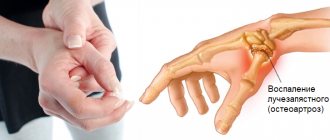
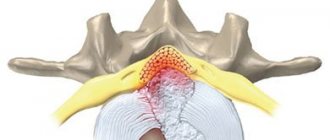
Brucellosis sacroiliitis
Brucellosis is characterized by the transient nature of tissue damage, which indicates the possible appearance of volatile arthralgias. In a number of clinical cases, persistent, long-term and, at the same time, difficult to stop inflammatory processes, expressed as synovitis or arthritis, can be observed.
Tandem with brucellosis can have different forms. Patients with this type of diagnosis complain of pain concentrated in the joint area, which can significantly intensify when performing various types of movements.
A conservative approach is required, involving a combination of specific therapy with the use of a complex of antibiotics, vaccination and the prescription of a number of medications.
Aseptic sacroiliitis
This is quite common for rheumatic diseases, in particular psoriatic arthritis.
X-ray examination makes it possible to make a diagnosis in the first stages of progression, which guarantees successful prognosis for recovery.
The primary stages involve a moderate widening of the joint gap, with unclear contours of the articulation.
The second stage involves a pronounced symptomatic picture, accompanied by a narrowing of the joint space and the formation of single erosions.
The third and fourth stages involve partial and complete ankylosis, respectively.
Symptoms of sacroiliitis of the presented type are mild. The pain can be of slight or moderate intensity, radiating to the thigh, increasing during a state of rest, and decreasing only with increased physical activity.
Diagnostic testing may require additional specific methods, which include laboratory testing.
Non-infectious sacroiliitis
Lesions of the sacroiliac joint of non-infectious origin do not belong to the concept of “sacroiliitis”, however, medical practice allows such a diagnosis.
Changes of this type may have a number of preconditions, the exact list of which is not easy to determine. Most likely, the pathologies are caused by previous injuries or systematic overload.
Among the complaints, spontaneous painful attacks are noted, localized in the sacral area. When performing movements, an increase in discomfort may be observed.
The main direction of treatment is the elimination of inflammation and pain. Physiotherapeutic procedures, taking a complex of medications and other solutions that can speed up recovery can be used as therapeutic methods.
Features of the course of pathological processes in children
At an early age, misdiagnosis often occurs with reference to an infectious lesion or acute appendicitis.
Children may experience symptoms of sacroiliitis such as:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Quite severe back pain radiating to the joints of the lower limb;
- spasms of the spinal muscle frame;
- moderate increase in body temperature.
In addition, it is worth paying special attention to the manifestation of symptoms characteristic of intoxication of the body, suggesting:
- chills;
- increased sweating;
- loss of appetite;
- headaches and disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus;
- slowing down of mental activity.
Preventive actions
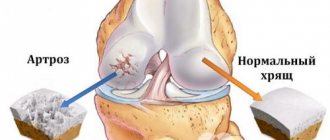
Considering that arthrosis almost cannot be completely cured, attention must be paid to the prevention of this disease, this requires an active and healthy lifestyle. You need to eat right so as not to provoke obesity and normalize metabolic processes.
During sedentary work, be sure to do regular warm-ups. The lumbar area should not be heavily loaded; if it is necessary to lift a load from the floor, then you need to squat, and not do it by bending your torso; when carrying, the load must be distributed evenly between both hands. Every day you need to do gymnastics to strengthen muscle tissue and prevent falls and back injuries.
Arthrosis of the coccygeal-sacral and iliac regions appears rarely and is expressed by moderate symptoms. The limitation of movement is not very noticeable, since these joints are inactive. The pain syndrome is usually tolerable and creates more discomfort than pain. Acute pain indicates the process of inflammation, which can be eliminated with the help of physiotherapeutic measures and medications.
However, during the destruction of the sacroiliac joints, the pressure on the hip joints increases, this is fraught with the development of coxarthrosis, and there may be other complications. Women often take the symptoms of this arthrosis as a sign of gynecological diseases. Therefore, to establish a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment for arthrosis of the coccyx, a comprehensive examination is required.
Diagnosis of sacroiliitis
The entire diagnostic technique of the disease in question lies in the study of clinical manifestations identified during the examination of the patient. A clarifying addition can be the results of additional research methods, the most important of which is considered to be x-ray.
The following diagnostic criteria are determined:
- intensity and nature of manifestation of existing symptoms;
- waking up at night due to discomfort;
- presence/absence of pain in the thoracic spine;
- study of existing inflammation;
- patient's medical history, taking into account various factors.
The main clinical signs remain:
- degree of limitation of mobility in the affected area;
- changes, violations of posture and the intensity of their manifestation.
Causes of arthrosis of the sacrococcygeal region
Arthrosis of the sacrococcygeal region is a pathological change in the articular surfaces of the fifth sacral and first coccygeal vertebrae. Normally, they are separated by an intervertebral disc, which lacks the nucleus pulposus. In essence, it is a thin cartilage pad, which is provided by synovial fluid through diffuse exchange with the articular endplates.
If the blood flow in them is disrupted due to the action of pathogenic factors, then gradual degeneration of the intervertebral disc occurs. It becomes thinner and falls apart. Constant contact of the surfaces of the first coccygeal and fifth sacral vertebrae begins. Cracks and chips form on their surfaces, which are filled with deposits of calcium salts. Sharp growths injure surrounding soft tissues. A secondary pain syndrome occurs against the background of the inflammatory process.
The main reasons for the development of arthrosis of the sacrococcygeal region are:
- uneven increase in physical and shock-absorbing load (for example, when performing unusual actions and movements);
- injury in the lower back (including a fall on the tailbone);
- decreased performance of the muscular frame of the lower back and sacrum in the form of a prolonged immobilized position of the body (for example, after a stroke or spinal fracture);
- metabolic and metabolic disorders, which can be caused by diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies;
- age-related changes in cartilage and bone tissues (osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, osteomalacia, etc.);
- anomalies of intrauterine development associated with splitting and defective formation of bone tissue of the last sacral and first coccygeal vertebrae;
- fusion of the first sacral and last lumbar vertebra (sacralization);
- curvature of the spinal column (pathological kyphosis, lordosis or scoliosis);
- pregnancy complicated by a negative medical history, polyhydramnios or multiple pregnancy;
- non-compliance by a pregnant woman with the recommendations of the attending physician regarding the choice of suitable shoes, adherence to a physical activity regimen, and wearing a prenatal bandage;
- excess body weight;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle with refusal of regular physical activity and sports;
- tumor and infectious processes;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
In women, arthrosis of the sacrococcygeal joint is most often provoked by pathological childbirth, during which the coccyx is maximally retracted posteriorly and in this case the integrity of the intervertebral disc separating it from the sacrum can occur. If the ligamentous apparatus is weak, this pathology can occur even in young women in labor. It is very important during the period of preparation for natural childbirth to undergo a course of manual therapy and physical therapy. This will strengthen the ligamentous apparatus of the spine and eliminate numerous problems with it in the future.
Degrees of sacroiliitis
The degree of pathology is determined taking into account the collected medical history, as well as the results of an x-ray examination, which make it possible to determine not only the focus, but also the intensity of the spread of inflammation.
Let's consider the main indicators characteristic of each degree.
1st degree of sacroiliitis
Symptoms are mild. It is impossible to track any changes in the image.
2nd degree sacroiliitis
The outlines of the joint are extremely indistinct, one might even say blurry.
There is significant compaction of bone tissue and numerous erosions.
3rd degree of sacroiliitis
The narrowing of the joint space noticeably increases, the signs of ankylosis intensify (loss of mobility).
With the purulent type of lesions, bone tissue loses density, creating the preconditions for the development of osteoporosis.
4th degree of sacroiliitis
The joint gap completely disappears, and the final fusion of bone tissue occurs, accompanied by destruction of their structure.
The outlines of the joint become extremely uneven.
General information
The coccyx is the lowest vertebral section; its shape is similar to a curved pyramid facing downwards. The coccygeal section is formed by five small fused vertebrae, different from the vertebrae of the other sections. All of them, except the first one, do not have processes. The first vertebra has two upper processes connected to the lower processes of the fifth sacral vertebra, and also has rudimentary longitudinal processes.
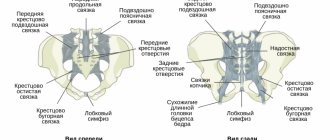
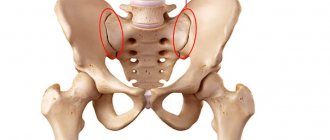
The sacrum is a bone formation, with its base facing upward and tapering at the bottom in the shape of a triangle formed by five vertebrae connected to each other. They have articular, longitudinal and spinous processes, but there is no interarticular tissue. The processes connect with each other, forming five ridges behind the sacrum. The scallop is connected to neighboring bones using joints:
- double sacroiliac joints connected to the iliac processes of the pelvis and the lateral surfaces of the sacrum;
- The coccygeal-sacral joint is located between the base of the coccyx and the apex of the sacrum;
- The sacrolumbar joint is located between the fifth lumbar vertebra and the base of the sacrum.
The coccygeal-sacral and sacrolumbar joints are modified vertebral discs that do not have pulpous fluid. Dense and practically immobile iliosacral joints have a flat shape, a slit-like opening and are located in a tight, stretched joint capsule.
Treatment of sacroiliitis
The main goal is to eliminate the cause of inflammation.
Working with the patient involves the use of mainly conservative methods, however, surgical interventions can also be used (for purulent forms), which involve opening the purulent focus and removing the affected tissue.
The methods used, the volume and duration of treatment procedures are determined based on the results of confirming the diagnosis, on an individual basis, taking into account the existing characteristics of a particular patient.
Drug treatment of sacroiliitis
Various groups of drugs are used, which may include painkillers, hormonal/non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), immunomodulators, as well as broad-spectrum antibiotics and chondroprotectors.
Particular attention should be paid to chondroprotectors, the action of which can accelerate regeneration and ensure high-quality restoration of articular tissues.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic techniques are used exclusively in conjunction with the use of medications. A complex of this kind makes it possible to limit changes occurring in the tissues of the joint, which also helps to maintain its mobility.
The acute and subacute period involves the use of techniques such as electrophoresis and ultraphonophoresis, implemented with the use of drugs.
Other procedures used during recovery include exposure to magnets, laser or infrared radiation, massages, and other specific therapies (mud therapy, steam therapy, etc.).
Healing procedures
When determining the symptoms of arthrosis of the coccyx, treatment is carried out only by conservative methods. The general course of therapy includes the following medications and physiotherapeutic measures:
- during severe muscle spasms, muscle relaxants are prescribed;
- for pain syndromes, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed; for severe pain and acute inflammatory reaction, blockade with anesthetics and corticosteroids is prescribed;
- Physiotherapy has an excellent effect - magnetic therapy, ultrasound therapy, ozokerite, amplipulse, laser treatment;
- Chondroprotectors help stop the destruction of cartilage tissue;
- taking hydrogen sulfide and radon baths;
- Massage allows you to relax muscle spasms, strengthen joints, and relieve pain;
- In the absence of contraindications, manual therapy is recommended.
Arthrosis of the coccyx can additionally be treated using different methods of reflexology, using acupressure, acupuncture, and hand pressure on reflex areas.
Inept actions can only cause harm, therefore this treatment must be performed only by a qualified doctor. For treatment at home, you can use the Kuznetsov applicator.
The pressure on the musculoskeletal system needs to be reduced. Avoid jogging and cycling; you cannot stay in one position for a long time. You can relieve the lumbar and sacral region with the help of bandages. To reduce stress, exercises are prescribed that can strengthen the muscular skeleton. This is rotation of the pelvis, turns, bends. They need to be done without jerking or sudden movements, at a slow pace. But strength exercises are prohibited. Some exercises have an effect that is similar to mobilization in manual therapy; bone cartilage is gently reduced:
- Lie on a healthy part of the body so that your knee can rest on the table. Then you need to press the palm of your hand on the ilium back and down.
- You need to get on all fours at the edge of the sofa, turning the healthy part of your body outward. Dangle your healthy leg slightly and relax it, while at the same time you need to tense the sore joint. Then you need to make springing movements with your healthy leg down.
Danger and forecasts
The disease extremely rarely acts as an independent pathology, being in most known cases a symptom. Lack of timely diagnosis can lead to a sharp deterioration in the mobility of the spinal column. There are real risks of achieving a situation of complete immobility and disability of the patient.
Timely elimination of pathologically dangerous causes for joint tissues and the use of correct therapy will lead to favorable prognoses.
The method and timing of treatment are determined taking into account the existing clinical picture and the characteristics of the individual patient.
ethnoscience
It is almost impossible to restore joints and mobility, completely relieve pain and the inflammatory reaction using traditional medicine recipes. But the involvement of this therapy in the general treatment course can help speed up recovery and get a positive effect in a short time.
As effective means of alternative medicine, thanks to which arthrosis can be cured, it is necessary to highlight:
- Honey and vinegar. The components are mixed in a 2:1 ratio, then rubbed into the affected area. For severe pain, the procedure is performed once an hour, for moderate pain - once every 4 hours. If relief occurs, you do not need to stop treatment immediately; you need to perform several more procedures to consolidate the effect.
- Tincture. The most effective remedy for external use during the inflammatory process in the articular processes is an infusion based on potato sprouts and alcohol. To get an effective result, the tincture must be applied daily to the affected area.
- Eggshell. This is an excellent recipe for strengthening bone tissue. You need to eat 1 tsp every day. pre-ground egg shells.
- Mumiyo. To restore joints, it is recommended to take mumiyo solution every day.
- Vishnevsky ointment. Moisten a small piece of cloth with this product, apply it to the affected part and secure it with an adhesive plaster. Do this compress before going to bed. Usually, several procedures can relieve the inflammatory process, which is why this method is one of the best.
Despite the fact that folk recipes are absolutely natural and quite safe, in certain cases their use can only aggravate the patient’s condition.
It is recommended to use homemade medications only after consulting a doctor.
Prevention of sacroiliitis
Everyone knows that it is worthwhile to treat any disease in a timely manner, at the initial stages of its progression, or better yet, long before its onset, which can be real thanks to the observance of preventive measures, which usually include:
- monitoring general health, monitoring well-being;
- timely, complete treatment of various types of infections;
- protecting the body from overheating/hypothermia;
- creating conditions for strengthening and maintaining an optimal level of immunity.
Remember the benefits of leading an active lifestyle, ensure a balanced daily diet and enjoy all the pleasures of life without having to deal with various diseases.
Avoid self-medication and if any symptoms appear, please seek qualified medical help.