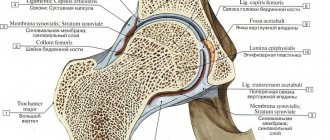
Dysplasia is a congenital defect in the structure of the hip joint, which is characterized by incorrect orientation of the articular components. Discongruence of the femoral head and acetabulum leads to functional overload of certain parts of the joint. Constant mechanical trauma causes degenerative changes in articular cartilage, capsule and subchondral bone structures. As a result, the patient develops early deforming osteoarthritis.
Severe degree of dysplasia.
According to various literature data, congenital defects in the structure of the hip joint lead to the development of dysplastic coxarthrosis in 40-87% of cases.
Typically, DTS is detected during the neonatal period or infancy. The child is immediately prescribed conservative treatment, which often has a positive effect. The need for surgery occurs in severe dysplasia that cannot be corrected by other means. The optimal age for surgery is considered to be 2-3 years of life. Table 1. Goals of surgical treatment of dysplasia
| Target | Curious information | |
| 1 | Restoring the concruence of articular surfaces | The main problem of DTS is a violation of the biomechanical correspondence between the femoral head and the glenoid cavity. During surgery, doctors eliminate it |
| 2 | Elimination of hip joint instability | Stabilization of the hip joint allows you to eliminate pathological mobility in it. This reduces trauma to articular cartilage and prevents their destruction |
| 3 | Complete restoration of limb function | During surgery, doctors try to return the joint to its anatomical position. They also ensure that the operated leg is of normal length. This creates favorable conditions for restoring gait, which is extremely important for the child’s development. |
| 4 | Prevention of complications and disability | As we have already found out, dysplasia often leads to deforming arthrosis. This, in turn, causes chronic pain and dysfunction of the hip joint. Over time, patients with this pathology lose their ability to work. This can be avoided by timely surgery. |
If your child is diagnosed with dysplasia, begin treatment without delay. The faster you react, the better your baby's chances. If doctors recommend surgery, do not refuse under any circumstances. Remember: any delay can lead to undesirable consequences.
Minimally invasive endoprosthetics in the Czech Republic: doctors, rehabilitation, terms and prices.
Find out more
Open hip reduction
Required for severe dysplasia accompanied by dislocation of the hip joint. Often, open reduction is combined with other manipulations on the hip joint . If the depth of the acetabulum is insufficient, doctors first correct its size and shape. They can remove part of the acetabular labrum or deepen the socket using special cutters. In case of insufficient centering of the head, a derotational osteotomy is performed.
Indications for open reduction:
- detection of dislocation at the age of more than 2 years;
- inability to perform closed reduction;
- relapse after closed reduction.
After open reduction, the child is placed in a cast for 2-5 weeks. After its removal, the baby must undergo rehabilitation. At the end of treatment, the hip joint returns to the desired position and its functions are restored. If the dislocation recurs, the child requires another operation.
Degree of pathology
Since joint immaturity can be expressed by various abnormalities, disorders are classified according to severity:
- A – normal joint without disorders;
- B – pre-dislocation: there are non-critical disturbances in the anatomical structure of the joint. The head is in the glenoid cavity, but is held weakly.
- C – subluxation: the femur is displaced, there is a valgus deformation of the glenoid cavity. This is the so-called borderline state, in which there is a high probability of developing pathologies in the future.
- D – congenital dislocation of the hip: the head of the bone is located outside the acetabulum.
Intertrochanteric corrective osteotomy of the femur
Today, descriptions of more than 40 OT techniques can be found in the literature. Many of these techniques are used for various types of underdevelopment of the femur. Osteotomy allows you to simultaneously correct a large number of changed or impaired parameters of the hip joint.
Results of a successfully completed operation:
- normalization of biomechanical conditions in the hip joint;
- more uniform distribution of pressure on different joint structures;
- elimination of factors that injure articular cartilage;
- positive dynamics of disease development.
Correction scheme.
Intertrochanteric osteotomies are rarely used as a single intervention. Most often they are combined with operations on the pelvic bones or performed in case of ineffectiveness of pelvic OT.
Intertrochanteric osteotomies lead to disruption of the anatomy of the femur. This can cause serious problems if the person requires hip replacement in the future.
Causes and provoking factors
Scientists are still debating why congenital dislocation of the hip joint occurs. There are different versions of the development of pathology, but each of them does not yet have a sufficiently convincing evidence base. It has been established that approximately 2-3% of anomalies are teratogenic, that is, they are formed at a certain stage of embryogenesis. Several theories have been put forward about what may serve as an anatomical prerequisite for the occurrence of orthopedic pathology:
- premature birth caused by impaired blood circulation between the placenta and the fetus;
- deficiency of microelements, fat- and water-soluble vitamins in a woman’s body during pregnancy;
- hereditary predisposition, joint hypermobility caused by the peculiarities of collagen biosynthesis;
- injury to a woman during pregnancy, exposure to radiation, heavy metals, acids, alkalis and other chemicals;
- injury to the newborn during its passage through the birth canal;
- violations of the proper development and functioning of individual organs and systems of the fetus due to inadequate tissue trophism;
- sharp fluctuations in hormonal levels, insufficient or excessive production of hormones that affect the production of bone and cartilage tissue cells;
- a woman taking pharmacological drugs of various groups, especially in the first trimester, when the fetus is developing the main organs of all vital systems.
All these factors cause the femur to fall freely from the acetabular cavity during a certain movement. Congenital dislocation of the hip joint should be differentiated from acquired pathology, usually resulting from injury or the development of bone and joint diseases.
Acetabuloplasty
The essence of the operation is to change the angle of inclination of the roof of the acetabulum without completely crossing the pelvic ring. Doctors manage to achieve this through osteotomy - cutting the upper part of the ilium. After this is completed, surgeons move the roof to the bottom and fix it in the desired position. These manipulations make it possible to restore the normal relative position of the hip joint structures, that is, to restore congruence.
Indications for acetabuloplasty:
- coverage of the femoral head - less than 2/3;
- the angle of inclination of the roof of the acetabulum is more than 40°;
- The Wiberg angle, which characterizes the centralization of the femoral head, is less than 20°.
Visual intervention diagram.
Acetabuloplasty is performed under general anesthesia. During surgery, the doctor cuts through the soft tissue to gain access to the hip joint. After completing all the manipulations, he sutures the wound layer by layer and applies a plaster cast. The baby's lower limb is fixed in abduction and moderate internal rotation. After 1.5-2 months, the plaster is removed, and the results of the operation are assessed using radiography.
When performing acetabuloplasty, surgeons can use corrective implants. They are installed along the edges of the acetabulum to create support for the head of the femur. In orthopedics, such operations are called shelf procedures.
Diagnosis of congenital hip dislocation
An immature joint that has not yet formed at the time of birth or has an anatomically incorrect shape can be suspected immediately after birth, even in the perinatal center. External manifestations of congenital hip dislocation in newborns and children of the first year of life:
- asymmetrical skin folds on the legs (one inguinal and/or gluteal fold is deeper than the other, located higher or lower)
- shortening of the leg (with straight legs, one knee is higher than the other)
- limited mobility of the joint, in which the hip is not sufficiently abducted to the side (normally, in a newborn, the legs are separated by 80-90°, after six months - by 60-70°. If the hip is abducted by 50° or less, then it is necessary to show the child to an orthopedist and share with him with his observations)
- symptom of a click or slipping (when the child’s hip is abducted to the side, a characteristic click appears - the head is mobile and is not held in the articular cavity, it slips)
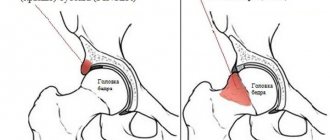
However, none of these signs by themselves is sufficient reason to make a diagnosis. For diagnosis, the child is prescribed an x-ray or ultrasound. Since the cartilage tissue in young children has not yet ossified, the picture is “read” using special tests - schematic axes are drawn through certain points of the cartilage and bones, which make it possible to measure two values: h and d. They talk about displacement of the femoral head, which can be used to judge whether it is normal or pathological.
Ultrasound of joints is a safer and no less accurate diagnostic method than x-rays. Therefore, it is now used much more often.
Triple pelvic osteotomy
There are several triple OT techniques. Each of them involves the intersection of all components of the pelvic ring (pubis, ilium and ischium). After this, the acetabulum is set in the desired position, and the bone fragments are fixed with titanium structures. The screws are removed after 1-1.5 years, that is, after the bones have firmly fused.
Disadvantages of triple osteotomies:
- high traumatic rate;
- high probability of damage to nerves and blood vessels;
- increased risk of developing avascular necrosis;
- the possibility of divergence of the pubic and ischial bones;
- long recovery period;
- narrowing of the pelvic ring in girls, which has negative consequences in the future.
Most often, several triple osteotomy techniques are used in orthopedics. These include OT according to Tonnis, Steel, Chiari, rotational acetabular and a number of modifications such as Bernese, Ganz, RAO. All of these techniques provide good mobilization of the acetabulum and allow it to be placed in the most advantageous position.
Differential approach to the treatment of DTS
The choice of surgical treatment method depends on the nature of the joint deformity. For example, with the acetabular type of dysplasia, patients have the shape and position of the acetabulum corrected, and with the femoral type, the spatial location of the femoral head is changed. In the case of combined DTS, doctors perform surgery on both structures at once. Table 2. Types of operations for different hip dysplasias
| Type of DTS | Most suitable operation |
| Newly diagnosed severe dysplasia | Triple pelvic osteotomy. If necessary, it is combined with open reduction of the hip joint and intertrochanteric OT |
| Residual dysplasia with preservation of congruence of articular surfaces | At the age of 2-10 years, acetabuloplasty is indicated for a child, after 10 years - triple OT. In both cases, the operation can be supplemented with intertrochanteric corrective osteotomy of the femur |
| Residual dysplasia with hip joint incongruity | Children aged 2-8 years usually undergo a triple pelvic osteotomy. At an older age, shelf procedures are performed with her |
Hip dysplasia in children
Prevalence, causes, treatment prospects.
Among the pathologies of the musculoskeletal system in children, hip dysplasia is the most common. Girls, however, make up about 80% of patients. There is also a racial-ethnic dependence on the spread of dysplasia: it is practically not detected in the Chinese and blacks, while 2-9% of white children suffer from this disease. In addition, risk factors for dysplasia are breech presentation, tight swaddling of straightened legs, toxicosis and drug correction of pregnancy. Heredity also plays a big role: a parental history of dysplasia increases the likelihood of a child developing this pathology tenfold.
These statistics require some explanation. There is an opinion that children have begun to suffer from this disease tens of times more often over the past 50 years. This is wrong. The real reason for the deterioration of statistical indicators is the improvement of diagnostic methods and detection of the disease at an early stage. If previously the diagnosis was made only in the case of the most severe stage of the disease, congenital dislocation of the hip, now it is possible to identify subluxation, preluxation and even physiological immaturity of the hip joint.
Normally, the hip joint of an adult is formed by the head of the femur, the acetabulum and the ligamentous apparatus that holds the head in the socket and provides a sufficient range of motion. With dysplasia, the ligaments cannot hold the head of the femur in the socket during certain movements and then subluxation occurs.
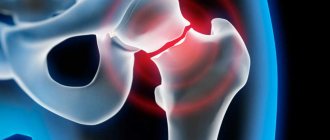
If the head of the femur comes out completely from the acetabulum, then this condition is called hip dislocation.
In the absence of proper treatment for a dislocation, the shape of the bones gradually changes, a new joint is formed (neoarthrosis), but the child grows up disabled - lameness and different lengths of the limbs, as well as the occurrence of further skeletal deformities are inevitable. With timely detection and adequate correction of pathological changes in the joint, complete rehabilitation of patients is recorded in the vast majority of cases. This is why early diagnosis of hip dysplasia is so important.
Diagnostic algorithms.
Ideally, while still in the maternity hospital, the orthopedic doctor conducts the first examination of the newborn for the presence of this pathology. In the first days of life, the presence of a “clicking symptom” (when, when the hips are moved apart, the joint is reduced into the acetabulum with a characteristic sound) is an absolute indication for the start of treatment, which is successful in almost 100% of cases. The next examination of the child by an orthopedist is scheduled at 1 month. The doctor assesses the symmetry of the popliteal, subgluteal and inguinal folds by straightening the child's legs. Then, with the knees bent, he checks the separation in the joints.
Limiting dilution on both sides most often means increased muscle tone and is corrected by a neurologist. If abduction is limited on one side, then most likely this is a congenital pathology of the hip joint. If the separation in the hip joint is too wide, a bilateral lesion should be excluded. The most gentle and at the same time the most informative diagnostic method for this age is ultrasound. On ultrasound, you can see not only bone, but also cartilaginous structures, evaluate how stable the morphology of the joint is and evaluate the dynamic capabilities during the study.
The next scheduled visit to the orthopedist should be made when the child is 4 months old (ossification nucleus). This period should not be neglected, even if the doctor previously said that the child was practically healthy. The hip joint of an infant is an unstable system at birth and immature; pre-development and ossification (ossification) of some structures occurs after birth, and a normally developing joint can unexpectedly slip by this age and result in pathology. At this age, with dysplasia, the shortening of the leg on the affected side will already be visually noticeable. Children with suspected hip dysplasia undergo an ultrasound scan, and if the diagnosis is confirmed by ultrasound, an X-ray examination is performed. It is impossible to do without radiation exposure, since only an x-ray gives a fairly clear picture of the exact angle at which the head of the femur is displaced. At this age, treatment is successful in approximately 80% of cases. The same assessment of the joint is carried out at 6 months, but if dysplasia is detected, its treatment is successful only in half of the cases.
In a one-year-old child, it is easier to diagnose a dislocated hip joint, since new symptoms are added at this age, but, unfortunately, only 4% of children are cured when the diagnosis is made so late. Such children begin to walk several months later and limp when walking, tilting the body to the affected side. With bilateral damage, a “duck” waddling gait is observed. But the most reliable picture of the condition of the hip joint is still provided only by an x-ray. In case of confirmed pathology, for a detailed assessment of the articular structures and the choice of treatment tactics, arthrography can be performed with the introduction of a radiopaque substance directly into the joint capsule. The technique is deeply invasive, but in some cases irreplaceable.
The need to conduct a radiation examination on a child at such an early age is, of course, a disadvantage of this diagnostic algorithm, and today ultrasound examination methods are considered more relevant for children under one year of age. In addition to ultrasound screening of the hip joint, performed through a lateral approach (with the child positioned on its side), Doppler ultrasound is increasingly being used as an additional harmless and non-invasive diagnostic method. This method allows you to determine the presence of pathological changes in the vessels that supply the joint structures. But today, unfortunately, there are no clear figures for normal indicators and degrees of pathology, since different authors give different values, so this method is used mainly for monitoring the condition during treatment.
The youngest diagnostic method is MSCT - multislice computed tomography, which makes it possible to establish in all details, including in 3D mode, the exact relationships of joint structures. This technique is used mainly in older children who have not been diagnosed with a dislocation in a timely manner.
Treatment methods.
Today, pediatric orthopedics is so developed that with early diagnosis, the prognosis is almost always conditionally favorable. If dysplasia is detected in a child during examination in the maternity hospital, depending on the situation, wide swaddling or treatment with a splint may be recommended. Many children with physiological immaturity of joint structures are prescribed wide swaddling for the purpose of prevention.
For wide swaddling, a diaper folded in 6-8 layers is placed on top of the diaper between the baby’s legs, preventing the legs from being too close together. This spread of the legs helps keep the hip joint components in the correct position.
In case of a more serious violation, a splint is applied: soft cuffs wrap around the ankles, the legs are passively spread to the sides and in this position are fixed with a bar fixed in the cuffs.
Weekly, and after a month - once every two weeks, they check how much freer the movements in the joint have become and, taking this into account, change the length of the spacer bar. These simple methods allow in most cases to achieve cure within 3-4 months.
Sometimes a Freika pillow is used, essentially the same wide swaddling, but allowing less movement in the hip joint.
“Pavlik stirrups” are also used - a device that does not allow straightening of the legs, but does not limit any other movements.
If the diagnosis is made later, from 3 to 6 months, or the treatment turned out to be not effective enough based on the results of the control x-ray examination, then a plaster cast can be applied with the maximum possible non-violent abduction, rigidly fixing the joint in the correct position, followed by treatment with a splint. The duration of treatment with such a bandage varies from 2 to 6 months. Next, to consolidate the result, a spacer splint is applied for a period of about 3 months. If the formation of articular structures is delayed, physiotherapeutic procedures may be prescribed.
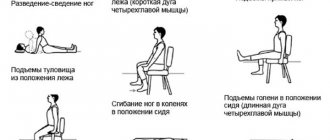
With a later diagnosis of dysplastic disorders in the hip joint and with high dislocations in a specialized hospital, reduction of the dislocation and subsequent treatment with a plaster cast in the Lorenz position, FTP, can be applied. In all cases, after completion of treatment, children are prescribed several courses of massage and physical therapy is required.
In children with severe dislocations, in case of ineffective conservative treatment or too late diagnosis, operations are performed, the purpose of which is to restore the relationship of the anatomical structures of the joint and its subsequent long-term immobilization. Sometimes not one, but several operations are required, and it is not a fact that the outcome of treatment will be the patient’s rehabilitation.
Recommendations for parents.
If your child has been diagnosed with hip dysplasia, you should under no circumstances panic, but you should prepare for what will be difficult. Children with splints, splints and Freika pillows may sleep worse and be more capricious, want to be held in their arms and, of course, parents have a completely natural desire to get rid of orthopedic structures as early as possible. This is absolutely impossible to do, since the state of stabilization in children occurs quickly, but is also quickly lost, so it is necessary to adhere to the period indicated by the orthopedist-traumatologist.
You should not skip routine examinations with an orthopedic doctor, since early diagnosis of diseases in general and hip dysplasia in particular is the key to a child’s health in the future. Do not neglect the recommendations for the use of wide swaddling for a baby. This type of swaddling does not cause any inconvenience to the child and is a guaranteed preventive measure for severe joint pathology.
Don't take lightly things like your child's limited hip mobility or unsymmetrical crotch folds. Even if your doctor said that everything is fine, but your parent’s heart is restless, in this case it is better to consult with another specialist and conduct an additional examination than to calm down and discover an obvious problem when it will be very difficult, and sometimes impossible, to correct it.
In what cases is it necessary to replace the hip joint?
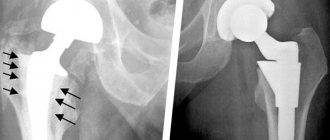
Total endoprosthetics is the most effective method of treating dysplastic coxarthrosis. The operation is performed for massive destruction of articular cartilage and destruction of subchondral bone tissue. Joint replacement in this case helps to get rid of chronic pain and restore impaired joint function.
Orthopedists try not to perform endoprosthetics on adolescents and young people. The reasons are the limited service life of the endoprosthesis, the need for subsequent revision operations, the high frequency of postoperative dislocations and loosening of the implant.
The flattening and deformation of the acetabulum makes it difficult to immerse the acetabular component of the endoprosthesis into it. This is what leads to instability of the hip joint, dislocations and loosening of the endoprosthesis.
How much does surgical treatment of dysplasia cost?
In Russia, the minimum cost of an operation for DTS is 35,000 rubles. In this case, the patient is required to additionally pay for preoperative examination and consultations, hospital stay, consumables, implants and rehabilitation. In total, such treatment can cost 70-100 thousand rubles.
As for treatment abroad, the cost there is calculated in euros. In Israel, the operation will cost 18-22 thousand euros, in Germany – 15-18 thousand euros. You will find the most affordable prices in the Czech Republic. There, you will pay about 2,500 euros for surgery combined with rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation is an important part of treatment that cannot be neglected. However, most Russian clinics do not offer it in full. They discharge patients a few days after surgery. Such tactics may negatively affect the results of treatment.