Detailed description of the study
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that is accompanied by the development of chronic damage to the joints—usually the hands and fingers—and internal organs. The course of RA can be rapidly progressive or slowly progressive. Along with damage to the joints, swelling and pain in them, stiffness of movement in the morning after sleep, the disease has such nonspecific manifestations as weakness, fatigue, and weight loss. The disease is characterized by the formation of specific rheumatoid nodules under the skin, as one of the most common extra-articular manifestations.
Delayed detection of RA has many adverse consequences. Long-term pathological changes in the joints cause impairment of their mobility and, without treatment, lead to disability. Deposits of pathological amyloid protein are found in organs and tissues, and amyloidosis develops. RA is also the cause of so-called tunnel syndromes, which are caused by compression of nerves and blood vessels in anatomical canals, or tunnels. The most common types are carpal tunnel syndrome and compression syndromes of the ulnar and tibial nerves.
Rheumatoid arthritis is differentiated from a number of other diseases that begin with joint damage. These include joint injuries, some acute infectious diseases such as influenza, rubella, measles, hepatitis, post-streptococcal arthritis, as well as gout, osteoarthritis and other rheumatic diseases.
This study is aimed at identifying RA and includes five important indicators. It is worth noting that RA has seropositive and seronegative forms, which are determined depending on the detection of rheumatoid factor in the blood.
Rheumatoid factor
Normally, immunoglobulins (antibodies, antibodies) protect a person from the harmful effects of microorganisms and foreign substances. They are proteins that differ in their structure and function. They are divided into five classes: IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD and IgE. Antibodies, united by the concept of “rheumatoid factor” (RF), most often belong to the IgM class, are produced against parts of one’s own IgG, altered in rheumatoid arthritis due to various not fully established reasons. Their determination is one of the key stages in establishing the diagnosis of RA.
SSR antibodies
Cyclic citrulline-containing peptide (CCP, CCP) is a protein in which the normally absent amino acid citrulline replaces the physiological amino acid arginine. Determination of antibodies to CCP makes it possible to determine the presence of the disease with a high probability, including in seronegative RA. For early arthritis, its sensitivity is 41-80% and specificity is 93-99%.
ASLO
Antistreptolysin-O (ASLO) are also a group of antibodies directed to bacterial molecules: group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus - streptolysin. This microorganism is one of the causative agents of sore throat, scarlet fever and some other diseases. Previous streptococcal infection is often associated with the subsequent occurrence of autoimmune diseases.
The study also contains two tests: determination of C-reactive protein and a clinical blood test. The concentration of the former may reflect the presence of an acute stage of RA and is associated with disease activity. Together, these two tests allow us to assess the presence of inflammatory processes and their intensity.
Thus, this complex study is widely used in clinical practice, since it can highly likely confirm or exclude RA; it is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and assess the prognosis of the disease.
A detailed description of the studies and reference values are presented on the pages with descriptions of individual studies.
Symptoms
Lesions of the musculoskeletal system during infection with COVID-19 are polymorphic in clinical symptoms. This:
- swelling of the joint
- soreness,
- redness,
- local increase in temperature to subfebrile values
- resting joint pain
- morning stiffness for more than an hour,
- general fatigue
- malaise.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects small joints, most commonly the hands and feet. However, large joints can also be affected. The main sign of rheumatoid arthritis is symmetry. First, inflammation occurs inside the joint, as a result the synovial membrane thickens, then the articular cartilage is damaged, and muscles, ligaments and tendons weaken. Against the background of persistent inflammation, the bones that form the joint are destroyed. In severe cases of the disease, the joints begin to lose their function, permanent deformities may occur and develop, resulting in a decrease in the patient’s functional ability and quality of life.
References
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical recommendations. Association of Rheumatologists of Russia, 2021. - 102 p.
- Rheumatology: National Guide / ed. E.L. Nasonova, V.A. Nasonova. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. - 720 p.
- Kishkun, A.A. Guide to laboratory diagnostic methods. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. - 800 p.
- Volkova, M.V., Kunder, E.V. Early arthritis: relevance, Immunopathology, diagnosis. Vestnik VSMU, 2013. - No. 3.
- Medical microbiology, virology and immunology: a textbook for medical students / ed. ed. A.A. Vorobyov. — 2nd ed., corrections and additions. - M.: Medical Information Agency, 2012. - 704 p.
Treatment
Timeliness is important in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Delaying treatment by a year reduces the likelihood of a favorable prognosis.
Medication methods
Basic antirheumatological drugs are prescribed as first-choice therapy: methotrexate, leflunomide (Arava), sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine. Taking them slows down the course of the disease, prevents bone deformities, improves the quality of life of patients and the prognosis of the disease. These drugs are prescribed for an indefinite period, sometimes for life. If we are talking about an aggressive and active course of the disease or intolerance to high doses of basic drugs, glucocorticosteroid drugs are prescribed, which very quickly and effectively relieve inflammation. The last group of drugs is the “heavy artillery”, genetically engineered biological drugs. The effectiveness and duration of therapy is assessed by a rheumatologist; his tasks also include dynamic monitoring of the patient.
In addition to taking medications, non-drug therapy methods are recommended:
- Exercise therapy (not contraindicated even in the highly active phase of the disease);
- physiotherapy,
- massage
- hydrotherapy.
In the later stages of the disease, with inadequate or late therapy, or with an aggressive course of the disease, surgical treatment methods are sometimes necessary:
- synovectomy (removal of the synovial membrane of the affected joint);
- reconstructive plastic surgery on bones, ligaments, tendons of large and small joints;
- endoprosthetics.
C-reactive protein
The exact criterion that determines the level of the inflammatory process is C-reactive protein (CRP). Determination in plasma is an important diagnostic criterion for arthritis.
Synovial fluid responds by increasing protein to the inflammatory process. In the blood of healthy people the amount is not higher than 0.002 g/l.
During autoimmune processes in the body, the concentration increases to 10 mg/l and higher. The level of C-reactive protein rises during exacerbation of ankylosing spondylitis.
C-reactive protein is a fast phase protein produced in the liver. Stimulates the body's immune response to the invasion of an inflammatory agent.
A few hours after the pathogenic agent penetrates the tissues, this protein is intensively synthesized in the liver. After a day, the protein concentration in plasma increases tens of times. If treatment is prescribed correctly, C-reactive protein quickly decreases to normal levels.
Testing for C-reactive protein
- Tests for rheumatoid arthritis: what tests to take and their meanings
The positive side of this laboratory criterion is that it allows for differential diagnosis of viral and bacterial infections. During a viral infection, protein levels increase slightly. If the pathological process has acquired a chronic course, gradually the content of this marker in the patient’s blood is reduced to zero and loses diagnostic relevance.
If joint pathology is caused by a bacterial infection, the content increases exponentially. Decoding a laboratory indicator requires attention in older people suffering from chronic diseases.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Erythrocyte sedimentation is studied in vitro over a certain period of time. The indicator characterizes the intensity of the development of pathology, the activity of the spread of destructive processes. High ESR values indicate progression of the disease and the need for effective medication measures. Moreover, the higher the settling rate, the more active the phase. This process is explained by the formation of inflammatory proteins in the patient’s blood, which cause the formation of red blood cells into aggregates, an increase in gravity and the rate of their sedimentation.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate indicates an inflammatory process in the body
About laboratory diagnostics and tests
To identify the rheumatoid type of arthritis, specific and nonspecific tests are taken:
- Specific - provide unambiguous confirmation or refute the fact of the disease with high reliability.
- Nonspecific - they work only in combination with other survey data, since they reveal only individual signs.
Tests are carried out of a specific and non-specific nature.
The attending physician must determine which tests need to be taken for rheumatoid arthritis. The patient’s examination plan includes undergoing a comprehensive diagnostic set of measures:
- blood biochemistry, its clinical examination, determination of ACCP (anti-citrullinated bodies), immunological analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- intra-articular fluid analysis;
- biopsy of the joint membrane.
You may need to submit your urine for analysis.
Specific indicators can reveal rheumatoid arthritis even before the first signs of the disease appear. Patients with a hereditary predisposition can use this method to prevent the disease and its transition to the chronic stage.
Rules for taking tests
Establishing an accurate diagnosis for rheumatoid arthritis of the joints is based on competent interpretation of clinical results and professional ability to interpret them in a complex manner. To obtain reliable results, special preparation is required before donating blood. A referral for laboratory tests must be issued by one of the treating specialists: a general practitioner, rheumatologist, surgeon or immunologist. To fully study the indicators, you need to donate blood from a vein, observing the following conditions:
- Do not eat food 12 hours before taking the test (for children under one year old - half an hour, from 1 to 5 years - 3 hours).
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages during the day.
- Stop taking medications the day before with your doctor's permission.
- Avoid physical activity and nervous stress an hour before the test.
- Do not smoke for at least 30 minutes before the test.
It is necessary to properly prepare for the tests.
Diet violations, use of medications or smoking distort the clinical data of blood composition and mislead when interpreting the results.
Approach to the treatment of seropositive arthritis in our clinic
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Specialists at the Paramita clinic in Moscow have extensive experience in treating seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. A patient who seeks help for the first time is first given a full examination and only then is prescribed a course of therapy, the peculiarity of which is a combination of the most modern Western and traditional Eastern, time-tested techniques. Treatment measures are selected for each patient strictly individually. Their effectiveness is periodically assessed. Our methods (how we treat):
- drug therapy with the inclusion of the latest drugs, herbal medicine, folk and homeopathic remedies; this combination allows you to carry out the course faster, more efficiently and reduce the drug burden on the patient;
- physiotherapeutic procedures - prescribed depending on the stage of the disease and the general condition of the patient;
- kinesitherapy, taping, complexes of therapeutic exercises and medical massage - the most effective treatment methods are used to maintain limb mobility, all procedures are prescribed by a doctor and carried out under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor;
- PRP therapy is the latest method that allows you to quickly restore lost motor functions; is based on stimulating the regenerative properties of the body with the patient’s own blood platelets, processed using special techniques;
- reflexology (RT) - the impact of acupuncture, moxibustion, acupressure on acupuncture points (AP) on the body, reflexively associated with internal organs and tissues; the doctors of our clinic are proficient in all RT methods, as they were trained in China and Tibet;
- pharmacopuncture – introduction of modern highly effective drugs into AT.
Treatment of seropositive arthritis in the clinic
Doctors at our clinic not only relieve, but also prevent exacerbation of seropositive arthritis by regularly carrying out anti-relapse measures. As a result, patients are free from exacerbations for a long time and have a high level of quality of life.
Increased indicators in a child
Even the youngest children can have pathologies of a rheumatic nature. Symptoms appear in a hidden form, and due to unconsciousness, it is more difficult for the child to explain what is bothering him. Complaints of pain in the legs, arms and knees, or simply constant crying may be the first signs of the development of the disease. A disease such as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis has a chronic nature of manifestation and develops in children under 16 years of age.
Pathology can be detected even in young children
During a diagnostic examination to clarify the diagnosis, the following is carried out:
- Blood test to detect infectious viruses: beta-hemolytic streptococcus, cytomegalovirus, herpetic type virus, chlamydia.
- Collection for the study of intestinal bacteria (Yersinia, Shigella, Salmonella) and parasites.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, heart, kidneys.
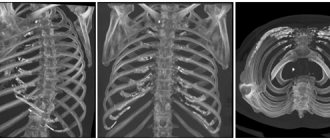
- X-ray of joints, sternum, sacroiliac joints and spine.
In addition to a general differential examination, all children with joint diseases are advised to visit an ophthalmologist and undergo a slit lamp examination.
Biopsy of the synovium of the joint
The rheumatoid type of arthritis is accompanied by inflammation of the synovial membrane of the joint. Research of materials in this area allows us to more accurately decipher the stages of the pathogenesis of the disease and develop more progressive treatment methods.
Immunohistochemical features of the synovium are excellent indicators of disease activity, and the use of biomarkers for laboratory purposes helps to identify new potentially effective agents in the fight against rheumatoid arthritis. An important quantitative indicator here is the content of macrophages in the subsynovial layer, which characterizes how treatable the disease is.
Antinuclear antibodies
This serological indicator is often determined in the laboratory diagnosis of rheumatological diseases of the joints, especially the knee. Relevant for initial diagnosis. The diagnostic method is indispensable as a screening method to exclude systemic connective tissue diseases with predominant damage to the joints.
When conducting the study, the technique of indirect immunofluorescence is used. The intensity of staining of cell nuclei is assessed.
The method detects the presence of immunoglobulins of various classes; the method is sensitive to immunoglobulins of classes G. Antibodies belonging to group A, M are determined by the method more difficult. The analysis of antinuclear antibodies is considered reliable at a dilution of 1 to 20; lower dilutions indicate a false positive reaction.
Biochemical analysis for antinuclear antibodies is not specific for joint diseases; it should be used in combination; laboratory and instrumental studies are prescribed.
Staining of nuclei with fluorescent dye can be of four main types.
- Diffuse, homogeneous type. The entire cell nucleus glows.
- Staining in the form of individual spots is due to the presence of specific groups of antibodies.
- Peripheral staining in the form of a bright luminous rim surrounding the outer part of the nuclear structure. Coloring is caused by antibodies in DNA consisting of two chains.
- Luminescence of nucleoli. Staining in joint diseases is rare.
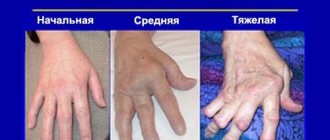
Stages of the disease
Seropositive rheumatoid arthritis has 4 stages of development:
- The initial stage
is the development of the disease lasting up to 6 months; The main symptom is morning stiffness. - Early stage
– from six months to a year; the symptoms of polyarthritis are more pronounced, significant swelling of the joint tissues appears. - Advanced stage
– from one to two years with all clinical manifestations. - The late stage
– more than two years, is accompanied by joint deformities, contractures, disability and complications from internal organs.
Radiological stages of seropositive arthritis:
- Development of osteoporosis of the articular surfaces of bones.
- Narrowing of the joint space, the beginning of the destruction of cartilage tissue.
- Significant destruction of cartilage and bone tissue of articular surfaces, deep erosion; subluxations;
- Closing of the joint space and the formation of ankylosis - immobility of the limb.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
General blood and urine analysis
A starter kit for identifying an inflammatory process in the body is a general analysis of the patient’s blood and urine. These tests also determine the nature of the symptoms (infection, autoimmune disease). Thus, a general analysis determines the following pathological changes in blood parameters in a sick person:
- Increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) – from 25 mm/h with a norm of 2–15 mm/h.
- Decreased hemoglobin - in women up to 120 g/l and in men up to 135 g/l.
- The quantitative growth of leukocytes is above 9000, while the norm is 4000–9000.
Tests will help identify pathological changes in the body.
Exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis is accompanied by leukocytosis and thrombocytosis of moderate severity, normocytic normochromic anemia. Sometimes chronic blood loss occurs through the gastrointestinal tract and, as a result, iron deficiency and anemia.
A urine test provides nonspecific information and only determines an increase in protein content and leukocyte levels, which only confirms the presence of inflammatory factors.
Data decryption
Making a definitive diagnosis is not easy. Sometimes patients learn about rheumatoid arthritis 5-7 years later, when treatment is no longer effective and the disease has become chronic. Therefore, deciphering the blood tests obtained for arthritis requires accuracy, an understanding of the overall picture of the disease and the relationship of various data.
Rheumatoid arthritis and the degree of its development are characterized by the level of deviation of indicators from the norm. The greater the difference in indicators, the more severe the form of the disease. Clinical confirmation of any 4 markers in a patient over a period of 6 months is a medical examination of the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Circulating immune complexes
These indicators make it possible to determine the immunological activity of the current acute, chronic disease.
If the biological fluid shows an excess of proteins that perform the functions of antigens, antibodies lose the ability to neutralize them. As a result, immune complexes are formed in the blood, deposited on the walls of blood vessels, the surfaces of the joint membranes, and in other organs. The result of the pathological process is the development of reactive inflammatory processes of the knee joint and others.
- Examinations necessary for differential diagnosis between arthritis and arthrosis
Immune complexes circulating freely in plasma are in direct contact with red blood cells. They do not have a damaging effect on organs. The concentration of free CECs in the blood is gaining increasing diagnostic importance.
A direct relationship between the development of the pathological process of the knee joint has been identified in cases of systemic lupus erythematosus.
The indicator is taken into account in the diagnosis of rheumatological diseases. The level directly affects the clinical picture and the prescribed treatment.
The high concentration of circulating immune complexes in the serum of patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis indicates the systemic nature of the pathological process and requires additional research.
When laboratory diagnostics of immunoglobulins and circulating immune complexes are carried out, it is worth taking into account an increase in content of at least 2-3 times. In a healthy person, circulating immune complexes are not detected.
Foot treatment