Effective drugs for healing bones in fractures
The modern pharmaceutical industry does not stand still and is constantly developing new drugs for rapid healing of bones during fractures.
To produce such a medicine, specialists face several tasks at the same time, since the skeletal system is classified as solid. That is, the process of getting the necessary substances is more complex when compared with the treatment of soft human organs. The tablets, capsules or injections must contain components that will: • promote the process of formation of cartilage tissue; • help the body absorb calcium better; • influence the nervous system for pain relief. In order to start the fusion process, you need to fix the fracture site with something. To do this, a plaster cast must be applied to the person at the junction of the damaged parts of the bone. Another difficulty in treatment lies in the fact that with any fracture the muscular system also suffers. In a person, not only the skeletal system is immobilized, but also the muscles, thanks to which there is the ability to move in principle. They require constant training, and over time can atrophy from inactivity. To do this, you need to restore the site of damage as quickly as possible, that is, deliver more nutrients. Thanks to the medicinal effect, the connecting process of bone tissue is accelerated, and is now an essential part of the treatment of fractures.
Calcium and vitamin D are the main vitamins for older people with fractures
Substances that help in the process of bone healing are primarily calcium and vitamin D. It is these vitamins that contribute to the active restoration of bones during fractures in older people. Thanks to these elements, bones grow together quite quickly and without any complications.
Calcium contains:
- In all dairy products (sour cream, kefir, yogurt, cheese, fermented baked milk, yogurt), especially in low-fat cottage cheese;
- Nuts, seeds (sesame, almonds and poppy seeds), legumes (beans, green peas, lentils, soybeans);
- Vegetables and fruits, herbs and berries (asparagus, carrots, seaweed, broccoli, celery, turnips, radishes, strawberries, gooseberries, blackberries, grapes, currants, cherries and apricots contain elements that promote good absorption of calcium);
- Seafood (especially sardines and salmon).
Vitamin D, which is also prescribed to treat fractures in older people, is found in:
- In fish oil. It is also important to note that this product is a source of omega-3 fats;
- Fish (cod and halibut);
- Raw egg yolk, vegetable oil and liver;
- Oats, nettle, dandelion, parsley and horsetail;
- Potatoes.
It is a well-known fact that the body is capable of independently synthesizing vitamin D through ultraviolet rays. This suggests that older adults should get more sun exposure during their recovery process.
However, calcium and vitamin D are not the only vitamins for older people with fractures. Doctors also often recommend using vitamin C. These elements must be taken in combination to get the desired effect. Vitamin C enters our body along with sweet bell peppers and citrus fruits. These products can be consumed pure or drunk as freshly squeezed juices.
As a substitute for this substance, older people with fractures can use pharmaceutical ascorbic acid, which also contains vitamin C, but in canned form. This beneficial element is found in parsley, black currants, fresh rose hips, honeysuckle, kiwi, sea buckthorn and juniper.
It is important to note that in case of a fracture, elderly people are contraindicated to use:
- Alcoholic drinks that interfere with the formation of bone and cartilage tissue, which leads to bone destruction;
- Fatty foods in large quantities, which interfere with the absorption of calcium;
- Coffee and strong brewed tea;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Chocolate and other sweets.
- For bone fractures in older people, not only vitamins, but also various folk remedies can be very effective and useful. But it is important to understand that their use is possible only after consulting a doctor . The most effective and popular recipes are presented:
- Onion broth. To prepare it, you will need two onions, which must be peeled, chopped and fried in vegetable oil. Then transfer the resulting mass into a saucepan, add one liter of water and boil for 10–15 minutes. Take one glass of decoction three times a day before meals. The course of treatment ranges from one to three weeks.
- Powder made from eggshells. Peel the egg, dip the shell in boiling water for 30 seconds, then dry and grind it into powder. The resulting mixture is taken half a teaspoon twice a day.
- Shilajit, which is also an excellent remedy for fractures in the elderly. To prepare the solution, add one tablet of the substance to a glass of warm water and stir. This composition is taken three to four times during the day. The course of treatment should be continued from five to seven days, then take a break from five days to a week. You can also mix mumiyo with oil and lubricate the fracture site with the resulting mass. This method activates the process of bone healing in older people after a fracture.
- Copper in powder form. You can buy this product at the pharmacy, but it is better to make it yourself. For these purposes you will need a copper coin. It should be rubbed using a file. Add a small pinch of the resulting powder to a glass of heated milk, then add one egg yolk to this solution. Elderly people should take this remedy during the rehabilitation process twice a week, one teaspoon.
- Comfrey-based ointment, which has a beneficial effect on cartilage, bone and joint tissue in older people. In order to make the ointment, you will need 100 grams of fresh comfrey, which should be mixed with the same amount of pork fat. Place the resulting mass in the refrigerator and leave for five days. When the ointment is ready, apply it to the fracture site three to four times a day.
- Composed of 50 ml of celery juice, cucumber and carrots. Dilute the resulting mixture with water so that you get a glass of this folk remedy. Take it twice a day, 200 ml.
Read material on the topic: Walking for older people
Composition of cartilage and human skeleton
To know what microelements are needed to formulate medications that help with fractures, you need to understand how the human skeleton works. Bones consist of bone marrow, nerves, and blood vessels. All this is protected by the periosteum, which also has a connecting function in case of slight damage to the hard part of the bones. Also, in some skeletal joints there is cartilage tissue, and it is more flexible than bone. This includes the growth plate. It allows a person to increase their size, and is cartilage that is not visible on x-rays.
The plate has the property of ossification, and this allows a person to stop growing by the age of twenty. Since the nervous and circulatory systems do not pass through cartilage tissue, the process of turning a child into an adult is painless. But not all cartilage has an ossification stage.
There are those that remain flexible forever to connect the hard component of the skeleton. They allow a person to sit down, run and make other body movements.
Bio-Gide Collagen Membrane
Bio-Gide is the standard collagen membrane for the restoration of soft tissue and bone after dental surgery. This is a highly purified natural product that contains pork collagen. Soft tissues contain a large amount of collagen fibers, so the collagen membrane is used in the restoration of bone and periodontal tissue. The use of Bio-Gide helps the surgeon achieve the best and most predictable results and provides excellent wound healing. Bio-Gide has high therapeutic safety, which is highly valued by all leading surgeons.
The excellent qualities of Bio-Gide are achieved thanks to its three-dimensional, natural matrix structure and high biocompatibility. The structure of the Bio-Gide membrane is very similar to human collagen. The photo above shows human collagen under a microscope and below is the Bio-Gide membrane. The natural structure of collagen helps in the healing process - blood vessels grow through the collagen fibers.
The membrane performs several important functions in the regeneration process: protective, stabilizing, and is the basis for soft tissues.
Bio-Gide membrane has a two-layer structure, one side is smooth and the other is rough. The smooth top layer guides soft tissue healing, which occurs more easily and with better aesthetic results. The rough side of the Bio-Gide membrane helps growing bone cells.
There is no need to remove the membrane. The breakdown of the membrane into natural amino acids occurs without side effects, without tissue irritation.
Treatment in the first week
All signals about problems in the systems of the human body come through the nervous system. Whenever it is damaged, a person experiences pain. Since the bone has nerve endings, everyone who has ever had a fracture knows about unbearable pain in the first week after the injury. During this period, analgesics are prescribed, which have an analgesic effect, as well as anti-inflammatory properties. If the injuries are very severe, the doctor will prescribe stronger medications to make the person sleep. To strengthen the immune system and as a natural antibiotic, after consulting a doctor, you can take propolis tincture. It helps suppress viruses and various bacteria. You should also take vitamin D.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
To relieve pain and reduce inflammatory reactions, doctors prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs in the first weeks after an injury. The duration of taking NSAIDs is determined by the doctor, but given that such drugs have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal mucosa and have many contraindications, they can be taken for no more than 10 days.
Drugs from this group are classified as symptomatic drugs. The principle of their action is due to a decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins, which reduces pain, swelling, and redness. NSAIDs mainly contain diclofenac, nimesulide, ketoprofen or ibuprofen. Similar medications are produced by domestic and foreign manufacturers under different trade names.
Nurofen
Nurofen is a drug from the NSAID group. The basis of the medicine is ibuprofen, which relieves pain, inflammation, and has an antipyretic effect. Prescribed for mild to moderate pain.
Adults take 1-2 tablets every 6 hours for 7-10 days. The drug has many contraindications that you need to familiarize yourself with before taking it.
Ketanov
To eliminate pain from fractures, Ketanov is often prescribed, which has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effect. The active component of the drug is tromethamine ketorolac 10 mg. Adults are prescribed 1 tablet every 4 hours.
It is recommended to take Ketanov in the first days after an injury to reduce pain. It is recommended to read the instructions before use. The drug is not prescribed to children and pregnant women, and is also contraindicated for diseases of the stomach, liver and kidneys.
Second decade of treatment
In order for bone fusion to begin at fracture sites, it is necessary to start the process of cartilage tissue formation. To accelerate the appearance of such cells in the primary callus, it is necessary to ensure increased formation of chondroitin. All large livestock, sturgeon and even sharks have it. It is needed for bone tissue cell renewal to begin and for the formation of primary cartilage. To quickly replenish the human body with natural chondroitin, in the old days, in case of fractures, they ate the joints of cows and pigs. The well-known jelly is brewed from the hooves of these animals. They contain quite a lot of this substance. Everyone knows about the famous saying about fish aspic. These dishes help prevent the development of arthrosis and rheumatism. They must be included in the menu for faster recovery from bone fractures.
Chondroitin also contains glucosamine, which is also found in synovial fluid. In the body itself, with age or due to metabolic disorders, these elements are produced in smaller quantities than necessary. This leads to brittle bones or other diseases of the human musculoskeletal system.
Pharmacy drugs
The drugs produced by pharmaceutical factories mainly use substances obtained by chemical means. There are drugs on sale that contain only chondroitin. Later, medications appeared that additionally included glucosamine. Now you can purchase dietary supplements that combine these two substances. They are produced in the USA and Germany. Glucosamine Chondroitin is produced in Russia.
Reviews are mostly positive and the price is significantly lower than imported ones. Pharmacies also offer the drug Arthro-plus, which additionally includes vitamins.
When purchasing medications, be sure to consult a specialist and read the instructions for use.
Preparations for restoring bones after a fracture
Treatment of a fracture requires immobilization of the injured limb and takes quite a long time . Usually, it takes at least a month for the formation of callus, healing of fragments and restoration of blood vessels and nerves, and in some injuries the patient spends up to six months in a cast. Special medications for fractures help speed up the process for rapid healing of bones. Some of them improve blood supply to the area of damage, others promote the regeneration of the bone tissue itself.
Photo 1. Calcium makes bones as strong as the shells from which it is extracted. Source: Flickr (Garrett Coakley)
Other drugs
An integral part of the rehabilitation period is the use of medications from the group of chondroprotectors, which are recommended to be taken for several months. Any medications for fractures for rapid healing of bones should be prescribed by the attending physician or rehabilitation specialist.
Local remedies will also help speed up recovery. These include various ointments, gels, infusions and rubs. Such medications may contain various substances of synthetic or natural origin, which, in combination with tablets, will increase the results of treatment.
Osteogenon
Osteogenon is an effective tablet for fractures. The composition contains calcium and phosphorus. Reception allows you to increase the content of magnesium in the blood plasma. In case of fractures, it regulates metabolic processes and strengthens bone tissue.
The dose of the medicine is determined by the doctor. In general, therapy can take up to 5 months. This drug is well tolerated, causes virtually no side effects, but is not prescribed to children with intolerance to the composition or increased levels of calcium in the blood.
Chondroitin
Chondroitin is a chondroprotector for the restoration of cartilage tissue. The drug enhances the production of synovial fluid, eliminating the development of stagnant processes in the joint cavity. Taking the medicine also increases the production of collagen and hyaluron and promotes bone healing after injury. On the pharmaceutical market, Chondroitin can be purchased in the form of tablets, injections or ointments.
The frequency of administration is 2 times a day, treatment lasts 4 months. After 3 weeks of systematically taking the capsules, the dose of the medication can be reduced to one dose. Chondroitin injections are given every other day for 2 months. The ointment is applied to the damaged area of skin after the plaster is removed.
In case of intolerance to the composition, thrombophlebitis, risk of bleeding, the medication should be avoided. This remedy is very effective for the prevention of joint diseases for people over 50 years of age.
Teraflex
Teraflex is a chondroprotector with anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic effects. The active component of the drug is glucosamine, which serves as the basis for the construction of cartilage tissue. The intake allows you to stimulate bone regeneration and is involved in the production of connective fluid. Using Theraflex you can not only restore bones after injury, but also reduce the need for painkillers, as well as reduce the risk of degenerative processes.
You need to take 1 capsule per day. Therapy may last 1–3 months. Not prescribed for allergies to the composition, pregnancy, children under 15 years of age.
Traumeel with
The medicine Traumeel is especially popular during recovery from fractures. It belongs to homeopathy, has a natural composition and is well tolerated. Taking the medicine allows you to have a regenerating, anti-inflammatory, and immunostimulating effect.
The advantage of the medicine is that it consists of 90% natural ingredients, also has no contraindications and can be used for several months.
Mumiyo
Natural remedies for recovery after fractures include mumiyo, which has a rich chemical composition and is widely used in both folk and official medicine. The medicine is a dietary supplement, you can buy it in tablets or powder. Application allows you to significantly accelerate bone fusion, increase immune defense, and provide the body with all the necessary components.
It is recommended to take mummy tablets 2 weeks after the injury. Use externally as a compress or ointment only after removing the plaster cast. This product has no significant contraindications and is intended for long-term use. One treatment course lasts 10 days, then take a 5-day break and continue treatment.
What affects the rate of bone recovery
The duration of fracture healing in each case is individual and depends on many factors . First of all, the rate of bone tissue regeneration is affected by:
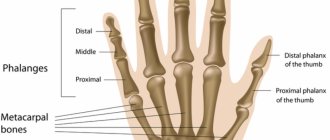
- Type of damage and its location . Large bones such as the femur, tibia or humerus heal more slowly than the phalanges of the fingers, and fractures without displacement always heal faster.
- Patient's age . A young body copes better with injuries to the musculoskeletal system, since mineral metabolism and the supply of bone tissue with calcium and nutrients slow down over the years.
- Speed of medical care . The earlier treatment is started (reposition of fragments and immobilization), the faster the recovery process goes.
- General state . In the presence of certain chronic diseases and decreased immunity, bones take longer to heal.
Bone regeneration: how can you help it?
2K 4 min.
Bones form the basis of the musculoskeletal system. Under the strong protection of the bones are valuable structures of the body - the bone marrow, in which all blood and immune cells are formed throughout life, as well as the brain and spinal cord, which regulate all functions of the body.
Photo: flickr.com/Yussef
Photo: flickr.com/Yussef
Long evolution has created a perfect mechanism for the formation of bone tissue in our body - the mechanism of osteogenesis. It ensures both its constant renewal (physiological regeneration or so-called remodeling) and restoration after injury (reparative regeneration).
Bone can formally be called a composite material, which includes organic substances (the main protein-collagen) and inorganic substances (the main salts - calcium and phosphorus). Two main types of cells—bone-destroying cells (osteoclasts) and bone-forming cells (osteoblasts)—work throughout our lives to ensure bone turnover and repair after injury.
Biomineralization of proteins could be carried out by organisms more than 600 million years ago. Clam shells, sea urchin spines, and the exoskeleton of arthropods are the result of this process. The process of biomineralization of collagen during the formation of bone tissue (that is, its inlay with calcium salts, phosphorus and some trace elements) is evolutionarily ancient, on the one hand, and on the other, under the control of the nervous and humoral (through the blood with the help of biologically active substances and hormones) systems. In addition, in bone tissue and bone marrow there is a deep reserve of the body - the central depot of stem cells, which replace aged or dead cells in many organs and tissues throughout life.
The study of the mechanisms and processes of osteogenesis gradually led to an understanding of what materials and constructs based on them need to be developed in order to carry out organotypic (that is, with the formation of structures typical for this organ) replacement of bone defects. This approach is called biomimetic.
When might help be needed for regeneration processes in bone tissue, if they are so perfect and evolutionarily ancient? There are such situations. Firstly, these are the so-called bone defects, larger in size than critical ones, bone defects in elderly people with calcium metabolism disorders and, finally, bone defects in cancer patients after chemotherapy or radiation therapy, when regeneration is difficult.
That is, such materials are in demand for reconstructive plastic surgeries in traumatology, maxillofacial surgery, dentistry and, of course, in oncology.
Today, bone tumors and metastases into bone tissue are not a death sentence. They are removed, replacing the defects with osteoplastic materials. The completeness of rehabilitation in this category of patients directly depends on advances in medical materials science.
The history of the creation of osteoplastic biomaterials goes back more than 60 years. The first generation of such materials were bioinert materials, the second - bioactive, biodegradable, the third - materials for stimulating specific cellular responses at the molecular level.
The gold standard, however, remains the use of autologous (own) bone tissue. However, the need for additional surgical intervention and the insufficient amount of material to close large defects led to the idea of using allogeneic (from another organism) bone tissue. But at the same time, there was a danger of transfer of unidentified infectious and allergenic agents from the donor. Materials scientists have proposed using synthetic calcium phosphate materials for these purposes, which are similar in composition to the inorganic component of bone tissue. They are still widely used today because they are biocompatible, have osteoinductive (osteogenesis-stimulating) properties, and are used by cells to build new bone. However, it turned out that they dissolve more slowly than bone is formed.
An unexpected impetus for the development of biomaterials came from studying the skeleton of corals. It consists of calcium carbonate, has a particularly strong aragonite crystal lattice, through porosity (which ensures the flow of nutrients, gases, and vascular sprouting) and a bioresorption rate similar to the rate of osteogenesis. It turned out to be a brilliant material of natural origin for replacing bone defects. However, coral harvesting is limited and it is difficult to standardize its trace element composition. This led to the idea of three-dimensional printing to create constructs to replace bone defects of a given shape, porosity and surface architecture, using calcium phosphate materials as “ink”.
The next stage in the development of this area was the 3D printing of composite structures containing both natural bone and organic components. Polymers of both natural (collagen, alginate, chitosan) and synthetic origin are used as such. It was possible to further stimulate osteogenesis by saturating such constructs with their own stem cells from the bone marrow, which opened up the possibility of manufacturing personalized implants of a given geometry, porosity and architectonics.
And finally, modern research in this area is devoted to the development of technologies for the functionalization of such 3D constructs with biologically active substances (for example, for the elderly or for large defects), antibiotics (for open bone injuries, the risk of infection and the development of inflammatory processes) or antitumor drugs. In the latter case, it is planned to use the constructs to carry out targeted delivery of chemotherapy drugs with a prolonged action, which will reduce the burden of systemic (intravenous) chemotherapy in cancer patients.
Natalya Sergeeva, Doctor of Biological Sciences, Professor, Head of the Laboratory of the Moscow Research Institute of Orthopedics named after. P. A. Herzen - branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center of Radiology" of the Ministry of Health of Russia
How to speed up bone recovery
In order for the fracture to heal correctly and quickly, you must first of all follow all medical instructions. Self-medication in this case leads to displacements and complications. How to speed up the healing of a fracture:
- Avoid physical exertion on the injured limb in the first weeks after applying the cast. Rest promotes the formation of callus and proper healing of the fracture.
- Eat properly . You need to include as many calcium-rich dairy products into your diet as possible, and regularly consume lean meat, fish, and fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Take tablets for fractures that improve blood circulation, and vitamin-mineral complexes with a high calcium content . The doctor will tell you which ones, but it is unacceptable to prescribe medications yourself.
- Rehabilitation after removing the cast goes faster if massage and physiotherapy , and a special set of exercises is performed.
Note! You should give up bad habits. Smoking and alcohol interfere with bone mineralization and healing.
Prevention of fractures
To prevent fractures, it is important to prevent osteopenia (a decrease in bone mineral density without structural changes in bone tissue) and osteoporosis. For this purpose, preventive doses of calcium and vitamin D are prescribed, a set of physical exercises is developed, or the optimal sport is selected (gymnastics, running, swimming).
If the diagnosis of osteoporosis has already been made, its treatment (regardless of the presence of fractures) requires drugs that can suppress the destruction of bone tissue and stimulate its formation. Only an integrated approach to the prevention of fractures, including osteoporotic ones, can accelerate bone healing, maintain its flexibility and necessary density, and ultimately, ability to work and quality of life.
L.RU.MKT.CC.04.2019.2709
Preparations for rapid bone healing
The pharmaceutical industry offers many medications that accelerate bone tissue regeneration, strengthen the immune system and restore blood circulation. The doctor prescribes complex drug therapy , which includes several groups of drugs.
Medicines with calcium
Calcium preparations for fractures for rapid healing of bones provide additional intake of the main building material . They can be mono-component (calcium gluconate) or consist of several ingredients that increase the effectiveness of therapy. The mineral may also be contained in a vitamin complex.
It is important! In case of a fracture, what to take for rapid bone healing should be decided by the doctor, since an overdose is fraught with disturbances in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, cholelithiasis or urolithiasis.
Mumiyo
This mineral-organic compound, used in medical practice since ancient times, significantly accelerates the restoration of bone tissue . So drinking mumiyo solution for fractures to quickly heal bones is useful, but only if there are no contraindications and the attending physician does not object.
Vitamin complexes
Combined products containing minerals and vitamins are used for the prevention and treatment of vitamin deficiency, help strengthen the immune system and increase the ability of tissues to regenerate .
Complivit
Contains, in addition to pantothenate and calcium phosphate , magnesium and various vitamins. Regular use in the dose prescribed by the doctor contributes to the overall strengthening of the body and restoration of bone tissue.
Alphabet
Inexpensive and effective vitamin tablets for fractures for rapid healing of bones, differing from other complexes in the separate intake of groups of minerals and vitamins. For example, calcium in this drug is combined with fat-soluble D3 and K1 .
Vitrum
In addition to calcium , necessary for bones, also contains vitamin D and phosphorus with magnesium , which promote its absorption. About 30 more mineral and vitamin components strengthen the body's defenses.
Multitabs
The variety of the complex called “Classic” does not contain calcium, so it is recommended to take Multitabs “Energy” containing 200 mg of this mineral. Multi-tabs Baby Calcium+ is suitable for children.
Other vitamin complexes
You can also use other complex drugs for fractures with a high content of calcium and vitamins. Which ones and in what dose – the attending physician will tell you.
Ointments and creams
These dosage forms for external use are also included in the complex treatment of bone injuries. Medicines for fractures in the form of ointments and creams perform the following functions:
- pain relief – Diclofenac ;
- removal of edema - Troxevasin ;
- tissue restoration – Viprosal B ;
- warming – Finalgon ;
- elimination of inflammation - Indomethacin .
All of them penetrate well through the epidermis into the underlying tissues and provide a pronounced therapeutic effect.
Glucosamine and chondroitin
Dietary supplements containing these substances are intended to restore cartilage and bones . Chondroitin and glucosamine during fractures significantly accelerate the metabolism in these tissues and regulate the processes of recovery and fusion. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Teraflex.
Immunomodulators
Drugs for fractures from the group of immunomodulators are intended to stimulate the functioning of the immune system and restore the body. In case of fractures, they can speed up the recovery of the body, increase tissue regeneration, and reduce the risk of developing all kinds of complications.
Immunomodulators are prescribed to patients with weakened immune systems, as well as those with severe fractures. They contain components of natural or synthetic origin. Available in different pharmacological forms. You can take medications from this group only according to strict medical prescription.
Timalin
Timalin is a drug from the group of immunomodulators that has the ability to improve metabolism at the cellular level. The composition contains bovine thymus polypeptides 10 mg. Available in a bottle for intramuscular administration.
Adults are recommended to take 5–20 mg/day. Treatment is determined by the doctor. The drug has a number of contraindications, including children under 6 months, pregnant women, allergies to the composition.
Pyrogenal
In case of reduced immunity, the doctor may prescribe Pyrogenalum, which not only activates the immune defense, but also has a moderate anti-inflammatory effect. For injuries and fractures, taking the medicine accelerates the resorption of scar tissue, enhances vascular permeability, restores nerve cells, and reduces the risk of formation of adhesions.
Contains bacterial lipopolysaccharide and auxiliary components. The frequency of taking the drug is 1 time per day. The duration of therapy depends on the underlying diagnosis and can take from 10 to 30 days.
Pyrogenal has a number of contraindications, including heart failure, severe kidney and liver pathologies, intolerance to the composition, autoimmune diseases, and the medicine is not prescribed to pregnant women.
Possible side effects in practice included increased body temperature, fever, headache, muscle and joint pain. If such symptoms appear, you should stop taking the medication as soon as possible and consult a doctor.
Drugs for fractures in old age
Aging of the body leads to a slowdown in metabolic processes and less complete absorption of nutrients, vitamins and minerals. Therefore, the fusion process is slower and complications arise more often. In order for recovery to proceed faster, supportive drug therapy is required, and the most effective drug for healing bones during fractures in the elderly is Teraflex . It is also necessary to take vitamins and calcium, since at this age there is always a deficiency of calcium.
Photo 2. To restore bone, the body requires additional building material. Source: Flickr (Tiina Allik).
Vitamins
For the full functioning of the skeletal system and rapid recovery after injury, it is recommended to replenish the body with vitamins, which take part in many biological processes. Food is considered the main source of vitamins, but if you have poor nutrition or poor absorption of nutrients, it is recommended to take multivitamin complexes. These medications contain all the necessary vitamins and minerals for the body’s daily needs. When choosing such complexes, attention should be paid to the following means:
- Centrum.
- Complivit.
- Vitrum.
- Duovit.
- Supradin.
When choosing vitamin complexes, you need to pay attention to the composition and study the instructions.
The largest medical portal dedicated to damage to the human body
It is quite natural that a person who has suffered a fracture wants to get better quickly. To do this, the following conditions are necessary: contacting a doctor as soon as possible after receiving an injury, accurately comparing bone fragments with them, ensuring their immobility (plaster, traction, osteosynthesis), regular and precisely dosed performance of physical therapy exercises, and observing prohibitions during treatment and rehabilitation.
Are there pills for healing bones during fractures and who should take them?
The body of a healthy person has a sufficient supply of all the necessary “building materials” to ensure the fusion and remodeling of bone tissue. To do this, he does not need to take anything additional, but should only follow the recommendations given in the final video.
Who needs tablets to heal a fracture?
Slow callus formation, decreased peak bone mass, unsatisfactory course of adaptation processes, too long or persistent nonunion of a bone fracture are possible in the following patients:
- Teenagers, during growth spurts and puberty, when hormonal changes occur in the body.
- People with concomitant diseases that inhibit the rate of tissue regeneration, including bone and cartilage, for example, diabetes, metabolic syndrome (obesity), gout, thyroid disease, tumors of glands and organs that produce hormones.
- Persons with pathologies that disrupt the metabolism of bone and cartilage tissue - osteopenia, osteoporosis, osteochondrosis, osteoarthritis, arthritis, bone tuberculosis.
- Patients with varicose veins or superficial thrombophlebitis (with a fracture of the lower extremities).
- Patients who have been treated for a long time with corticosteroids or anticonvulsants.
- Athletes taking anabolic steroid drugs.
- Patients with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract that interfere with the absorption of calcium.
- Pregnant women.
- Women (after menopause).
- Men over 60 years of age.
- Heavy smokers, alcoholics, drug addicts.
Also on this list are people who have suffered a second fracture in a place where the bone was previously broken.
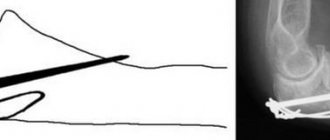
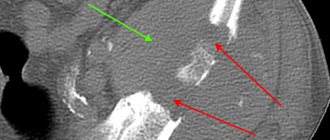
The decision on the need to take pharmacological drugs is made exclusively by the doctor and on an individual basis. In some cases, this will require waiting for a control x-ray confirming the slow rate of primary callus formation (pictured above).
Attention. Tablets for fractures to quickly heal bones have not yet been invented. Adjuvant drug treatment helps the remodeling mechanism, but does not speed up the process.
The price for ignoring exercise therapy and self-medicating with certain tablets for limb fractures is a slowdown in the rate of fusion, persistent nonunion and/or the formation of a pseudarthrosis.
How to heal a fracture 4 times faster
Russian scientist Arnold Popkov, chief researcher at the Scientific Research Institute named after. Academician G.A. a monograph in the German Palmarium Academic Publishing on new implants with a bioactive coating that accelerate the healing of fractures. The research was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (RSF).
The cages and the roads they choose
The bone grows together thanks to the division of living and active stem cells, which have not “determined their fate” definitively since the time of embryonic development. How does a bone cell get to this state? Its development is similar to how we choose a profession: first a humanities or mathematics class, then a faculty, then a department or department, obtaining a specialty, and so on. Initially, during the first few cycles of division after fertilization, not a single cell of our future body “knows” which path it has to take, and “all roads are open” to it.
As the embryo develops, a more complex structure is formed from simple and identical cells - three germ layers, endoderm, ectoderm and mesoderm, which in the future will give rise to organ systems. Mesenchyme is formed from mesoderm. Mesenchyme cells are already different from the rest, but very similar to each other, and it is not yet known which of them will choose the “profession” of blood cells, which will become a muscle cell, and which will become bones. A group of cells is released from the mesenchyme that do not yet want to make a decision, limiting their future choice. Then the body goes through many more stages of development, at each of which the cells are determined more and more until they finally choose their “profession”.
Stem cells, including this group of “indecisive” mesenchymal cells, remain in a frozen state of “eternal childhood”, so that if differentiated cells die in the body, they can finally make their choice and take their place.
At first, such cells are called osteogenic (literally, bone-producing cells). They can produce growth factors, stimulating bone marrow formation. They then differentiate again, becoming osteoblasts, cells on the inner surface of the periosteum. Angular and actively dividing osteoblasts produce collagen proteins and components of loose intercellular substance. Osteoblasts then lose their ability to divide, “retire,” harden, and become osteocytes. These mesenchymal osteogenic cells play a major role in fracture healing.
ByRobert M. HuntBone formation by osteoblasts
“Fracture, lost consciousness, woke up - plaster”
In Russia, more than 13 million people a year suffer injuries, the consequences of which are the most common cause of disability among citizens of working age. An additional risk factor is congenital diseases of the musculoskeletal system. In Russia, for every 10 thousand newborns, there are 219 people with such disorders.
To treat fractures and post-traumatic complications, special implants are used - metal inserts that help connect broken bones, secure and maintain them in this condition until they heal. The implant material itself can affect healing (consolidation) in different ways, but none of the metals known to modern doctors can accelerate it.
Therefore, over the past 100 years, with all the development of medicine, the healing time of fractures has not changed.
Kurgan scientists proposed combining the metal base of the implant with a coating of hydroxyapatite, a substance based on calcium and phosphorus present in the bone in the form of nano-sized crystals. Hydroxyapatite promotes osteogenesis and stimulates osteogenic cells to act, but in itself it is too fragile a material for implantation (organic components give flexibility to bones, which are increasingly replaced by calcium compounds with age, which makes bones more fragile in old age).
Therefore, it was decided to combine a biotolerant (that is, not harmful to ostenosynthesis, but also not improving it) titanium alloy and a rough bioactive (encouraging bone to recover) nanohydroxyapatite coating.
The developed 3D mathematical modeling technology makes it possible to form an implant individually for each patient, taking into account the overall bone density, the number of channels, pores and vessels, and implant it into the internal cavity of the bone (intramedullary). The controlled arrangement of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals allows one to “mimic” individual bone roughness. The materials are manufactured after tomography using selective laser sintering technology, and then a layer of hydroxyapatite is applied to them.
“The use of stimulation methods based on intramedullary implantation with ceramic nanohydroxyapatite coating allows us to guarantee a positive treatment outcome and a real reduction in the time of osteosynthesis for bone fractures by 2–4 times,” says the author of the monograph, Doctor of Medical Sciences Arnold Popkov.
— Simplicity, accessibility and economic feasibility of use at the earliest stages of medical evacuation (district hospital) are especially important during the transition of the Russian Federation to a compulsory health insurance system. New technologies easily fit into the scope of basic trauma care and care provided for urgent indications and on a planned basis during the rehabilitation treatment of the consequences and complications of injury, financed from compulsory medical insurance funds.”
The author adds that his work can contribute to import substitution and makes it possible to produce implants in Russia that are not only comparable to Western counterparts, but even superior to them in terms of healing speed.
Tags
media about the Foundation, Medicine, Special project
Drugs that help bone healing
Let us list the pharmacological agents prescribed (recommended) to patients in whom, for one reason or another, bone tissue may heal more slowly than in the prescribed time frame.
Osteogenon
The instructions for this drug indicate that it can be used as a means for healing bones during a fracture. It is a combination of ossein, non-collagen peptides and collagen proteins, calcium and phosphorus.
This combination stimulates the synthesis of osteoblasts and inhibits the production, maturation and function of osteoclasts.
The dosage regimen may vary and is selected individually:
- in the first 3 months - 6 tablets per day, every 4 hours, from 4 to 7 months - 1 tablet during breakfast, lunch and dinner;
- during the first 3 months, 2-3 tablets, 3 times a day;
- in the first month - 2 tablets 3 times a day, and from the 2nd to the 12th month inclusive - 2 tablets 4 times a day, from 13 to 24 months - 2 tablets 3 times a day.
Doctors usually prescribe Osteogenon tablets to patients with bone fractures who have a history of pathologies of bone metabolism, the elderly, women who have undergone amputation of the uterus and ovaries, pregnant women, people with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis caused by hyperthyroidism, as well as children (over 10 years) with a deficiency of bone mass and rapidly growing adolescents who have suffered severe fractures.
Cholecalciferol
For teenagers, pregnant women and people with gastrointestinal diseases that complicate the absorption of calcium, the doctor may recommend taking medications containing cholecalciferol.
There are a lot of trade names for products containing cholecalciferol, each containing a different amount of easily digestible form of calcium, so the dosage regimen must be agreed with your doctor.
On a note. People who have suffered a fracture need to monitor their daily drinking balance - min 35 ml per 1 kg of body weight. The body needs water to build bone tissue no less than vitamins, minerals and proteins.
Taking several vitamin complexes containing calcium at the same time, especially Osteogenon, is prohibited. During treatment, it is also recommended to ensure that the calcium content in the daily diet does not exceed 1000 IU.
Troxevasin
For those who have broken the tibia, ankle joint or foot bones, starting from the 2nd day after the injury, it is recommended to take Troxevasin tablets or capsules (active ingredient: troxerutin). They will help relieve post-traumatic swelling, restore and improve blood circulation in small blood vessels, and also increase the tone of the veins of the lower extremities.
After you have the opportunity to use the external remedy, you should continue to take 300 mg tablets in the morning and evening, + apply 2% Troxevasin-gel 2-3 times a day. The duration of such auxiliary drug treatment is until complete rehabilitation of the broken lower limb.
And in conclusion, we suggest watching the video announced at the beginning of the article. In it, a traumatologist talks about diet and gives other advice to ensure that a broken bone heals in the time required by nature and without complications.
Calcium preparations
Calcium-containing preparations are the basis of the rehabilitation period. Such drugs are prescribed to everyone without exception. Taking them strengthens cartilage and bone tissue, accelerates bone healing, and reduces the risk of developing osteoporosis and other joint diseases.
It is necessary to take calcium-based medications according to medical prescription, since such drugs are poorly absorbed by the body, and if taken for a long time, they can contribute to the appearance of kidney stones.
Calcium gluconate
A domestically produced drug, Calcium gluconate, will help replenish calcium deficiency. Using this remedy for fractures, you can increase bone density, improve the production of nutritional components, as well as the functioning of the cardiovascular system. This product is affordable. For injuries, take 1 tablet 3 times a day. In hospitals, a solution is often used for intravenous administration.
You need to take calcium gluconate in combination with vitamin D3, this will increase the absorption of the microelement.
The drug is well tolerated; only in rare cases, after its use or when the recommended dose is exceeded, nausea, vomiting, heart rhythm disturbances and other unpleasant symptoms may occur that require stopping the medication.
Calcium d3 nycomed
Intended for complex therapy of diseases in which there is increased fragility and fragility of bones. The basis of the complex is calcium carbonate and vitamin D3, as well as auxiliary components.
Adults take 1 tablet 3 times a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor, but it can take up to 3 months.
Contraindications include hypercalcemia, vitamin hypervitaminosis, active form of tuberculosis, children under three years of age.
Kalcemin
Calcemin is a complex for the treatment and prevention of a number of diseases that arise against the background of impaired phosphorus-calcium metabolism. Used in the treatment of fractures of varying degrees of complexity, for the prevention of joint pathologies, including osteoporosis. Calcemin tablets contain several minerals, as well as vitamin D3. Each of the components of the tablets has its own therapeutic effect, but together they created a powerful formula to combat increased bone fragility.
It is recommended to take Calcemin for 1–3 months, 1 tablet per day. Can be prescribed to children from 5 years of age, pregnant women after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Preparations for healing and strengthening bones during fractures
Many of us have experienced such an unpleasant condition as a broken bone. This can happen to anyone at home or at work, in icy conditions or out of the blue, because we are always in a hurry somewhere, sometimes neglecting basic caution and risking our health.
A fracture is a complete or partial damage to the integrity of bone tissue when the strength of the bone is inferior to the magnitude of the external load (during a fall, impact, pressure). More often the long tubular bones are damaged - the tibia, ulna and radius, femur, humerus. This condition can occur not only with injuries, but also with certain diseases (tumor metastases, osteomyelitis, osteogenesis imperfecta, etc.). In addition to the integrity of the bone, during fractures there is a rupture of surrounding tissues - muscles, blood vessels, nerves.
Whatever the fracture, it requires immediate examination using X-rays, MRI or nuclear magnetic resonance and further treatment taking into account the type of fracture, severity, presence of an open wound, displacement of fragments, as well as the patient’s age, state of health, presence of underlying diseases.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a traumatologist, or less often by a surgeon. The main diagnostic method is radiography in two projections - frontal and lateral. For some types of fractures, special projections are used (for example, iliac and obturator for an acetabulum fracture). A more informative (and expensive) method is X-ray computed tomography (XCT) , which allows one to obtain a three-dimensional 3D image of the damaged segment. For additional diagnosis of soft tissue damage, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound (ultrasound) , and, less commonly, angiography and electroneuromyography are used.
How are bone fractures treated?
The main symptoms of a bone fracture are acute pain at the site of injury, aggravated by movement, swelling of the tissue and hematoma due to rupture of blood vessels. It is very important to provide a person with first aid, because with such injuries there is a danger of developing complications in the form of painful shock and bleeding. Principles of emergency care for a bone fracture:
- stop the bleeding;
- fix the limb;
- introduce anesthesia (Analgin, Ketorol or 0.5% Novocaine);
- call an ambulance. Complex fractures and associated injuries are treated in a hospital.
Joint fractures
Joint fractures are considered quite complex fractures:
- shoulder;
- ankle;
- knee;
- hip
An ankle fracture can be closed or open. The open form is very complex and often carries the danger of inflammatory processes. After the diagnosis is made, the leg is injected with anesthetics to relieve pain shock. Next, the joint is set and the leg is cast. The rehabilitation period should include taking calcium-containing medications, electromagnetic therapy and therapeutic exercises.
The largest joint in the human body is the hip. Its fracture threatens a person with disability. Surgery is used to restore joint mobility and the ability to walk to the patient. The conservative method of treatment is indicated only for elderly people or those who have had a heart attack.
A fracture of the knee joint can lead to subsequent lameness or, if serious complications occur, completely deprive a person of the ability to walk. Depending on the complexity of the injury, conservative treatment or surgical intervention may be offered. The rehabilitation process includes physiotherapy, exercise therapy, and taking medications containing calcium.
In case of a fracture of the shoulder joint, the site of injury is injected with novocaine to relieve pain. If confusion is not established, then most likely treatment will be limited to the application of a fixing bandage. But in case of a complex fracture with displacement, surgical intervention is indicated.
Medicines for fractures
Medicines for bone healing are designed to help this natural biological process occur as quickly as possible. The rate of bone fusion at the fracture site and its strengthening depends on the location of the damage, on the timeliness and quality of the reposition of bone fragments and fixation of the limb, on the age of the patient, and his state of health.
The healing process occurs much faster in young people than in older patients or those with aggravating circumstances such as: hypo- and vitamin deficiency; pathology of the adrenal glands and parathyroid glands; chronic infectious and non-infectious diseases (tuberculosis, syphilis, diabetes, oncology, etc.); receiving long-term treatment with corticosteroids, aspirin, and drugs from the NSAID group as pain relievers.
Any medicine, including those for healing and strengthening bones and painkillers, should be prescribed by a specialist. At the stage of callus formation, tablets with chondroitin and glucosamine are needed (Teraflex, Chondroitin, Glucosamine Maximum and others). Their goal is to increase the activity of cartilage formation processes, they have a positive effect on the nutrition of bone tissue and have a regulating effect on the mineral density of the new bone structure, which promotes rapid healing of the bone at the fracture site.
After the formation of cartilage (primary callus), it is necessary to take tablets to strengthen bone tissue, especially in people with increased fragility who are prone to repeated fractures. These are calcium supplements in several forms:
- monomedicines - contain only calcium salts;
- a combination of calcium salts with vitamins (D3) and minerals (phosphorus and magnesium), which improve the absorption process (Calcium-D3, Vitrum-Calcium, Calcium lactate, Calcium chloride, Calcide, etc.);
- multivitamin preparations containing calcium (Complivit, Nutrimax).
The second group of drugs is the most preferable for use in terms of calcium content and the degree of its digestibility.
Calcium preparations are contraindicated for people with hypersensitivity to it and with hypercalcemia; in this case, monotherapy with vitamin D (Aquadetrim) or fish oil is used. With long-term use of the above drugs, laboratory monitoring of the content of minerals in urine and blood is necessary.
Patients with open fractures, due to the risk of developing complications in the form of osteomyelitis and after surgery, require therapy with immunomodulators (Levamisole, Timalin and others); anabolic steroids are sometimes used to accelerate the healing of bone tissue and strengthen it.
Human bone is a complex organ with a complex hierarchical structure that performs a number of mechanical and biological functions. Bone tissue takes part in metabolic processes due to its mineral content. It creates a specific microenvironment for red bone marrow blood precursors.
Reparative regeneration of bone tissue, or reparative osteogenesis, is the process of bone restoration after damage, which to one degree or another is an enhanced physiological process. Reparative osteogenesis is an important theoretical and practical problem in dentistry and surgery.
Ideally, consolidation of the fracture should lead to the formation of new bone tissue identical to its condition before the fracture. However, in practice, fracture healing is a rather long multi-stage process, which occurs under the influence of numerous internal and external factors.
According to Russian researchers, bone tissue has significant reparative potential. But restoration processes are difficult to control from the outside.
Normally occurring and pathologically slow processes of reparative osteogenesis can be accelerated by activating metabolism only to a small extent. On the other hand, the process can easily be slowed down if there is insufficient understanding of bone physiology and disruption of the conditions that promote regeneration.
Methods for stimulating reparative bone tissue regeneration
The development of methods for regulating influence on reparative osteogenesis is an urgent task of modern dentistry, surgery, traumatology and orthopedics.
The active use of modern fixatives does not always ensure complete fusion of bone fragments. Often, specialists do not pay due attention to the dynamics of the process, the influence of new important factors and rational tactical decisions during treatment.
The experience of using minimally invasive osteosynthesis techniques for fractures of long tubular bones, which are preferred in less than 20% of cases, indicates that the development and improvement of fixators cannot definitely solve the problem of bone regeneration.
Based on a systematic approach to solving this problem, it is possible to effectively develop preventive measures and predict the consequences of fracture healing. At the same time, the issues of finding ways to stimulate the fracture area in order to reduce the time of fusion are not new.
The search and provision of optimal conditions for the occurrence of reparative and regenerative processes in cases of violation of the integrity of bone tissue is recognized as a promising and priority direction of scientific research in the 21st century.
At the moment, a large number of methods have been developed to optimize reparative osteogenesis. In particular, a method of directed mechanical local impact on the zone of bone distraction regenerate was proposed.
There are domestic and foreign experimental studies that assessed the effectiveness of mechanical and hydrodynamic influences on the formation of bone tissue in the fracture site when stimulating the healing of a bone wound.
A number of authors have noted a positive reflexotherapeutic effect on the dynamics of the reparative process of bone tissue during transosseous distraction osteosynthesis.
Over the past decades, the possibility of using physical methods of influence to stimulate osteogenesis has been intensively studied. These methods are not specific, but are accessible and minimally invasive. As a rule, they do not require special personnel skills or expensive equipment, and are characterized by good clinical results and an incomparably lower number of complications compared to traditional methods.
The use of physical factors provides a stimulating effect and optimization of reparative regeneration of bone tissue. Domestic authors often note the positive effect of high-frequency alternating electromagnetic fields on the process of bone tissue regeneration and the treatment of infectious complications.
Lasers are widely used to stimulate bone tissue regeneration. A number of studies have noted the positive effect of using mechanical-acoustic waves. Ultrasound waves also have a pronounced stimulating effect on regenerative processes inside bone tissue.
Unsatisfactory treatment results from the point of view of surgeons, the excessive complexity and traumatic nature of surgical interventions encourage researchers to search for new, more advanced methods and means of influencing bone tissue repair.
Modern osteotropic therapy
Numerous works in Russia and abroad are devoted to the problems of osteotropic therapy and the advisability of its inclusion in the treatment of patients with bone fractures and impaired consolidation of bone fragments.
This scientific information, despite its relevance, is quite scattered, and each of them contains a limited number of observations and considers only certain aspects of the problem of fracture healing.
However, it has been proven that pharmacological drugs can have a positive effect on various stages of reparative osteogenesis. But the connection between various schemes for the use of drugs and the fusion of bone fragments, their influence on the formation of the regenerate at different stages of the process continues to cause debate.
The following are drugs for reparative bone tissue regeneration:
- Osteogenon
- Cyclo-3-fort
- Bisphosphonates
- Tivortin
- Mexidol
- Biophen
- NSAIDs, etc.
The International Society for Fracture Repair convened a multidisciplinary workshop to develop evidence-based recommendations for clinical practice on the use of osteotropic therapy for fractures, including in the treatment of osteoporosis.
It was unanimously recognized that there is no reliable evidence base, so experts called for continued research in this direction and its systematization.
In the literature there are a few studies that analyzed the frequency of violations of the consolidation of bone fragments in patients of different ages who received osteotropic therapy or placebo.
As a result, the authors drew conclusions about the positive effect of osteotropic therapy on the processes under study. However, to confirm this from the perspective of evidence-based medicine, it is necessary to conduct double-blind, placebo-controlled studies.
Particular importance is given to drugs that affect the mass and quality of cortical bone, which plays a leading role not only in ensuring the ability of the bone to withstand mechanical stress, but also in achieving stable osteosynthesis.
One of these promising drugs is osteogenone
, which, according to histomorphometric analysis, significantly inhibits the loss of cortical bone.
Data from experimental studies demonstrated the morphological features of the regenerate in the area of the bone defect when osteogenone was administered to animals at different stages of the process. Experiments have shown that taking osteogenon minimizes destructive-dystrophic changes in newly formed callus and increases bone formation around implants implanted into the femur.
Osteogenon also stimulates the activity of osteoblasts, promotes the timely formation of the organic matrix of the regenerate, prevents the excretion of calcium and promotes its preservation in bone tissue.
An interesting work is devoted to studying the effect of osteogenon on the density of regenerated bone tissue using spiral computed tomography in the treatment of patients with fractures of long bones and their consequences.
The use of the SCT method made it possible to quantitatively and qualitatively assess the progress of the formation of regenerate in the damage zone and study the dynamics of its development.
Further clinical studies have demonstrated promising results with the use of osteogenone in the treatment of fracture nonunion. The data presented indicate the effectiveness of use and tolerability in the treatment of traumatic fractures in young people.
It has been proven that the drug can be used to accelerate the consolidation of bone fragments in traumatic fractures. The use of osteogenon with calcium and vitamin D3 after transosseous osteosynthesis in patients with nonunion of bone fragments indicated the positive effect of this therapy.
The clinical effect of osteogenon is due to the acceleration of bone remodeling due to the activation of bone resorption and osteogenesis with the predominance of the latter; growth in the potential of bioenergetic reactions, the predominance of local regulation.
Clinically, a reduction in treatment time and positive dynamics of bone mineral density were observed, which was due to the optimization of bone remodeling.
Ukrainian authors studied the effect of combination pharmacotherapy, including osteogenon, a multivitamin drug with a hypohomocysteinemic effect, Decamevit, and a nitric oxide donor, Tivortin.
(arginine hydrochloride). Yu. Bessmertny and co-authors proved its positive effect on osteoreparative potential, significantly increasing the effectiveness of treatment of false joints.
The positive effect of osteotropic therapy with osteogenon on the effectiveness of treatment of disorders of reparative osteogenesis is also noted by other authors.
There is some evidence in the literature that although osteogenon accelerates the formation of callus by 5-6 days, the process of callus formation is less intense compared to other stimulants (for example, the drug cyclo-3-fort
).
The drug also has a number of contraindications, which significantly narrow the scope of its use in surgery and traumatology.
Today, in order to activate reparative osteogenesis, synthetic calcium phosphate biomaterials in the form of ceramics or composites are used.
Another current area is the study of bone regeneration under bisphosphonate
. Data for various bisphosphonates are mixed.
There is a large evidence base that bisphosphonates reduce the risk of fractures. However, the literature contains conflicting data regarding the effect of various drugs of the bisphosphonate class on the process of regeneration and post-traumatic bone remodeling.
According to preclinical studies on the effect of bisphosphonates on reparative osteogenesis, bisphosphonates in the early stages of regeneration promote the formation of voluminous regenerates and increase the mechanical strength of bone, but subsequently lead to a slowdown in the process of regenerate remodeling.
After conducting experiments on animal models, some researchers concluded that bisphosphonates do not interfere with the consolidation of bone fragments of a fracture, but they slow down the processes of endochondral ossification.
Further clinical studies evaluating the effects of bisphosphonates on bone regeneration are sporadic, inconsistent, and incomplete. Not all clinical studies have confirmed the data obtained during experimental development.
Experts note that the negative effect on bone remodeling in the late stages of regeneration, indicated in most preclinical studies, does not reduce the value of bisphosphonate therapy, which increases bone strength characteristics and reduces the risk of recurrent fractures.
The effect of calcitonin on bone tissue regeneration in fractures has become the subject of discussion in domestic and foreign literature. A number of researchers have not noted a significant effect of calcitonin on the rate of callus formation. Others, on the contrary, note a positive effect of the drug on regeneration, and in some studies a deterioration in the quality and strength characteristics of the regenerate was observed.
An experimental study of the effect of salmon calcitonin on the reparative regeneration of bone tissue indicates the inappropriateness of using the drug at the stages of reparative osteogenesis, which involve the inflammatory process.
At the same time, there was a slowdown in the restructuring of maternal bone fragments and a decrease in the reparative potential. According to some authors, a more optimistic prognosis is possible after administration of the drug at the stage of proliferation, cell differentiation and the beginning of the formation of tissue structures.
In recent years, works have appeared devoted to the influence of pharmacological agents with antioxidant effects on the optimization of reparative regeneration of bone tissue.
These drugs reduce the oxygen demand of cells and increase their viability under hypoxic conditions, inhibit lipid peroxidation and proteolysis, stimulate regeneration, enhance detoxification, improve microcirculation and rheological properties of blood.
One experimental morphological study demonstrated optimization of reparative osteogenesis using Mexidol
and
biofen
, confirming the regenerative properties of these drugs.
It should be noted that in-depth study of osteotropic drugs plays an important role in the treatment of patients with fractures to reduce the risk of developing disorders associated with delayed consolidation and various types of nonunions.
The role of NSAIDs in osteotropic therapy
The effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) on bone tissue regeneration is currently being discussed.
An analysis of studies examining the effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on osteo- and chondrogenesis demonstrated that NSAIDs have different effects on the differentiation of fibroblasts, osteoblasts and other progenitor cells in cultured human mesenchymal cells.
The results of experimental studies of the effect of NSAIDs on chondrogenesis remain ambiguous: some authors deny, while others, on the contrary, confirm the presence of the effect. of ibuprofen was revealed
(reduced healing time for bone wounds).
There are a small number of retrospective and even fewer prospective randomized clinical studies in the literature that focus on fracture consolidation when taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
A double-blind, randomized study demonstrated no effect of piroxicam on fracture healing. Another similar study found no negative effect of ibuprofen on fracture healing.
However, Bhattacharyya et al documented a higher risk of fracture union failure in patients taking NSAIDs.
Taking into account the data from experimental and clinical studies, we can conclude that large randomized studies are necessary. Until their results are available, it is advisable to limit the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs of all groups in patients at high risk of nonunion.
Selection of materials for reparative bone tissue regeneration
In case of nonunion of fractures, atrophic hypovascular false joints and significant defects of long bones, biological stimulation of bone formation in the form of bone grafting (osteoplasty) is often necessary.
Recently, to optimize the reparative process, doctors have been paying great attention to the use of biological osteoplastic materials with osteoinductive or osteoconductive properties.
The largest volume of research is devoted to auto-bone and allo-bone, as well as ceramic hydroxyapatite and other osteoplastic materials. However, the problem of prevention and treatment of disorders of reparative osteogenesis is still relevant.
In this regard, it is fundamentally important to develop technologies for optimizing reparative osteogenesis using osteoplastic materials that provide:
- No toxicity
- Bacterial and viral safety
- Complete biodegradation
- Biological compatibility
- Combination of osteoinduction and osteoconduction.
Such biological materials include autologous platelet-enriched fibrin gel, which is a product from the patient’s own blood.
According to modern data, platelet-fibrin gel contains a large number of growth factors, has a stimulating and osteoconductive effect, and is capable of influencing osteogenesis due to the presence of the above growth factors and an extensive network of fibrin fibers.
The effectiveness of the simultaneous use of autologous blood and various biological implants as optimizing factors for reparative osteogenesis has been experimentally proven. The simultaneous use of autologous blood and these components stimulates the metabolic processes of the osteoblastic cellular elements of the regenerate.
Bone grafts are used in clinical practice to replace, restore structural integrity and increase the osteogenic potential of bone tissue.
Autograft as the gold standard of osteoplasty
The “gold standard” for replacing bone defects is considered to be an autograft made from cancellous bone. From a biological and clinical point of view, the material is ideal for bone grafting.
Autogenous cancellous bone, due to its lack of immunogenicity, has osteogenic and osteoinductive properties, as well as an ideal structure for osteoconduction. It is an ideal osteoplastic material among all biological positions, although its use is limited in scope due to harvesting complexity and mechanical strength.
The ability to obtain sufficient autograft to replace large bone defects is indeed limited by the need for additional surgery and increased risk for the patient.
Taking an autograft is associated with serious complications, and the disadvantage of this method is the infliction of additional surgical trauma, increased blood loss and the time of the surgical intervention itself and anesthesia.
Other materials for reparative bone tissue regeneration
The advantages, disadvantages and risks associated with the used alloimplants are well described in the specialized literature. For this reason, an active search for substitutes that can compete with autologous bone continues.
The sources provide a detailed description of the ideal implant, classifications of materials depending on their origin, composition, production technology and behavior in the body, as well as the mechanisms of influence of these materials on the processes of bone tissue regeneration.
In recent years, a significant number of publications have accumulated in the world press devoted to studying the nature of induction osteogenesis that occurs in response to the use of demineralized bone grafts.
It has been established that they combine osteoinductive and osteoconductive properties. These properties are provided by the release of a number of substances from the extracellular matrix that promote the regeneration of the receptive bone bed.
Demineralized grafts deprived of their mineral base are more quickly vascularized in the recipient's body and replaced by newly formed bone tissue. With a combined transplantation, demineralized bone significantly increases the rate of reconstruction of other biological grafts.
It is considered proven that the osteoinductive properties of demineralized bone grafts are determined not by any chemical substance, but by a whole complex of inducing bone morphogenetic proteins, the osteogenic activity of which increases as mineral elements are removed.
There are a few studies that provide data on the morphological analysis of reparative osteogenesis and chondrogenesis during implantation of a granular mineralized bone matrix into the area of articular cartilage damage and bone defect.
Calcium phosphate osteoplastic materials occupy a special place among artificial implants. Numerous studies have shown that calcium phosphate materials, compared to other biomaterials, have unique properties that facilitate their use in replacing bone defects.
These materials are similar in composition to human bone tissue and induce similar biological responses during bone remodeling. According to the literature, calcium-containing implants made from marble flour can also be biocompatible, undergo bioresorption, and have osteoinductive properties.
Selection of treatment methods for osteoreparation disorders
Modern recommendations regarding the choice of treatment method for disorders of osteoreparation processes are quite contradictory.
Unsatisfactory treatment results occur when using various methods. According to V. Klimovitsky and co-authors, the choice of treatment tactics for bone dysregeneration should begin with the search and elimination of factors that harm the natural course of reparative osteogenesis.
To achieve fusion in the area of pseudarthrosis of long bones, a number of authors call the leading method compression osteosynthesis with an external fixation device. At the same time, according to Yu. Barabash, bone exposure and osteoplasty are optional.
If surgical osteosynthesis for a pseudarthrosis is performed with a submersible fixator, the authors recommend treating the bone ends at the fracture site, tightly connecting the fragments in the correct position, and conducting biological stimulation of regeneration using osteoplasty with synthetic materials or osteoperforation.
In surgery and traumatology, a number of effective methods of transosseous and intraosseous osteosynthesis have been developed that can optimize the reparative properties of bone.
However, the actual time frame for bone tissue fusion remains significant.
The emergence of new technologies based on the use of bioactive intramedullary implants is intended not only to guarantee a positive result in the treatment of long bone fractures, but also to reduce the time of osteosynthesis and reduce the number of complications.
Currently, there is no consensus regarding the tactics of surgical treatment, time, volume and method of fixation of bone fragments, and indications for changing fixators.
Domestic researcher K.M. Several decades ago, Klimov formulated the basic principles of surgical treatment of non-union fractures and false joints of long bones, in which he named the indications for surgical treatment:
- Delayed callus formation—surgical treatment is not indicated.
- A non-union fracture without a tendency to heal or a pseudarthrosis - treatment with osteoplasty is considered irrational. A gentle operation.
- Non-union fracture with a tendency to form a pseudarthrosis - stable osteosynthesis as an internal prosthesis.
When performing surgical intervention, Klimov proposed not to remove the scar tissue that surrounds bone fragments, and economical resection of fibrous and cartilaginous tissue was recommended only for comparison of bone fragments.
Based on previous morphological studies, the researcher argues that the sclerotic ends of bone fragments are capable of osteoreparation. Although there is a strong opinion among doctors that the potential reparative capabilities of sclerotic tissue are reduced to nothing, and the latter must be removed.
The first postulate is also debatable, since there are supporters of surgical treatment, even revision osteosynthesis for delayed consolidation of fragments.
A. Kalashnikov and co-authors focus on an objectified assessment of the processes of fracture healing. It makes it possible to avoid excessive expansion of indications for surgical treatment of patients with delayed healing of bone fragments and the need for osteosynthesis in borderline cases, when all possibilities of conservative treatment have not been exhausted.
The general rules for surgical interventions for various types of dysregeneration are:
- Maximum preservation of blood supply to fragments
- Ensuring the highest possible contact plane
- Removal of non-viable bone tissue
- Adequate fixation of fragments.
In the post-Soviet space, Professor V. Klimovitsky and co-authors proposed the following approaches to the treatment of dysregeneration.
When treating hypertrophic false joints of single-bone segments, axial compression is performed between the fragments. During the procedure, destruction and resorption of bone and scar tissue occurs, inflammatory processes in the interfragmental zone and osteoreparation processes are restored.
On the two-bone segment (tibia), it is first necessary to perform an osteotomy of the fibula, which acts as a spacer. The authors believe that during surgical treatment of hypertrophic false joints in most cases there is no need to intervene in the area of damage.
Exceptions include cases where the metal retainer is removed.
Treatment of the oligotrophic type of dysregeneration requires intervention at the sites of damage in order to activate the reduced osteogenic potential through various surgical techniques (Beck tunneling or osteoperiosteal decortication).
Treatment of hypotrophic forms of disorders of reparative osteogenesis is considered the most problematic, since osteoreparative potential in this case is absent.
Surgical treatment must necessarily include interventions in the area of the pseudarthrosis. During the procedure, resection of the altered ends is performed, followed by covering the nonunion area with a cortical-cancellous graft.
The choice of one or another method of replacing a bone defect should be made individually, including taking into account the capabilities of the surgeon.
To optimize the conditions for the formation of the regenerate, reduce the duration of treatment and prevent complications, a method of targeted stimulation of bone tissue regeneration is used by introducing intramedullary wires with a calcium phosphate coating.
The literature describes the morphological features of osteogenesis during the consolidation of bone fragments of long bones under conditions of intramedullary injection of fixators with a bioactive calcium phosphate coating of hydroxyapatite.
The results of numerous studies indicate that intramedullary fixators coated with hydroxyapatite have a positive effect on the intensity of reparative osteogenesis during fracture healing.
One of the ways to stimulate osteoreparation is to stimulate local sources of osteogenesis by creating through channels in the metaphyses and diaphyses of long bones (tunnelization) or a perforated defect (osteoperforation), providing stimulation of intraosseous circulation.
Studies on the morphological features of reparative osteogenesis during the healing of tibial fractures under conditions of transosseous osteosynthesis and disruption of the local source of osteogenesis in the contralateral limb have demonstrated promising results.
It has been proven that osteoperforation activates reparative osteogenesis, accelerates compaction and development of bone tissue, increases its maturity and ensures the formation of full-fledged bone regenerate in the early stages.
The data presented indicate that the problem of stimulating reparative osteogenesis has not been resolved, since each of the methods, along with positive properties, has significant disadvantages and limitations in clinical practice.
There will be a search for new factors, drugs and materials for the reparative regeneration of bone tissue in dentistry, surgery, traumatology and other areas of medicine.
Shilajit for fractures
After fractures, doctors recommend mummy in tablets as a general strengthening, anti-inflammatory, moderate pain reliever that improves mineral metabolism in the bones due to the content of biologically active components (vitamins, amino acids, minerals).
It has been proven that taking mumiyo can reduce the treatment period by 15-20 days. And all thanks to the fact that this product promotes the formation of bone callus and accelerates the fusion process. If you take mumiyo from the very beginning of treatment, you can restore bone integrity in 20 days.
The use of mumiyo not only allows bones to grow together faster and strengthen, but also has a beneficial effect on the body as a whole. The body temperature and general condition of the patient are normalized, and the appetite is awakened. Shilajit is great for helping with sleep disorders.
The course of taking mumiyo depends on which bone is broken. If the shoulder or forearm is injured, then 1-2 courses of treatment are indicated. For all other fractures, mumiyo should be taken orally for at least 3-6 courses.
To summarize, we can say that the treatment of fractures should be complex, long-term and using various medications, physical therapy methods, exercise therapy and be carried out under medical supervision.
What calcium supplements are best to take for bone fractures?
Many minerals and trace elements are involved in the building of bone tissue6. To speed up the healing process, after a fracture you should take products that contain:
- Magnesium. Regulates metabolism in bone tissue, its mineralization, maintains flexibility and strength, enhances the ability to recover after fractures. Its use helps to increase bone mineral density7. Insufficient magnesium intake can cause osteoporosis and low bone mass. The consumption rate is 400 mg/day.
- Zinc. Participates in many metabolic processes and is fundamentally important for DNA reproduction. Bone tissue contains approximately 30% of the body's zinc6. Its concentration in the bones quickly drops if intake decreases or absorption of the microelement is impaired. Due to zinc deficiency, defects in bone tissue development are possible. The intake rate for adults is 12 mg/day6.
- Copper. A component of enzymes that are involved in iron metabolism and providing tissues with oxygen. In bone tissue, it is responsible for the formation of collagen, its connection with elastin and general mineralization of the skeleton. Lack of copper leads to disturbances in the formation of bone and connective tissue, and inhibition of bone growth. Requirement for adults: 1 mg/day6.
— Manganese. Also involved in all types of metabolism (carbohydrates, fats, amino acids). Manganese deficiency can cause disorders in the reproductive system and also lead to increased bone fragility8. A daily intake of 2 mg of manganese is required.
— Boron. Affects the metabolism of vitamin D, the content of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium in the bones. Improves calcium absorption, prevents loss of bone density and the development of osteoporosis. The body should receive up to 2 mg of boron daily6.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment of fractures, it is advisable to take additional calcium as part of combination medications (especially for older people). Preparations in the Kalcemin® line provide additional supply of calcium, vitamin D and other microelements necessary for the timely healing of fractures4. They also promote callus formation and increase bone density to prevent re-injury.