Currently, calcium is widely used to treat bone fractures, promoting faster bone recovery and normalizing blood flow. After a fracture, an injured person has to wear a cast for a long time in order for a callus to form that will bind the fragments. This has many disadvantages, since prolonged immobilization can result in venous congestion and muscle atrophy.
Systematic intake of calcium supplements for bone fractures can significantly shorten the rehabilitation period and facilitate a faster return to normal life.
The role of calcium in fractures
The body is a highly organized self-regulating system capable of self-healing. However, sometimes the body lacks the strength to heal effectively, which can slow down or cause improper healing.
After a fracture, a person has to wear a cast for a long time.
Every bone fracture has its own phase of fracture healing. The period of calcification is considered the most sensitive because it is during this time that the body directs the lion's share of its own calcium reserves to the injured area to effectively store calcium. However, with serious injuries, the body's reserves may not be enough, and calcium supplements come to the rescue.
For bone fractures, calcium must be prescribed along with vitamin D, which supports the absorption of this microelement. In addition, experts say that this substance is absorbed much better in the evening. Since this element is usually lost by the body at night, taking it in the evening will help slow down the process.
In addition, it should be remembered that it is better to consume microelements during or after lunch, since then they are better absorbed. Periodic electrophoresis will also help improve calcium absorption.
This causes calcium particles to move towards the affected area under the influence of an electric field. In addition, this type of physiotherapy improves the penetration of microelements into bone tissue.
Compression fractures of the spine due to osteoporosis
With advanced osteoporosis, you don’t need to put in much effort to get a fracture. The bone can break suddenly when lifting a heavy object, going down stairs, or even when moving suddenly or turning from one side to the other. And if you are exposed to a traumatic factor, for example, getting into an accident or falling from a height, the likelihood of getting one or more fractures increases exponentially.
At the same time, it is the spine that suffers greatly from osteoporosis. It is formed by 33 vertebrae, and each of them can “flatten” at any time under the influence of the body’s own weight if the patient has a severe form of osteoporosis. The vertebrae that bear the greatest vertical load are most often affected: the lumbar region and the last two thoracic regions.
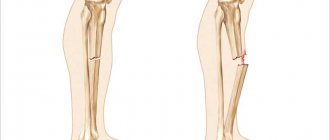
In such cases, compression fractures are usually diagnosed. They are characterized by a decrease in the height of the vertebral body. It seems to be compressed, as a result of which the front part takes on the shape of a wedge. This leads to a change in the natural deflections of the spinal column and the emergence of a number of symptoms.
Depending on the severity of the compression fracture, there are 3 degrees of injury:
- Grade 1 – vertebral height decreases by less than 30%;
- 2nd degree – the decrease in vertebral height is in the range of 30–50%;
- Grade 3 – the vertebra is flattened by more than 50%.
If a compression fracture occurs due to osteoporosis, the probability of getting a second fracture within the next year is 15–25%.
Calcium fortified foods
Calcium is the main building material of bone tissue, so it is not surprising that people called it “liquid stone”. Calcium is essential for bone fractures, so most victims immediately seek a therapeutic form of this substance for these types of injuries.
However, calcium supplements, like other medications, should only be used when there are no other alternatives.
Foods high in calcium
As a rule, doctors recommend, first of all, adjusting your own diet to include foods rich in calcium. The fact is that this element is contained in products in a form that is easier to digest and more suitable for humans. Therefore, any competent specialist, when asked which calcium is best to take for fractures, will indicate organic.
This calcium is found in the following foods:
- green leafy vegetables (spinach);
- fish (salmon, herring, sardines);
- whole wheat bread;
- dairy products;
- Nuts (almonds);
- poppy; sesame seeds;
- shrimps.
For more effective absorption, it should be combined with other micronutrients. Of particular importance are zinc and vitamin D. They act as catalysts. Sources of zinc include pumpkin, buckwheat, oatmeal and mushrooms.
Diagnosis of spinal compression fractures and osteoporosis
Diagnosis of a compression fracture is the task of a traumatologist or vertebrologist. Initially, the doctor interviews the patient and conducts an examination. There are a number of signs that allow you to determine the presence of spinal damage and suggest a fracture of one or more vertebrae.
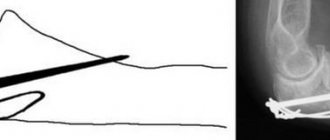
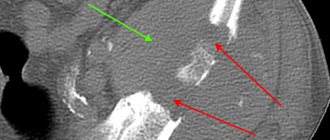
Compression fractures of the spine are diagnosed using x-rays taken in two projections. In the resulting images, you can also notice abnormal bone transparency, typical of osteoporosis. Only CT provides a more complete picture of the condition of the spine. If ligament damage or spinal stenosis is suspected, patients are prescribed an MRI.
If neurological symptoms are present, electromyography may be performed, which evaluates the conduction of nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the limbs and other parts of the body.
If it is assumed that the cause of the compression fracture was osteochondrosis, ultrasound densitometry is performed. During the examination, the speed at which ultrasound passes through the bone being examined is assessed, which makes it possible to accurately determine its density. Therefore, based on the results obtained, the diagnosis is refuted or the stage of osteoporosis is established.
Calcium for bone fractures: preparations
Pharmacies offer a wide range of products containing calcium. Since this element is the main component of bone, a person who has broken several bones tries to buy the product with the highest concentration of calcium. And he doesn't delve into what is the best preparation for him. But with such drugs, not everything is so simple.
As already mentioned, in some products calcium remains in its form and is then poorly absorbed through the body. In addition to this element, it is also important to observe the dosage and control the level of substances in the blood, because excess calcium is just as destructive as its deficiency.
Hypercalcemia can lead to heart problems and also trigger the formation of kidney and gallstones. Therefore, you should also be careful when choosing calcium-containing products. wisely.
Calcium gluconate
This drug is one-component. Calcium gluconate is widely used to treat bone fractures. The drug is available in two pharmacological forms - solution for injection (in ampoules) and tablets. The dose of the drug in each individual case is prescribed by a doctor, but, as a rule, the drug is taken three times a day, before meals, in combination with vitamin D.
The drug should be taken with clean water, as tea and coffee impair the absorption of calcium. The daily dose of the drug for an adult should not exceed 9 g.
During hospitalization, calcium gluconate can be administered intramuscularly and intravenously. The drug is prescribed with caution to pregnant and lactating women and only if the benefits of using the drug outweigh the possible harm. However, throughout the entire period of taking the drug, the level of calcium in the blood is monitored.
The most common side effects while taking the drug are constipation, stomach discomfort, as well as nausea and vomiting. In addition, when using high doses of the drug, symptoms of hypercalcemia may occur: drowsiness, weakness, irritability, abdominal and muscle pain, increased blood pressure and heart rhythm disturbances.
In addition, calcium gluconate also has contraindications:
- atherosclerosis;
- stones in the kidneys;
- hypercalcemia;
- tendency to form blood clots;
- renal and liver failure;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Therefore, it is recommended to take the drug only after consulting a doctor and after carefully studying the instructions for the drug.
When are calcium gluconate injections given?
Among the indications for the course of injections of the drug:
- pathologies of the parathyroid glands;
- allergic complications;
- liver intoxication;
- hyperkalemia;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- diabetes;
- rheumatism.
The solution is administered intravenously and intramuscularly once a day. If necessary, the product is diluted in saline and heated to +35°C.
Single dose: 5–10 ml of the drug. For children from the first days of life and adolescents under 14 years of age, the medicine is administered intravenously. The dose is calculated from 0.1 to 5 ml.
The treatment regimen involves daily injections or 2-3 injections per week.
Calcium for bone fractures: calcium-D3 Nycomed
This pharmacological agent is also prescribed for fractures for rapid healing of bones. Since the drug contains both calcium and vitamin D3, it is perfectly absorbed in the digestive tract and is evenly distributed in the tissues of the body. Nicomedicine calcium-D3 for fractures promotes rapid bone regeneration and helps replenish micronutrient deficiencies.
The drug is available in the form of chewable tablets with a mint-orange flavor, which is especially popular with children. Another plus is that the product can be taken regardless of meals. The dosage and frequency of administration are determined by the doctor. The age of the patient is taken into account, as well as the stage of his disease. However, often the dose does not exceed 2-3 tablets per day.
The drug has virtually no side effects and is quite easily tolerated by patients. For women during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is prescribed strictly by a doctor with subsequent monitoring of calcium levels in the blood. However, it is better for the following people to avoid taking the drug:
- With increased concentrations of Ca and vitamin D in the body;
- In case of excessive sensitivity to the components of the drug;
- with renal failure;
- with phenylketonuria;
- with sarcoidosis.
What is Calcium Gluconate good for?
Mineral ions ensure the functioning of muscle tissue, bone restoration, and hematopoiesis. Calcium Gluconate has a systemic effect, regulating metabolic processes and the functioning of internal organs. The drug has a hemostatic, anti-allergenic effect, reduces the intensity of inflammation, stabilizes the permeability of cell membranes, helps prevent swelling, supports heart function, and strengthens tooth enamel.
Calcium gluconate is non-toxic, absorbed into the blood in the small intestine, and penetrates fluids and tissues. Excess ionized substance is filtered by the kidneys and excreted in the urine.
Calcium for bone fractures: calcemin
This is a multicomponent drug that contains not only calcium and vitamin D, but also zinc, magnesium, copper and other elements. This composition promotes better absorption of the drug in the intestines and more efficient absorption of calcium in the body. Calcemin is available in tablet form, but, as with other calcium preparations, the dosage and number of doses is determined by the doctor.
Typically, adults are prescribed 2 tablets per day (morning and evening), and children are prescribed only one tablet. Since the composition already contains vitamin D, there is no need to take it additionally to avoid an overdose.
The drug is prohibited for use in the following cases:
- hypercalcemia;
- stones in the kidneys;
- Allergy to any of the ingredients;
- increased risk of developing blood clots.
If you experience dizziness, nausea, vomiting, or heart discomfort while taking this medication, stop taking it and call your doctor.
Symptoms of a compression fracture of the spine
Features of the clinical picture of a compression fracture of the spine are determined by which vertebra was affected. Therefore, patients may experience:
- constant pain in the area of the fracture, which intensifies during the day during physical activity and can radiate to the chest, shoulder girdle, arms, legs, buttocks;
- reflex muscle tension;
- limited mobility;
- change in posture;
- increased fatigue;
- adoption of a forced posture, attempts to reduce the load on the affected spinal motion segment;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system;
- reduction in growth.
With osteoporosis, multiple compression fractures often occur, i.e. injuries to 2 or more vertebrae. In such situations, there is a combination of symptoms typical for damage to each of them.
In older people, sometimes compression fractures of the spine occur unnoticed and do not appear in the future. This cannot be called a positive feature, since over time the defect grows together on its own, but forms an irregular shape and position of the vertebra. This leads to a number of complications, including kyphotic curvature of the spine, poor posture, limited mobility, etc.
In severe cases, an undetected compression fracture can be complicated by compression of nerve endings and spinal stenosis, which can lead to decreased sensitivity and paralysis.
How to check calcium levels in the body
Because drug treatment of Calcium requires regular monitoring of the concentration of substances in the body, patients must undergo regular tests. Since direct testing for calcium in bones is not possible, blood tests are usually performed.
The laboratory test determines the level of calcium, which is present in the blood serum in three forms: free calcium, albumin-bound calcium, and their derivatives.
A value of 2.15 to 2.5 mmol/l is considered normal. However, these results are quite relative, since it is possible that relatively high levels of calcium in the blood cause calcium deficiency in the bones and vice versa.
What is Calcium Gluconate?
Medicinal mineral concentrate replenishes the lack of calcium ions, promotes the regulation of metabolism, and participates in many physiological processes. The drug is produced in several forms:
- non-coated white tablets: in dosages of 250 and 500 mg;
- chewable lozenges;
- aqueous solution for parenteral administration in ampoules: with 100 mg of active substance in 1 ml.
Among the auxiliary compounds of the drug: silicon dioxide, starch and other form-building additives. The solution additionally contains calcium sucrose.