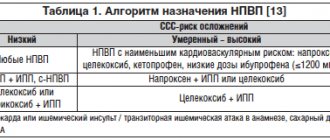
The appearance of topical corticosteroids (GCS) in the early 50s of the last century is considered one of the most significant events in dermatology. And today, drugs of this group occupy a leading position among all external dermatological drugs [1]. A wide range of indications, high activity, pleiotropic effects and a convincing evidence base, along with a favorable safety profile, are a solid foundation for the rapid movement towards the heights of popularity of these drugs among doctors and consumers. As a result, first-line physicians need to keep in mind and be able to use knowledge about the drugs of this group in pharmaceutical consulting. Especially considering that some topical drugs containing corticosteroids are available without a prescription. How local glucocorticosteroids work, when they can be recommended, and what to warn clients about is in our new article.
Contraindications and adverse reactions
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the most powerful in pharmacology, so they cannot be taken arbitrarily. Treatment is prescribed by a specialist. The main contraindications include:
- Infectious tissue damage.
- Diseases caused by bacteria.
- Risk of bleeding.
- Taking blood thinners.
- Significant erosive lesions of joints and tissues.
- Weakened immunity.
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Individual intolerance.
- In cases where three injections of SPVP are performed per month.
If the patient has various lesions and infectious diseases, steroids cannot be used. The active substances included in the products help reduce the body's defenses and suppress the immune system. In turn, this does not allow the body to overcome pathogens, which increases the spread of infection.
If a patient is taking blood thinners and is at risk of bleeding, steroid medications may cause severe bleeding at injection sites. Such drugs should not be used more than three times a month, as there is a possibility of infection as a result of weakening of the tissues.
Steroids belong to the group of hormonal drugs, so they cannot be used for a long time. This is due to the fact that there is a risk of developing various adverse reactions. The main ones include:
- Hypertension.
- Exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease.
- Swelling.
- Osteoporosis.
- Decreased protective functions of the immune system.
- Increased blood clotting.
- Masculinization in women.
- Increased amount of subcutaneous fat.
In order to avoid such undesirable consequences, taking anti-inflammatory steroid drugs should last no more than two weeks. It is also advisable to take them with meals.
Preventing Negative Reactions
It is not recommended to take anti-inflammatory steroid drugs during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is necessary to take into account the list of contraindications in which their use is completely excluded. There are certain recommendations that can reduce the risk of negative consequences. It includes:
- Body weight control.
- Regular blood pressure measurement.
- Study of sugar levels in blood and urine.
- Monitoring the electrolyte composition of blood plasma.
- Diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract and musculoskeletal system.
- Consultations with an ophthalmologist.
- Testing for infectious complications.
These measures make it possible to avoid various negative consequences, since they are aimed at studying exactly those indicators that may indicate the presence of changes in the body.
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are very strong substances that should only be used for specific purposes. They cannot be used at your own discretion. The prescription should only be made by a doctor, based on the patient’s condition and the type of disease.
Mechanism of action of SPVP
The principle of action of SPVP is based on intracellular effects. During the use of such funds, the following processes occur:
- When entering the body, substances begin to interact with receptors in the cytoplasm of cells, penetrating into the nucleus. Due to their action on DNA, they influence some of the genes, which allows you to change the balance of purines, water, proteins and fats.
- The mechanism of action includes the process of activating gluconeogenesis, which increases the amount of glucose in the blood and increases the concentration of glycogen in liver cells. This, in turn, helps to impede protein biosynthesis and increase the breakdown of structures located near muscle fibers, connective tissue and skin.
If there is an inflammatory process in the body, it includes protection from various pathogenic microflora. If the immune system is weakened, this protection is not enough, which often leads to the destruction of joints, tissues, and the development of other pathologies. The affected areas turn red and begin to feel painful.
SPVPs relieve pain and eliminate the inflammatory process. According to their chemical structure, they are classified as 17, 11-hydroxycorticosteroids. The first substance of the group to be obtained is a glucocorticoid from the adrenal glands. Now there is a large selection of these substances of both synthetic and natural origin.
Glucocorticoids help inhibit the process of protein synthesis, while enhancing catabolic reactions in muscle fibers, connective tissue and skin, providing an anti-anabolic effect. If you use such drugs for a long time, muscle weakness, slower regeneration processes, developmental delays, an increase in the amount of fat in the body and other adverse reactions may develop. In this regard, you should consult your doctor before taking such substances.
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Glucocorticosteroids (hormones of the adrenal cortex) began to be used for the treatment of joints more than 50 years ago, when their positive effect on the severity of joint syndrome and the duration of morning stiffness became known.
The most popular drugs from the group of steroids in rheumatology are:
- Prednisolone (Medopred);
- Triamcinolone (Kenacort, Kenalog, Polcortolone, Triamsinolol);
- Dexamethasone;
- Methylprednisolone (Metypred);
- Betamethasone (Celeston, Diprospan, Flosteron).
It is worth noting that non-steroidal hormones are not used in the treatment of joint diseases.
Mechanism of action
The pronounced anti-inflammatory effect of drugs with a steroid structure is achieved in several ways:
- an obstacle to the movement of neutrophils (the main inflammatory cells) from the vessels into the tissue, to the affected area;
- decreased permeability of biological membranes, which inhibits the release of proteolytic enzymes;
- suppression of cytokine formation;
- influence on epithelial cells;
- stimulation of lipocortin formation.
This mechanism of action, which slows down all phases of the inflammatory response, leads to rapid relief of symptoms and improvement in the condition of patients.
Indications
All anti-inflammatory steroid drugs have a strict list of indications for use. This is due to the fact that hormones have a large number of side effects. Therefore, they are a reserve group in the treatment of joint diseases.
Steroid drugs are prescribed for conditions such as:
- High disease activity.
- Systemic manifestations of pathology.
- Weak effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- The presence of contraindications to the prescription of NSAIDs that prevent their use.
Side effects
Like any other drugs, steroid hormones have a number of undesirable effects. These include:
- dyspepsia (feeling of nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating, hiccups, loss of appetite, perversion of taste);
- increased pH of gastric contents;
- development of myocardial failure, if present - worsening of the condition;
- increased blood pressure numbers;
- liver enlargement;
- blood clot formation;
- obesity;
- increased excretion of potassium and calcium, retention of sodium ions;
- osteoporosis;
- muscle weakness;
- skin rashes;
- increased sweating;
- weakness;
- depressive states;
- allergic local and systemic reactions;
- weakened immunity, decreased body resistance to infections, exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- increased blood sugar levels;
- impaired wound healing;
- menstrual irregularities, etc.
Almost all steroids have these side effects to a greater or lesser extent. Their quantity and strength depend on the method of administration of the drug, dosage and duration of use.
Contraindications
Anti-inflammatory steroid drugs should be prescribed with caution in the following conditions:
- ulcers and inflammation in any part of the gastrointestinal tract;
- previous episodes of thromboembolism, the presence of blood clots;
- heart failure, heart attack;
- high blood pressure;
- fungal infection of a systemic nature;
- bacterial infections or parasitic infestations;
- herpetic infection;
- tuberculosis;
- HIV AIDS;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- severe renal and liver failure;
- obesity;
- osteoporosis;
- passing of kidney stones;
- glaucoma, cataract.
The listed contraindications do not mean that steroid drugs cannot be used. However, concomitant pathologies should always be taken into account when prescribing medications.
LEARN MORE: Results of clinical studies of the use of hyaluronic acid for arthrosis of the knee The use of folic acid in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis Painkillers for joint pain Comparison of NSAIDs for arthrosis: which painkiller to choose Everything you need to know about chondroprotectors in the treatment of joints
The effect of using SPVP
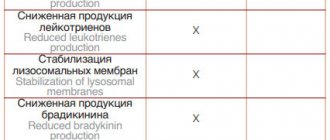
The anti-inflammatory effect provided by steroid drugs is ensured by their ability to be inhibited through lipocortin. They also inhibit the gene that encodes the production of COX-2, which is actively involved in areas of inflammation. Glucocorticoids also suppress prostaglandin activity. They provide an antioxidant effect, slowing down lipid oxidation and maintaining the integrity of cell membranes. Thus, the spread of the inflammatory process is prevented.
The main actions of SPVP include:
- Anti-inflammatory. Glucocorticoids are inhibitors of all inflammation in the body. They help stabilize cell membranes, ensure the release of proteolytic enzymes from cells, prevent destructive changes in tissue, and also slow down the formation of free radicals. When the substance enters the body, the number of mast cells in areas of inflammation decreases, small vessels narrow, and capillary permeability decreases.
- Immunosuppressive. SPVPs reduce the level of circulating lymphocytes and microphages. They disrupt the production and action of interleukins and other cytokines that regulate various immune responses. There is a decrease in the activity of B and T lymphocytes, a decrease in the production of immunoglobulins and the amount of complement in the blood. Fixed immune complexes are formed, and the formation of factors that inhibit the movement of microphages is inhibited.
- Antiallergic. This effect is achieved by suppressing different stages of immunogenesis. Glucocorticoids slow down the process of formation of circulating basophils, and also reduce their number and prevent the development of the synthesis of sensitized cells, basophils, which contribute to the development of an allergic reaction and reduce the sensitivity of effector cells to them. The production of connective and lymphatic tissues is suppressed, as well as the formation of antibodies.
- Antitoxic and antishock. SPVPs are involved in ensuring vascular tone, water and salt balance. They improve the activity of liver enzymes, which are involved in the process of converting exogenous and endogenous substances. There is an increase in the sensitivity of blood vessels to catecholamines and their permeability decreases. The amount of blood plasma increases as the substances retain sodium and water in the body. This allows you to reduce hypovolemia, improve vascular tone and the process of myocardial contraction.
- Antiproliferative. This effect is associated with a decrease in the migration of monocytes in areas of inflammation and a slowdown in the process of fragmentation of fibroblasts. The synthesis of mucopolysaccharides is suppressed, which helps slow down the binding of plasma protein and water to tissues that have entered the site of inflammation.
Each of the drugs, depending on its type, can provide a certain effect. The selection of funds should only be carried out by a specialist.
General characteristics of the funds
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/nPLhG5iz808
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (SAAIDs) are derivatives of glucocorticoid hormones produced by the adrenal glands. They are divided into the following types:
- Natural.
- Synthetic: non-halogenated and halogenated.
The first group includes drugs such as Hydrocortisone and Cortisone. Non-halogenated steroids are presented in the form of Methylprednisolone and Prednisolone. Fluoridated - Triamcinolone, Dexamethasone and Betamethasone.
The effect of taking such substances is ensured by influencing the body at the cellular level. By binding to DNA, drugs can have a strong effect on various processes. The main ones include:
- Water-salt exchange.
- Protein.
- Carbohydrate.
- Zhirovoy and others.
Among the most pronounced actions of glucocorticoids are the following: antipruritic, antiallergic, and naturally anti-inflammatory. They produce products for both external and internal use. Very often, various gels, ointments and creams are used to treat skin diseases, and injections are used for joint diseases.
Most popular SPVP
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs cope well with the inflammation process and relieve pain. The means that are most often used in medical practice include:
- Dexamethasone. It is used for inflammations that require immediate administration of such substances and for various states of shock. The product is sold as an injection solution.
- Cortisol. Can be used both orally and intramuscularly, if necessary, to relieve pain and acute rheumatoid arthritis. Presented in the form of a suspension.
- Sinalar. Used for skin diseases. Most often, with psoriasis and dermatitis, as well as other skin lesions accompanied by itching. It can be produced both in the form of a gel and an ointment.
- Bematethasone. Sold in the form of a gel, which is applied to the skin for allergies and inflammation with itching.
New anabolic agents are also now being introduced. They have pronounced effects and are used to treat various diseases. The most popular of them include:
- Celeston. Used for dermatitis, allergic conjunctivitis and inflammation of internal organs. Produced in injection and tablet form.
- Mendrol. Prescribed for severe situations of stress, multiple sclerosis and slow development in children. Sold in tablet form.
- Urbazon. Used in states of shock. Available in injection form.
- Momat. Relieves inflammation and also eliminates itching. Used for various skin diseases. Sold as a cream or ointment.
- Berlicourt. Prescribed for asthma, acute rhinitis and allergies. Available in tablet form.
Each of the drugs is prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient, the nature of the course of the disease and its type. The dosage and course of treatment are also determined only by a specialist.
General classification of NSAIDs
The scope of use of NSAIDs is quite extensive. These medications are used to treat acute and chronic forms of diseases that are accompanied by inflammation, and therefore pain.
This group of drugs includes a long list of different types of drugs. However, they are united by a similar principle of action: the enzyme cyclooxygenase is suppressed, which contributes to the development of the inflammatory process in the body.
As a result, the intensity of the pathological condition increases, which provokes the appearance of characteristic symptoms: fever, pain, swelling, redness.
The body produces 2 types of cyclooxygenase enzymes: COX-1, COX-2. The first of them is involved in the functioning of the body in a healthy state, which means there is no need to influence it. The second (COX-2) is produced in cases where the inflammatory process begins to develop.
- selective COX-1;
- non-selective COX;
- predominantly selective COX-2;
- highly selective COX-2.
Due to the inactivation of inflammatory mediators, a decrease in pain, swelling, and sclerotic process in the inflammation site is observed.
All NSAIDs according to the mechanism of action are divided into two large subgroups:
- non-selective anti-inflammatory drugs are distinguished by their inhibitory effect on cyclooxygenase of the first and second types (COX-I and COX-II);
- selective drugs - selectively inhibit cyclooxygenase of the second type (COX-II).
Based on their chemical composition they are divided into:
- formation of acetic acid - ketorolac, indomethacin, diclofenac;
- formation of propionic acid - ketoprofen, ibuprofen, fenoprofen;
- formation of oxicams - meloxicam, piroxicam, tenoxicam;
- formation of coxibs - rofecoxib, etoricoxib, parecoxib;
- formation of butylpyrazolidone - clofezone, phenylbutazone;
- formation of other chemical groups - nabumetone, glucosamine, nimesulide.
By composition:
- Increasing the acidity of gastric juice (pyrazolidines, salicylates, oxicams, derivatives of propionic, phenylacetic, indoleacetic acids).
- Non-acidic: sulfonamide derivatives, alkanones.
By effect on enzymes that promote the production of prostaglandins:
- Non-selective NSAIDs. They inhibit the work of the enzymes COX-1 and COX-2. However, the first substance is not harmful. On the contrary, the enzyme has a good effect on platelets and restores the gastric mucosa.
- New generation NSAIDs. Such remedies are well suited for the treatment of respiratory pathologies or for joints, as they cause less harm to the body. Medicines negatively affect only COX-2, which is produced in the presence of an inflammatory process, enhancing it.
According to the selectivity of their effects, all NSAIDs are divided into:
- Non-selective, inhibiting all types of COX, but mainly COX-1.
- Non-selective, affecting both COX-1 and COX-2.
- Selective COX-2 inhibitors.
The first group includes:
- Acetylsalicylic acid;
- Piroxicam;
- Indomethacin;
- Naproxen;
- Diclofenac;
- Ketoprofen.
A representative of the second category is Lornoxicam.
The third group includes:
- Nimesulide;
- Rofecoxib;
- Meloxicam;
- Celecoxib;
- Etodolac.
Important: Acetylsalicylic acid and Ibuprofen mainly reduce body temperature, and Ketorolac (Ketorol) reduces the intensity of pain. They are ineffective in reducing joint inflammation and can only be used for symptomatic therapy.
Corticosteroids during pregnancy and lactation
Although there are many side effects, taking corticosteroids, especially prednisone, is relatively safe during pregnancy. However, your doctor will decide to prescribe these medications based on your condition.
If you are taking corticosteroids and are planning to become pregnant, be sure to discuss this with your doctor! If you become pregnant while taking these medications, do not suddenly stop taking them - it may not be safe!
Corticosteroids can pass into breast milk, so breastfed babies may experience side effects from these medications. Discuss alternative treatments with your doctor or switch your baby to formula feeding.
Withdrawal symptoms
Reducing your dose of corticosteroids or stopping them can be difficult. If you have been taking these medications for a long time, sudden withdrawal can be dangerous. Your body should produce corticosteroids in response to stress, but if the drugs are abruptly discontinued, the adrenal glands will not be able to quickly readjust and increase the synthesis of their own hormone. That is why doctors gradually reduce the dose, eventually stopping the medicine completely.
If you have been taking steroids for weeks or months, you may experience unpleasant withdrawal symptoms as you taper your dose. These may include muscle, bone and joint pain, nausea, weight loss, headache, and even fever. Fortunately, these symptoms are usually mild and go away quickly.
Konstantin Mokanov
The use of glucocorticoids, even short-term, can “program” for decades to come the work of many organs and systems in the unborn child (control of blood
, metabolic processes, behavior formation). Synthetic hormone mimics signal
for the fetus on the mother's side and thereby forces the fetus to force the use of reserves.
This negative effect of glucocorticoids is enhanced by the fact that modern long-acting drugs (Metypred, Dexamethasone) are not deactivated by placental enzymes and have a long-lasting effect on the fetus.
Glucocorticoids, by suppressing the immune system, help reduce a pregnant woman's resistance to bacterial and viral infections, which can also negatively affect the fetus.
Glucocorticoid drugs can be prescribed to a pregnant woman only if the result of their use significantly outweighs the risk of possible negative consequences for the fetus.
Previously, there was a practice of prescribing glucocorticoids to maintain pregnancy. But no convincing data on the effectiveness of this technique have been obtained, so it is not currently used.
In obstetric practice, Metypred, Prednisolone and Dexamethasone are most often used. They penetrate the placenta in different ways: Prednisolone is destroyed by enzymes in the placenta to a greater extent, and Dexamethasone and Metipred - by only 50%.
Therefore, if hormonal drugs are used to treat a pregnant woman, it is preferable to prescribe Prednisolone, and if to treat the fetus, it is preferable to prescribe Dexamethasone or Metypred. In this regard, Prednisolone causes adverse reactions in the fetus less often.
Glucocorticoids penetrate into breast milk in small doses poorly and do not pose a danger to the baby.
Drugs in higher doses and a long course of treatment of a nursing mother with hormones can cause growth retardation in the child and suppression of the function of the endocrine glands (pituitary gland, hypothalamus, adrenal glands).
FAQ
What is the difference between hormonal and steroid drugs?
Steroid medications are a type of hormonal medication. In addition to the adrenal hormone, there are drugs that can replace pituitary hormones, sex hormones, anabolic hormones, pancreatic hormones, thyroid and parathyroid hormones.
How is treatment carried out with both steroid and non-steroidal drugs?
Many diseases are recommended to be treated with steroidal and nonsteroidal (NSAIDs or NSAIDs) drugs simultaneously. Anabolic steroid drugs help reduce inflammation and tissue swelling, and non-steroidal drugs act on the cause of inflammation. When taking steroid drugs, be sure to take into account that they can provoke an allergic reaction to the medications and vitamins that you take at the same time. Only a highly qualified attending physician can draw up the correct dosage plan and combination of steroid hormones.
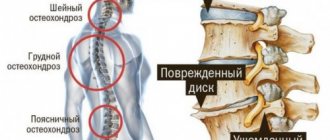
What is the best way to use such drugs for osteochondrosis?
Steroid drugs relieve pain well and relieve tissue swelling in osteochondrosis of the joints. Ambene is a fairly popular drug. This is a medicine that consists of two solutions for infections. This drug relieves swelling of tissues, relieves pain, reduces fever and has a calming effect on the nervous system.
What are new generation steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs?
Recently, a new generation of anabolic steroid anti-inflammatory drugs have begun to be produced, which have fewer side effects. The use of such drugs is more preferable, but their anti-inflammatory effect is lower than that of traditional drugs.
How are anti-inflammatory drugs with a steroid structure produced?
Anabolic steroid drugs are obtained through a series of chemical and biological transformations and deep purification of the resulting raw materials. Special immobilized microbial cells participate in these transformations.
Steroid and non-steroidal drugs. What is the difference?
The difference between steroidal and non-steroidal drugs lies in their effect on the body. The effect of steroid drugs is that they suppress the human immune system. Non-steroidal non-narcotic painkillers have an analgesic effect on the body. They slow down the enzyme reaction in the membranes of nerve cells. Both medications have significant negative effects on the body, so they should not be used regularly.
The modern pharmaceutical market offers the use of steroid drugs that help avoid a large number of problems associated with allergic reactions of the body or exacerbation of inflammatory processes.
Such drugs have a fairly large number of side effects, so they should be used with great caution.
Indications
Anti-inflammatory steroid drugs relieve inflammation by suppressing immune function. They ensure a reduction in the production of leukocytes and anti-inflammatory enzymes, which makes it possible to achieve relief of inflammation. These drugs are most often prescribed for the following disorders or diseases:
- State of shock.
- Skin diseases.
- Systemic connective tissue diseases.
- Various types of hepatitis.
- Allergies.
- Pathologies of joints and muscles.
- Disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels.
- Inflammatory processes in internal organs and tissues.
Glucocorticoids are often used for rheumatism and rheumatic carditis, osteochondrosis, diseases of the hematopoietic organs, dermatomyositis, lupus erythematosus and other diseases. Anti-inflammatory steroid medications can treat a wide variety of conditions. In order for the effect of the products to be as effective as possible, they are most often administered locally.
Non-steroidal drugsNSAIDs, NSAIDs
Medicines from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are first-line drugs for the treatment of joint diseases. They are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, reactive systemic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, osteoarthritis of any localization, osteochondropathy, osteochondrosis, and other systemic pathologies.
The history of the creation of non-steroidal drugs goes back to ancient times. Our ancestors also knew that when the temperature rises, it is necessary to make a decoction from willow tree branches. It was later discovered that willow bark contains the substance salicyl, from which sodium salicylate was later created. It was only in the 19th century that salicylic acid, or aspirin, was synthesized from it. It was this medicine that became the first non-steroidal remedy for inflammation.
Pathogenetic mechanism, effects
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins (the main mediators of inflammation) from arachidonic acid. This is possible by blocking the action of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX).
It was found that non-steroidal drugs act on 2 types of enzyme: COX-1 and COX-2. The first affects platelet activity, the integrity of the gastrointestinal tract, prostaglandins, and renal blood flow. COX-2 primarily acts on the inflammatory process.
Nonsteroidal drugs that inhibit COX-1 have a large number of undesirable properties, so the use of selective NSAIDs is more preferable.
For therapeutic purposes, the following properties of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used in traditional medicine:
- Analgesic: the drugs effectively relieve pain of mild to moderate intensity, which is localized in ligaments, articular surfaces, and skeletal muscle fibers.
- Antipyretic: acute stages of inflammatory joint diseases are often accompanied by an increase in overall body temperature. NSAIDs do a good job of reducing it without affecting normal temperature readings.
- Anti-inflammatory: The difference between NSAIDs and steroids is the strength of the effect. The latter have a different mechanism of action and a more powerful effect on the pathological focus. For the treatment of joint manifestations, Phenylbutazone, Diclofenac, and Indomethacin are most often used.
- Antiplatelet: more typical for aspirin. It is used not only to treat joint diseases, but also for concomitant pathology in the form of coronary heart disease.
- Immunosuppressive: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs slightly suppress the immune system. This occurs due to a decrease in capillary permeability and a decrease in the possibility of interaction of antigens with antibodies of foreign proteins.
Indications
Unlike steroid drugs, NSAIDs for the treatment of joints are prescribed in the following cases:
- the need for long-term medication;
- elderly and senile patients (over 65 years);
- severe somatic pathologies;
- the occurrence of side effects from taking hormonal medications;
- peptic ulcer (only for COX-2 inhibitors).
Treatment of almost all joint diseases is associated with the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Therapeutic courses differ in duration, dosage, and method of drug administration.
It is important to remember that NSAIDs do not affect the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases. The drugs significantly alleviate the condition of patients, relieving pain and stiffness
But they are not able to stop the pathological process, prevent joint deformation or cause remission.
Side effects
The main negative symptoms observed when using non-steroidal medications are gastrointestinal disorders. They manifest themselves in the form of dyspeptic disorders, the development of erosive-ulcerative disorders and perforation of the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum. Side effects are most common for COX-1 inhibitors (Aspirin, Ketoprofen, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac).
Other undesirable effects include the following:
- renal blood flow depletion and renal failure;
- analgesic nephropathy;
- development of anemia;
- bleeding from damaged surfaces of the skin and mucous membranes;
- hepatitis;
- allergic reactions;
- spasm of the bronchial muscles;
- weakening of labor and prolongation of pregnancy.
These side effects of nonsteroidal drugs should be taken into account when choosing a treatment regimen for patients with joint diseases.
special instructions
The dosage regimen depends on the nature of the pathology, the patient's response to the steroid drug used, age and weight. But even with effective therapy without serious manifestations, the withdrawal syndrome characteristic of hormonal drugs should be taken into account. It consists of an exacerbation of the degenerative or inflammatory process after abrupt cessation of treatment. The following pathological conditions may also occur:
- increased body temperature;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- weakness, fatigue, drowsiness.
Sometimes (usually under stress) an Addisonian crisis occurs - vomiting, collapse, convulsions. To prevent the development of withdrawal syndrome, at the last stage of treatment, dosages are gradually reduced, as is the frequency of their administration. The main principle of treating joint diseases with glucocorticosteroids is to ensure maximum therapeutic effects using minimal doses. It is unacceptable to use any hormonal drugs without a doctor's prescription.
Anti-inflammatory ointments for joint pain based on diclofenac
Note! Effective ointments for joints based on diclofenac are both preparations containing one component and combined ones. Anti-inflammatory ointments for joints and ligaments with diclofenac, containing one component, are:
Anti-inflammatory ointments for joints and ligaments with diclofenac, containing one component, are:
- Diclofenac;
- Diclofenac-Acri;
- Diclofenacol;
- Diclak gel;
- Diclovit;
- Dicloran;
- Dicloran plus;
- Diclonate P gel;
- Diclobene;
- Ortofen ointment;
- Voltaren Emulgel;
- Naklofen;
- Olfen;
- Fanigan;
- Dikloberl 75.
Effective ointments for joint pain that have a combined composition are:
When using the listed drugs:
- pain subsides at the site of application of the ointment;
- swelling decreases;
- the number and amplitude of movements of the affected joints increase.
They are used to relieve pain from:
- inflammation of muscles, ligaments, cartilage;
- degenerative joint diseases;
- rheumatic muscle lesions;
- post-traumatic pain;
- neuralgic phenomena in the muscles.
- urticaria - the appearance of rashes, blisters;
- bronchospasm - a sudden contraction of the muscles of the bronchial wall, limiting the supply of oxygen;
- angioedema or Quincke's edema - an increase in the size of the face, its parts, and limbs.
- Hypersensitivity to diclofenac.
- Skin damage.
- State of pregnancy.
- Lactation.
- Under six years of age.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/_T2LQTOZ5Ko
Withdrawal syndrome
The hormone cortisol is involved in the body's energy metabolism. It helps break down proteins. When the level of this hormone in the body increases, and then when it sharply decreases, problems with metabolism arise. Muscles may become more flabby and the percentage of body fat may increase.
Therefore, drugs containing cortisol should be used only in courses.
Early menopause Nope, never heard of it
Soothing herbs for the prevention of early menopause
The female body reacts sensitively to constant stress, under the influence of which the production of prolactin, the hormone responsible for lactation and suppresses ovulation, increases. If the situation is not corrected, this may lead to fading of ovarian function, and this should not happen ahead of time. Calming herbal infusions will help you cope with nervous tension and improve your health. Valerian, lemon balm, and motherwort have an excellent effect on the nervous system and make a woman more resilient. Such medicinal herbs can also be added to tea.
Clover drink
Often the first symptoms of menopause are fatigue, irregular periods, pain in the lower abdomen, and lack of sexual desire. They warn about reduced levels of estrogen - sex hormones. Clover will help normalize their level. A tea is prepared from a spoon of its leaves and a glass of boiling water, which is drunk three times a day.
Milk thistle seed meal
If a woman often takes medications, her body is filled with toxins that negatively affect the liver and ovaries, suppressing the functions of the latter. You can remove toxins using meal - a powder obtained by squeezing the oil from milk thistle seeds. It is taken a teaspoon once a day, washed down with slightly warmed water. It is best to take this medicine in the morning before meals. The course of treatment is a month.
Decoction of boron uterus
A universal remedy for early menopause and many gynecological problems is the boron uterus. A decoction is prepared from it by adding a spoonful of the raw material to a glass of boiling water and boiling the mixture in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. After cooling for 4 hours, take the product by spoon 4-5 times a day.
It also makes sense to take phytoestrogens, but I will talk about them in the next article.
Nicotine doesn't just kill horses.
Scientists conducted studies to determine the connection between the occurrence of premature menopause and smoking. So, women who smoked experienced menopause a year or two earlier. Year after year, the number of women who smoke is only growing, which means the number of women experiencing hormonal disorders ahead of time is growing.
If, nevertheless, early menopause occurs, then medication is required. It is best to use folk remedies that have a gentle effect on the body, for example, phytoestrogens, are characterized by the absence of toxic substances and restore a woman’s health and youth.
With warmth and care, Dilyara Lebedeva.