directions
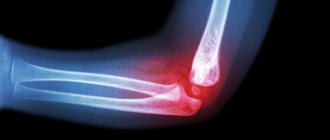
The elbow joint is a rather vulnerable place, subject to frequent loads, injuries and disorders. It has a complex anatomical structure and consists of the brachioradial, humeroulnar and radioulnar joints, connected in one capsule.
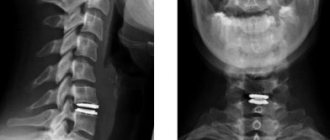
A traumatologist is mainly treated with dislocations, bruises, fractures of the elbow joint and with unpleasant symptoms that may be harbingers of diseases and pathologies. To determine the nature and extent of the damage and to make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an x-ray of the elbow joint.
Currently, work is underway on the website to change the price list; for current information, please call: 640-55-25 or leave a request, and an operator will contact you.
Prices for services
- X-ray of the forearm, ulna and radius in direct posterior projection 900a
- X-ray of the elbow joint in direct posterior projection 900a
- X-ray of the elbow joint in axial projection 900a
- X-ray of the elbow joint in lateral projection 900a
- X-ray of the forearm, ulna and radius in lateral projection 1350a
The information and prices presented on the website are for reference only and do not constitute a public offer.
Related and Complementary Research Methodologies
Modern digital X-ray equipment provides doctors with images on the screen of a connected computer, on paper or digital media.
At the same time, radiologists say that pathological conditions of the joints cannot always be fully displayed on an x-ray, so other examination methods are used for them:
- computed tomography of joints;
- ultrasonography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Each of the above methods demonstrates to specialists certain tissues, including the soft tissues of patients - muscles, tendons and ligaments. The high accuracy of these diagnostic methods makes it possible to mutually complement information about the pathological aspects of various periarticular tissues.
To analyze the cavities inside the joints, it is necessary to puncture the synovial capsule. The procedure is carried out with the collection of joint exudate. Impurities are easily detected in this joint fluid, which may indicate a number of diseases. These impurities are studied in more detail in laboratories under a microscope, and on the basis of such conclusions, experts draw conclusions about the infectious or non-infectious nature of the disease.
If it is necessary to study the structure of the joints, another diagnostic technique is used - arthroscopy.
Arthroscopy is performed through two punctures, into the first of which an arthroscope with a special camera is inserted, and in the second, the necessary manipulations are performed with special instruments.
In this case, such a procedure is very informative and provides specialists with the opportunity to see firsthand the development of various pathologies.
Based on the clinical manifestations of diseases, doctors choose those diagnostic methods or their complex that can most accurately provide information about all the processes occurring in the human elbow joint in order to make a timely and accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Structural subdivision of Polikarpov Alley Polikarpov 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Structural subdivision of Zhukov Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Structural subdivision Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
We draw your attention to the schedule of technological breaks in the CT and X-ray rooms.
X-ray of the elbow joint allows you to detect inflammation, tumors, various changes in the joint space and adjacent tissues, examine adjacent areas of the elbow joint, and determine the nature of the damage.
You can have an X-ray of the elbow joint done as quickly and efficiently as possible using the latest Italian equipment in the Medicenter clinic network. The clinics have a trauma department, where experienced and competent specialists will provide you with the necessary first aid for injuries and injuries, take an x-ray of the elbow joint, identify the presence of pathology and disease, and prescribe competent, effective treatment.
Indications
The elbow joint is rightly considered one of the most vulnerable places in the human body. Due to regular stress and various impacts, dislocations, bruises and injuries occur. Their appearance can be facilitated by age-related changes in the bones, an unbalanced diet, excessive physical activity or a sedentary lifestyle. The situation is complicated by the fact that many do not pay attention to moderate pain and discomfort and put off visiting a doctor while the disease progresses.
X-ray assesses the condition and structure of bone tissue, shows the presence of cracks and fractures, pathological formations and the degree of their manifestations. Doctors of various specializations prescribe x-rays of the elbow joint: orthopedic traumatologist, surgeon, oncologist, rheumatologist.
The main indications for taking an x-ray of the elbow joint:
- Arthrosis, arthritis and other diseases of an inflammatory, infectious and degenerative nature.
- Injuries to the shoulder and elbow joint.
- Forearm dislocation.
- The appearance of a benign or malignant tumor.
- Congenital developmental pathologies.
- Monitoring the healing process or dynamics of changes in chronic diseases.
Indications and contraindications for x-rays of the elbow joint
X-ray of the elbow joint is indicated for pain in the elbow area, clubhand (deviation of the hand from the longitudinal axis of the ulna and radius), impaired mobility, tumor processes, inflammatory-degenerative pathologies, injuries such as dislocations, fractures, bruises, subluxations, if various kind of pathology and disease, etc.
Contraindications to x-ray examination of the elbow joint are pregnancy, the patient's critical condition, the presence of mental and neurological diseases that do not allow them to remain at rest. For children under 15 years of age, any X-ray examination is carried out strictly according to indications with a referral from the attending physician.
Alternative diagnostic methods
- Ultrasound of the joint is a highly informative method for diagnosing the pathology of the soft tissues surrounding the elbow joint, articular structures (cartilage, ligaments), and the presence of effusion or blood in the joint capsule.
- MRI is a more expensive, but highly informative research method. Allows you to diagnose tumors in the elbow area, their size and extent of spread, examine the cartilage, ligaments and tendons of the joint.
- - associated with radiation exposure (unlike MRI). Allows you to study in detail the bone and other structures of the elbow joint, the depth and nature of bone and ligamentous damage.
The procedure for radiography of the elbow joint
X-ray - a picture of the elbow is taken in three projections: direct, lateral and axial. During an X-ray of the elbow joint, the patient sits and his arm is placed on the table. In some cases, the patient is placed on his back or side, or the image is taken in a standing position.
After receiving the images and their description, the patient is referred, depending on the identified injury, disease, pathology, to a traumatologist, orthopedist, surgeon, rheumatologist or more specialized specialists, such as an oncologist, endocrinologist, etc.
Features of the procedure
On any x-ray of the elbow joint, traumatologists will be able to see bone growths that are not characteristic of the normal state of bone structures, discrepancies in the surfaces of the joints, as well as areas where calcium salts have begun to be deposited.
Content:
- Features of the procedure
- Related and Complementary Research Methodologies
- Symptoms for radiography
- Indications and contraindications for radiography of the elbow joint
- Methodology of the procedure
In this case, radiography will be able to help identify all existing anomalies, make a diagnosis, diagnose complications and those signs of this pathology that can affect or are already affecting other organs and systems, prescribe a treatment regimen and monitor its dynamics.
X-ray diagnostics of the elbow area is a research medical method with which you can obtain a complete picture of the condition of the corresponding part of the human body by directing X-rays at it with a special device. This ultimately gives the specialist an objective image of the area being examined. It is important to know that soft tissues are capable of transmitting X-rays, while hard tissues, on the contrary, absorb them.
Because of this difference, in the images, specialists can see bone tissue painted in a very light, almost white color, and all soft tissues will have shades of gray - from lighter to almost black. Based on this change in shades, the doctor can judge what pathologies are present in the area under study.
At the same time, experts believe that X-rays are the best diagnostic technique for analyzing the condition of bone tissue.
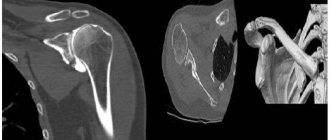
What do you receive after undergoing a CT scan?
The results of a CT scan of the elbow joint are given to the patient 1-1.5 hours after the examination. The specialist records all layer-by-layer images and 3D images obtained during scanning onto electronic media. For this purpose, use a memory card or CD (DVD) disk.
In addition to photographs, the radiologist must provide a description of the picture he sees in the photographs. The conclusion is also duplicated on electronic media and handed over to the patient.
The information can also be obtained in printed format, but in any case it is necessary for the attending physician to diagnose the disease.
| CT scan of joints and bones | Discount from 7 to 11 October |
| Prices for CT scan of forearm bones | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the humerus | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the femur | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of lower leg bones | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the pelvic bones | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the shoulder joint | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the elbow joint | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the wrist joint | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the hip joint | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the knee joint | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the ankle joint | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the foot | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the hand | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scans of the temporomandibular joints | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the sternoclavicular joints | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the sternum | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the sternum, ribs | 3000 rub. |
| Prices for CT scan of the scapula | 3000 rub. |
X-ray of a child’s joints at SM-Clinic
At the SM-Clinic in St. Petersburg, x-rays are performed on young patients using a high-quality Siemens Sireskop device. The modern device has a special design that allows even infants to be examined. The device provides high-quality images with a minimal radiation dose.
Babies who cannot remain in a motionless position are gently fixed with special devices. If necessary, anesthetic or sedative drugs are used. Thus, the doctor carries out the procedure much faster, and the time of negative effects on the child’s body is significantly reduced.
Examinations of children at SM-Clinic are carried out by the best pediatric radiologists with experience from 3 to 26 years. You can sign up for an examination by phone or through the feedback form on our website.
Fracture of the ulna
Treatment of an isolated fracture
In the absence of displacement, treatment on an outpatient basis is possible. If bone fragments are displaced, hospitalization in the trauma department is indicated.
- Conservative treatment
. For damage without displacement, a regular or polymer cast is applied for 6-10 weeks. If there is displacement, reposition is performed, a control photograph is taken after 10 days, and the plaster is kept for 10-12 weeks. - Surgical interventions.
Operations are performed when reposition is unsuccessful and it is impossible to keep the fragments in the correct position. Osteosynthesis of the ulnar diaphysis is performed with a plate or pin. Immobilization also lasts 10-12 weeks.
In the postoperative period, antibiotic therapy is prescribed, UHF, analgesics, antibiotics, exercise therapy and massage are used. The sutures are removed after 8-10 days, then the patient is discharged for outpatient treatment.
Treatment of Monteggia fracture
The patient is hospitalized in a trauma hospital and closed reduction is performed.
- For extensor injuries, transarticular fixation is sometimes performed using a thin pin to prevent re-dislocation.
- For flexion fractures, fixation of the head with a pin is usually not required.
A plaster cast is applied, a control x-ray is taken, the limb is elevated to reduce swelling (the arm is placed on a pillow or suspended from a special stand), and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. The needle is removed after 2-3 weeks. After 4 weeks, the plaster is replaced, changing the position of the limb. Immobilization is stopped after 8-12 weeks.
Surgical treatment is more often required for the extension type of fracture. Osteosynthesis of the ulnar diaphysis with a pin and suture of the annular ligament are performed. If the ligament cannot be sutured, plastic surgery is performed using an autograft cut from the patient's fascia. The beam head is adjusted and fixed with a knitting needle.
For neck fractures, resection of the radial head is performed; in such cases, a suture of the annular ligament is not required. To speed up fusion, auto- or homografts (small plates of cancellous bone) are applied to fragments of the ulna in some cases. The wound is stitched up. After the operation, physiotherapy, massage, and physical therapy are prescribed. Immobilization is carried out for 3 months.
In children, the surgical tactics are the same as in adults, the only difference is that they try to avoid head resection for any type of injury, since this can negatively affect the growth of the radius and the function of the forearm.
Advantages
The main advantages of x-ray:
- Simplicity - no preparation required before the procedure.
- Painlessness and absence of injuries to the skin and blood vessels.
- Affordable price.
- Information content and accuracy of images.
- X-rays help identify a wide range of diseases.
Radiography makes it possible to determine the diagnosis as accurately as possible and choose the most appropriate treatment method.