Hernia L5-L4 is very common in the practice of a vertebrologist. It accounts for more than 40% of all violations of the integrity of the fibrous ring in the lumbosacral spine. More often, only hernial protrusion in the L5-S1 area is diagnosed.
L5-L4 disc herniation is dangerous due to its potential complications. When the radicular nerves are compressed, paralysis of the muscles of the lower limb can develop with gradual atrophy of myocytes. The internal organs of the abdominal cavity and pelvis are also affected. The functioning of the small and large intestines is disrupted. Patients complain of frequent urination or urinary retention, reactive bladder syndrome, etc.
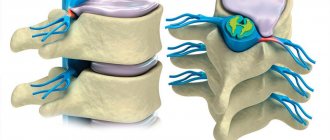
In most cases, a hernia of the lumbar region L5-L4 is formed against the background of long-term developing osteochondrosis. This degenerative disease leads to gradual dehydration and cracking of the surface of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc. It loses its elasticity and strength. The tissues of the fibrous ring do not have their own circulatory network; they have no place to get fluid from to restore their functionality. Therefore, at the stage of calcification (deposition of calcium salts in the cracks of the fibrous ring), cartilaginous tissues begin to gradually take fluid from the structures of the corpus pulposus of the nucleus pulposus.
As a result, it loses its mass and can slip partially or completely into the cracks formed in the fibrous ring. Any herniation of the L5-L4 lumbar disc requires emergency medical intervention. This localization is dangerous because sequestration can occur (severation of a section of the protruding nucleus pulposus). In this case, treatment can only be surgical; during the operation, not only the fragment of the nucleus pulposus that has separated, but that segment of the intervertebral disc that has lost its elasticity and performance is removed. After this, a procedure is carried out to fuse adjacent vertebral bodies. The spinal column loses its physiological flexibility and mobility.
Intervertebral hernia L5-L4 may have a traumatic etiology. It develops when there is a strong impact, a fall from a height, lifting an excessively heavy load, etc. At the moment of traumatic impact, the integrity of the fibrous ring is disrupted and part of the nucleus pulposus passes through the resulting crack. The patient at this moment experiences severe pain, reminiscent of an electric current discharge. Weakness appears in the leg on the affected side, and paresthesia may occur in the area of the skin of the thigh and lower leg, followed by a decrease in sensitivity. It is necessary to show the patient to a neurologist or vertebrologist as soon as possible. Typically, traumatic disc herniations L5-L4 are easily amenable to manual reduction and subsequently the doctor is able to completely restore the integrity of the damaged intervertebral disc.
If you have been diagnosed with an intervertebral hernia of L5-L4 in the lumbar spine, we recommend that you do not delay the start of treatment. The longer a violation of the integrity of the claim is present, the stronger the inflammatory reaction will develop. The nucleus pulposus consists of a large number of specific proteins. They have an irritating effect on soft paravertebral tissues. Under their influence, an inflammatory reaction develops, which further aggravates the patient's condition.
In Moscow, you can make an appointment with a neurologist or vertebrologist at our manual therapy clinic. The initial appointment for each patient is free of charge. The doctor will review the medical documentation (if any), conduct a manual examination and a full examination. Will make a preliminary diagnosis. Recommend additional research methods as necessary. He will talk about the prospects and possibilities of treatment using manual therapy methods.
Causes of L5-L4 disc herniation
Potential causes of the development of L5-L4 disc herniation are factors leading to degenerative dystrophic changes in the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc. Osteochondrosis is the most common reason why hernial protrusions occur. In second place is osteoporosis and cicatricial deformation of the ligamentous tendon apparatus.
The following risk factors should be excluded:
- excess body weight, which greatly increases the shock-absorbing load on the intervertebral discs;
- poor posture and curvature of the spinal column;
- unstable position of the vertebral bodies against the background of deformation of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus;
- violation of the tone and atony of the muscular frame of the back, often caused by leading a sedentary lifestyle with a complete lack of regular sufficient physical activity on the muscles;
- a decrease in the intensity of microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the spinal column, which sharply reduces the percentage of fluid absorption during diffuse exchange;
- incorrect placement of the feet and curvature of the lower extremities lead to incorrect distribution of the shock-absorbing load along the spine during movements;
- hard physical labor;
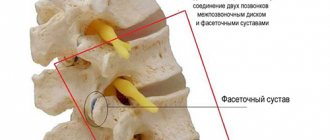
- diseases of the uncovertebral, facet, and facet joints of the spine;
- diabetic angiopathy, smoking and alcohol consumption;
- numerous pregnancies carried out without following the recommendations given by the attending physician.
Also, this type of hernia can be caused by ankylosing spondylitis, injuries, or the spread of certain infections that have a destructive effect on cartilage tissue in the human body.
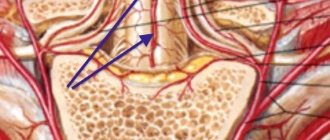
Dorsal disc herniation L5-L4
With a dorsal hernia of L5-L4, a rupture of the fibrous ring is observed in the projection of the spinal canal. This is the most dangerous localization, since there is simultaneous compression of the spinal cord structures and an irritating inflammatory effect on the dural membrane. Clinical symptoms of myelitis develop rapidly. Both legs may suddenly become paralyzed at once. The person experiences severe weakness in all the muscles of the lower extremities. The pain syndrome increases quickly.
Dorsal disc herniation L5-L4 is located in the dorsal part towards the spinal cord structures. It is difficult to correct. It is necessary to seek help in the first hours after the appearance of characteristic symptoms. These may include:
- a feeling of weakness in the muscles of the lower extremities (the patient describes this condition as rags, the inability to hold his body in a standing position);
- rapid loss of skin sensitivity in the lower extremities;
- Involuntary bowel movements (bowel movements) and urination may occur;
- increase in pain in the area of the damaged intervertebral disc.
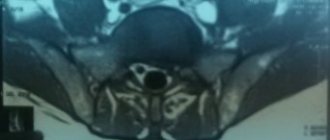
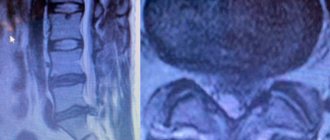
Diagnosis often requires an MRI examination. It is quite difficult to discern this type of hernial protrusion on an x-ray.
general information
The protrusion of the hernia puts pressure on the nerve roots, which causes pain. Symptoms depend on which direction the protrusion is directed. In this regard, diffuse hernia occurs:
- Front. It faces not towards the spinal cord, but more ventrally. Even if the bulge is large - from 5 mm, the hernia is not as dangerous and does not give the same symptoms as with a dorsal, posterior location;
- Posterior or dorsal. The protrusion is directed towards the spinal canal. Leads to compression of the nerve roots and sometimes the spinal cord. Manifests itself with serious neurological disorders.
The disease is diagnosed mainly at the age of 40–55 years, but hernias appear even after 20 years. In 80% of all cases, the pathology develops against the background of previously appeared osteochondrosis. In 20% of cases, patients are indicated for surgical intervention.
Median disc herniation L5-L4
Median hernia M is a protrusion of the nucleus pulposus into the space between the vertebrae. Compression of the radicular nerves occurs and healthy areas of the disc are displaced. Without timely treatment, median disc herniation L5-L4 leads to paralysis of the lower extremities and persistent dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
In general, median disc herniation L5-L4 responds well to conservative treatment. It is often diagnosed in young people involved in active sports and weightlifting. To prevent this disease, it is recommended to use special bandages that protect the spinal column from excessive shock-absorbing and mechanical effects.
Paramedian disc herniation L5-L4
An uncomplicated paramedian hernia L5-L4 is a protrusion of the nucleus pulposus in the area of the lower or upper surface of the fibrous ring. It is located on the left or right. Symptoms corresponding to:
- numbness and muscle weakness in only one limb;
- pain syndrome is localized mainly in the area of the affected disc;
- paresthesia is quickly replaced by a decrease in skin sensitivity;
- on the lower limb on the affected side, tendon reflexes quickly fade away;
- gait changes, lameness appears;
- overstrain of the muscular frame of the back on the affected side is visible.
Paramedian L5-L4 disc herniation can be treated using manual therapy methods. Surgery may only be required if sequestration occurs.
Diffuse circular disc herniation L5-L4
A diffuse hernia of L5-L4 affects the entire fibrous ring at once. It develops with serious degeneration of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc. A circular herniation of the L5-L4 disc develops without external traumatic influence. There is no rupture of the fibrous ring. It stretches excessively in the form of a bulge. This indicates a total loss of elasticity in the tissues of the fibrous ring.
Unfortunately, at the stage of circular hernia the disease is diagnosed very rarely. Most often, patients come to see a neurologist at the moment when there is a violation of the integrity of the fibrous ring.
Examination at the doctor's office
To diagnose a hernia in the lumbar region, the neurologist usually asks the patient to lie on the couch and bends his legs, moving them in different directions to determine the occurrence of pain and discomfort.
The doctor checks reflexes, muscle strength and tone, skin sensitivity, coordination and balance.
In most cases, diagnosing a herniated disc is not difficult during a neurological examination. But in order to assess the location, size of the hernial protrusion, the degree of nerve damage and understand the cause of the disease, additional instrumental studies are required.
Sequestered hernia L5-L4
Posterior hernia L5-L4 undergoes sequestration more often than other localizations. This is due to anatomical features. This sector is subject to maximum pressure from neighboring vertebral bodies.
A herniated intervertebral disc L5-L4 with separation of part of the nucleus pulposus gives a pronounced inflammatory reaction. Inflammation involves muscles, ligaments, tendons, subcutaneous tissue and radicular nerves. The variety of clinical symptoms that arise does not allow a quick diagnosis to be made. Therefore, if a sequestered hernia of L5-L4 is suspected, surgery is often prescribed. In fact, you can completely do without it if you don’t let your condition get worse until part of the nucleus pulposus is torn off.
Symptoms of L5-L4 spinal hernia
A sudden herniation of the L5-L4 spine gives pronounced clinical signs. Main symptoms of L5-L4 hernia:
- sharp pain in the lumbar region, which may intensify when coughing, sneezing, trying to bend over or turn to the side;
- a gradual decrease in the intensity of painful omissions in a standing position with a straight back;
- spread of pain along the thigh and lower leg;
- numbness of the lower extremities and anterior abdominal wall;
- disruption of the process of urination and defecation;
- sweating, general weakness, dizziness.
A characteristic clinical symptom of a L5-L4 hernia is that when lying on the back, the patient cannot raise a straight leg. This can be done easily with a bent knee.
Drug therapy
First of all, treatment of spinal hernias is aimed at combating pain and other symptoms. Ibuprofen and other drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. In case of severe pain, blockades are performed: glucocorticosteroid drugs are injected near the pinched nerve root. In severe cases, narcotic analgesics can be used.
In addition to painkillers, the doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants (drugs that relax muscles) and anticonvulsants.
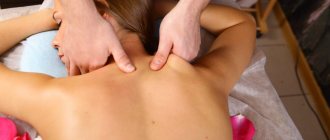
Drug therapy is supplemented with massage, physiotherapy, various manual techniques, and later physical therapy is included.
Treatment of spinal hernia without surgery in Moscow, as well as modern minimally invasive surgical interventions, are carried out at the international clinic Medica24.
Treatment of L5-L4 disc herniation: what to do?
Treatment of L5-L4 hernia is possible using conservative and surgical methods. It is preferable to carry out conservative treatment using manual therapy methods. They allow you to completely restore the integrity of the intervertebral disc and eliminate potential causes of destruction of cartilage tissue.
To treat L5-L4 disc herniation, our manual therapy clinic uses different methods:
- traction traction of the spinal column eliminates compression of the nerve fiber and restores the normal height of the intervertebral discs;
- osteopathy restores microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid;
- massage restores physiological elasticity to all soft tissues;
- kinesiotherapy and therapeutic exercises improve the condition of the muscular frame of the back and trigger the lost diffuse nutrition of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc, which becomes the foundation for restoring its integrity;
- reflexology starts the regeneration processes of all damaged tissues;
- laser vaporization allows you to restore the integrity of a damaged intervertebral disc;
- physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary treatment method.
If you have a hernia of L5-L4, the first thing to do is contact a neurologist or vertebrologist. Avoid using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They do not provide any therapeutic effect, but provide a disservice. They relieve pain, and the patient gets used to living with a herniated disc, which creates a potentially high risk of developing paralysis of the lower extremities.
Make an appointment for a free appointment with a spine specialist at our manual therapy clinic. After the examination, the doctor will tell you about all the possibilities and prospects for using manual therapy in your individual case.
Diagnostics
An important diagnostic task is not only to identify a hernia, but also to determine its type and size. The tactics of further treatment directly depend on these factors.
The first stage of diagnosis is an examination by a vertebrologist or neurologist. The doctor collects anamnesis and can make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm it, instrumental research methods are prescribed.
Neurological examination.
MRI can provide the most comprehensive information. Other diagnostic methods include laboratory examinations, CT scans and x-rays of the spine.