3 January 2021
22622
0
3.7 out of 5
Some diseases of the spine, vascular disorders and even endocrine pathologies can provoke the occurrence of such an unpleasant and very detrimental condition as cervical myelopathy. It is accompanied by disturbances in sensitivity and mobility, and can also lead to serious complications. Therefore, it is important to diagnose it in the early stages of development, establish the cause of its occurrence and effectively influence it in order to avoid worsening the condition.
What is cervical myelopathy and the causes of its occurrence
Cervical myelopathy is a well-studied clinical syndrome, the occurrence of which is caused by damage to the spinal cord as a result of various factors, including trauma, degenerative changes in the cervical spine, tumor formation, and the development of infectious, neurological and vascular diseases. In other words, cervical myelopathy and the accompanying set of symptoms are not an independent disease, but are only a consequence of a narrowing of the spinal canal, malnutrition of the spinal cord, and an inflammatory process in it, due to one reason or another.
The spinal cord, surrounded by its own membranes, passes through the spinal canal with its nerve roots and blood vessels. Therefore, its narrowing, especially progressive, will sooner or later affect the state of this nervous structure, which is responsible for the proper functioning of almost all organs and tissues of the human body, which will lead to corresponding neurological disorders, and in case of damage to blood vessels - ischemia (acute malnutrition) and other undesirable consequences. Therefore, the development of symptoms of cervical myelopathy requires an early visit to a neurologist, comprehensive diagnosis and treatment, which may include decompression surgery.
The main reasons for the development of cervical myelopathy are:
- inflammatory diseases of the spine, which include rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, spinal tuberculosis;
- injuries of the spine and spinal cord, especially comminuted vertebral fractures and direct lesions of the spinal cord;
- vascular disorders, which may include atherosclerosis, thrombosis and aneurysms of the spinal arteries, leading to spinal cord infarction;
- compression of the spinal cord by tumors, large intervertebral hernias, osteophytes of vertebral bodies, displaced vertebrae, hematomas, etc.
The most common cause of cervical myelopathy is complications of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
The disorder can occur at any age, although it is most common in older people with severe degenerative changes in the spine. But if we consider each age group separately, then in children the pathology most often becomes a consequence of an enterovirus infection, in young people - injuries to the back and spine in particular. In the middle age category, cervical myelopathy is caused by neoplasms and injuries.
In general, 2 types of cervical myelopathy can be distinguished:
- progressive – accompanied by a rapid increase in the severity of symptoms and most often becomes a consequence of injury;
- chronic - manifestations of pathology intensify gradually.
Myelopathy can affect any part of the spine, including the thoracic and lumbar, although the cervical spine, due to its anatomical features, is most often affected. In each case, its development is caused by stenosis of the spinal cord or its vessels. But the manifestations of pathology directly depend on the location of the affected area and can vary dramatically.
Congenital narrowness of the spinal canal significantly increases the risk of developing cervical myelopathy. Thus, with a diameter of less than 12 mm, the likelihood of this violation occurring is extremely high.
Prerequisites for the development of pathology may be:
- obesity, as this leads to increased load on the cervical and other parts of the spine;
- a sedentary lifestyle, especially long-term static loads on the spine that occur when sitting at a computer or gadgets for a long time;
- unhealthy diet that does not meet the body's nutritional needs;
- smoking, since this bad habit negatively affects the condition of blood vessels;
- alcohol abuse;
- excessive physical activity, causing increased stress on the cervical spine;
- prolonged wearing of high-heeled shoes, which provokes improper distribution of the load on the spine.
In some cases, cervical myelopathy develops after surgical interventions on the cervical spine. In such situations, tissue degeneration is sometimes observed with the formation of areas devoid of functional activity. As a result, they prevent the free flow of oxygen and nutrients to the spinal cord. But in the vast majority of cases, cervical myelopathy is a consequence of natural aging of the body.
Acute type
All three forms of myelopathy differ in the speed of development of symptoms, as well as the degree of pronounced functions that were once lost. The most severe type of spinal cord compression is considered to be the most severe. In this case, there is a loss of motor and sensory functions of the body, and a flaccid type of paralysis may develop. Usually sensitivity disappears in the lower extremities. In addition, the functionality of the bladder or rectum is impaired. This condition is called spinal shock. After a certain time, a flaccid type of paralysis may develop, which passes into the spastic stage with the manifestation of its characteristic reflexes or convulsions. The joints may become stiff and contracture develops.
Kinds
Depending on the causes of development, there are quite a few types of cervical myelopathy. Determining a specific one allows you to develop the most effective treatment tactics and achieve a better outcome.
Vertebrogenic
It is this form of cervical myelopathy, which is also called spondylogenic, that is diagnosed in the vast majority of cases. It develops as a result of disorders in the condition of the spine against the background of congenital characteristics, for example, congenital narrowness of the spinal canal, or diseases acquired during life.
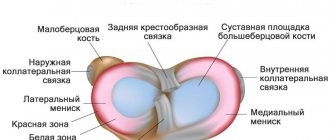
Osteochondrosis is the main cause of the development of vertebrogenic cervical myelopathy. With this disease, degenerative-dystrophic changes gradually occur in the intervertebral discs, which over time leads to the formation of protrusion, and then intervertebral hernia. In such cases, the affected disc bulges and, as a rule, this occurs towards the spinal canal. If left untreated, the hernia tends to gradually increase in size and thereby lead to compression of the anatomical structures passing near it: spinal roots, vertebral arteries, spinal cord. This becomes a consequence of the development of so-called discogenic myelopathy.
Also, a consequence of osteochondrosis can be the proliferation of bone tissue of the vertebral bodies with the formation of bone protrusions on their surface, which are called osteophytes. They can also compress nerve roots, blood vessels and affect the quality of the spinal cord.
Another consequence of degenerative changes in the spine is thickening of the yellow ligaments, hypertrophy of the facets, i.e. complications of osteoarthritis, which can also provoke the development of cervical myelopathy.
Most often, vertebrogenic cervical myelopathy is diagnosed in people over 50 years of age.
Also, cervical myelopathy can be the result of curvature of the spinal column, in particular kyphosis or scoliosis, or ankylosing spondylitis, which gradually affects all joints of the body.
The pathology is characterized by a chronic course with a gradual increase in the severity of symptoms and moments of exacerbation. Most often, patients complain of decreased muscle strength in the neck, shoulders and arms, pain in the neck, sensory disturbances, and tremors in the hands.
Vascular
Vascular or discirculatory myelopathy is caused by the occurrence of circulatory disorders and damage to blood vessels, which may be caused by atherosclerosis, thrombosis, venous stagnation and other changes. Damage to the arteries responsible for supplying the cervical spinal cord provokes atrophy of nerve fibers. Moreover, the severity of the manifestations of the disorder largely depends on what caused their development and the age of the patient.
It is in the cervical spine that the risk of developing vascular myelopathy is highest. Its main manifestation is considered to be the occurrence of the so-called Lhermitte phenomenon, accompanied by trembling in the neck, which can spread to the wrist and feet, while tilting the head or moving it back. After the trembling attack ends, weakness is observed. Sometimes vascular cervical myelopathy causes encephalopathy.
Post-traumatic
This type of cervical myelopathy is a consequence of injury that leads to damage to the spinal cord. These can be fractures, including compression fractures, dislocations, impacts that provoke displacement, compression, injury to nerves, blood vessels or the spinal cord. This may be accompanied by paralysis, decreased sensitivity in areas of the body corresponding to the level of damage, and impaired functioning of internal organs.
Carcinomatous
As the name suggests, this type of cervical myelopathy results from the formation of benign or malignant neoplasms, metastases in the spine, spinal cord or surrounding tissues. When they reach a certain size, they can mechanically compress the spinal cord, lead to disruption of its nutrition and thereby provoke the development of a symptom complex characteristic of cervical myelopathy.
The most common causes of carcinomatous myelopathy are lymphoma, leukemia, spinal hemangiomas and some other tumors.
Infectious
As already mentioned, infectious diseases can also cause the development of cervical myelopathy. It can occur in connection with the transmission of enteroviral infections, tuberculosis, herpes infection, spinal osteomyelitis, Lyme disease and some other diseases.
As a rule, initially patients are concerned about symptoms characteristic of an infectious disease, including fever, weakness, etc. Subsequently, they are replaced by signs of myelopathy, among which shortness of breath is especially common.
With severe viral and fungal infections of the spinal cord, the consequences can be irreversible.
Toxic
This type of disorder occurs when the body is exposed to organic and inorganic neurotoxins that can adversely affect nerve cells. Toxic cervical myelopathy is characterized by rapid development, as well as the appearance of signs of impaired sensitivity and mobility. But damage to the spinal cord in the cervical region is not as common as in the thoracic region.
Radiation
The cause of the development of radiation cervical myelopathy is the effect of ionizing radiation, for example, during radiation therapy for laryngeal cancer or suppression of tumors localized in the mediastinum.
Symptoms of myelopathy may not appear until 6–36 months after the end of radiation therapy. Initially they are weak and tend to disappear periodically, but their intensity constantly increases. Radiation myelopathy is often accompanied by additional formation of ulcers, decreased bone density, etc.
Metabolic
Metabolic disorders can also lead to the development of cervical myelopathy. In particular, it can be a complication of diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies.
Demyelinating
Cervical myelopathy is a common consequence of demyelinating diseases, including multiple sclerosis, Balo's disease, and Canavan disease. In such situations, the sheath surrounding the nerve fibers is destroyed, which makes them vulnerable and sensitive. This is accompanied by disruption of the functioning of the organs corresponding to the affected nerve, for example, disturbances in vision, swallowing, etc.
Hereditary
Some hereditary diseases can cause the development of cervical myelopathy. One of them is Strumel's spastic paraplegia. In such cases, there is increasing weakness in the arms over time, visual impairment, coordination of movements, the development of epilepsy, mental retardation or dementia.
Forecast
Absolute recovery depends on the factors that caused the disease, and not just on its timely detection. For example, post-traumatic and compression myelopathy are completely cured if the causes of their development are eliminated .
Many forms of myelopathy are difficult to predict . If the cause is an incurable disease, then only stabilization of the condition can be achieved. These include metabolic as well as ischemic types of myelopathy.
With an infectious and toxic form, recovery always depends on the severity of the spinal cord injury. A persistent remission may be observed in the initial stage, but if the nervous tissue is already destroyed, then sometimes complete immobility occurs.
If the progression of the disease can be stopped, the prognosis is very optimistic. Lost functions are restored in almost 80% of cases.
Symptoms of cervical myelopathy
The nature of the manifestations of cervical myelopathy largely depends on the causes of its development and the degree of damage to the spinal cord structures. Thus, the patient may have one or a number of symptoms of the following nature:
- pain in the neck, which can radiate to the head, shoulder blades, shoulders and arms;
- movement disorders, which may consist of excessive relaxation or, conversely, muscle spasms, impaired coordination, fine motor skills, the appearance of convulsions, trembling, twitching, involuntary movements, less often paralysis, spastic gait with legs wide apart;
- disturbances of sensitivity in areas of the body corresponding to the level of damage, which may consist of a decrease or absence of sensations when touching, pain or temperature, the development of numbness, a sensation of goosebumps, a burning sensation, as well as a sensation of current passing in the limbs during rapid flexion or extension of the neck;
- disruption of the senses, swallowing, speech, sleep, etc.;
- impaired hand reflexes;
- mental disorders, mood swings, irritability, causeless anxiety, less often a decrease in the acuity of intelligence and memory;
- signs of infectious diseases, including fever, general weakness, chills, headaches, etc.
But such violations are typical for advanced, severe cases. Initially, the disease manifests itself only as minor discomfort, which people usually mistake for typical fatigue after a long day of work.
Classification of myelopathy according to ICD
Rational division of pathology forms based on the International Classification of Diseases 10th revision by etiology:
- Necrotic;
- Idiopathic;
- Edema;
- Thrombophlebotic;
- Neurogenic;
- Non-embolic;
- Embolic.
The choice of treatment is based on the neurological classification of forms:
- Infectious;
- Carcinomatous;
- Post-traumatic;
- Ischemic;
- Spondylogenic;
- Metabolic;
- Toxic;
- Demyelinating;
- Radiation.
With all varieties, loss of sensitivity in the limbs, spasm of the leg muscles, and weakness develop.
Loss of sensitivity forms paresis, paralysis, weakening of vibration and pain activity.
Diagnostics
If signs of cervical myelopathy occur, you should consult a neurologist. In some cases, if several symptoms are present, already during the interview with the patient, the doctor may suspect the development of this disorder, especially if the patient mentions receiving blows to the neck in the recent past, suffering from specific infectious diseases, or having certain chronic diseases. In other situations, it can be extremely difficult to differentiate cervical myelopathy from other pathologies, since its characteristic sensory disturbances, movement disorders, and pain accompany a number of other common spinal diseases.
However, in both cases, patients are prescribed a comprehensive examination to assess the condition of the spine, spinal cord, its roots and blood vessels. These data will make it possible not only to diagnose cervical myelopathy, but also to establish the causes of its development, and therefore to find the most effective way to eliminate them.
At the appointment, the doctor will not only conduct a thorough interview with the patient to collect anamnesis, but will also perform a physical examination, i.e., examination. During it, the strength of reflexes, muscle tone, the severity of motor and sensory disorders, etc. are assessed.
Next, a number of instrumental studies are required:
- X-ray – allows you to assess the position and condition of the vertebrae, the distance between them, the formation of osteophytes, but if possible, CT is preferred;
- CT or computed tomography is an informative method for studying the condition of bone tissue, making it possible to assess the condition of the spine in great detail;
- MRI or magnetic resonance imaging is the most informative diagnostic method to date, providing comprehensive data on the condition of soft tissue structures, including the spinal cord, intervertebral discs, tumors;
- myelography is an auxiliary research method with which it is possible to establish the causes of signs of neurological disorders if other studies have not provided the necessary information;
- electromyography is a diagnostic procedure that allows you to assess the quality of nerve impulses to various parts of the hands;
- angiography is a method used to assess the condition of blood vessels in order to determine the degree of their patency and the quality of blood supply to tissues.
To obtain more complete data on the patient’s health status and the causes of the development of cervical myelopathy, a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test, a cerebrospinal fluid test and some other laboratory tests may be prescribed. When tumors are detected, a biopsy is performed to accurately determine the nature of their origin.
After establishing the cause of the development of cervical myelopathy, the neurologist may recommend that the patient additionally consult an endocrinologist, cardiologist, orthopedist, infectious disease specialist, or phthisiatrician.
Treatment at the Echinacea Clinic
The sooner treatment for myelopathy is started, the better the prognosis. Our clinic provides non-surgical treatment of myelopathy, including the consequences of previous operations.
The specialists of our center will perform the most complete examination and, based on its results, will draw up an individual treatment and rehabilitation program. The treatment program will not require regular visits to the clinic - you will be able to follow most of the recommendations at home with periodic monitoring by your doctor.
If surgical intervention is necessary, we will help you seek the help and experience of a serious specialist in the field of low-traumatic endoscopic neurosurgery of the spine.
When going to our clinic, be sure to take all the medical documents available to you: pictures, disks with tomograms, tests, maps, ultrasound reports, ECG and others, even, at first glance, not related to spinal cord problems.
You can contact Dr. E.A. Engels or the head of the clinic K.A. Shlyapnikov.
Treatment of cervical myelopathy
Since cervical myelopathy is only a consequence of the development of a particular disease, efforts are first directed towards eliminating the very cause of its occurrence. Therefore, the nature of the treatment directly depends on what led to the compression of the spinal structures. It may involve the use of conservative therapy or surgical intervention. Patients are also usually prescribed symptomatic therapy aimed at reducing the severity of manifestations of cervical myelopathy and improving the quality of life until the main treatment gives results.
Thus, conservative therapy is usually indicated for infectious, vascular, toxic and metabolic cervical myelopathy. This may include:
- drug therapy, which consists of prescribing antibiotics, antimicrobial, antiviral agents, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, glucocorticosteroids, muscle relaxants, drugs to improve metabolism, neuroprotectors, statins, heparin preparations, antihypoxants, nootropics, B vitamins, etc.;
- physiotherapy, which includes courses of electrophoresis, UHF, electrical stimulation, magnetic therapy, paraffin therapy;
- manual therapy aimed at normalizing the condition of the spine and releasing compressed vessels and spinal roots, improving tissue trophism and normalizing muscle tone;
- Exercise therapy, which aims to strengthen the muscle corset, increase blood circulation in the neck, and improve the course of metabolic processes.
In case of vertebrogenic, post-traumatic myelopathy, as well as the absence of effect from conservative therapy, patients may be recommended surgical treatment. Good reasons for carrying it out are:
- progression of muscle weakness;
- gait disturbances;
- urinary disorders and the development of urinary incontinence;
- complete loss of hand coordination and fine motor skills.
The goal of surgical treatment is decompression of the spinal cord, i.e., elimination of the factor that compresses it. Therefore, depending on the situation, surgeries can be performed to correct spinal deformities caused by vertebral fractures, as well as discectomy and laminectomy. If necessary, the post-traumatic cyst that has formed and has an effect on the spinal cord is drained, the removed intervertebral disc is replaced with an endoprosthesis, etc.
Discectomy involves the complete or partial removal of an intervertebral disc, which is indicated when it forms as a result of the progression of osteochondrosis or the action of a traumatic factor of a large hernia, which provokes the occurrence of neurological disorders. The operation can be performed using methods with varying degrees of invasiveness, but the choice of a specific one is made by a neurosurgeon based on the individual characteristics of the patient. This:
- Classic discectomy is a fairly traumatic operation that requires a large incision to gain access to the damaged disc. During it, either just the hernia itself or the entire disc is removed, which eliminates pressure on the spinal cord, blood vessels or nerve roots and leads to a solution to the problem of cervical myelopathy.
- Microdiscectomy is a less invasive alternative to classic discectomy as it requires a much smaller incision but has the same capabilities. The operation also allows you to remove the disc or just the hernia, achieving decompression of the nerve structures and blood vessels. It involves the use of special microsurgical instruments, the sizes of which are much smaller than traditional ones.
- Endoscopic surgery is the least invasive type of decompression surgery, since it requires pinpoint incisions with a diameter of less than 1 cm. It has the same capabilities, but due to the peculiarities of the technique, it cannot always be used.
If it is necessary to remove the intervertebral disc completely, during the operation it is replaced with an artificial implant, of which there are many types today. Less commonly, a bone graft taken from the patient's own bone is used. The operated and adjacent segments of the spine can also be fixed with special metal structures, eliminating the risk of vertebral displacement and re-development of cervical myelopathy, possibly with more serious consequences. In such situations, screws with holes in the heads are mounted at the points of connection of the processes of adjacent vertebrae. Special rods are passed through them to securely fix the spine. This technique is called transpedicular fixation.
In case of comminuted fractures and a number of other situations when it is necessary to gain open access to the spinal structures, laminectomy is used to eliminate compression. The essence of the operation is to remove the spinous process, possibly the arch, and in some cases the entire vertebra. This allows you to create a fairly large space for the spinal cord, eliminate compression of blood vessels and spinal roots, be able to remove a tumor, etc. As a result, the symptoms of cervical myelopathy disappear, and the patient’s quality of life improves. If necessary, the vertebrae are also fixed using transpedicular fixation or other methods.
If it is necessary to perform surgical intervention on the cervical spine, the size of the incision is of great importance, since access to the affected area is not always through the back of the neck. Often the surgeon needs to “go in” from the front using an anterolateral approach.
Thus, anyone can experience cervical myelopathy, and no effective preventive measures have been developed to reduce the risk of its development. Therefore, to avoid its occurrence, it can be recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, and if a disorder has already formed, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. In 60% of cases, with timely treatment, including surgery, it is possible to achieve complete or significant regression of neurological disorders. In 20% of patients in this case, the condition does not change, but does not worsen, and progression of myelopathy is observed in 10% of patients who have undergone treatment. But in the absence of this, the disease will certainly progress and can cause paralysis, disability and more severe complications.
What are the reasons for the development
The disease can occur in any area of the spinal cord, but thoracic myelopathy is most common. The classification of forms of the disease is based on the causes that provoke it:
- Atherosclerotic - formed due to the occurrence of blood clots and the accumulation of cholesterol plaques in the vascular system. In some cases, the cause may be hypertension, which causes disruption of the functionality of the vascular system of the spinal column. Characteristic symptoms of this form of myelopathy are decreased sensitivity of the limbs, speech impairment, paresis and even paralysis.
- Vascular - localized in the upper parts of the thoracic spine. The patient may experience weakening of muscle tissue and numbness in the fingers. Vascular myelopathy is usually caused by a herniated disc. The symptoms of myelopathy can be confused with signs of a tumor, so for accurate diagnosis it is necessary to use professional equipment.
- Degenerative - occurs due to impaired blood circulation in the spinal cord. The main factor in the formation is the deficiency of minerals and vitamins. A complication of this form of the disease can be compression myelopathy of the musculoskeletal system.
- Spondylogenic - the cause is usually trauma, due to which the patient has to be in an unnatural position for a long time. This form of pathology is characterized by a chronic course, while patients can experience muscle spasms, as well as impaired functioning of the chest organs. In the case of post-traumatic damage to the brain of the back, decreased sensitivity and paralysis of the limbs are possible.
The consequences of myelopathy of the thoracic spine can be very serious and even deprive a person of his ability to work. Therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
How is myelopathy treated?
The attending physician prescribes therapy based on the causes and intensity of the disease. It can be conservative or surgical. If the patient complains of severe pain, he is prescribed painkillers, anti-inflammatory, decongestant drugs (Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Ortofen). If there is compression of the nerve endings, causing unbearable pain, injections of steroid hormones are prescribed.
When tests reveal an infection in the body, it is recommended to take antibacterial drugs, which are selected depending on the pathogen. To improve metabolic processes and prevent tissue hypoxia, Piracetam, Actovegin, and Cerebrolysin are prescribed. To relieve muscle spasms and neck pain, Baksolan, Tolperisone, Mydocalm, Sirdalud are suitable.
During the treatment process, it is important to monitor a varied diet so that the body receives the necessary substances and the immune system works without interruption. This is especially true for vitamins B6 and B1.
It is recommended to take vitamin and mineral complexes, which can be purchased at any pharmacy.
To relieve stress on the muscles of the cervical spine, the doctor may prescribe a cervical collar. The device strengthens the structure of muscle tissue, gives it rest, and reduces compression of the nerves. You cannot use the collar for too long, otherwise the muscles will weaken and the effect will be the opposite.
In severe cases, cervical spine myelopathy is treated with surgery. The operation is performed if long-term drug treatment has not brought positive results, when severe pain is observed against the background of a progressive disease. Surgical removal of intervertebral hernia and tumors. Poor prognosis for myelopathy secondary to arthritis. This pathology cannot be completely cured, so the doctor gives recommendations to prevent the progression of the disease and prescribes medications to help reduce pain.
Cervical myelopathy can result in quite serious negative consequences in the form of paralysis, impaired motor function, phantom pain, impaired reflexes, and decreased sensitivity. The milder the injury, the faster medical care is provided, the greater the chances of a speedy recovery.
source
Basic treatment methods
It is possible to cope with cervical myelopathy only by carrying out competent treatment of the underlying disease that caused its development. Directly to eliminate muscle weakness and circulatory disorders of the spinal cord, drugs of various clinical and pharmacological groups are used. To enhance their effect, physiotherapy, manual therapy, and acupuncture are performed.
Pharmacological drugs
Treatment of cervical myelopathy is aimed at the maximum possible restoration of damaged discs, vertebrae, blood vessels, and spinal roots. For this, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with anti-edematous and analgesic effects. To relieve acute pain, injection solutions are used: Ketorolac, Ortofen, Xefocam; for moderate pain, Nimesulide, Diclofenac, Ketoprofen tablets; for mild pain, Finalgel, Voltaren, Artrosilene gels;
- muscle relaxants to relax spasmodic skeletal muscles. Therapy with Mydocalm, Sirdalud Baklosan, Tolperisone has proven itself especially well;
- antihypoxants to increase the brain's resistance to oxygen deficiency - Solcoseryl, Cerebrolysin, Piracetam.
We advise you to study - Lumbago (lumbago in the lower back)
Diclofenac-based drugs are in demand in the treatment of cervical myelopathy
Injections of Eufillin, Xanthinol nicotinate, Pentoxifylline, and Nicotinic acid help improve blood circulation in the cervical spine. Then the result is secured by taking tablets of the same name. To improve the functioning of the central nervous system and prevent the death of spinal cord and brain cells, Cavinton, Nootropil, and Piracetam are included in treatment regimens.
Be sure to use drugs with B vitamins in treatment - Milgamma, Combilipen, Neurobion. They have a positive effect on the transmission of nerve impulses and trigger regeneration processes in the discs and vertebrae. Combilipen for injection contains lidocaine, an anesthetic that quickly relieves pain.
If myelopathy has developed against the background of osteochondrosis, then the patient is prescribed long-term (up to 2 years) treatment with chondroprotectors - Teraflex, Arthra, Structum. The drugs prevent further destruction of the discs and narrowing of the spinal canal.
Non-drug treatment
Patients with myelopathy are recommended to attend physiotherapeutic procedures - magnetic therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, galvanotherapy, as well as applications with paraffin and (or) ozokerite. Their action is aimed at increasing the temperature in the area of damaged areas of the spinal cord in order to improve blood supply to the tissues. Neurologists prescribe up to 15 sessions of electrophoresis with B vitamins, calcium solutions, and antispasmodics to speed up reparative processes.
The best method of non-drug therapy is considered to be dry or underwater traction of the spine. Under the influence of physical forces, the distance between the vertebral bodies increases, promoting better blood circulation. With small intervertebral hernias, it is possible to return the disc to its anatomical position.
In the complex treatment of cervical myelopathy, acupuncture, classical, acupressure, and vacuum massage are also used. To strengthen weakened muscles, patients are advised to exercise regularly. Yoga and swimming are also helpful.
How is cervical myelopathy treated?
After carrying out all diagnostic measures, the doctor prescribes the most effective therapy, based on the intensity and cause of the disease. Treatment of myelopathy of the cervical spine can be carried out using both conservative and surgical methods.
The patient’s age and the presence or absence of concomitant diseases are also taken into account. If the disease is detected in a timely manner during the treatment process, it is possible to do without surgical intervention, while the patient is prescribed complete rest for the cervical spine, which can be ensured with the help of a cervical collar.
Surgery for cervical myelopathy
If complex myelopathy is diagnosed and conservative treatment methods do not provide the desired result, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment. Surgical procedures can be performed only if the patient does not have any contraindications and the risk of brain damage. The main purpose of the operation is to eliminate the risk of paralysis of the limbs, which can lead to disability of the patient.
We advise you to study - Protrusion of lumbar intervertebral discs
In case of partial destruction of the spinal column, the patient needs to have implants installed. After the operation, the patient is prescribed medication and a rehabilitation course designed to restore the functionality of the injured area.
What medications are indicated for cervical myelopathy
Drug therapy for cervical spine myelopathy depends on the cause of the disease. Patients are almost always prescribed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs designed to eliminate characteristic symptoms, reduce swelling and inflammatory processes. Patients can also be prescribed medications that improve metabolic processes.
For infectious cervical myelopathy, treatment may include taking antibiotics to eliminate the underlying disease causing the pathology. The patient is also required to be prescribed medications to strengthen the overall immune system, vitamins and minerals necessary for the body.