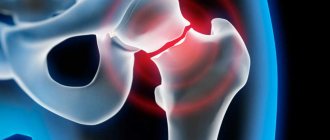
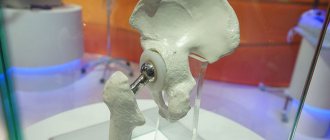
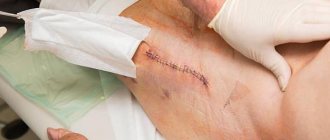
Hip arthroplasty (HJ) is a partial or complete replacement of joint components. During the operation, worn parts or a completely destroyed natural joint are replaced with an artificial one. Restoring mobility depends not only on the quality of the intervention itself and the initial state of the body. A huge role in this is played by the patient’s recovery and the use of effective rehabilitation methods. One of the first places in importance is occupied by exercises after hip replacement.
Regular exercise helps restore muscle tone and functionality of the musculoskeletal system. The main principles of rehabilitation measures are reasonable limitation of physical activity and physical therapy exercises. An early start, an individual approach to their implementation, as well as consistency, continuity and complexity of actions guarantee the effectiveness of recovery and allow you to return to normal life in about a year.
General principles of rehabilitation
After hip replacement, the following patient care goals are pursued:
- achieving painless movements in the hip joint;
- maintaining the patient’s normal lifestyle and independence;
- normalization of the muscular-ligamentous complex, which brings the articular bones into coordinated movement;
- maintaining correct movement patterns;
- strengthening weak muscle groups;
- achieving correct coordination in individual muscle groups.
The basis of recovery is the use of physiotherapy procedures, gentle statistical exercises, and competent medication assistance. Thanks to this approach, the following results are achieved:
- blood circulation is stimulated in the lower extremities;
- muscle strength and range of motion in the damaged part increases;
- swelling, pain, inflammation are eliminated;
- the statics of the spinal sections is corrected;
- immunity against possible consequences is developed;
- possible negative reactions are prevented.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy includes the use of specific compounds, namely:
- the use of antibacterial drugs against the development of infection;
- the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain and inflammation;
- the use of protein and calcium supplements to accelerate the recovery of bone and muscle structures;
- anticoagulant drugs projectors that protect against the formation of blood clots in the veins;
- for the prevention of heart failure;
- the use of gastroprotectors and drugs that improve the functioning of the urinary tract;
- drugs to eliminate intestinal atony.
Comprehensive physiotherapy
Physiotherapy after hip replacement is an important component of rehabilitation, which helps ensure blood microcirculation, stimulates metabolic processes, increases muscle tone and reduces spasms.
There are a number of complex procedures aimed at post-rehabilitation surgery. These procedures include:
- kinesiotherapy – is a set of specially selected programs that help speed up the recovery process already in the early postoperative periods;
- hydrokinesitherapy - differs from the previous method in that all exercises are performed in the pool, which reduces the load on the joint capsule and eliminates discomfort;
- cryotherapy – forms filled with hydrogel are applied to the patient at the site of prosthetics for 15 minutes, which helps eliminate swelling and pain that arise after prosthetics;
- electrical stimulation - the patient is exposed to tissues with current with certain parameters, which causes muscle contraction, helps strengthen them and increase tone, which stimulates metabolic processes and increases blood circulation in the hip joint;
- magnetic therapy – with the help of a special device, microcirculation in the tissues is stimulated for the patient, which helps accelerate healing;
- WATSU technique – represents deep muscular and emotional relaxation, which reduces pain and increases the efficiency of muscle function;
- orthosis – the patient is selected with a bandage necessary for fixation, unloading and correction of limb functions;
- laser therapy – a light beam is used, which mobilizes the body, stimulates the functioning of its self-regulation mechanisms, reduces swelling, pain, inflammation, and also improves the condition of the immune system;
- massage - prescribed in the absence of acute pain in order to increase blood flow and saturate tissues with oxygen, which promotes their speedy regeneration.
Why is it important to do exercise therapy and gymnastics?
The recovery period should begin immediately after surgery in a hospital setting. After discharge, rehabilitation takes place at home or in a special center. It ends in a dispensary, sanatorium or special rehabilitation treatment center. Exercises after hip replacement at home should be continuous. For complete recovery, it is necessary not only to regularly engage in exercise therapy, but also to pay appropriate attention to therapeutic walks. An integrated approach will help strengthen the muscular-ligamentous system and securely fix the implanted prosthesis.
If you neglect rehabilitation measures, there is a high risk of:
- dislocation of the head of the endoprosthesis;
- periprosthetic fractures;
- development of neuritis and other complications.
Restoring your ability to work is hard work. Without perseverance, an unshakable desire to be healthy and strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations, it is almost impossible to achieve a positive result.
Rehabilitation periods
All rehabilitation measures aimed at restoring the functionality of the operated leg and the full development of the artificial joint are usually divided into three time periods:
- Gentle includes the initial and early stages. The first lasts from the transfer of the patient from the operating unit to the ward until the end of the first week of his stay there. The second starts from week 2 and ends with week three. The prescribed manipulations are performed in an inpatient trauma department or a specialized center.
- immediate recovery period is also divided into early (from 4 to 9 weeks) and late (from 10 to 12 weeks) stages. It takes place at home or in a rehabilitation center. Exercise therapy after hip replacement takes an important place here.
- The adaptation (remote) period begins from the 13th week and ends on the 24th. The place where it passes is a house or a sanatorium.
For each stage, average times are indicated. Their fluctuations depend on a number of factors, including:
- a person’s age, the presence of concomitant pathologies, disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- the option of access to the operated hip joint used during the intervention (anterior, posterior, lateral);
- the condition of bone tissue, their fragility and ability to recover.
Also, a lot depends on the patient himself, his diligence and desire to follow all available recommendations.
Periods of rehabilitation of the hip joint
Doctors may prescribe hip replacement for the following injuries or pathologies:
- femoral neck fracture;
- coxarthrosis;
- osteonecrosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
Previously, the presence of such diseases or injuries meant disability, but now, with successful treatment, the patient can restore the functional activity of the joint.
To speed up the rehabilitation period, you should follow all the recommendations of your doctor and perform special exercises. There are several periods of rehabilitation and each of them has its own specific rules.
Conventionally, rehabilitation is divided into 3 periods:
- Early period – lasts from the first day after the operation and up to 3 weeks after it. The early period is also divided into 2 stages:
- gentle – 1-7 days, during which inflammation of the wound occurs after surgery;
- tonic – 7-15 days, during which the wound begins to heal.
- Late period – rehabilitation during this period is carried out in a physical therapy room, where the patient goes immediately after discharge from the hospital. The late period is also divided into 2 stages:
- early - lasts from the 15th to the 60th day, when bone structures are utilized;
- late - from 45-60 to 90 days, when the internal structure of the femur is restored.
- Long-term period - lasts from the 3rd to the 6th month, when the femur takes its final shape and structure.
Early period
The early period of rehabilitation for the patient begins exactly at the moment when he recovers from anesthesia after surgery. This period helps the patient achieve the following goals:
- reduce swelling;
- improve blood circulation in the operated area;
- accelerate the healing of the postoperative suture;
- learn how to first sit in bed and then get out of it;
- prevent the development of various complications such as bedsores, thrombosis, pleurisy or congestive pneumonia.
There are certain rules for the early period:
- the first few nights after hip replacement, you should sleep only on your back;
- you can turn on your healthy side at the end of the first day, on your stomach - after 5-8 days; a nurse should help the patient perform all manipulations;
- changing into street shoes can only be done with the help of a stranger; if the patient changes shoes independently, then he definitely needs a shoehorn;
- making sharp turns or rotations in the hip joint is contraindicated;
- before lying on your side or turning over on your stomach, you should spread your legs slightly to the sides;
- hospital shoes must be without backs;
- the affected leg should not be bent at an angle greater than 90 degrees;
- You can’t bring your legs together or cross them; you should place a wedge-shaped pillow between your knees;
- you need to sit up in bed using your hands;
- you need to perform simple exercises to prevent blood stagnation;
- You can’t squat for a long time;
- You need to walk without leaning on the operated limb.
Basic exercises
Consist of exercises for the calf, thigh and gluteal muscles for both legs:
- every 10 minutes you need to move the toes of the sore foot;
- 6 approaches per hour should be performed by bending and extending the fingers;
- Press your heels onto the bed 6 times;
- move your arms - rotate, bend at the elbows, wave, lift at the shoulders;
- strain the buttocks, thighs and legs on the healthy side - this is called isometric tension;
- after 2-3 hours you need to activate the ankle of the operated leg - perform slight flexion and extension, rotate clockwise and counterclockwise;
- slide your foot along the surface of the bed, pull your leg towards you, bend it at the knee, repeat this 10 times;
- move one leg away from the other, then return it to the previous position and do the same procedure with the other leg, repeat up to 10 times with each limb;
- alternately lift your straight leg a few cm above the bed 10 times.
A set of exercises that can be performed at the initial stage of rehabilitation after hip replacement is shown in the video below:
There are rules for performing such exercises:
- do several approaches, spending 15-20 minutes every hour throughout the day;
- make sure the pace is slow and smooth;
- When you tense your muscles, inhale deeply; when you relax, exhale;
- perform breathing exercises to avoid congestion in the lungs;
- in the early period, exercises are performed only while lying on your back.
An hour or two after the operation, the patient must go to the toilet - if he cannot do this on his own, he will need to ask the doctors to insert a urinary catheter and remove the urine.
Additional exercises
After the patient learns to sit down, roll over and stand up correctly, he is replaced with another set of exercises, which must be performed every day in a standing position, leaning on the back of a bed or chair. This complex consists of the following exercises:
- stand facing the head of the bed and alternately lift your right and left leg and bend it at the knee;
- starting position - lean on one leg, then on the other, move it to the side and lift it slightly;
- the starting position and basis of the exercise are the same as in the previous one, but the leg must be slowly moved back, straightening the hip joint.
The sooner the patient begins to walk after surgery, the less likely it is to develop muscle contractures in the hip area.
Late postoperative rehabilitation
The main goal of this stage is to develop the leg in such a way as to restore full functionality to it, work on posture, and improve the ligamentous-muscular center. Great importance is given to the section of physiotherapy, and all treatment and rehabilitation measures are aimed at:
- increasing muscle endurance;
- the maximum possible expansion of musculoskeletal functions;
- correction of adaptive habits when moving;
- achieving absolute stability of the hip joint;
- practicing symmetrical work of both legs.
When performing exercises at the late postoperative stage, you should gradually increase the load, as if preparing the limb for the fact that it will soon have to move independently, without the use of crutches and a cane.
The exercises are supplemented by walking - several times a day, from 3 to 10 minutes, increasing the duration over time to 20 minutes. You need to repeat it either every day or every other day.
You need to start walking, leaning on a cane, and remove it only when the patient is completely confident in his abilities and balance.
To perform some exercises you will need a special elastic band. They need to be done in a standing position, with additional load on the limb:
- Fasten one edge of the tape to a special wall or door, and the other near the shin. Standing with your back straight, hold on to the support and move your leg forward, as if overcoming the resistance of the band.
- In the same position, slightly lift your leg up without bending it at the knee.
- Holding onto the support, stand sideways at the place where the tape is attached and move your leg to the side. Do the exercise smoothly, repeat 10 times.
There is also a basic complex of late exercise therapy, with the number of repetitions of one exercise - 6-10 times and the cyclicity of the complex - 2-3 times a day:
- squeeze the ball placed between your legs in the knee area;
- lie on your stomach and bend your knee, trying to reach your buttocks with your feet;
- while lying on your back, place your feet on the floor and bend your legs at a right angle, then lift your pelvis, stay in this state for 3-5 seconds, then return to the original position;
- lie on your back and alternately bend your legs at the knees, without lifting the heels of your feet from the floor or bed;
- lie down on a hard surface on your stomach, lift your leg without jerking and lift it, straining your gluteal muscles, lock in this position for 5 seconds, then smoothly lower your leg to its original position and repeat with the second leg;
- imitate riding a bicycle, sit on the couch, stretch your legs slightly forward and begin to perform movements as if you were pedaling.
We recommend watching how to perform therapeutic exercises yourself after hip replacement:
Turning onto your stomach is done with a pillow between your knees through your healthy thigh.
Functional recovery period
Rehabilitation after prosthetics ends after 3 months, however, functional recovery should still continue. If the specified period has already expired, and the pain in the leg still bothers you or there is a feeling of discomfort, you should use a cane, and active sports are allowed only after 8-12 months.
Rehabilitation at home
Performing exercises at home is quite a risky undertaking, since there are many dangers in the home for a person with such an injury, but, nevertheless, there are several reasons to undergo rehabilitation at home:
- there is a rehabilitation specialist in the family;
- the patient is feeling unwell and constantly needs help, which can only be provided to him at home;
- if the patient, on the contrary, is in such good health and condition that he does not need any outside help.
Home rehabilitation has its advantages, which include the following factors:
- for some people, being in their home, among family members, is a source of additional strength;
- At home you can set your own individual daily and exercise schedule;
- many people can work from home.
In order for the patient to comfortably and successfully engage in rehabilitation, the following conditions should be provided:
- there must be order in the house and every thing needed by the patient must be in a place accessible to him;
- a special place for sitting should be equipped, ideally it should be a shallow chair with high armrests;
- if the patient lives in a private house, then he should arrange a room on the ground floor so that he can leave the house without any difficulty;
- the bathroom should have benches and handrails for support when standing up;
- The house should have adequate lighting, rugs should be secured, and the floor should not slip.
Gymnastics on simulators
During the functional recovery period, the adaptive motor mode is expanded due to physical therapy on simulators. By this point, the ligaments and muscles should be strong enough, which means that the intensity of the load can be increased.
Let's look at the most common exercises on simulators:
- Exercise bike. First you need to pedal backwards, if you can do this without much effort, then start pedaling forward. Do this exercise for 15 minutes twice a day, gradually increasing the duration to 25-30 minutes 3-4 times a week. You cannot raise your knees above your joints.
- Treadmill. Stand with your back to the control panel and grab the handrails. Start walking backwards at a slow pace (speed 1-2 km/h). When the foot touches the track, the leg should be completely straight.
- Exercise bike with low pedals. Adjust the pedals so that you can simulate riding a bicycle, but when you lower the pedals, each leg remains completely straight.
What rules must be followed in the postoperative period?
In order for a person’s motor function to be restored as quickly as possible, the following rules should be followed:
- using handrails, you can sit down and stand up already on the second day after surgery;
- physical activity should increase gradually;
- on the 5th day, you can try to climb several steps of the stairs, taking the first step with your healthy leg (vice versa when descending);
- You cannot make sudden movements;
- do not cross your legs;
- you cannot carry objects heavier than 5 kg;
- you cannot bend over and pick up objects from the floor without the help of special devices;
- you need to keep your weight within certain limits;
- do not overload the operated leg - you should change its position every half hour;
- you can drive at least 2 months after home rehabilitation;
- when traveling in a car in the passenger seat, you should stretch your legs as far as possible;
- You can sleep on your back or side with a cushion between your knees;
- the diet should be balanced;
- Sexual relations can be resumed 2 months after the operation.
Lifetime recommendations to follow
After hip replacement, the patient should understand that from now on a number of nuances will appear in his life that he will have to observe throughout his life:
- take care of the joint and ensure that there is no bending of more than 90 degrees;
- lead an active and mobile lifestyle;
- do not quit training even after full recovery;
- keep in touch with your doctor on an ongoing basis;
- exclude alcohol, smoking;
- improve nutrition;
- do not self-medicate if the functioning of the prosthesis worsens.
What are the consequences of lack of proper rehabilitation?
If, after hip replacement, rehabilitation is not carried out in the required sequence or is absent altogether, then the injured muscles begin to lose tone, and scars may form at the incision sites. If the patient does not strain the limbs, the ligaments will remain in a stretched position, which will lead to the following consequences:
- dislocation of the prosthesis head;
- inflammation of the nerves that are located near the prosthesis;
- broken bones near the prosthesis.
Nutrition rules
Within 6 weeks after the operation, the process of fusion of the head of the prosthesis with the pelvic bone occurs. The success of this process largely depends on proper nutrition. If the diet is not followed, the risk of dislocation of the head of the prosthesis, constipation, and enterocolitis increases.
Why is a diet prescribed after surgery?
- To normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. After application of anesthesia, temporary intestinal atony develops. You can only eat semi-liquid, pureed foods. These can be soups in vegetable broth with chopped dietary meat, slimy porridges. It is forbidden to consume any fast carbohydrates, fatty, fried, spicy foods.
- To compensate for blood loss. To restore the volume of circulating blood immediately after the end of anesthesia, you must regularly drink water in small sips. During the week you need to drink more, limit the daily amount of salt. To restore hemoglobin, consume foods high in iron, ascorbic acid, and vitamin B
- Strengthen the body's protective functions. Consume more fermented milk products to improve intestinal microflora.
- Accelerate the process of bone tissue restoration. The menu should include protein products.
Proper nutrition must be maintained even after rehabilitation is completed. This will help avoid excess weight gain and increased stress on the joint. Therefore, the basis of the diet is proteins, slow carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
Diet during rehabilitation:
- Proteins are necessary for the body to build its own proteins, collagen fibers of bone tissue. Sources of healthy animal protein include dietary meat and fatty fish. You definitely need to eat jelly and jellied meat - these dishes contain gelatin, which is a protein in its pure form. Plant sources of protein include soy, peas, beans, lentils, buckwheat and oatmeal.
- Complex carbohydrates. After endoprosthetics, you must give up sweets, pastries, white bread, and pasta. The menu includes foods with healthy carbohydrates - vegetables, grains, which contain few calories, but are rich in fiber and vitamins.
- Unsaturated fatty acids. After endoprosthetics, it is useful to consume foods with Omega-3 acids, which are found in fatty fish, crab meat, shrimp and red caviar. Unsaturated acids reduce the manifestations of the inflammatory process, cleanse blood vessels of harmful cholesterol, prevent the development of obesity, and accelerate wound healing.
- Bran as a source of fiber and vitamins. There is also a lot of fiber in flax seeds, dried mushrooms, and dried fruits.
- Calcium and vitamin D are essential to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and lysis. After endoprosthetics, it is necessary to consume 1-1.2 thousand mg of calcium per day. Sources: cheese, fish, sesame, almonds, herbs, garlic, hazelnuts. Calcitriol is required for normal calcium absorption. Vitamin D is found in cod liver, mushrooms, and egg yolk.
- Iron-rich foods. Chicken, shrimp, tuna, beets, pumpkin, nuts, buckwheat porridge.
Possible complications
Given the seriousness of the operation, the doctor must inform the patient about all possible complications or consequences. Most often, prosthetics ends successfully, especially if the patient obediently complied with all the requirements and recommendations.
The operation is an external intervention in the human body, therefore, you should be prepared for any situation:
- bleeding;
- prosthesis rejection;
- displacement of the prosthesis;
- infection in the wound;
- the development of asymmetry, in which one leg will be different from the other;
- dislocation of the prosthesis head;
- pulmonary artery thrombosis;
- complete destruction of the structure.
Also, the patient will be accompanied by pain for quite a long time. In a situation where complications cannot be eliminated using conservative methods, revision endoprosthetics is used. During which the implant will be replaced with another one, taking into account all the body’s reactions.
Rehabilitation for injuries and diseases of the hip joints should not be neglected. Yes, it can be hard, and it takes a lot of time. But without an adequate recovery process, returning to a normal, fulfilling life will not be possible in principle. Therefore, you should try hard so as not to receive disabled status in the future.
Drug treatment
Medicines are prescribed to relieve pain, signs of inflammation, accelerate regeneration and prevent the development of complications.
Main groups of drugs and their action:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics prevent the development of secondary bacterial infections after surgery.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - eliminate pain and manifestations of the inflammatory process.
- Vitamin complexes with calcium, chondroitin, collagen accelerate the regeneration of muscles and bone structures.
- Anticoagulants - prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Cardioprotectors - reduce the risk of developing heart failure.
- Gastroprotectors - protect the walls of the stomach and duodenum from the aggressive effects of other drugs.
- Anticholinesterase drugs - eliminate intestinal atony.
After antibacterial therapy, a course of probiotics and dental antibiotics is prescribed to restore the balance of the intestinal microflora.