Highly accurate diagnostics is the basis for effective treatment with lasting results. In modern medicine, methods are increasingly in demand that exclude the effects of ionizing radiation, the high accuracy of which is based on detailed and high-quality visualization of internal organs and body systems. These types of safe diagnostics include ultrasound and MRI. The choice of method depends on the competence of the doctor, who takes into account:
- anatomy of the organ or area of the body that is being examined;
- symptoms;
- health and characteristics of the patient - age, body weight, mental state, presence of metal implants.
The doctor has to choose what is better - ultrasound or MRI for each individual patient. And the main selection criterion is the answers to the questions: what is more informative when examining, for example, hollow organs (intestines, stomach, etc.), and what is more accurate when examining soft tissues or ligaments.
Differences and common principles of operation
The difference between ultrasound and MRI lies in the differences in the principles of their effects. In the first case, the ability of high-frequency sound waves to penetrate through body tissues and be reflected from them is used. Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the creation of resonance by a magnetic field.
The resulting image in the scale required for study is transmitted to the monitor screen during the examination using both methods.
Make an appointment now!
How to sign up for diagnostics?
You can book a time for any type of scanning through the consulting service of the “Unified Recording Center” in St. Petersburg. Choose a procedure, compare medical institutions by ratings, locations and prices, and reserve an appointment. The telephone number for registration is located at the top of each page of the portal. Book a test and receive a special discount from the service for the selected type of screening.
Pelvic organs
Ultrasound examination or MRI of the pelvis - which is better? Here the choice depends on whether a woman or a man is undergoing pelvic examinations. Transabdominal or transvaginal examination using ultrasound equipment is indicated for women even during pregnancy at different stages.
The male pelvis, which contains organs such as the prostate, urethra, and bladder, is preferably examined using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. Ultrasound or MRI of the prostate - which is better? The experience of doctors says that prostate studies using magnetic resonance imaging are more informative than ultrasound.
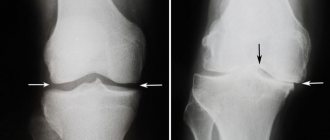
MRI or ultrasound of the knee joint: which is more informative and when is it better to choose?
Only the attending physician at the orthopedic department can choose the diagnostic method that is right for you. If there is pain or dysfunction of the joint without an obvious reason, a medical professional should check the condition of the bones and tissues. Ultrasound and radiography are usually prescribed. Both of these tests can be replaced by one thing - a magnetic resonance examination, which visualizes the hard and soft areas of the joint perimeters. If there is no need for an X-ray assessment, doctors prefer ultrasound.
It is recommended to undergo an ultrasound session for inflammatory reactions, and an MRI examination to detect the formation of tumors and for injuries. A tomogram is prescribed for patients who have limitations in undergoing other examination techniques that use radiation exposure.
According to a survey among medical representatives, which is more informative than MRI or ultrasound of the knee joint, it became known that layer-by-layer examination shows the highest results if surgical intervention is necessary for arthroscopy or endoprosthetics. With a conservative method of treatment (without surgery), an ultrasound examination is prescribed. This simple technique will help you determine the qualifications and experience of the doctors in the clinic where you seek help. If you are sent for an X-ray without diagnosing previous injuries, then you can safely say that the doctor is not competent or indifferent, and when the doctor writes out a referral for an MRI without an established reason for the formation of painful sensations, they want to extract more money from you.
Kidneys
Kidney ultrasound is prescribed to detect changes in the shape and size of organs. For a more detailed examination, kidney diagnostics using magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed.
Ultrasound examination is more often used to diagnose organ dysfunction and disorders in the structure of various tissues, and is effective for identifying internal bleeding and neoplasms.
Magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed for a more detailed study; with this method, computer processing of the results is carried out, which reduces the impact of the human factor on the conclusions.
Osteodensitometry. Densitometry
Bone densitometry is a procedure for measuring bone density. There are two main methods of osteodensitometry:
- ultrasonic,
- x-ray
Osteodensitometry (densitometry) allows you to reliably assess the condition of bone tissue. Densitometry is an absolutely painless procedure.
The result of osteodensitometry is displayed in the form of a visual graph
We recommend osteodensitometry for diagnosing osteoporosis . X-ray osteodensitometry is a highly effective study because sees the slightest changes in bone density.
The density of the studied bones is assessed in a numerical format, so during the treatment we can always check:
- Are we doing enough for the patient?
- bone density increases or decreases.
We recommend consulting with your doctor if you suffer from arthritis or excess weight. This may affect the results of the study.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gonarthrosis depend on the degree of tissue damage. The most noticeable and pronounced is pain. In the initial stages of development, it is represented by mild discomfort after excessive stress on the knee (for example, climbing stairs with a heavy object in your hands or long walks). After rest, all unpleasant sensations disappear.
Subsequently, the pain becomes stronger and begins to occur after the usual exercise, intensifying towards the end of the day. Simple rest is not enough to quickly relieve symptoms. In the final stages, the knee hurts constantly, and any movement aggravates the problem.
Another characteristic sign of gonarthrosis is limitation of movements. Stiffness first appears only in the morning and is associated with cartilage damage. Further restrictions are associated with the proliferation of osteophytes. As the disease progresses, the range of motion becomes less until complete ankylosis.
At this time, signs of damage that are clearly visible from the outside appear: knee deformation and severe lameness. Deformation occurs due to changes in the outlines of the bone heads, as well as the appearance of osteophytes. Subsequently, muscles and ligaments are involved in the process, which further changes the contours of the joint and the entire leg.
Lameness, like pain, occurs gradually. At first it is associated exclusively with pain, the person is forced to spare the leg. The situation gets worse as stiffness and deformity increase. In the later stages of gonarthrosis, a person cannot walk independently.
How is it carried out?
Before performing an MRI, the doctor finds out what the patient’s weight is, whether he has claustrophobia and other contraindications, and whether he needs to take sedatives.
Children are often given sleeping pills because they cannot remain motionless for a long time, and to obtain reliable results it is necessary that the affected joint be securely fixed.
Next, the patient is told how the procedure will take place, after which he removes all metal objects from himself and the examination begins. The patient lies down on the retractable table of the tomograph, his knee is additionally fixed to ensure maximum immobility.
During the procedure, the tomograph makes characteristic clicking sounds; this is absolutely normal. If extraneous sounds disturb the patient, he can wear special noise-absorbing headphones before starting the procedure.
The duration of a knee MRI depends on the type of scanner and whether contrast is used during the procedure. Tomography of the knee without contrast takes 30-40 minutes, with contrast – 40-60 minutes.
After the MRI is completed, the patient can return to his business. The doctor's report and tomography results can be obtained within a few hours or the next day. Photos can be received in printed or electronic form.
An integrated approach to treating fluid in the knee
After a comprehensive examination of the patient in our clinic, he is prescribed individually selected complex therapy, which includes advanced Western and traditional Eastern methods of treatment:
- diagnostic and therapeutic arthroscopy and arthrocentesis; when exudate accumulates in the joint, this is the most effective procedure;
- prescription of the latest generation of drugs;
- reflexology - acupuncture, cauterization with wormwood cigarettes, acupressure, etc. - our doctors were trained in clinics in China and Tibet and learned to treat patients using Chinese methods;
- PRP therapy is the latest Western technique using the patient’s own platelets; promotes rapid elimination of inflammatory processes, prevents the development of contractures;
- physiotherapeutic procedures – selected strictly individually according to the patient’s condition;
- herbal medicine – treatment with herbs that partially replace medications in order to reduce their dosage;
- physical therapy, including kinesitherapy - the latest techniques that allow you to quickly restore knee function and prevent the development of contractures.
Do not tolerate joint pain, seek medical help at the Paramita Clinic. We will cure you, relieve you of pain, discomfort when walking, and restore the joy of life!
Sources:
- Bazarny V.V. Synovial fluid. Ekaterinburg, USMA, 1999. - 62 p.
- Panasyuk E.Yu., Tsvetkova E.S., Olyunin Yu.A., Smirnov A.V. Arthroscopy in the diagnosis of gonarthrosis. Scientific and practical rheumatology 2000, No. 2, p. 12–17.
- Beloenko E. D. Differential diagnosis and treatment of chronic synovitis of the knee joint: abstract. dis. for the scientific competition. Ph.D. degrees honey. Sciences: spec. 14.00.22 “Traumatology-orthopedics” / E. D. Beloenko. – M., 1983. – 28 p.
- Edelson R, Burks RT, Bloebaum RD, Short–term effects of knee washout for osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med 1995, 23(3), 345–9
- Paus AC, Pahle JA Arthroscopic evaluation of the synovial lining before and after open synovectomy of the knee joint in patients with chronic inflammatory joint disease. Scand J. Rheumatol. 1990, V. 19, p. 193–201.
Themes
Joints, Pain Date of publication: 01/27/2020 Date of update: 02/02/2020
Reader rating
Rating: 4.25 / 5 (4)
Consequences and complications
Many people think that gonarthrosis is just a crunch and periodic pain in the knee. In fact, without treatment, this disease brings a lot of suffering and turns a person into a disabled person. In the final stages, a person expects:
- severe deformation of the leg and its shortening;
- inability to bend and straighten the knee;
- lesions of other parts of the musculoskeletal system: hip joint, spine, ankle;
- inability to move independently;
- constant intense pain in the knee.
You can prevent these problems if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and thoroughly follow his recommendations. In this case, the process can be successfully slowed down and even reversed, especially at the first stage of development.
Prevention
Preventing joint diseases is not difficult. If you follow the rules, the question of how to treat gonarthrosis is unlikely to become relevant. Help keep your joints healthy:
- moderate physical activity: hiking, swimming pool, gym, etc.; the main thing is not to strive for records and titles, since professional sport is not at all useful;
- minimum stress and good sleep;
- balanced and rational diet with sufficient vitamins and microelements;
- weight within normal limits;
- minimum of harmful factors at work: people prone to developing arthrosis should avoid carrying heavy objects and standing on their feet for long periods of time;
- good, comfortable shoes (preferably orthopedic);
- regular comprehensive examination of the body, even if you feel well.
The same rules are relevant for people already suffering from arthrosis, as they help slow down the progression of the disease.
Diet
Following a diet for gonarthrosis helps reduce the risk of inflammation in the joint and salt deposition, and also helps to reduce body weight and reduce the load on the knee. Doctors recommend adhering to the following nutritional principles:
- a diet balanced in fats, proteins and carbohydrates;
- control of food calories: if you are overweight, you should reduce your intake by 15-20% of the standard requirement;
- sharp limitation of excessively fatty, spicy, salty foods, canned food and products with artificial flavors;
- complete exclusion of alcoholic beverages and soda from the diet.
Vitamins of all groups and microelements should be present in sufficient quantities in food. Particular attention should be paid to products with a high collagen content: jellied meat, jelly, aspic. It is a natural chondroprotector and stimulates the restoration of cartilage tissue. Omega-3 acids have a similar effect, which, moreover, can stop inflammatory processes. They are found in large quantities in fatty northern fish.
Kinds
Depending on the cause of the disease, osteoarthritis of the knee joint can be:
- primary: occurs on its own against the background of increased load or failure of cartilage tissue;
- secondary: appears as a complication of other diseases or injuries; Within this type, specific varieties are distinguished: gouty, post-traumatic, etc.
There are also unilateral (affecting only the right or only the left knee) and bilateral gonarthrosis.
Electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography (Echo-CG) in rheumatology
There is a well-known medical saying: “rheumatism licks the joints but bites the heart.” If you suspect rheumatic diseases, we will definitely suggest that you check the structure and function of the heart. We largely rely on Echo-CG data when prescribing treatment. Your doctor may recommend performing both an ECG and an Echo-CG; These studies do not replace, but complement each other well. Section of our website about inflammatory heart diseases
Watch our video about diagnosing the heart, blood vessels and external respiration function
Electrocardiography (ECG) helps to assess disturbances in the electrical activity of the heart, recognize disturbances in the rhythm and conduction of electrical impulses, and indirectly judge the condition of the heart muscle.
The condition of the heart valves and heart muscle is most easily examined using ultrasound - Echocardiography (Echo-CG). An echocardiograph (ECHO-CG) sees heart defects and inflammatory changes (carditis, pericarditis).
Echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart). The operation of the valves is visible: the valves open and close
Contractions of the heart muscle occur at the command of a special system of nerves - the conduction system of the heart. Electrical impulses passing from the conduction system to the heart muscle cause it to contract rhythmically and pump blood.
Causes
All reasons for the development of gonarthrosis can be divided into several groups:
- associated with severe damage to parts of the joint: intra-articular fractures;
- meniscus damage;
- dislocations;
- sprains;
- joint surgery;
- inflammatory processes and their consequences (arthritis of various origins);
- increased body weight;
- congenital connective dysplasia;
- diabetes;
The presence of articular pathology in parents or close relatives also increases the chance of developing gonarthrosis.
Advantages of ultrasound over x-ray
X-ray diagnostics is widely used in traumatology and allows identifying bone tissue pathologies. However, ultrasound allows you to assess not only the condition of bones, but also cartilage, articular surfaces, synovial bursa and ligaments. Under ultrasound control it is possible to perform punctures and other therapeutic procedures.
The main advantage of ultrasound examination methods is their complete harmlessness to the body. While X-rays are not recommended for pregnant women due to the impact of ionizing radiation on the fetus. In addition, it is necessary to strictly take into account the radiation exposure children received during diagnosis.
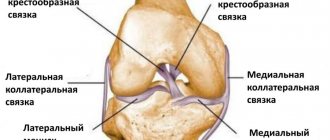
Features of the structure and functioning of the knee
The knee can withstand the heaviest loads. Therefore, in case of injuries, including microtraumas caused by lifting weights or working on the knees, it suffers first.
The knee joint connects the femur and tibia, as well as the patella - a flat, convex bone that prevents lateral displacement of the bones. The inner articular surface is covered with cartilage tissue and surrounded by a synovial membrane that produces fluid. A healthy person contains no more than 2–3 ml of synovial fluid, which performs the following functions:
- shock absorption - as a lubricant for the sliding of bones;
- nutrition - it contains nutrients necessary for cartilage tissue;
- preventing thinning and destruction of bones.
The structure of the knee joint