Computed tomography of joints (CT joints) is the most modern and fastest method of studying this part of the human body. This diagnostic method is used at the Yusupov Hospital to determine or exclude destructive, tumor and inflammatory processes in the joints. The modern tomograph of the new generation, which the clinic is equipped with, allows you to quickly obtain the clearest images, which are interpreted in detail by experienced, highly qualified specialists.
Compared to conventional radiography, CT of the joints provides more accurate information, so computed tomography is one of the most informative diagnostic methods.
Is CT scanning of joints dangerous?
CT scans of joints are based on X-rays. For many patients, this fact is the basis for worries about the possible harm to health that an x-ray can cause. However, these fears are absolutely unjustified, since the radiation exposure provided by modern equipment and software and hardware systems is biologically determined and is considered very low. Computed tomography does not harm human health; it can even be performed several times throughout the year.
How to prepare for a CT scan of the joints?
Due to the fact that computed tomography of the joints is performed without the use of a contrast agent, the patient does not require any special preparation.
The radiologist may need the following documents that the patient needs to take with him:
- referral from the attending physician;
- outpatient card or extract from medical history;
- results of previous studies with images and descriptions (both CT and others);
- other documents that relate to the subject’s disease.
Preparing for the study
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Specific preparation is needed only when conducting contrast diagnostics. The patient must refrain from eating food 6 hours before the CT scan. This is necessary to minimize side effects. Moreover, the contrast agent will spread faster and more efficiently through the “clean” gastrointestinal tract. In addition to refusing to eat, the patient must choose comfortable and safe clothing. These should be simple pants/T-shirt made of natural or synthetic fabric without metallic decorative elements. Metal particles can distort the image, leaving empty white spots in the final 3D image.
How is a joint CT scan performed?
To conduct the study, the patient enters the equipment room, takes off clothes that may interfere with the procedure, metal jewelry, glasses, watches, leaves unnecessary items there, and a mobile phone. After this, it is placed on a mobile table.
During a computed tomography scan, the tomograph ring rotates around the table on which the person being examined lies. One of the conditions for obtaining high-quality images is complete immobility of the patient, for which special belts can be used.
The duration of the procedure is, on average, about five minutes. As a rule, it takes experienced specialists at the Yusupov Hospital no more than one hour to draw up a conclusion. No preliminary preparation is required.
CT of the joints is an absolutely safe procedure, with virtually no contraindications, except for those standard for any tomography.
Computed tomography of joints is not recommended:
- children under 14 years of age (except in cases of emergency);
- pregnant women (due to possible negative effects on the fetus);
- patients with excessive body weight - more than 150-160 kg (due to the limited size of the tomograph).
procedure
Computed tomography is carried out in a specially equipped diagnostic room. After the patient assumes a horizontal position on the retractable part of the tomograph, he is moved into the scanning cavity of the device. Until the end of the procedure, you should maintain a motionless position to avoid distortion of the results and motion artifacts on the tomograms. The average duration of a CT scan is several minutes.
During diagnosis, the structure of bones and joints is visualized on a computer screen. The doctor can monitor their condition in real time and build three-dimensional projections of various areas. Interpretation of CT images takes about an hour, and in most cases the patient can leave the medical center after an hour and a half with a full package of examination data and recommendations for further actions.
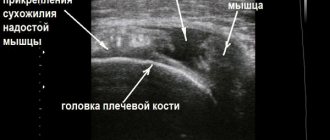
Indications for CT scan of the shoulder joints
A CT scan of the shoulder joints may be prescribed to patients to identify the following diseases and conditions:
- shoulder dislocation;
- fractures of the scapula or humerus;
- arthritis and arthrosis;
- neoplasms of bones or cartilage;
- humeroscapular periarthritis;
- shoulder pain;
- osteochondropathy;
- changes in the shoulder joint.
In addition, computed tomography of the shoulder joints is used before surgery and to clarify the results of radiography.
Research process
The patient needs to lie down on the tomograph table. The pelvic area should be under a special ring-scanner, which, rotating, sends impulses through the body. You should be prepared that all this is accompanied by a little noise. During the photographs, the patient must remain as still as possible, otherwise they may turn out to be of poor quality or distort the results. If necessary, the physician can use soft straps to secure the limb and give a sedative. The rest of the body is covered with a special apron that will protect against radiation.
A regular CT scan without contrast takes a few minutes, but a contrast-enhanced CT scan, designed to visualize the soft tissue and blood vessels surrounding the joint, takes about 20 minutes.
Indications for CT scan of the hip joint
CT scan of the hip joint is necessary for the following pathologies:
- arthritis of any etiology (infectious, traumatic, rheumatic);
- destructive changes in the joint (due to tuberculosis, sepsis, tumor, etc.);
- tumors in cartilage, synovial capsule or surrounding tissues;
- deforming osteoarthritis;
- osteochondropathy of the hip joint;
- accumulation of pus, blood, inflammatory fluid in the hip joint;
- fractures of the pelvic bones or femur, incl. intra-articular, etc.
Indications for CT scan of the ankle joint
CT scanning of the ankle joint is part of a comprehensive diagnosis of the following diseases:
- various ankle injuries;
- degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the ankle joint;
- inflammatory diseases of the ankle;
- joint dislocation;
- infectious diseases of the joint (osteomyelitis);
- benign and malignant tumors of the ankle joint, soft tissues, bones.
Computed tomography of the joints also allows you to verify the diagnosis if other research methods do not allow this. In addition, CT scans of joints are used in preparation for surgical treatment and to monitor the results of surgery.
Adverse reactions after CT
Computed tomography is painless and does not cause any complications. Only when using contrast can side effects occur: heat, dryness and metallic taste in the mouth, numbness and tingling of body parts. These symptoms disappear within an hour after the procedure, so no treatment for the symptoms is provided.
Serious side effects are extremely rare: urticaria, vomiting, nausea, rhinitis, chills, fainting, anaphylactic shock, swelling of the neck and face, shortness of breath. For more serious adverse reactions, seek medical help and undergo symptomatic treatment.
Indications for CT scan of knee joints
CT scan of joints is prescribed for the following purposes:
- determination of the bone structure of the proximal tibia, distal femur and patella;
- obtaining information about the structure of the soft tissues of the joint;
- assessment of the integrity of bone and other structures in case of injury;
- identification of various patella and knee fractures;
- diagnosis of Baker's cyst, Osgood-Schlatter disease;
- assessment of the anatomical features of the knee joint when planning surgical intervention;
- assessment of surgical results.
In what cases is CT scan necessary?
The longest and thickest bone in the human skeleton is the femur, and its most vulnerable part is the articular head, which forms the hip joint together with the ilium.
The bone itself can be subject to various diseases, such as osteoporosis or osteomyelitis. Determining the root cause of a disease can be quite difficult, and the manifestations of the disease can be numerous. To understand the nature of the disease and identify an anomaly, doctors resort to research using a tomograph.
CT scan is performed for Perthes disease. This disease most often affects children aged 3-15 years, but can also occur in adults. Symptoms include necrosis (death) of the joint. The reliable reasons for the development of the disease have not yet been established. There is a genetic predisposition, and under the influence of unfavorable factors the disease develops. Often occurs against the background of a congenital pathology - myelodysplasia, i.e. underdevelopment of the lumbar spinal cord.
Computed tomography is prescribed for arthritis of the hip joint, an inflammatory disease. There can be many reasons for the occurrence of coxitis; depending on this, the disease is divided into various types: infectious, gouty, psoriatic, rheumatoid, reactive, osteoarthritis. For example, with osteoarthritis, inflammation occurs against the background of increased loads on the joint, and can occur due to severe bruising. Another name for the disease is coxarthrosis, for which it is advisable to carry out X-ray diagnostics with a tomograph. Coxarthrosis occurs due to degenerative changes in the hip joint, which lead to its slow deformation.
A CT scan of the femur should also be prescribed for: dysplasia (when normal bone tissue is replaced by fibrous connective tissue, which contributes to bone deformation and loss of integrity), osteomyelitis (purulent bone lesions with subsequent destruction), osteoporosis (a disease characterized by impaired bone density due to lack of calcium, which leads to uncontrolled excessive fragility of bones), tumors, injuries (bruises and fractures).
Computed tomography is used to monitor the effectiveness of disease treatment and is recommended before surgery.
MRI or CT of joints: which is better?
Several methods are used to diagnose joint diseases at the Yusupov Hospital: ultrasound, X-ray, magnetic resonance and computed tomography. The most modern and informative of them are MRI and CT. When prescribing one or another diagnostic method, the attending physician takes into account the task of examining the joints and the individual characteristics of each patient.
For example, magnetic resonance imaging is not used for patients who have various implants, pacemakers, pins, etc. installed in their bodies, when the above factors are not contraindications for computed tomography.
Bruises and various injuries, as a rule, require the use of MRI, since such injuries damage soft tissues, the visualization of which is better provided by magnetic resonance imaging. For diseases affecting bone structures (various fractures, tumors, osteomyelitis, etc.), the optimal diagnostic method is computed tomography.
You can get a CT scan of joints in Moscow at an affordable price in one of the most modern multidisciplinary medical centers - the Yusupov Hospital. Experienced, highly qualified clinic specialists conduct research using the latest spiral computed tomograph, which guarantees the most accurate results. Thanks to the high information content of CT, doctors select an effective treatment regimen individually for each patient.
Contraindications and restrictions for magnetic resonance imaging
The study does not aggravate the course of existing chronic diseases of patients, but it is not suitable for everyone. Please note that the MRI procedure of the hip joint is not performed in the following cases:
- devices and pacemakers implanted into the body - pacemakers, myostimulators, neurostimulators;
- electronic implants for the middle and inner ear, drug dispensers;
- the presence in the body of vascular clips, artificial heart valves, as well as foreign bodies and fragments;
- endoprostheses, plates, pins made of ferromagnetic metals - iron, stainless steel, nickel, cobalt.
The possibility of performing an MRI of the hip in the presence of a femoral endoprosthesis is determined by the composition of the implant. If titanium and chromium predominate in the prosthesis, the procedure can be performed. These metals are paramagnetic - they do not heat up or move in a magnetic field. The presence of impurities of cobalt, nickel, and iron requires analysis of the composition, size and shape of the prosthesis, since these materials react to the magnetic field created by the tomograph.
Contraindications to MRI with contrast
Modern contrast agents are usually well tolerated, and allergic reactions are extremely rare. Before the procedure, a test with a small amount of the drug must be performed.
MRI with contrast cannot be performed in the following cases:
- severe forms of renal and liver failure;
- pregnancy;
- an allergic reaction to a contrast agent recorded during previous studies.
Breastfeeding women can undergo studies with contrast agents, but breastfeeding should be stopped for two days after administration of the drug.
There are some patient conditions that are not absolute contraindications, but impose certain restrictions on the possibility of performing the procedure. These conditions include:
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- epilepsy, claustrophobia, convulsive syndrome, mental illness;
- severe pain that prevents the body from standing still;
- serious condition of the patient;
- for children under 7 years of age, MRI of the hip is performed under general anesthesia;
- Having extensive tattoos in the pelvic area can cause significant heating of the skin.
In case of moderate claustrophobia or nervous agitation, take sedatives before performing the procedure. In many centers, the study is carried out on open-type tomographs.