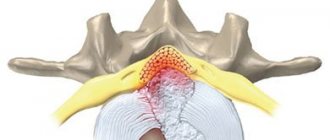
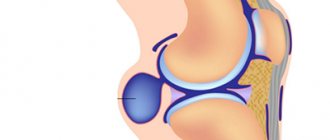
Inflammations localized in the joint of the lower extremities can provoke the formation of a neoplasm in the popliteal tissues, which is commonly called a Baker's cyst. Clinical manifestations of the neoplasm can be traced only after the cyst reaches a certain size, at which nerves and blood vessels are compressed.
Identification and approval of the diagnosis is carried out based on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies. Often the pathology is recorded in the fair sex, but it can also be observed in men.
What is a Baker's cyst?
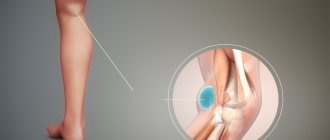
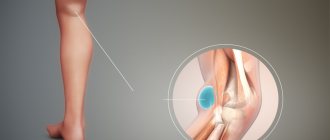
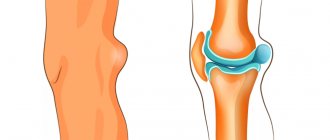
Baker's cyst is a pathological neoplasm that involves the accumulation of varying volumes of fluid in the synovial sac, which is localized on the back of the knee joint.
The morphological signs of the existing pathology allow us to assert the benign nature of the formation, without classifying it as a cancerous tumor.
Popliteal synovial cysts most often occur when the patient has an intra-articular disease, such as osteoarthritis. The formation can have a different size (from 2 mm or more) and occurs at any age.
Drugs for popliteal formation
Baker's cyst
Baker's cyst in the popliteal region is a secondary type of disease that arises from pathologies that develop against the background of underlying joint damage. The most common cause of cyst formation is injuries to the knee joint of varying severity. In addition, the appearance of a tumor is associated with such factors as:
- Constant heavy loads on the knee.
- Overweight.
- Joint diseases: arthritis, arthrosis, gout, rheumatism.
At risk are athletes, people engaged in heavy physical labor, carrying heavy objects, elderly people and those suffering from obesity.
For Baker's cyst, the following medication groups are used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Aspirin;
- "Diclofenac";
- "Dimexide";
- "Ketoprofen";
- "Meloxicam";
- "Indomethacin";
- "Nimesulide".
- "Dexamethasone";
Baker's cyst symptoms
According to average statistical data, Baker's cyst is accompanied by the manifestation of a symptomatic picture of meniscal or chondral disorder, which usually includes:
- pain localized in the knee or popliteal fossa, occurring both when performing various types of loads and in a calm state;
- extraneous clicks, crunches inside the joint;
- feeling of stiffness when moving.
- pain;
- swelling of the arteries of the popliteal region;
- loss of joint functionality due to mechanical blocking of its mobility.
The actual symptoms of a Baker's cyst, as such, appear extremely rarely and are often associated with progressive growth and an increase in the size of the tumor (from 3 cm in diameter). These include:
When a Baker cyst reaches a noticeable size, it can be noted that the formation often has a hard structure when the knee is fully extended and softer when the leg is bent. This phenomenon is called “Foucher's sign” and is observed in a situation where the cyst is compressed between muscle tissue.
It is also worth paying attention to the fact that patients with this diagnosis may experience signs and general symptoms of thrombophlebitis, which include pain and mild swelling of the lower extremities.
Physical exercise
Exercises that strengthen the muscular system will help improve the patient’s condition. At the same time, it is necessary to avoid excessive efforts that can cause harm. Daily gymnastics is enough, which does not require significant energy expenditure. Treatment at home for the disease is recommended to be combined with exercises developed by Professor Bubnovsky:
- Firmly fix one end of the resistance band at knee level to some support. Insert your foot into the loop of the expander, move away from the support a few steps, pulling the tape. When you feel tension, you need to straighten and bend your leg, overcoming resistance.
- Place weights on your ankles and sit in a chair. You need to straighten your legs straight and hold them for one minute, fixing the position. After this, the sore leg should be bent at an angle of 45 degrees and held for half a minute.
- Sitting on the floor, you need to bend your healthy leg at the knee, pressing the limb to your chest. Straighten the sore leg on which the weight is placed and lift it above the floor, fixing it for 10-20 seconds. At the same time, the back should remain straight.
It is recommended to perform all exercises in 3 sets of 10 times.
Water aerobics will also improve the patient’s condition.
Pathogenesis of Baker's cyst
The pathogenesis of Baker's cyst under the knee is based on the non-standard anatomical location of the articular tissues, as well as the popliteal fossa.
Statistics show that in more than 40% of cases, when examining healthy people of different ages and genders, there is an intertendinous mucous bursa between the tendons of their muscular frame of the knee joint, which is not a pathology, but is considered an acceptable deviation from the norm.
The progression of joint inflammation and the formation of fluid in the joint tissues lead to an increase in the size of the cyst. The presence of a valve mechanism allows liquid to leak into its cavity, but does not allow reverse flow to occur.
Surgical intervention
The operation is carried out in the absence of effectiveness from physiotherapeutic procedures and the use of pharmacological drugs. In some cases, conservative treatment is not even considered by doctors, and the patient is immediately prescribed surgical intervention. The reason for this is the following diagnostic results:
- significant size of the popliteal hernia;
- compression of large blood vessels by the cyst;
- knee meniscus tear;
- severe limitation in movements;
- rapid increase in tumor size;
- regular exacerbations and relapses of pathology.
During the operation, only local anesthesia is used. After soft tissue incisions, the Baker's cyst is excised with special surgical instruments. During the manipulation, an arthroscope is used, which is a thin tube with a diameter of several millimeters. The device is equipped with a miniature video camera and a device for illuminating the surgical field. After the popliteal hernia is removed, stitches are placed in the areas where the tendons connect to the joints.
The duration of the operation varies depending on the number of dystrophic-degenerative changes that have developed, but the manipulation rarely takes more than 30-40 minutes. The operated knee is immobilized using a cast or a tight bandage. As a rule, surgical intervention does not require the patient to be in a hospital during the rehabilitation stage.
If treatment of a Becker cyst with conservative methods is ineffective, surgery is performed.
Baker's cyst classification
Baker's cyst has several variations in manifestation and development, which makes it possible to classify cases according to their location in the popliteal fossa and distinguish two types:
- typical - located between the muscles of the knee joint;
- atypical – posterolateral cyst.
In addition, it is worth noting that Professor Raushing’s research made it possible to prove the existence of two forms of cysts:
- symptomatic – is a symptom of a pathogenic joint disease;
- idiopathic - a cyst in which no pathological articular processes are detected.
The benefits of ointments
Ointments for Baker's cyst are also considered very effective. They are prepared from medicinal herbs and folk remedies.
Bee glue cream with calendula
Use a remedy to relieve inflammation and resolve formation. Treatment is carried out at home. Pound the calendula flowers thoroughly and pour in goose fat (it needs to be melted). Add propolis to the heated mixture. You need to stir everything until the propolis is completely dissolved.
The ointment is applied to the cyst after cooling.
Rub it very thoroughly. Then they wrap it in warm material (shawl, scarf) and leave it for several hours.
Hemlock ointment
It is considered a very powerful tool. The effect of the ointment is aimed at reducing the size of the cyst, eliminating pain and other unpleasant signs of the disease. This product is poisonous, so it should only be used under the supervision of a doctor.
Ointment from marigold flowers
It is advisable to use any remedy after consultation with your doctor. This approach will help prevent the development of complications and rupture of the tumor.
Diagnosis of Baker's cyst
Clarification of the clinical picture is realized using methods such as:
- laboratory blood test (clinical and biochemical analysis;
- instrumental research methods.
The process of diagnosing Baker's cyst involves a differential approach that excludes the possibility of such pathologies as:
- popliteal artery aneurysm;
- soft tissue tumor;
- meniscal cyst;
- hematoma of various origins;
- thromboembolism;
- seroma.
In order to confirm existing symptoms, instrumental research methods such as:
- radiograph;
- arthrography;
- ultrasonography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Let's look at each of the methods used in more detail.
X-ray examination
X-ray studies are indicated for use in the initial stages of assessing the patient’s condition, since they can be used to identify other pathological processes accompanied by the presence of popliteal neoplasms. Among these diseases:
- arthritis of various groups;
- free bodies of cartilage and bone type.
Arthrography
Arthrography involves intra-articular injection using a high-contrast agent with mandatory mobilization of the limb. The use of this diagnostic method can improve the effectiveness of x-ray examination.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
Ultrasound examination falls into the category of preliminary diagnostic techniques for Baker's popliteal cyst.
Among the key advantages of the presented method are:
- availability;
- non-invasive;
- safety.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI is a key diagnostic method in identifying Baker's cysts and differentiating them from other pathological phenomena.
Using MRI, it is possible to fully cover and study the entire existing spectrum of pathological processes.
When should you see a doctor?
To find out whether you can use certain medications to treat a cyst, you need to consult a specialist. He will conduct an examination. will select a course of therapy. Typically, Baker's cyst acts as a consequence of pathologies such as injury to tendon cartilage, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis.
Seeing a doctor
Also, contacting a specialist is considered necessary if a tumor rupture is suspected. Consultation is also needed if complications develop. Rupture of the cyst is dangerous due to the penetration of fluid into the calf muscle. The following symptoms occur:
- Swelling, redness of the dermis;
- sensation of fluid inside the calf muscle fibers;
- acute pain. It is triggered by the penetration of fluid into the muscle, the development of inflammation. Possible thrombosis.
Baker's cyst of the knee joint is considered a rather serious pathology. It is very important to detect it in a timely manner and take appropriate measures. It is better to prevent the cyst from rupturing than to then treat its complications.
Baker's cyst treatment
Treatment of Baker's cyst involves the use of both conservative and radical methods based on orthopedic and traumatological treatment.
The key purpose of conservative treatment methods is the implementation of therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating the pathological process. Among the main approaches in the treatment of conservative therapy are such approaches as:
- maximum relief of the load on the affected joint;
- prescription of physiotherapeutic treatment;
- taking a puncture followed by evacuation of the contents of the cyst and administration of specialized drugs.
The determination of the method of therapeutic treatment is determined by such criteria as:
- the degree of inflammation present;
- volume of accumulated liquid;
- the exact location of the pathological cavity.
In order to treat Baker's cyst as effectively as possible, it is recommended to use an integrated approach and combine drug therapy with physical therapy (physical therapy) and other methods.
Drug treatment for Baker's cyst
The use of drugs in the treatment of Baker's cyst is used to enhance the results of conservative methods and can reduce or completely eliminate inflammation inside the joint.
The following groups of drugs may be prescribed as drug treatment:
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- painkillers;
- antispasmodics;
- vitamin and mineral complexes;
- hormonal;
- chondroprotectors.
Particular attention is paid to the group of chondroprotectors that help accelerate regeneration processes. Artracam is considered to be one of the most effective drugs in this group.
IMPORTANT! Drug treatment should be carried out exclusively under the supervision of the attending physician, taking into account the individual characteristics of the clinical picture of a particular patient. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Physical therapy (physical therapy) as a method of treating Baker's cyst
In order to restore the functionality of the knee joint, therapeutic physical education is used as a component of complex treatment.
Performing a number of exercises allows you to speed up the rehabilitation process, the duration of which is determined by the characteristics of the body. Before starting classes, consultation with a treating specialist is required.
Complexes of exercise therapy are based on certain principles and pay special attention to muscle groups such as:
- calf;
- quadriceps;
- gluteal
Among the general recommendations for performing exercises are:
- Be sure to warm up your muscle fibers before exercising and do quality stretching.
- Avoid using gymnastic exercises with increased intensity.
- Limit your loads, making sure to eliminate the possibility of muscle fatigue.
- Carefully prepare the location of the classes by preparing the necessary clothing, surface and equipment.
Surgical intervention
Radical therapy is used in situations where conservative treatment methods are not effective enough or are not applicable at all in the current situation.
Surgical intervention involves an open operation, the key task of which is to isolate the tumor from the surrounding tissue.
Despite the obviously successful solution to the problem, the result of surgical intervention is not in all cases capable of producing a guaranteed positive result. The recovery period may be complicated.
Home treatment methods
• 30g of the root part of elecampane is filled with water, at the rate of 3 liters of water for this amount of substance, adding 1 tbsp. l. yeast. Infusion occurs for 48 hours. The liquid is placed in a place protected from light rays. Take 0.5 cups before meals 4 times a day. The anti-inflammatory effect of treating Baker's cyst with a folk remedy will reduce the active development of the process.
There are alternative treatments for Becker cysts. These treatment programs include Sujok therapy, which involves influencing certain points located on the hands. Reflexology, manual therapy, kinesitherapy and psychocorrection can also be used. However, the use of alternative methods is permitted only after approval by the attending physician.
In some cases, the formation may disappear on its own. But more often physiotherapeutic or surgical treatment is required. Obviously, for this a person goes to the hospital. An alternative to the hospital is to treat small cysts at home. Some physiotherapeutic techniques can be used at home, but more often in such an environment traditional methods of treating Baker's cyst are recommended.
Compress to relieve inflammation
The pathological formation itself is most often not threatening, and usually goes away without treatment after 2-3 years when the load on the joints is reduced.
There are still complications. Firstly, there is pain and tension when moving, joint blocking, and the development of varicose veins due to stagnation of blood in the veins. Sometimes the membrane may rupture and fluid may leak under the skin.
Home therapy is aimed precisely at alleviating the condition, designed to prevent complications, discomfort and cure the knee completely.
X-ray for Baker's cyst
The diagnosis of the disease should be carried out by a specialist with a special medical education - this is an indisputable statement. Especially if it concerns a child.
Treatment with traditional methods for Baker's cyst of the knee joint will be more effective if it takes place in parallel with medical prescriptions and under the supervision of a medical professional.
Individual intolerance to any components in folk recipes cannot be ignored.
When preparing mixtures, it is important to use a quantitative formulation. Some components in excessive doses turn from drugs into poisons.
Methods such as external procedures and taking internal healing tinctures can be combined.
Clove decoction for compresses
Mix one tablespoon of dried elderberry and raspberry leaves and steam with 100 ml of boiling water. Leave for half an hour with the lid closed. Place the steamed leaves on a waterproof material and apply to the affected area for at least two hours.
Celandine lotions help to cure many ailments associated with the knee joints. A medicinal lotion is prepared according to the principle of the first recipe.
For this compress you need pre-crushed dandelion root and spicy cloves. A tablespoon of cloves is steamed in 100 ml of boiling water for 10 minutes, but the root should be boiled in 150 ml during this time, after which these products are combined and a spoonful of medical alcohol is added. Wrap the cloth soaked in the composition around the knee, insulate it, and keep it there for 3 hours every day.
Mix 250 gr. Bile and 160 ml of camphor alcohol. The mixture can be stored in the refrigerator in a glass container. Place a cloth soaked in the mixture behind the knee, cover with compress paper, and insulate it. Time – 4 hours every day for a month.
Medicinal ointments
Ointment for the treatment of Baker's cyst
A good way to cure growths, lumps and cysts is ointments based on medicinal herbs and other components.
Calendula and propolis. Crush a tablespoon of marigolds and pour in goose fat. Place in a water bath and stirring continuously, add propolis until completely dissolved. Do not allow it to boil, as the beneficial properties of propolis disappear with strong heat.
Regular unrefined sunflower oil treats Baker's cyst well. Warm oil compresses are applied twice a day - morning and evening.
Grind fresh marigold flowers and mix with melted badger fat in a 1:1 ratio. Lubricate the cyst site at night.
Apple cider vinegar and honey for compresses
It is more effective to treat Baker's cyst with external medications in combination with internal cleansing.
The same marigolds from the home flower bed are taken in the form of a decoction. To do this, boil a tablespoon of chopped flowers for 5 minutes in 0.5 liters of water and leave for 40 minutes. Take 150 ml before meals 2 times a day. After 20 days of use, take a break for a week. Three such courses can be conducted.
Golden mustache is infused with vodka. A three-liter jar is filled three-quarters with green mass and topped up to the brim with vodka. The mixture is ready for use after 20 days. Take 2 tablespoons twice a day. The herb from the tincture is used as a compress.
Herbal tea, which includes two parts of St. John's wort and one each of birch buds, nettle, lingonberry, mint, knotweed and plantain, is drunk three times a day, one hundred grams. Prepare as an infusion: 1 tbsp. spoon of mixture per 300 ml of water.
Apple cider vinegar in combination with honey helps reduce the amount of fluid in the cyst bursa. Use 3 times a day as follows: a tablespoon of vinegar, a teaspoon of honey in a glass of warm water.
Possible complications if Baker's cyst is left untreated
Uncontrolled development of a popliteal Baker's cyst can cause a large number of complications, the most likely of which are:
- development of an infectious disease;
- rupture of the cyst membrane;
- forceful effect on the neurovascular bundle, leading to thrombophlebitis.
In rare cases, untreated Baker's cyst under the knee can cause compression of the popliteal vein or even an artery. If a complication of this type is detected, urgent hospitalization and surgical intervention are indicated.
Treatment with ointments, gels, balms and creams
In the treatment of Becker cysts, external agents are actively used to stop the inflammatory process at an early stage of the pathology. As a rule, the doctor prescribes them as part of complex therapy along with glucocorticosteroids, NSAIDs, and chondroprotectors. The first choice drugs are external anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Voltaren gel,
- Fastum gel,
- Indomethacin ointment,
- Piroxicam,
- Ketonal.
When diagnosing a cyst pressing on small and large blood vessels, patients are recommended to use external agents that improve microcirculation - Indovazin, Troxevasin, Lyoton. To eliminate pain, swelling in the joints, and stiffness of movement, frequent rubbing with creams and balms with bear fat, golden mustache, shark fat, cinquefoil, and horse chestnut is used.
Disease prevention
The best treatment for any pathological condition is to prevent its occurrence.
In order to prevent the formation of a Baker's cyst, the following preventive measures should be followed:
- prevention of injuries to the joints of the lower extremities;
- tracking optimal body weight;
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- balanced diet;
- timely treatment of pathological processes found in articular tissues;
- the use of specialized structures to reduce the load on the knee joints.
Having information about what a Baker's cyst is, pathologists can promptly recognize it and begin its treatment, preventing the likelihood of its rupture.
Taking medications
Take a pain reliever. You can use the product that is available at the pharmacy without a prescription. The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is allowed. The following are considered the most effective:
- Aspirin.
- Ibuprofen.
- Naproxen.
- Acetaminophen.
These products should be used with caution. It is worth following the recommendations from the notation. These medications help relieve inflammation and relieve pain. Take painkillers with meals. Be sure to wash them down with water.
Using Aspirin
Children and adolescents are not recommended to use Aspirin. This medication can affect important organs (brain, liver). If a child has influenza or chickenpox, Reye's syndrome may develop.
Before taking NSAIDs, consult your doctor. Applies to subjects who have impaired functioning of the following organs: stomach, kidneys, liver.
It is also possible to treat pathological Baker's cavity with folk remedies. There are quite a lot of them and most of them have been verified by our ancestors.