- October 6, 2018
- Sports nutrition
- Matela Victoria
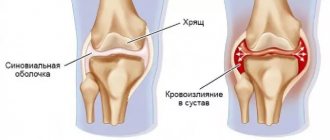
To improve tendon conditions, doctors often prescribe steroids for joints and ligaments. Due to the fact that the medicine retains water in the body, joints are strengthened. Steroids contain testosterone, which slows down the growth of tendons. During the development of the inflammatory process in the body, special cells are formed that activate the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. In addition, the immune response is stimulated. Steroids for joints and ligaments help the body eliminate inflammation and speed up recovery.
Main groups
There are several groups of steroid drugs. Natural ones include “Cortisone” and “Hydrocortisone”. Synthetic ones include Prednisolone and Betamethasone. These drugs affect the body at the cellular level. You should be aware that self-medication can be harmful, since the steroid drug should be prescribed strictly by a specialist. During the treatment process it is necessary to maintain proper nutrition. It is undesirable to consume large quantities of protein, since the body spends a lot of energy to absorb protein.
What is important to know during steroid treatment
The main goal of treatment is to regenerate damaged areas as much as possible. If a large amount of protein is present in the body, this process may be disrupted. It is recommended to include more carbohydrates in your diet. The dose and duration of treatment should be determined by a strict doctor, depending on the type of disease and its complexity. To get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to administer intra-articular medication. In this case, the hormone does not disrupt the functioning of other organs and does not worsen overall health.
Period after surgery
The postoperative period is the most important stage on which the success of the patient’s rehabilitation largely depends. Surgery is only the first step. This is followed by postoperative treatment, which includes several stages:
- For the first weeks (usually up to a month), the patient is in a specialized rehabilitation center and wears a plaster cast to fix the joint. During this period, physiotherapy is used, wearing an orthosis designed to protect the joint, promote its speedy recovery and control muscle tone.
- After a month, the patient can begin to load the joint. This is only possible if the muscles are completely controlled and there is no swelling. After another two weeks, the patient can return to normal life.
Main rehabilitation measures:
- Compresses.
- Massage.
- Trituration.
- Physical therapy exercises.
- Low-intensity walks.
The total time for graft engraftment is about three weeks. During all this time, the ligaments remain vulnerable and weak. Handling should be as careful and delicate as possible. The patient should not kneel, squat sharply, or jump. The orthosis provides additional protection.
Restoring leg function after transplantation requires effort and exercise. In total, complete adaptation takes about a year. All this time, the patient may feel some discomfort, warmth in the intervention area, and also observe some swelling. The knee after plastic surgery will not be absolutely the same as before. However, with the right approach, it is quite possible to restore full functionality and even return to sports activities.
How do steroids affect ligaments?
If you actively engage in sports, degenerative processes in joints and ligaments may occur. In some cases, chronic diseases appear. To prevent the occurrence of various injuries, athletes are recommended to take steroids for ligaments, as they accelerate the regeneration of connective tissue and have a strengthening effect. Most often, steroids for joints and ligaments are prescribed:
- people who are involved in professional bodybuilding and powerlifting;
- if there is a risk of injury;
- it is necessary to strengthen joints and ligaments.
Only a doctor should prescribe the drug. Self-medication may cause side effects.
Preventive measures
To prevent injury, it is important to strengthen the skeletal system and ligamentous apparatus. To do this you need:
- Take curcumin. This is a herbal medicine that relieves inflammation.
- It is necessary to consume minerals and vitamins. They will have a positive effect on joints and ligaments.
- With the help of shark cartilage, you can strengthen bone tissue, since it contains glucosamine, calcium and collagen.
- To strengthen bone tissue, it is necessary to include in your diet those foods that contain large amounts of vitamin D and calcium.
The average duration of treatment is several months. Many doctors prescribe Ketanov, Aspirin and Diclofenac to their patients. As medical practice shows, such drugs have a temporary effect. Therefore, it is best to use steroids for the joints and ligaments that affect the disease.
Conclusions:
Today, many modern high-tech methods have been developed for the treatment of injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system, bones, joints, tendons and muscles. These are various arthroscopic surgical techniques that, using the most modern equipment, make it possible, using the most modern equipment, to quickly, effectively and less traumaticly eliminate the cause of pain and dysfunction of the limb, return the person to the joy of movement, and not just alleviate the symptoms for a while, postponing the solution to the problem until later or not at all. deciding, as in the case of diprospan injections. Then it may already be too late.
Contraindications for use
In some cases, steroids should not be taken. It is not recommended to treat with the drug if the patient has the following pathologies:
- stomach ulcer;
- herpes;
- diabetes;
- kidney disease.
Before taking steroids to restore joints and ligaments, you should consult your doctor and undergo a thorough medical examination. Most often, athletes take an anabolic steroid because it helps burn fat and build muscle. This drug is also actively used in the treatment of injuries. The anabolic drug accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissue. It is not recommended to take the drug for people under 25 years of age, since the development of bone tissue may stop.
Hormone replacement therapy for men with age-related androgen deficiency
Specialization: urology, andrology
Age-related androgen deficiency syndrome in men is a biochemical imbalance that occurs in adulthood due to insufficiency of androgens in the blood serum, often accompanied by a decrease in the body's sensitivity to androgens. As a rule, this leads to a significant deterioration in the quality of life and adversely affects the functions of almost all body systems. Naturally, the issues of androgen deficiency therapy are of great interest, since it poses a difficult task for the clinician: to choose from a wide arsenal of methods and drugs of hormonal therapy the most optimal one, combining quality, efficiency, and ease of use.
Currently, urologists and andrologists most often use testosterone replacement therapy. This method allows you to solve a number of problems: reduce the symptoms of age-related androgen deficiency by increasing libido and overall sexual satisfaction, reduce the severity or completely eliminate vegetative-vascular and mental disorders. In addition, if testosterone replacement therapy is used for more than 1 year, patients experience an increase in bone mass density, a decrease in the severity of visceral obesity, and an increase in muscle mass. Also, after a long course of treatment, laboratory parameters are normalized: there is an increase in hemoglobin levels or the number of red blood cells, a decrease in the level of VLDL (very low density lipoproteins) and LDL (low density lipoproteins) with an unchanged level of HDL (high density lipoproteins). Many authors believe that this effect can be achieved by restoring the concentration of testosterone in the blood to normal levels (10–35 nmol/l). It should also be taken into account that *17α-alkylated testosterone preparations fluoxymesterolone and methyltestosterone have pronounced hepatotoxicity, having a toxic and carcinogenic effect on the liver, and also negatively affect the lipid spectrum of the blood (a sharp increase in the level of atherogenic and a decrease in the level of antiatherogenic lipoproteins). Therefore, the use of these testosterone derivatives in clinical practice was discontinued. Currently, testosterone undecanoate (Andriol) is the preferred oral drug. This testosterone ester does not undergo primary hepatic metabolism, as it is absorbed into the lymphatic system, bypassing the liver. After hydrolysis of testosterone undecanoate in the lymphatic system, testosterone enters the systemic circulation, which has a therapeutic effect both on its own and through its main metabolites - dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and estradiol, which determine the full spectrum of androgenic activity of testosterone. Thus, testosterone undecanoate retains its activity when administered orally. At the same time, bypassing the portal vein system and passing through the liver, testosterone undecanoate does not have a hepatotoxic or hepatocarcinogenic effect. The half-life of the drug from plasma is 3–4 hours. In connection with this, the dosage regimen for testosterone undecanoate is 2 times a day, which is not always convenient for patients. Based on our own experience, we believe that Andriol is a fairly mild drug and helps only in cases of initial and minimal manifestations of age-related androgen deficiency.
Intramuscular injections of long-acting testosterone esters are also a widely used method of replacement therapy in men with hypogonadism. The two most well-known testosterone esters, testosterone cypionate and testosterone enanthate, have similar pharmacokinetics. When these drugs are administered intramuscularly, a depot is created from which the drug is released into the bloodstream. During the first 2–3 days after administration, testosterone levels rise to supraphysiological levels, and then slowly decrease over the next 2 weeks to subnormal values. The positive side of these drugs is the duration of the therapeutic effect. Nevertheless, sudden changes in testosterone levels, often felt by the patient himself in the form of increases and decreases in libido, general well-being, and emotional status, are undesirable qualities of these drugs. In this regard, great hopes are placed on the new drug Nebido (Schering), the pharmacokinetics of which are significantly different from other testosterone esters. Nebido is testosterone undecanoate and is a non-peak drug. Over the past two decades, much attention has been paid to research into the benefits of transdermal use of testosterone preparations. Scrotal patches are effective and some patients find them the most convenient treatment option. Skin patches are most well accepted by patients and provide effective serum testosterone levels. However, there are some differences between the two types of patches regarding their allergenic potential: skin patches have a much higher incidence of allergic reactions and skin irritation than scrotal patches. Testosterone gel has all the benefits of patches and does not cause skin reactions. Its only drawback is the possibility of contact of the gel with a partner and the insufficient number of long-term studies on its use. The transdermal route of testosterone administration avoids its primary metabolism in the liver and inactivation, as occurs with the use of oral androgen drugs, and also allows it to simulate the circadian rhythms of release of physiological unmodified testosterone and its natural metabolites, estradiol and DHT. In addition, therapy using patches and gel can be easily interrupted if necessary. The positive aspects of this treatment method also include the low risk of drug dependence. The European drug 5-α-dihydrotestosterone gel (DHT), although found to be effective, is unknown whether the isolated use of a non-aromatized androgen, such as DHT, has the same effect as testosterone, due to the fact that testosterone metabolites include estradiol. According to many authors, the use of the drug is not recommended, since DHT, due to the inability to convert into estradiol, does not have the full range of therapeutic properties of testosterone (for example, effects on bone tissue and the cardiovascular system). Some of the replacement therapy drugs, such as testosterone undecanoate, DHT gel and scrotal patches, cause a significant increase in serum DHT concentrations. DHT is known as the main androgen of the prostate, and there has been much discussion regarding its ability to cause prostate disease. However, despite these assumptions, in the last 10 years there has been no evidence of an increase in the incidence of prostate pathology when prescribing DHT drugs.
Thus, there are many drugs for androgen replacement therapy, but they all have certain side effects and also have an inhibitory effect on spermatogenesis. Recently, more and more studies have appeared demonstrating the secondary nature of age-related androgen deficiency. According to WHO materials, data were obtained on the preservation of the secreting function of Leydig cells in elderly men, which allowed scientists to propose a fundamentally new approach to the treatment of age-related androgen deficiency, based on stimulation of the synthesis of endogenous testosterone. However, we should not forget that along with absolute contraindications for androgen replacement therapy (breast and prostate cancer), there are also additional ones (benign prostatic hyperplasia with severe obstruction, prolactinoma, polycythemia). Relative contraindications include sleep disorders in the form of apnea, obstructive pulmonary diseases, and heavy smoking. Side effects of androgens include increased sleep apnea, polycythemia, gynecomastia, priapism, fluid retention, increased blood pressure, edema, increased prostate size, and inhibition of spermatogenesis. That is, today there are methods for treating age-related androgen deficiency, which can be divided into two groups, fundamentally different in their mechanism of action: replacement therapy with exogenous androgen drugs; therapy that stimulates the synthesis of endogenous testosterone. Thus, we can say that there is no optimal treatment for age-related androgen deficiency in men. And the choice of drug should be approached strictly individually, taking into account the patient’s age, body mass index, the need to preserve spermatogenesis, hematocrit values and concomitant diseases.
Bibliography:
- Kalinchenko S. Yu. Age-related androgen deficiency in men // Medical newspaper. – June 28, 2002 – No. 49.
- Cunningham GR Management of male aging: which testosterone replacement therapy should be used? The Aging Male 2000;3:203-209.
- Jordan WP Allergy and topical irritation associated with transdermal testosteron administration: a comparison of scrotal and nonscrotal transdermal systems. Am J Contact Dermat 1997;8:108-13.
- Yu Z, Gupta SK, Hwang SS, et al. Testosterone pharmakokinetics after application of an investigational transdermal system in hypogonadal men. J Clin Pharmacol 1997;37:1139-45.
- Gorpinchenko I. I., Miroshnikov Ya. O. Erectile dysfunction. – Lviv: Medicine of the World, 2003. – 80 p.
- Duncan C. Gould Hypoandrogen-metabolic (HAM) syndrome: an important men's health issue//IMNG.– 2007. – V.2. – P. 174–178.
- Shabsigh R. Testosterone therapy in erectile dysfunction and hypogonadism//J. Sex. Med. – 2005. – V.2. – P. 785–792.
- Traish AM, Kim N. Weapons of penile smooth muscle destruction: androgen deficiency promotes accumulation of adiposities in the corpus cavernosum // Aging male. – 2005. – V.8. – P. 141–146.
The material was published in the specialized publication for doctors ProTest, issue 5, May 2021. When using materials, a link to the journal is required.