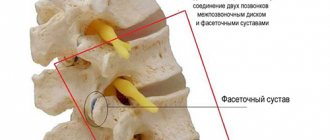
Diffuse herniation of the intervertebral disc is one of the types of hernias in which the integrity of the fibrous ring is not compromised, but uneven displacement of the disc is observed. The difference from other types of hernias is the absence of a hernial sac and the presence of a bulge similar to a hernia. It is worth noting that with this disease the disc is partially affected - however, if the process is started and is more than 50%, it can lead to rupture of the annulus fibrosus.
The most dangerous subtype of this pathology is posterior diffuse disc herniation, which is directed inside the spinal canal and can lead to compression of the spinal cord and spinal nerves, especially with the simultaneous presence of stenosis and narrowing of the spinal canal.
If you are diagnosed with diffuse disc herniation and want to know what it is, read this article. It provides all the necessary information about the dangers, symptoms, as well as diagnosis and treatment of this disease at the CELT clinic.
Depending on the type of operation and category of complexity from 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
Included in the price:
surgery, anesthesia, dressings, medications, food and hospital stay, observation by a surgeon in the postoperative period.
40-60 minutes
(duration of operation)
2-3 days in hospital
Indications
- persistent and severe symptoms of compression of the spinal nerves by a herniated disc, not amenable to conservative therapy
- the patient's desire to get rid of pain
Contraindications
- chronic diseases in the stage of decompensation
- acute inflammatory processes in the body
Clinical manifestations of diffuse hernias
The most common is diffuse L4-L5 disc herniation, along with diffuse L5-S1 disc herniation. This is due to the fact that the lumbar region bears the greatest load.
It is worth noting that in the stage of formation of a dorsal hernia, symptoms are practically not manifested, so patients often seek medical help much later, when treating the disease is much more difficult. Clinical manifestations of diffuse hernias are as follows:
- the appearance of pain of a different nature, from pulling to stabbing;
- radiating pain to other parts of the body in the limbs, arms, legs;
- decreased sensitivity, and often its loss;
- decreased muscle tone in those parts of the body for which the nerves compressed by the hernia are responsible for the innervation.
If the lumbosacral region is affected, pain symptoms are accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the sphincters of the rectum and bladder.
If the hernia is located in the thoracic or cervical region, the following may occur:
- blood pressure surges;
- pain in the heart area;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- headache.
Advanced forms are characterized by paralysis of the upper/lower limbs.
What is dorsal protrusion?
In itself, this disease does not pose a great danger to humans. However, the type of protrusion under consideration is characterized by the following features:
- The doctor makes a similar diagnosis when the deformation in the intervertebral disc area has reached 25-50%. That is, the lesions are quite serious, the disc protrusion is quite large;
- This type of disease is called dorsal because the protrusion of the disc occurs towards the spinal canal. That is, the patient may experience an increased load on the spinal cord, which leads to severe pain. They are especially strong when pressure is exerted not only on the spinal cord, but also on the nerve roots. In particularly difficult cases, two nerve roots can be pinched at once, which poses a certain danger to human health.
Symptoms of protrusion depend on its parameters, degree of complexity, and direction of formation.
As mentioned earlier, the disease usually occurs without symptoms, but sometimes the following symptoms may occur:
- Discomfort, painful sensations in the lumbar area that do not go away for a long time. Over time, the pain becomes stronger. She begins to have seizures. Discomfort is especially felt after physical exertion or after being in the same position for a long time. Before attacks of pain, a person may hear a click or crunch in the spine;
- During attacks, the pain becomes more intense even after inhaling and coughing. Over time, the pain begins to radiate to the legs. The consequence of a worsening situation is discomfort in the lumbar area when lifting a straightened leg, impaired knee reflex and other symptoms.
These symptoms are unpleasant, but do not pose a great danger if the protrusion was detected and appropriate measures were taken in a timely manner.
If the situation is neglected, small problems can develop into the formation of a herniated disc, which is a much more serious disease.
Intensive development of the disease can lead to leg paresis, urinary incontinence, and the inability to lead an active lifestyle. In particularly difficult cases, dorsal protrusion leads to the fact that the person remains disabled.
There is a possibility that problems with the intervertebral discs will cause the annulus fibrosus to rupture, which can lead to complete paralysis.
In order to choose the right set of treatment measures, the doctor must determine the causes of the disease. Without this, the measures taken will be ineffective, and the protrusion will develop into a herniated disc.
Diagnostics
In order for a doctor to diagnose protrusion, one visit to the clinic is usually not enough. 3-4 inspections are required. Only in this case can you be sure of the accuracy of the results obtained.
Before visiting a specialist, it is advisable to sign up for a computed tomography scan.
This will provide information for making a primary diagnosis, which will help determine the direction of subsequent examination. An analysis of existing symptoms should also be performed, including:
- Intense painful sensations;
- “Aching” in the spine;
- The skin changes its shade, its humidity changes relative to the norm;
- There is a tingling sensation in the fingertips.
If the disease has entered a severe stage, symptoms such as intense pain in the legs and problems with the normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system may appear.
Treatment of diffuse hernia
Treatment of diffuse hernia is carried out by conservative and surgical methods. The latter, as a rule, are used only if there are indications for this, or if conservative treatment has not achieved the desired effect.
Conservative treatment involves taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and performing a number of physical procedures. Epidural blocks are often used and provide excellent pain relief that lasts from six weeks to six months. They also have a therapeutic purpose, allowing them to relieve swelling and inflammation, and often allow them to completely avoid surgery.
Surgical treatment at the CELT clinic is carried out using endoscopic intervention technology and involves a minimal incision no more than one and a half centimeters long. The operations last no more than 40–60 minutes and are accompanied by minimal blood loss and risks to the patient’s health. They always bring the desired result and allow their patients to return to their normal lifestyle within two weeks!
Diagnosis of dorsal hernia
Treatment of dorsal disc herniation in the CELT clinic is prescribed only after the diagnosis has been accurately established. This is where our specialists primarily focus their efforts. The best foreign-made diagnostic equipment helps them in this, which allows them to quickly and accurately establish a diagnosis, determine the size, degree of protrusion and location of the dorsal hernia.
In addition to a visual examination and history taking, the following may be performed:
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- radiography;
- electroneurography.
Prevention
To avoid the development of intervertebral hernia, it is recommended:
- monitor posture from childhood;
- exercise to strengthen the back muscles, this will keep the spine in the correct position;
- sit on chairs that are suitable for your height; when working at a desk, your feet should be on the floor;
- sleep on orthopedic mattresses and pillows;
- eat right and lead an active lifestyle, which will maintain normal weight.
The development of herniated intervertebral discs often occurs as a result of a person constantly remaining in one position. Only physical activity will help unload the spine, swimming with measured movements is especially beneficial.
University
→ Home → University → University in the media → Disc herniation: to have surgery or not?
You often hear from patients: they say, doctors treated osteochondrosis and radiculitis, then they did an MRI/CT scan of the spine, but it turned out that there was a herniated intervertebral disc (IVD), and now it seems that only surgery can save it. Is this really the only way out?
There are many opinions on this matter, since doctors of different specialties deal with the problem. Neurologists discourage surgery, chiropractors guarantee a complete cure, and neurosurgeons declare that only they will relieve suffering, otherwise irreversible damage may occur.
Which method of treating a herniated intervertebral disc is better, which hernia should be operated on with an open approach, and in which cases should it be minimally invasive? Particularly impressive are films demonstrating minimally invasive, expensive interventions, for example, laser vaporization, after which the patient is completely cured - send him into space right now.
To properly understand the problem, it is necessary to recall the main points of the pathogenesis of the disease.
How do intervertebral disc herniations grow?
A healthy intervertebral disc consists of end plates, a fibrous ring, in the center of which is the nucleus pulposus - this is a very strong elastic formation that can withstand significant loads. Therefore, with spinal trauma, spinal fractures are more often observed than damage to the IVD. Over the years, degenerative processes (eating disorders) develop; they begin with the intervertebral disc, move to other elements of the spinal motion segment and are defined as spinal osteochondrosis. This is a chronic multifactorial relapsing disease; a genetic predisposition to it is observed in 80% of people. It is important to note that disc degeneration (degeneration) and its natural aging are one process, but at different speeds, complicated by herniation. Early age-related wear and tear of the spine is an expression of the lack of human biological perfection - as a tribute to nature for the transition to a vertical position.
Initially, intradiscal changes (protrusion) of the IVD are observed, then the fibrous ring cannot withstand the load, and the nucleus pulposus ruptures it, forming a true IVD hernia (prolapse). Nuclear prolapses can have different directions: upward or downward, the so-called Schmorl’s hernia (clinically insignificant); anterior; and the most unpleasant - posteriorly, when fragments of the nucleus fall into the epidural space of the spinal canal and often lead to a disco-radicular conflict. In this case, the degenerative process spreads both up and down to other IVDs (most often to L4-L5, L5-S1, C5-C6, C6-C7) and even parts of the spine - most often the lumbar, then the cervical (up to 30%) and less often - chest (less than 1%).
The best known in clinical practice is the scheme of stages of posterior hernia formation proposed by Armstrong J. (1952):
- Stage 1: initial dystrophic changes in the nucleus pulposus and the posterior part of the fibrous ring (Fig. 1),
- Stage 2: posterior displacement (protrusion) of the nucleus pulposus (Fig. 2),
- Stage 3: prolapse of the sequestra of the nucleus pulposus into the spinal canal, where its resorption or fibrosis begins (Fig. 3).
In the “pre-computer era,” many researchers noted that disc sequestration resolves, and this process occurs faster in the vascularized epidural space. New high-resolution neuroimaging methods have made it possible to observe this process over time. The first portion of the prolapsed nucleus pulposus can significantly decrease in size on CT during the period of remission, but unsuccessful movement or overload leads to the repeated prolapse of another portion of the nucleus, causing an exacerbation.
At first, neurosurgeons who removed IVD hernias considered them benign tumors-chondromas and did not associate the pathology with the IVD.
The research of the Dresden School of Pathologists, led by G. Schmorl (1926), helped to understand this. In a post-mortem analysis of 5,000 spines of people of different ages, cartilaginous nodules were found in 38% of cases (usually in people over 50 years of age). These results are echoed by modern data obtained on volunteers: in 50% of CT scans of the spine and in 37% of myelographies performed on the population of all ages, pronounced pathological changes in the IVD were determined. And the patients had no complaints. The older the patient, the more often spinal osteochondrosis appeared on CT/MRI, and in old age (>60 years) it is observed in 100% of cases.
What to do with a 10 mm hernia if conservative treatment is ineffective
The question is posed specifically, but it cannot be answered unambiguously. It is clear that surgical assistance is already necessary.
In Belarus, several methods of surgical treatment of intervertebral disc herniations are used.
Percutaneous minimally invasive hernia removal . This is an attempt to eliminate the disc-radicular conflict with minimal trauma to the spine without disturbing its stability. During percutaneous operations, when the nucleus pulposus is reduced (evaporated) or mechanically removed (without opening the spinal canal) to reduce intradiscal pressure. It is impossible to influence the prolapsed sequestra of the IVD hernia. Therefore, the indications for these interventions are hernias less than 6 mm (see “Medical Bulletin” dated 02.12.2009 No. 7, “HERNIA AND THE “HUNDRED” OF THE NEUROSURGEON’S ROADS, Percutaneous methods for treating intervertebral disc herniations (IVD)’). It is believed that with this size, the fibrous ring has not completely ruptured and the process of hernia formation is at stages 1–2.
For hernias larger than 10 mm, other surgical technologies are suitable. Now there are already more than a hundred of them known, and new ones are appearing.
Standard microdiscectomy . It is called the gold standard for neurosurgical treatment of IVD hernias. The prolapsed part and remnants of the nucleus pulposus in the IVD are removed. With the acute development of the disease (patients note that something “crunched” or “shot” in the back), treatment results are good in middle-aged and young people. Although the operation involves minimal tissue trauma (the skin incision for experienced neurosurgeons is 2–3 cm), it still aggravates the degenerative-dystrophic process in the operated IVD and reduces its height, as a result of which the predicted result is not always achieved. To preserve the functionality of the IVD after removal of the hernia, it was proposed to suture the wound of the fibrous ring. A new operation was specially developed - annuloplasty (J. Cauthen, 2002). However, it turned out to be ineffective due to high loads and low regenerative potential of the fibrous ring; relapses of the hernia were observed again.
The results of standard microdiscectomy worsen due to the age of the patients, long duration of the disease, and repeated microdiscectomies at the same level; improve - manifestations of osteochondrosis only at one level, removal of large IVD hernias (> 6 mm according to CT).
Indications for standard microdiscectomy have been developed for a long time and are based on the neurological manifestations of hernias. They are divided into relative and absolute. Regarding the absolute indications for standard microdiscectomy, all authors are unanimous: compression of the cauda equina, intractable severe pain, or myeloradiculoischemia with paralysis of certain muscle groups (similar to an acute abdomen) require urgent intervention. But the justification of microdiscectomies for relative indications is not recognized by everyone (Ya. Yu. Popelyansky, 2003; E. L. Tolpekin, F. V. Oleshkevich, 2006).
Epidurochemonucleolysis. Targeted prolonged treatment with a complex of drugs (bupivacaine, lidase, Vit. B12) through a catheter placed through the lower sacral opening into the epidural space, under RTG control. The technique makes it possible to deliver drugs directly to the area of the disc-radicular conflict without violating the integrity of the anatomical structures. The criterion for effectiveness is a reduction in the size of the hernia during control CT examinations. When analyzing the results of treatment using this technology, it was revealed that the best results were obtained for hernias larger than 6 mm, when there is a rupture of the fibrous ring and posterior longitudinal ligament, and lidase directly affects the sequestra of IVD hernias.
Based on the facts of the pathogenesis of the disease and the above treatment results, it cannot be argued that the size of IVD hernias is a fundamental factor for indications for surgical treatment. There is no clear correlation between the size of the hernia and the severity of neurological manifestations, and, conversely, with acutely developed intractable low back pain with a pronounced clinical picture of radiculopathy, in most cases we find large IVD hernias.
Who will judge the neurosurgeon and orthopedist?
Posterior intervertebral disc herniation is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system and peripheral nervous system, therefore, in the principles of providing surgical care, there are two positions - neurosurgeons and orthopedists.
Most neurosurgeons believe that the main cause of suffering is compression of the nerve structures caused by IVD herniation, and its surgical removal is the key to recovery.
Orthopedists adhere to other positions, paying primary attention to the degenerative-dystrophic process in the IVD, and therefore direct their efforts to restoring the correct anatomical relationships in the spinal motion segment.
The ideal solution to the problem would be not only the elimination of the disc-radicular conflict, but also the restoration of the function and height of the IVD. This is not yet an achievable goal. Surgical treatment for multilevel lesions also remains unresolved.
In recent decades, at the intersection of these disciplines, a new science has emerged - vertebroneurology. Conferences and symposia on this topic are convened almost every year. In 1992, at a Soviet-American symposium on the treatment of spinal osteochondrosis, the American vertebroneurologist A. White noted that the effectiveness of treatment for such patients depends on the quality of the teamwork of multidisciplinary “spinal” teams, which should include a therapist, surgeon, psychiatrist, radiologist, physiotherapist. The leading doctor of the team should not be a surgeon, but a specialist who knows the patient better, his psychosocial status, working conditions, financial circumstances, and rehabilitation resources. Such a doctor would take responsibility in making decisions on surgical treatment, pre- and post-operative management. In our country, the solution to this problem lies in the creation of vertebroneurology centers, where patients could receive emergency and planned care from all specialists working in this field. Patients with back pain would not have to visit a neurologist (therapist) at the clinic several times, then wait for a CT/MRI examination, which significantly increases the preoperative period.
In the clinic of neurology and neurosurgery of the Belarusian State Medical University, a method of step-by-step treatment of patients with neurological manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis has been developed and implemented according to the principle of increasing radicalism:
1. therapeutic paravertebral blockades with hormonal and enzyme preparations, or transsacral epid-urochemonucleolysis;
2. standard microdiscectomy with endoscopic assistance;
3. standard microdiscectomy + epidurochemonucleolysis (for multilevel pathology);
4. standard microdiscectomy + dynamic stabilization of the spine with a U-implant (in case of severe dynamic instability and repeated operations).
Evgeniy TOLPEKIN, neurosurgeon, candidate of medical sciences. Sciences Medical Bulletin , November 26, 2009
Share
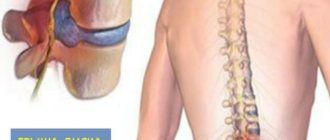
Description of the pathology
Intervertebral discs are a kind of cushion with a spongy structure. The main function of the discs is to fix the vertebrae at the required distance between each other. Intervertebral discs also create a shock-absorbing effect, which is necessary for the spine to withstand intense stress during walking or physical exercise. Otherwise, a person would not be able to lift any weight or even move, since when a load occurs, the vertebrae rest against the intervertebral discs.
The development of a dorsal hernia is associated with the entry of an intervertebral disc into the cavity of the patient’s spinal canal. This pathological process is accompanied by pinching of the nerve roots. If at an early stage of development the disease manifests itself as painful sensations in the lumbar region, then as the pathology progresses, the pain syndrome spreads to other parts of the body.
How is disc extrusion treated?
To treat disc extrusion, it is necessary to restore the lost shape of the fibrous ring and increase the elasticity of the cartilage tissue. Several sessions of traction traction will help, which will restore the original length of the spinal ligaments and create conditions for increasing the height of the intervertebral disc affected by protrusion.
Disc extrusion therapy is carried out using the following methods of influence:
- kinesiotherapy strengthens the muscular frame of the back and eliminates the risk of developing recurrent osteochondrosis and extrusion over the next 3-5 years;
- therapeutic exercises accelerate capillary blood flow and restore lost myocyte tone, which has a good effect on the diffuse nutrition of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc;
- massage increases the elasticity of all tissues;
- osteopathy restores the movement of blood and lymphatic fluid, reduces spastic tension in the paravertebral muscles;
- acupuncture affects biologically active points on the human body; the process of natural regeneration of cartilage tissue is triggered by using the body’s hidden reserves;
- physiotherapy and laser treatment speed up the healing process and improve tissue condition.
Other types of therapeutic effects can be used to treat disc extrusion. All of them are aimed at stopping pathological changes, and not at eliminating the symptoms of the disease.
Changing the patient's lifestyle is also important for successful therapy. It is imperative to normalize body weight, introduce the habit of physical activity into your life, and create ergonomic conditions for work and night sleep.
There are contraindications, consultation with a specialist is required.
You can use the service of a free initial consultation with a doctor: neurologist, chiropractor, vertebrologist, osteopath, orthopedist on the website of the Free Movement clinic. At your free initial consultation, your doctor will examine and interview you. If there are results of MRI, ultrasound and x-rays, he will analyze the images and make a diagnosis. If not, he will write out the necessary directions.
source
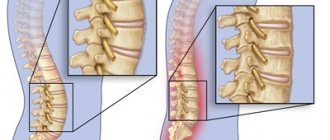
Spine extrusion. First stage of disc herniation
Extrusion of spinal discs is the very initial stage of the formation of an intervertebral hernia. Therefore, if such a diagnosis is made by MRI, the most important thing is to take action as quickly as possible to stop the destruction of the disc, preventing the development of a hernia, which can cause pain and other unpleasant symptoms: burning sensation, stiffness, numbness of the arms and legs.
How does extrusion differ from protrusion and hernia?
Extrusion, protrusion and hernia are all stages of gradual destruction of the spinal disc, or rather its hard shell - the fibrous ring. A crack forms in the ring, and through it the internal contents of the disc, the nucleus pulposus, slowly seep out, forming a noticeable protrusion in the photographs, which is called a spinal hernia.
If a diagnosis of disc extrusion is made, it means that the herniation is barely beginning to form, and only a small part of the nucleus protrudes beyond the disc. At this stage, as a rule, there is no pressure on the nerve roots, severe inflammation and spasms - the main sources of pain. Therefore, disc extrusion usually does not produce noticeable spinal pain, but only some neurological symptoms.
Symptoms of disc extrusion
When localized in the neck - headaches, especially in the back of the head, dizziness, convulsions when turning the head, blurred vision. Cervical extrusion often occurs in young people and students, especially with poor posture, hyperkyphosis (stooping), and scoliosis.
Localization in the lower back is typical for older people (over 25 years): numbness and tingling in the legs, thighs, and toes.
Disc extrusion can be detected not only with MRI. There is a simpler, but sufficiently informative procedure - myofascial diagnosis. An experienced doctor, using manual muscle testing and certain manipulations, examines the individual reaction of the body, reflexes, sensitivity and muscle strength in the lower and upper extremities, and thus can quite accurately predict the presence and location of a disc herniation.
And this, in turn, helps to prescribe adequate treatment, develop the necessary algorithm of therapeutic movements in order to restore blood circulation and microcirculation in tissues, and, consequently, trophism - nutrition, microcirculation, lymph and blood circulation of organs, discs and joints. Restoring the power of the disc promotes the natural regeneration of osteochondral tissue, as a result of which the extrusion can completely disappear.
If you do not see a doctor in time and undergo treatment, the destruction of the disc will continue. Over time, the annulus fibrosus gives way to the emerging nucleus pulposus, after which disc rupture leads to the formation of a full-fledged hernia. Dorsal hernia and sequestered hernia of the spine are especially dangerous, since they are the most common cause of severe spinal pain.
But the sooner extrusion is detected, the greater the chance that the process will be stopped and will not develop into a hernia. Disc extrusion can be treated quite successfully without surgery or medication.
Even more articles in our VKontakte group: https://vk.com/cktkzn
Promotion at the Kazan Kinesitherapy Center. Doctor’s consultation + diagnosis of the spine and joints – 600 rubles.
Sign up by phone.
(843) 570-55-25
or in
the VKontakte group
.
source
Dorsal disc protrusion - what is it?
When dorsal disc protrusion occurs, what it is and how aggravated it can be and what consequences it can cause, not many people actually know.
But for effective treatment and timely detection of this abnormality in the spinal column, it is necessary to clearly understand the processes by which it forms and progresses.
Wherever dorsal protrusion occurs, ignoring this disease is dangerous, as it can develop into an intervertebral hernia. As a result, the spinal canal is pinched, compressed and the nerve endings can be pinched.
But this state itself does not arise on its own. It is preceded by various degenerative changes, such as scoliosis, osteochondrosis, kyphosis and other abnormalities.
It is the initial diseases of the spine that lead to the fact that bone and cartilage tissues do not receive enough nutrients. As a result, the elasticity of the annulus fibrosus decreases and it becomes thinner. The discs move closer to each other, which can result in pinched nerve endings. This, in turn, causes inflammation in the soft tissues surrounding the spine. And in the fibrous ring, the body cracks and the core moves from its normal position.
As a result, a deviation is formed in the form of dorsal protrusions.
Classification of the disease
Types of protrusions.
Today, all types of protrusion are classified depending on the location where they are located and in what direction the displacement occurred. Classification of the disease depending on the displacement of the fibrous ring:
- Dorsal protrusion - pathology forms in the posterior region. It includes median, diffuse and foraminal subspecies. In the diffuse subtype, protrusion occurs unevenly in different directions. In the foraminal subtype, the protrusion occurs towards the root, the spinal nerve. When a dorsal medial protrusion is diagnosed, the protrusion occurs inside the canal, to the very center.
- Circumferential dorsal protrusion is a rare and complex disease. In this case, the spinal disc protrudes completely. Only a certain part of the spinal column expands.
- Paramedian protrusion is accompanied by protrusion of the canal slightly to one side.
- Ventral - protrusion of the discs in this case occurs without affecting the nerve fibers. Therefore, the ventral type of protrusion occurs without symptoms.
Complications and consequences of intervertebral hernia
If there is no timely treatment for a hernia, this is fraught with the development of consequences and complications that negatively affect a person’s life. The most striking complications of intervertebral hernia are:
- paresis of the back or limbs;
- paralysis of limbs;
- chronic pain syndrome;
- dysfunction of the bladder and intestines. This happens when the nerve bundles that are responsible for nerve patency are compressed.
Intervertebral hernia is a serious disease that requires a careful approach to treatment. It is important to consult a doctor on time, undergo appropriate examinations, and follow all medical prescriptions. This is the only way a doctor can prescribe competent therapy. With the right approach to treatment, it is possible to stop the growth and development of the disease and prevent serious consequences and complications.
How to treat spinal diseases?
Step 1. It is recommended to contact a trainer involved in physical therapy. Sometimes it is this type of physical activity that helps not only heal, but also eliminate the development of back diseases altogether.
Working with a trainer is necessary at first - it is important to learn how to perform the exercises correctly. Then you can practice at home on your own
Contact a trainer
Step 2: You can take medications prescribed by your doctor
It is important to remember that you cannot prescribe medications yourself - they may have contraindications
Take medications if necessary
Step 3. In some cases, it is necessary to wear a back support corset. However, before purchasing this device, it is also important to consult a specialist.
Use a corset
Supportive corset for the spine
Step 4. Massage therapy is also a good therapy option. You should find a good massage therapist and take a course.
Massotherapy
Step 5. In case of severe pain, you can ask your doctor for an appointment for a blockade.
Blockade
Step 6
In any case, it is important to visit a specialist’s office, receive advice regarding treatment, and discuss any concerns regarding back health
Talk to your doctor
Step 7
It is important to monitor your body weight and reduce it if necessary. Excessive weight negatively affects the condition of the spine and increases the already heavy load on it.
Watch your weight
Causes
Very few people understand what their spine looks like from a medical point of view. The spinal column has the following composition: body, spinal canal, arch. Inside the canal is the spinal cord with roots. The intervertebral disc is located between the bodies that make up the spinal column. In the middle of the spinal cord there is a nucleus, surrounded by a fibrous ring. The vertebrae receive nutrients and nutrition from adjacent soft tissues. Disturbance in the supply of nutrition leads to wear and tear of the intervertebral disc and its destruction.
The reasons leading to malnutrition, and subsequent protrusion of the nucleus pulposus, are:
- Age-related changes are the main cause of extrusion. Over time, the amount of nutrients supplied to the vertebrae decreases due to drying of the paravertebral tissues;
- Received injuries to the spinal region, leading to changes and displacements in the surrounding vertebral tissues, and as a result, destruction of the vertebrae;
- Already existing diseases of the spine: osteochondrosis, scoliosis, etc., not treated or not treated correctly;
- Disorders of hormonal levels, metabolism, diet, in particular obesity;
- Illnesses associated with the profession, lifting heavy objects, long-loaded back.
Tips for preventing illness
In the ranking of the importance of medical actions in relation to extrusion, one of the first places is occupied by the prevention of this disease. To effectively prevent extrusion or its complications, certain measures can be taken:
To effectively prevent extrusion or its complications, certain measures can be taken:
- do physical exercise regularly. Overworking is harmful, but in order for the spine to be healthy, sufficiently trained back muscles are necessary;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- when working in a job that is harmful to the spine, it is better to change profession;
- take care of your posture, avoid wearing shoes with high (more than 40 mm) heels;
- organize your workplace wisely;
- take timely measures against infections and inflammations in the body;
- If you experience the slightest discomfort, consult a doctor immediately.
To prevent the disease from occurring, it is important to carry out prevention
Trying to treat yourself on your own is dangerous: it can lead to severe complications, as a result of which the person will lose his ability to work and may even remain disabled. At the first signs of discomfort, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Complications
Timely initiation of treatment for L4–L5 intervertebral hernia is the key to its success and elimination of the risk of complications. If you do not intervene or ignore the doctor’s recommendations, the disease can lead to:
- spinal canal stenosis;
- paresis and paralysis of the lower extremities;
- loss of control over the process of urination;
- persistent impotence;
- infertility;
- disability.
Therefore, we recommend not to delay contacting a doctor. In the early stages of development, L4–L5 hernia responds well to conservative therapy and does not lead to the development of undesirable consequences.
0 0 votes
Article rating