealt with in different ways: diet and exercise, the implementation of which should be supervised by a specialist.
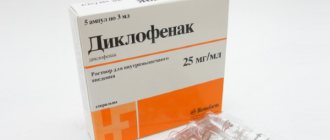
- Treatment of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine with medications. Several groups of medications are used: anti-inflammatory, painkillers, and anti-edema. Each drug is prescribed to reduce pain and suppress the feeling of stiffness in the lumbar region.
- Use of heat and cold. With the help of heat, the muscle structure relaxes, which is convenient and effective during exercise. Cold helps eliminate pain and reduce the inflammatory response.
- Manual therapy. A very popular method based on special manipulations in the lumbosacral spine. Of course, it will not be possible to completely restore the affected area, but you can correct the structure of the spinal column, which will have a positive effect on mobility.
- Massage. Helps relax muscles and reduce stress on them. If the symptoms of the pathology have not become acute, you can carry out the procedure yourself, but after consulting a doctor. Frequent massage is prohibited.
Other methods are also used to treat spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine: acupuncture, magnetic therapy, epidural injections, and weak current. All of the above methods are not dangerous to human health, have a minimum number of side effects and contraindications, which makes them indispensable for pathology of the spinal column.
Two tips to make your workouts more effective
Take a professional exercise therapy course
It is highly advisable to take a professional exercise therapy course at least once a year. Physical therapy for spondyloarthrosis, performed in medical institutions, has a number of advantages over home gymnastics:
- it is safe because it is carried out under the supervision of a doctor;
- gives quick results due to the use of the most effective and individually adjusted exercises;
- there is the possibility of using gymnastic apparatus and special equipment;
- As a rule, such physical education is combined with other therapeutic measures (manual therapy, massage, physical therapy).
Sign up for the pool
Some of the most effective options for therapeutic exercises are swimming and exercises in water. While in the water, the spine experiences virtually no stress, and you can exercise quite intensely, which strengthens the muscles well without creating a feeling of fatigue and overwork.
Self help
If you don’t have time to visit the hospital or pain prevents you from getting there, you can try to help yourself. This must be done with caution so as not to provoke a worsening of the situation.
The following tips are used:
- Sleep with a pillow between your legs. Reduces the amount and aggressiveness of pain.
- Use heat and cold alternately in the affected lumbar region.
- Do not lift heavy objects, avoid possible physical exertion.
- Buy an orthopedic pillow and mattress. Special items help keep the spine in good shape and reduce the load on the muscles.
- Stick to a diet. Excess weight is a direct provocateur of spondyloarthrosis.
These measures are only temporary and are not a direct treatment for the disease. If the situation begins to deteriorate sharply, you should immediately visit the hospital or call an ambulance at home.
Types of exercises for the spine
Basically, exercise therapy for the treatment of cervical spondyloarthrosis consists of gymnastic exercises for flexibility. Complex loads cannot be given in this situation; all classes must be conducted under the supervision of a trainer.
Basic complex for lumboarthrosis
Perform each exercise 10-12 times for 3-5 approaches.
- IP: standing. Perform a slow turn of the head from side to side with maximum amplitude, avoiding the occurrence of pain.
- IP: sitting on a chair. Lower your head as far as possible, trying to touch your chest with your chin.
- IP: sitting on a chair. Try to tuck your chin in while moving your neck back.
- IP: sitting. Place your elbow on a hard, flat surface, place your palm on your temple. Tilt your head to the side, overcoming the resistance of your hand. Next, place your palm on your forehead and press on it.
- Raise your shoulders up, holding at the top point for 10 seconds.
- IP: sitting or lying down. Using your fingers, stretch the back of your head.
Additional exercises
This exercise will help you prepare your neck muscles before performing therapeutic exercises. It can also be done at the end of the main complex to relax the muscles. IP: lying on your back. On the count of 1-2, inhale smoothly; on the count of 3-4-5-6, exhale slowly. Repeat 5-10 times.