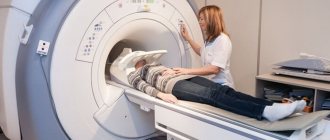
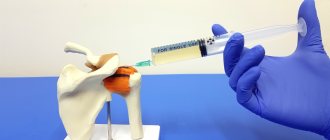
From this article you will learn:
- When is an MRI of the shoulder indicated?
- What diseases can be detected with MRI of the shoulder joint?
- Who should not undergo MRI of the shoulder joint?
If it is necessary to determine the cause of pain in the shoulder joint, the doctor will prescribe an x-ray or ultrasound. In cases where traditional research methods are unsuccessful, the patient is referred to an MRI of the shoulder joint. Magnetic resonance imaging is a high-tech way of obtaining images of tissues and internal organs. Diagnostic screening allows you to accurately determine the signs of pathology. In this article we will talk about who is recommended for an MRI of the shoulder joint, how the procedure is performed, and what contraindications there may be for prescribing the study.
The essence of the MTP method of the shoulder joint
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is actively used in modern medicine. MRI is an effective, very informative and safe method of instrumental diagnostics. High intensity magnetic waves affect a specific area of the human body and influence the hydrogen atoms inside cells, causing them to move in a certain order.
Against the background of cell movement, energy is released. A specially designed device scans these processes and creates a tomogram. A picture is displayed on the monitor screen, which the doctor can print on a special film.
To diagnose the shoulder joint, classical research procedures such as radiography or ultrasound are more often used. But MRI of the shoulder joint differs from traditional methods in its high accuracy and information content. This completely eliminates the impact of harmful ionizing radiation on the human body.
In some cases, gadolinium contrast agent is used to clearly determine the structure and size of pathological changes.
What determines the price of a shoulder tomography?
The price of an MRI of the shoulder joint is largely determined by three factors: the power of the tomograph, the qualifications of the personnel and the need to use contrast. A good way to reduce diagnostic costs without losing the quality of the examination would be to use the MRI service at night, when the maximum discounts apply.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| Shoulder MRI | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| Appointment with an orthopedist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| First aid program for joints (8 studies + appointment with an orthopedist + MRI of the joint) | 13000 rub. | 7500 rub. | 7500 rub. |
What determines the cost of tomography?
Tomograph power
Applying Contrast
Personnel qualifications
Promotions and discounts
Benefits of MRI of the shoulder joint
- Unlike X-rays or CT (computed tomography), the influence of harmful radiation on the human body is completely excluded.
- MRI is an absolutely safe diagnostic method that does not cause adverse reactions in the body. There may be a risk of an allergic reaction when using a contrast agent.
- The procedure is minimally invasive and painless. Magnetic resonance imaging does not use ionizing radiation harmful to the body.
The main advantage of magnetic resonance technology is the high accuracy of the results.
MRI of the shoulder joint allows you to diagnose even the most minor pathological changes:
- In just one research procedure, a doctor can obtain complete information about the condition of all tissues of the shoulder joint, muscle tissue, tendons, and nerve fibers. The introduction of a contrast agent makes it possible to diagnose vascular changes.
- The image clearly shows the boundaries between healthy and damaged tissues.
- 100% reliability of the result. Due to the complex structure of the shoulder joint, other diagnostic methods do not always accurately determine the area of pathological changes.
- The device records any tissue damage, necrosis, congestion, tumors, neoplasms of various etiologies, even at the initial stage of development. Other methods are not always so accurate and informative.
- MRI of the shoulder joint allows you to clarify the need for surgical intervention.
- Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to determine the area of bone tissue damage even in cases where radiography in two projections is unsuccessful.
- If all traditional methods of examining the shoulder joint are unsuccessful, MRI will help establish the correct diagnosis.
A significant advantage is the absence of age-related contraindications to the procedure. Tomography can be performed at any age. To ensure immobility and reduce mental stress, young children (up to 1 year) and patients suffering from claustrophobia are immersed in medicated sleep.
Disadvantages of magnetic resonance imaging:
- The procedure cannot be performed with metal implants.
- Difficulties in examining people who experience fear in closed or cramped spaces. For such patients, more modern open-circuit devices have been created.
- Due to the high cost, the procedure is not available to every patient.
Despite all the shortcomings, MRI of the shoulder joint is a fairly common diagnostic method, as it allows you to most accurately determine even subtle changes in bone and muscle tissue, tendons and ligaments. The results of magnetic resonance imaging often help to establish a correct and accurate diagnosis.
Contraindications
MRI is the safest way to examine the shoulder joint. Unlike radiography, during diagnosis there is no unwanted radiation exposure to the human body. And an informative arthroscopic examination occurs when the integrity of the soft tissues is violated. But MRI has absolute contraindications:
- the presence of ferromagnetic or electronic implants;
- implantation of artificial heart valves;
- surgical implants located in one of the organs of the central nervous system, for example, hemostatic clips.
Surgical devices installed in other parts of the body do not serve as absolute contraindications to the study. But there is a possibility of distortion of the results due to artifacts (interference) formed under the influence of the magnetic field. The decision to use magnetic resonance imaging to detect a specific pathology is made by the radiologist.
The disadvantages of the diagnostic procedure include the rather high cost, the presence of serious contraindications, and the unavailability of equipment in sparsely populated areas. But the advantages of MRI far outweigh its disadvantages. The study is minimally invasive, absolutely safe and highly informative.
Indications for MRI of the shoulder joint
If a doctor orders an MRI of the shoulder joint, the cost of the procedure will be higher than the cost of traditional instrumental diagnostic methods. Typically, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed to patients in cases where it is impossible to detect pathological changes in tissues and organs using X-rays and ultrasound.
Tomography makes it possible to diagnose various diseases with high accuracy even at the initial stage. Why does a doctor prescribe an MRI of the shoulder joint, what does this procedure show?
Using nuclear magnetic resonance, you can identify:
- Injuries and mechanical damage to connective and muscle tissue - cartilage, muscles, ligaments. The study is primarily designed to diagnose soft tissue pathologies, since bone tissue does not lend itself well to visualization.
- Various neoplasms inside the joint, oncological tumors, metastatic tissue lesions.
- Infectious or reactive arthritis.
- Pain syndrome of unknown origin.
- Inflammatory pathologies – bursitis, arthritis.
- Degenerative diseases of cartilage tissue and ligaments (bundles of collagen fibers).
- Osteoporosis – lack of bone tissue, Hass disease.
- Injuries and hemorrhages into the joint cavity.
- Degenerative changes in the joint - arthrosis or glenohumeral periarthritis.
- Violation of the integrity of articular elements.
- Rotator cuff pathologies.
- Impingement syndrome.
- Osteochondropathies.
- Congenital abnormalities.
- Infectious lesions of the shoulder (for example, osteomyelitis).
- Sports or occupational injuries.
- Internal bleeding.
- Connective tissue pathologies.
- Damage to the nerve plexus.
- Reduced range of motion.
- Pinching of the nerve endings of the cervicobrachial region.
- Habitual dislocation.
- Pathological changes and diseases that are difficult to diagnose using other methods.
Magnetic resonance imaging is used not only for diagnostic purposes, but also to monitor the patient's condition during treatment. For example, a doctor can monitor how a fracture heals or a prosthesis takes root.
MRI of the shoulder joint can detect diseases that cannot be diagnosed by other means:
- viral plexitis in acute form;
- injuries to the nerve endings of the brachial plexus;
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease;
- thoracic outlet syndrome;
- Pancoast tumor;
- tunnel syndrome;
- atrophic changes in the joint.
Magnetic resonance imaging can be prescribed as a one-time diagnosis or as a regular procedure to monitor the course of the disease and control the patient’s condition. The ability to see even the most minor changes in tissue allows you to track the dynamics of the disease.
Tomography helps to identify not only anatomical changes in the shoulder joint, but also the presence of indirect signs of various functional disorders. This facilitates the doctor’s task when developing a treatment regimen.
Magnetic resonance imaging can be prescribed by any doctor, but most often the patient is referred to this diagnostic procedure by a therapist, traumatologist or surgeon.
Read material on the topic:
Manual therapy of the cervical spine as a worthy replacement for alternative treatment
What the examination can show
MRI is performed to diagnose sports and household injuries, as well as their consequences. In case of complex fractures or complete separations of ligaments and tendons, scars remain that disrupt trophism. There is a risk of developing post-traumatic arthrosis - a progressive degenerative disease. Detecting it at an early stage allows you to stop the pathology and achieve stable remission. What else can be discovered during an MRI of the shoulder joint:
- acute and chronic articular pathologies of an inflammatory and degenerative nature - osteoarthritis, rheumatic, psoriatic, juvenile, gouty arthritis;
- various injuries of the rotator cuffs;
- diseases of infectious etiology - osteomyelitis, synovitis, bursitis;
- plexitis - inflammatory processes of large nerve plexuses of various localizations;
- osteochondropathy (Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, Ostgood-Schlatter disease, Köhler disease, Scheuermann-Mau disease, Schinz disease) - disturbances in the nutrition of bone tissue and their subsequent necrosis;
- bleeding into the joint cavities, formed hematomas, accumulation of pathological exudate;
- humeroscapular periarthritis, occurring against the background of an inflammatory process in the synovial capsule, muscles, ligamentous-tendon apparatus;
- abnormalities in the structure of the shoulder that arose during intrauterine or postpartum development;
- systemic pathologies affecting connective tissue structures (lupus erythematosus);
- hypermobility of the shoulder joint;
- neuropathies - non-inflammatory nerve lesions of traumatic or non-traumatic origin;
- benign neoplasms, cancerous tumors, distant foci of the oncological process.
Magnetic resonance imaging is also prescribed to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy. Surgeons monitor the rate of tissue regeneration, traumatologists and rheumatologists monitor the effect of pharmacological drugs.
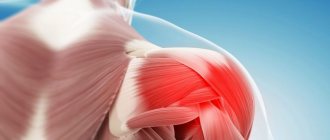
The head of the humerus is affected by arthritis.
Contraindications for MRI of the shoulder joint
The diagnostic procedure for studying internal organs and tissues using nuclear magnetic resonance is absolutely safe, but in some cases it has contraindications.
1. Complete contraindications:
- Electronic implants are devices that are implanted into the human body and regulate the functioning of organs and systems.
- Non-removable metal elements that are located in the patient's body.
- Metal pins, plates, knitting needles that are installed to fix bones in severe fractures.
2. Time limit:
- Pregnancy (especially the first trimester).
- Ilizarov compression-distraction apparatus.
- Metal plates for connecting bones in case of fractures of ribs and collarbone.
3. Contraindications for the use of contrast:
- Liver and kidney failure.
- Breast-feeding.
- Individual intolerance to contrast media.
MRI of the shoulder joint is not prescribed if there are metal objects in the body. This contraindication is due to the fact that under the influence of a magnetic field they shift, and in a shallow position they can even be torn out of the body. Implanted electronic devices (neurostimulators, pacemakers) may malfunction during a diagnostic procedure, and this is dangerous for the patient’s life.
Tomography is contraindicated in early pregnancy, as well as in young children under 7 years of age. For patients suffering from claustrophobia, this diagnostic procedure can only be performed in an open-type tomograph. Magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended for people with tattoos on their bodies because the ink may contain metal particles. The procedure itself is safe for such patients, but during diagnosis, burning sensations and pain in the tattoo area are possible.
Before performing the procedure, the doctor must examine the patient, assess his condition and make a conclusion about the possibility of prescribing an MRI of the shoulder joint.
Recommended articles on the topic:
- Thermal detoxification: lightness of the body and clear skin
- Lipolytic therapy: indications, contraindications, stages of the procedure
- Weight correction: everything you need to know about the procedure
For women who are breastfeeding, the doctor usually suggests postponing the examination. But if there is an urgent need for diagnosis, the patient is recommended to express milk to feed the baby 1-2 days before the procedure. A woman can continue feeding no earlier than 24 hours after diagnosis.
After cardiac bypass surgery, MRI of the shoulder joint is prescribed only if urgently necessary and no earlier than 3 months after surgery. The diagnostic procedure is accompanied by careful monitoring of the patient's condition. If abnormalities in the functioning of the heart are detected, the examination should be stopped and the patient should be given medical assistance.
Symptoms of a sprained or torn ligament
When the shoulder ligaments are damaged, the following symptoms often occur:
- shooting pain in the shoulder when moving your arms up or to the side;
- swelling in the injured area - usually a couple of hours after the injury;
- increased temperature on the surface of the edema;
- hematomas and tumor;
- limited shoulder mobility.
If a child is injured, the joint may move unnaturally, which is also a symptom of a sprained or torn ligament.
Pain is the main symptom that appears immediately after injury. Over time, the pain may change to aching or dull.
To provide first aid if a ligament rupture or sprain is suspected, it is necessary to immobilize the injured limb and apply a cold compress. If the pain is severe, the victim can be given a painkiller. After which it is necessary to take him to the hospital.
It is not recommended to treat joint ligament injuries on your own - this can be dangerous for the injured arm and lead to negative consequences.
Possible risks of MRI
If all recommendations and rules are followed, magnetic resonance imaging is not dangerous to the human body. But you should always remember about contraindications - MRI of the shoulder joint can provoke a shift of the metal implant or disrupt the operation of the implanted electronic device.
An MRI with a contrast agent may cause an allergic reaction. The doctor, as a rule, treats this risk prudently and always has on hand means to eliminate the symptoms of an allergic attack.
Experts recommend that nursing mothers refrain from breastfeeding their baby for 24 hours after a diagnostic procedure using contrast. And although no negative effect of the contrast agent on children has been identified, the mother who has undergone the procedure with contrast must still follow this rule.
Experts consider the assumption about the influence of contrast tomography on the development of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) controversial. However, some scientists believe that the cause of NSF development is gadolinium-based contrast. But only patients with already impaired kidney function are exposed to this risk.
Despite all the undeniable advantages, MRI as a method has its drawbacks. The quality of the images obtained depends on how long the patient was able to remain motionless. MRI of the shoulder joint can only be performed on high-field closed-type machines, since low-field tomographs produce images of poorer quality. Consequently, not all patients can undergo the diagnostic procedure, for example, people suffering from claustrophobia.
Read material on the topic: Therapeutic back massage: main types, indications and contraindications
Operating principle
Magnetic resonance imaging is an examination method in which the shoulder joint is placed in a magnetic field. Cartilage, bones and connective tissue structures contain different concentrations of hydrogen ions, which are directly dependent on tissue density. In a magnetic field, protons change their characteristics - charges, motion vectors, spatial orientation. This is detected by the tomograph sensors and the collected information is transmitted to the computer. The device reads the changes that have occurred and converts the data into images colored in different colors. The images are dominated by gray shades, the intensity of which depends on the density of the structures being examined. If necessary, a three-dimensional image is created on the monitor screen, which is most informative when performing MRI with a contrast agent.
MRI installation.
Preparing for an MRI procedure of the shoulder joint
MRI of the shoulder joint does not require special preparation; the patient can adhere to a normal lifestyle. Immediately before the diagnostic procedure, the patient is asked to remove all metal jewelry, glasses, and watches. As mentioned above, the presence of metal objects affects the quality of the pictures.
Doctors often tell patients to fast before other types of diagnostic testing. The results of magnetic resonance imaging are not affected by a person’s diet, with the exception of MRI with contrast. In this case, the patient is advised to stop eating and drinking 4-5 hours before the contrast agent is administered. The body's reaction to contrast can be expressed in a rather unpleasant feeling of nausea.
Before starting a contrast procedure, your doctor should do a gadolinium test to rule out an allergy. The patient is given a test dose of contrast agent and monitored. If after a certain period of time an allergic reaction occurs (suffocation, rash, urticaria), then diagnosis is contraindicated for the patient.
In large diagnostic centers, before the procedure, the patient is asked to change into a disposable non-woven shirt. There is no particular need for this, so many medical centers examine the patient in his usual clothes. The main requirement for clothing is the absence of metal buttons, zippers, snaps and other elements. Also, before conducting the study, you should remove any jewelry made of metal, watches and glasses.
Even before performing an MRI of the shoulder joint, you should inform the doctor about the presence of chronic diseases, possible pregnancy, and a tendency to develop attacks of claustrophobia. The person must lie still during the scan. Any movements lead to distortion of images and unreliable results. If it is impossible to exclude motor activity even before the procedure, it is recommended to take a sedative.
Since magnetic resonance imaging does not require special preparation, the examination can be performed on the day of the appointment. After MRI, no rehabilitation is required and the patient can immediately go about their normal activities. The only exception is immersion in medicated sleep. In this case, the patient will have to stay in a medical facility for some time.
Read material on the topic: Treatment of spider veins - the most modern and effective methods
What does a patient get after an MRI, where to go with the results
After completing the MRI procedure, you will receive images and their description.
If you underwent research on the direction of your doctor, you need to show the conclusion to him. He will prescribe the necessary treatment or give a referral to another doctor who will take care of your problem.
If you underwent an MRI on your own initiative, the choice of doctor will need to be made depending on the identified disorder.
If you don’t know where to turn, you can clarify this issue with a specialist who will describe your results.
How is an MRI of the shoulder performed?
Having received a referral for a procedure, a person wants to know how an MRI of the shoulder joint is done. Diagnostic procedures are performed in the following sequence:
- The patient, wearing clothes without metal elements, lies down on the tomograph table. To prevent mobility, the nurse secures the patient’s limbs with special belts and fixes the head on a special cushion. If the procedure is prescribed for a child, he is explained in detail how an MRI of the shoulder joint is performed.
- Injection of contrast agent. When a contrast-enhanced tomography is prescribed, an intravenous injection of the drug is given. As the substance spreads throughout the body, the patient may feel hot. The contrast colors the vessels, so tumors with an abundant blood supply are clearly visible on the image.
- The table on which the patient is secured is pushed into the tomograph capsule. Inside the device there is a button for contacting a doctor. A person can always press it if he feels unwell. During the procedure, the operating device makes sounds - clicks, buzzing. If they are unpleasant for the patient, you can wear special headphones.
- In the tomograph, a special magnetic ring rotates around the shoulder and takes a series of layer-by-layer images. After an MRI of the shoulder joint, the areas and boundaries of pathological changes will be clearly visible in the photo. If necessary, the doctor can combine all the images on the monitor screen into a single 3D image of the area under study. During the procedure, the person does not experience pain or discomfort. The patient can freely communicate with the doctor. To ensure high-quality images, the patient is prohibited from moving or making sudden movements.
The MRI of the right shoulder joint is no different from the MRI of the left shoulder joint. The entire process is automated, so the doctor can only enter all the necessary data into the computer to automatically screen the desired side of the body.
The entire shoulder examination procedure lasts no more than 30–40 minutes. MRI with contrast will require more time - from 1 hour.
To obtain a more accurate and detailed image of small areas of the body, the doctor may prescribe a special type of examination - magnetic resonance arthrography (MRA). A few minutes before the start of the procedure, the patient is injected with a contrast agent containing gadolinium, a rare earth metal with paramagnetic properties that is inert to the body.
MRA with contrast is prescribed if the doctor suspects the following pathologies in the patient:
- Neoplasms and metastases. The intensive blood supply to the neoplasm makes it possible to visualize its boundaries with high accuracy. Using a contrast agent, the doctor can identify the origin of the tumor, the presence and number of metastases, the degree of their penetration into neighboring tissues, and the characteristics of the blood supply.
- Inflammation of the joint. The contrast agent allows the doctor to see even the smallest inflammatory foci in ligaments, tendons, and muscles. X-ray is ineffective in this case.
- Vascular anomalies. One of the reasons for the development of shoulder joint diseases is a disruption in the supply of tissues with nutrients due to the unsatisfactory condition of the blood vessels of the shoulder girdle.
Before undergoing an MRI of the shoulder joint with contrast, the patient is given a test to determine the body's sensitivity to gadolinium. For most people, the contrast agent does not cause allergic reactions and is completely eliminated from the body naturally after a few hours.
The purpose of MRI with contrast depends on which tissues and organs need to be examined. For example, when diagnosing pathologies of the brachial plexus, there is no need for contrast. The drug can be administered into the body in two ways: intravenously (indirect arthrography) and directly into the mobile joint (direct arthrography). The second method of administering a contrast agent is more effective, but the procedure requires more time and does not eliminate the risk of infection.
Indications for magnetic resonance arthrography:
- partial/complete rupture of the rotator cuff tendons or the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle;
- diagnosis of the condition of the periarticular bursa above the rotator cuff in connection with bursitis (inflammation);
- examination of the labrum around the glenoid fossa and cartilage.
The contrast agent is safe, well tolerated and improves image quality. Such preparations do not contain iodine; their chemical composition differs from radiopaque agents. A few hours after the procedure, the contrast agent is completely eliminated from the body naturally.
If gadolinium causes an allergic reaction in a patient, an MRI of the shoulder joint is performed without contrast. The administration of a contrast agent is not required in cases where it is necessary to identify:
- soft tissue tumor;
- fracture;
- changing the moving connection;
- presence of infection;
- inflammatory process.
In case of infections and inflammatory processes, contrast is not only useless, but also makes it difficult to diagnose the condition of the synovial membrane.
The contrast agent can be administered in two ways:
- The drug is infused slowly before the procedure.
- The contrast is introduced dropwise into the body during the study.
Before performing an MRI with contrast, the doctor must find out whether the patient has had an allergic reaction to medications and whether there is a history of any diseases of the urinary system. Particular attention should be paid to patients prone to allergies and pregnant women. MRI is not recommended for such patients; screening should only be prescribed in the most exceptional cases.
Read material on the topic: Ozone therapy: methods, effect, reviews, photos
Interpretation of MRI results of the shoulder joint
After completing the procedure, the diagnostician begins to decipher the images. Next, the results obtained are interpreted by a radiation diagnostics specialist. If there are no difficulties or doubts, the result of the study will be ready in 1 hour. For severe illnesses, doctors may need up to two days to decipher and interpret the images.
Interpretation of MRI results of the shoulder joint is based on visual analysis of the images generated by the device. A qualified doctor carefully examines all abnormalities and makes a diagnosis.
The resulting image is transferred to the media and can be viewed on a computer monitor. In most cases, tomography is performed remotely, and its results are given to the patient on film or digital media (disk, USB). This allows the treating physician to view the images at any time.
MRI of the shoulder joint shows:
- Inflammatory foci, destructive and degenerative changes in bones and hyaline cartilage. They appear as intensely colored areas.
- Cavities formed around tissue that indicate inflammation.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms, which are visualized as areas with a denser structure. They are intensely colored and located on the border between bones and muscles.
- When a ligament ruptures, the torn parts are displaced into the joint cavity.
- Overgrown edges of bone plates and calcified areas, which indicate irreversible destruction of cartilage tissue and the development of osteoarthritis.
- Complete or partial fusion of the joint space, which is a sign of ankylosis (immobility of the joint) and confirms the need for surgical intervention.
- The formation of sequestra (dead tissue) is a sign of infectious arthritis.
- Accumulation of fluid in the synovial bursa. This indicates the development of bursitis, and the formation of effusion in the joint cavity indicates synovitis.
- Changes in heat transfer. Identified during diagnosis, they can be a symptom of various pathologies of the shoulder joint.
When interpreting MRI results, the doctor must pay attention to the condition of the bone surfaces lined with cartilage tissue. Normally, they should not show noticeable pathological changes. The specialist also evaluates the condition of ligaments, tendons, nerve bundles, and muscle fibers located near the joint. Any changes in soft tissue structures indicate a sluggish inflammatory process.
After deciphering and interpreting the results, the patient visits a doctor who referred him for an MRI of the shoulder joint. The doctor will study the diagnostic results, make a diagnosis based on them and prescribe adequate treatment.
Read the material on the topic: What is PRP therapy
What does an MRI of the shoulder show?
MRI scanning allows you to accurately visualize the area of interest layer by layer. During the test, tissue layers up to 1 mm are scanned. This allows you to fully assess the condition of the shoulder, identifying vulnerable or damaged areas:
- soft fabrics,
- vessels,
- bones,
- nerve roots.
The study allows timely detection of compression or dilation of blood vessels, identification of inflammatory processes, neoplasms, cracks and thinning of cartilage tissue.
Alternatives to MRI
- Computed tomography (CT) is a less informative method for diagnosing pathological changes in the shoulder joint. CT scans can only detect significant damage to the joint.
- MSCT is a sensitive and effective diagnostic method, but it is more suitable for studying damage to bone structures. Ionizing radiation, which is used to perform CT and MSCT, is harmful to the human body.
- X-ray – allows you to examine only the internal bone structures.
- Ultrasound is an insufficiently accurate method of rapid diagnosis.
- PET-CT can detect many functional disorders in the shoulder joint, but is a rather expensive procedure.
You can do magnetic resonance imaging, including the shoulder joint, by seeking help from real professionals - the Veronika Herba beauty and health center, equipped with effective and modern equipment.
Why clients choose Veronika Herba Beauty and Health Center:
- This is a beauty center where you can take care of yourself at a reasonable cost, while your face and/or body will be treated not by an ordinary cosmetologist, but by one of the best dermatologists in Moscow. This is a completely different, higher level of service!
- You can receive qualified help at any time convenient for you. The beauty center is open from 9:00 to 21:00, seven days a week. The main thing is to agree with your doctor in advance on the date and time of your appointment.
Sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone +7 (495) 085-15-13
, and you will see for yourself!
Indications
The attending physician may send the patient for an MRI if the following indications exist:
- limitation of joint mobility, pain when extending and flexing the limb;
- discomfort in the area of the affected joint;
- morning swelling, swelling of the joint;
- previous injuries (dislocations, ruptures, fractures of tendons, bones, ligaments);
- pain that intensifies or disappears during physical activity;
- crunching, clicking in the joint when changing body position, turning, bending;
- blocking movements.
Make an appointment with a specialist, without queues, at a convenient time
+7
Sign up