What is arthritis
A joint consists of an articular capsule, a cavity filled with fluid, and articular surfaces of bones covered with cartilage.
With arthritis, inflammation occurs in the synovium of the joint. Then it spreads to other elements of the joint and periarticular space. The disease leads to changes in the articular cartilage, surfaces, ligaments and capsule. In severe cases, the joint becomes deformed. Arthritis (inflammation of the joints) first affects the hands, feet, shoulders and elbows, and then moves to the knees and hip joints.
Diagnosis of reactive arthritis
The treatment strategy for reactive arthritis is determined by its causes. To determine, confirm and predict the diagnosis, 3 types of studies are carried out:
- Laboratory. Blood and urine tests, synovial fluid tests, detection of infections, immunological studies.
- X-ray. X-rays allow you to see the extent of joint damage.
- Ultrasonic. Detects pathologies in periarticular tissues.
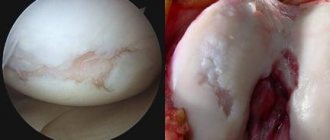
To accurately diagnose, relieve symptoms and treat reactive arthritis, it is recommended to conduct all available types of research. For other types of this disease, arthroscopy is also performed: examination of the inner surface of the joint using optical equipment. But when identifying and treating reactive arthritis, it is not very informative and does not allow one to establish the cause, as well as give a reliable prognosis.
Causes
There are the following causes of arthritis:
- injuries, bruises of joints, damage to the ligamentous apparatus;
- bacterial, fungal or viral infections;
- metabolic disorders, deficiency of bone and cartilage tissue density;
- physical overload;
- bone diseases;
- immune disorders;
- hereditary predisposition.
The disease can occur due to hypothermia, allergies, excess weight, sedentary lifestyle, smoking. Arthritis of the fingers is an occupational disease of massage therapists, seamstresses, and hairdressers. Builders and loaders are susceptible to inflammation of the joints of the limbs.
Factors that stimulate the development of arthritis also include:
- Age. Older people suffer from this problem more often due to natural changes in the body. Osteoarthritis occurs most often in older people.
- Floor. Females are relatively more susceptible to arthritis.
Prevention of arthritis
Prevention of arthritis comes down to avoiding and eliminating all possible triggering factors. A healthy lifestyle, weight control, a balanced diet, avoidance of excessive alcohol consumption and regular preventive examinations with a doctor will significantly reduce the likelihood of developing arthritis, and following all the doctor’s recommendations in the early stages of the disease will significantly increase the likelihood of recovery or significantly reduce the likelihood of relapses.
Up to contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease develop gradually. In the morning, a person feels stiffness in the joints, they begin to hurt, especially during movement, and crunch during physical activity. As the disease progresses, the joint swells, increases in size, becomes hot to the touch, and the skin around the affected area turns red. The person feels weak and has difficulty moving the leg or arm with the affected joint.
Signs of infectious arthritis: fever, chills, joint pain when pressed. Acute arthritis is accompanied by severe pain in the joints, which occurs suddenly. In the chronic form of the disease, symptoms increase gradually.
Treatment of reactive arthritis
The goal of treatment is to relieve inflammation, pain and eliminate the causes of reactive arthritis. For this purpose, the following methods are used:
- Medication;
- Non-medicinal;
- Folk.
The treatment regimen for reactive arthritis is selected based on the results of the examination, which makes it possible to make a prognosis for recovery. Until its end, it is possible to prescribe painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. They will relieve pain, swelling and allow you to restore mobility.
Drug therapy
The basis for prescribing medications is the diagnostic results. Medicines are designed to solve two problems: relieve painful symptoms and eliminate the cause of inflammation.
Relieving pain and inflammation
At this stage, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs suitable for the treatment of reactive arthritis. The composition, dosage and application regimens are selected individually. It all depends on the patient’s condition, location, degree of inflammation, age and the presence of concomitant diseases. Injections, tablets and capsules from the NSAID group are only the first step to alleviate the condition and allow you to closely identify and eliminate the causes of reactive arthritis. If NPS drugs are insufficiently effective, glucocorticoid hormones are prescribed. They are taken in the form of tablets, intravenous, intra- or periarticular injections. If there is a threat of transition to the chronic stage, basic drugs are added to suppress immune reactions. Most painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs have a large number of contraindications and side effects, including the leaching of salts, minerals, and vitamins, without which it is impossible to restore the functionality of the joints. Therefore, it is strictly forbidden to take analgesics on your own, without a doctor’s prescription. The modern range of drugs for the treatment of reactive arthritis includes agents with chondoprotective effects. They simultaneously work in two directions: relieve pain, swelling, and also restore damaged cartilage and joint tissue. One of the most effective drugs of the latest generation is Artradol. In addition to the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, it suppresses the production of enzymes that cause the destruction of joint tissue, normalizes the production of joint fluid and phosphorus-calcium metabolism. This promotes rapid healing of damaged areas and restoration of joint functionality.
Eliminating the cause of reactive arthritis
Relieving pain and inflammation is not enough. Without eliminating the cause, the likelihood of relapse is high. It can only be identified after a thorough comprehensive examination. If the causes of reactive arthritis are not hereditary or allergic in nature, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. Its composition is determined by the nature of the infection:
- Genitourinary - antibiotics of the macrolide, tetracycline, fluoroquinolone group for both partners.
- Intestinal – antimicrobial therapy for at least a month.
- Dental or respiratory tract – individual antibiotic therapy according to the doctor’s decision.
Taking any antibiotics is accompanied by taking medications to maintain and restore the gastrointestinal microflora. Thus, probiotics are added to the painkillers, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents.
Non-drug methods
It is auxiliary, but mandatory, enhancing the effect of drugs for the treatment of reactive arthritis. Prescribed mainly after the removal of acute symptoms. Non-medicinal methods include the following.
- Physiotherapy. A number of procedures are also indicated at the acute stage. For example, electrophoresis, ultrasound, magneto-, cryo- and laser therapy, and salt baths effectively eliminate swelling. Mud therapy, SMT, and hydrogen sulfide baths are recommended as restorative procedures at the end of the drug course.
- Reflexology. This is a professional targeted treatment of bioactive points, designed to normalize the functioning of internal organs.
- Diet. There is no special table. But, including the following products containing glucosamine and chondroitin in your diet will significantly improve joint function:
- Fish (especially salmon and sturgeon), seafood;
- Animal cartilage and skin;
- White meat, beef;
- Hard cheeses,
- Butter;
- Gelatin-containing dishes (jelly, jellied meat);
- Eggs;
- Dairy products;
- Soy;
- Vegetables and fruits (especially avocados, legumes, nuts, dried fruits)
- Linseed oil.
If arthritis is of an allergic nature, it is necessary to adhere to a neutral, hypoallergenic diet, avoiding the consumption of hazardous foods. Allergy tests and careful monitoring of the body's reaction will help determine them.
- Exercise therapy and massage. Therapeutic exercises are recommended in the remission stage. It allows you to effectively develop and activate the work of joints, strengthen the surrounding muscles, and increase overall tone. Exercises are selected by a specialist and carried out under his supervision. This is a complex for the knee, shoulder, ankle, and finger joints. General massage involves manual treatment of tissues, muscles, and joints by an experienced specialist.
The use of non-drug methods contributes to overall health and strengthening of the immune system. Most procedures are pleasant, allowing you to rest and relax, which has a positive effect on your overall health.
Folk remedies
There are traditional methods of “treating” reactive arthritis.
The quotation marks were used here for a reason. Given the bacterial or allergic nature of the disease, it is impossible to eliminate its cause without serious drug therapy. But folk remedies are successfully used to relieve pain and reduce swelling. For this purpose, compresses made from horseradish, hard radish, sea salt, fir oil, ointment from comfrey leaves in vegetable oil with the addition of beeswax are suitable. Any of these products has side effects, contraindications and can cause an allergic reaction, aggravating the condition of the damaged joint. Folk remedies are recommended to be used as part of auxiliary therapy after relief of the acute phase of the disease, taking into account their composition, causes of inflammation and medications taken. Any unwanted reaction can negate all achieved results, causing new inflammation. The noticeable relief after compresses often makes you want to give up pills and injections, which is absolutely unacceptable. For this reason, relying on herbs alone is not recommended. Being familiar with the symptoms and treatment methods, you cannot do it yourself. Relapses can affect not only previously affected areas, but also be of a new nature. Only an experienced rheumatologist can determine it, select and adjust the treatment regimen. We advise you not to delay your visit to him. Timely administration of the correct treatment will avoid aggravation of the situation and the development of complications. Are you experiencing discomfort in your knees? Is your ankle swelling? Are your fingers swollen? Listen to our recommendations and start treatment as early as possible! I wish you health, freedom of movement and joint flexibility! To previous article To next article
Symptoms, stages and forms of arthritis of the shoulder joint
The treatment strategy depends on the etiology and nature of the pathology. The main signs of joint inflammation are:
- pain;
- limited mobility in the shoulder;
- specific crunch in the joint;
- swelling;
- local temperature increase;
- deterioration of the patient's general condition, weakness.
To treat arthritis of the shoulder joint, it is important to differentiate its form:
- post-traumatic (occurs after dislocations, sprains, fractures);
- rheumatoid (appears against the background of reduced immunity, after infectious diseases);
- osteoarthritis (associated with age-related degeneration of joint structures, develops after 50 years, often affects athletes involved in throwing equipment, wrestling, as well as people lifting weights due to their profession).
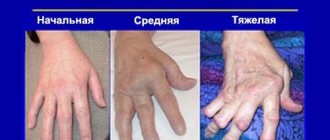
Treatment for arthritis of the shoulder joint is developed taking into account the degree of development of the pathology:
- The first stage is characterized by the appearance of pain, which increases with exertion and subsides with rest. The pain depends on the weather and intensifies at night. The hand gets tired quickly;
- on the second the pain becomes constant. There is a feeling of stiffness and clicking in the shoulder;
- on the third, irreversible changes affect the structures of the joint, it becomes deformed.
How the disease develops
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, that is, associated with a malfunction of the immune system. In arthritis, immune cells mistakenly mistake joint cells for foreign elements - viruses, bacteria - and try to destroy them. This process continues for years..
Often the disease begins with damage to the knee joint. At the beginning of the disease, the patient feels weak, unwell, loses appetite, loses weight, and the temperature can rise to 37-39 degrees. In this case, joint problems fade into the background or are completely absent. As the disease develops, more and more joints are involved in the process, and after treatment of exacerbations, the joints become less mobile and deformed.
Over time, symptoms associated with damage to internal organs and systems appear: lungs, heart, blood vessels, kidneys, eyes, salivary glands. With rheumatoid polyarthritis, dense subcutaneous nodules often form.
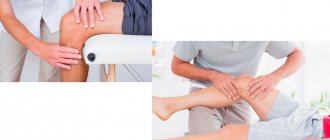
Diagnosis of joint pain
To understand why the joints of your legs and arms hurt, you need to see a doctor. The doctor prescribes a number of diagnostic procedures for the patient. To begin with, laboratory tests are taken:
- General blood analysis. Makes it possible to detect deviations taking into account the nature of the joint damage and the degree of its severity.
- Blood chemistry. For inflammation of the joints, they look at the levels of C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, total protein, seromucoid, diphenylamine reaction, as well as some other indicators that confirm a rheumatic diagnosis.
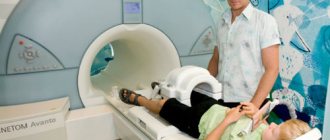
Additionally, the following examinations may be prescribed:
- Radiography. It is mandatory for painful joints, since without photographs the doctor cannot carry out a differential diagnosis and assess the degree of damage to the skeletal system;
- CT scan. Used to study the location of injured or inflamed bone areas;
- Ultrasound examination is an accessible diagnostic method that describes in detail the joint and adjacent tissues;
- Densitometry. An additional type of diagnostic that shows how much bone density is preserved. Used to diagnose osteoporosis;
- Arthroscopy. During the procedure, the specialist visually examines the structure of the joint, its structure, and takes a tissue sample from the desired area;
- Radionuclide (radioisotope) scanning. Effective in the early stages of joint diseases;
- Arthrography. The doctor injects special contrast agents into the joint (contrast may not be used). Changing the initial picture gives him the opportunity to judge the presence of affected parts in hard-to-reach parts of the joint.
If the doctor deems it necessary, a biopsy is performed - a diagnostic sampling of cells from the affected area.
Non-drug treatments for rheumatoid arthritis
Conservative therapy is preferable in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
. Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis; placement of the patient in a hospital and compliance with bed rest is required only in exceptional cases.
In addition to physical therapy, clinical guidelines for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis include the following:
- avoid physical activity and stress;
- dress warmly and do not overheat in the sun;
- travel to other climate zones as little as possible;
- quit smoking and alcohol;
- go to bed before midnight;
- use special insoles (if there are deformities);
- engage in swimming and other supportive sports.
Patients need alternating rest and physical activity and normalization of their diet.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Physiotherapeutic procedures help relieve pain, strengthen the muscles and ligaments that support the joint, and increase the amplitude of voluntary movements. Most techniques are used during remission and are contraindicated in case of exacerbation
. However, magnetic therapy and drug electrophoresis are widely used to relieve inflammation in the acute phase.
- electrophoresis with lidocaine;
- cryotherapy;
- ozone therapy, ozokerite;
- amplipulse;
- shock wave therapy
; - phonophoresis;
- ultrasound therapy;
- radon, iodine-bromine, sodium chloride and hydrogen sulfide baths, mud therapy, other balneological techniques;
- mechanical and kinesiotherapy;
- massage and manual therapy;
- paraffin applications.
To treat pain in rheumatoid arthritis of the feet, sports or orthopedic shoes with a pronounced heel and metatarsal pads are also recommended. “Physiotherapy” is also possible at home - to relieve pain, you can apply ice compresses for 5-15 minutes.
Therapeutic exercise for rheumatoid arthritis
Gymnastics for rheumatoid arthritis prevents contracture and helps maintain range of motion in the joint. Its role in relieving inflammation is also important - the stronger the muscles, ligaments and tendons, the less the load on the structural elements of the joint and the easier the disease.
Clinical recommendations for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis during exacerbation allow only passive flexion-extension movements
(when the patient performs movements in the joint manually, without loading the muscles), in some cases - swimming. Passive movements with severe pain and muscle tone are best performed in a warm bath.
To maintain muscle mass and finger motor skills, the following exercises for the hands are used:
- Place your hands on the tabletop, palms down, and then raise your hands so that your palms are facing straight in front of you. Lower your brushes. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Place your hands on the tabletop, palms down, and then turn them over, palms up. Perform 10 times.
- Connect each finger in turn with the tips of the thumb - from the index to the little finger and back. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Stretch your arms in front of you and rotate your hands, first clockwise and then counterclockwise. Repeat 6-8 times. Then clench your fingers into fists and rotate your fists.
- Take an apple, a tennis ball or a silicone expander ball and clasp it with the fingers of one hand, squeezing lightly. Then do the exercise for the other hand. Repeat 5-6 times.
At the end of the session, rub your palms together.
It is recommended to perform this complex daily, and also do not forget about 5-minute warm-ups if your professional activity involves stress on your arms. If rheumatoid arthritis has affected other joints, you can perform standard sets of exercises recommended for arthritis of these joints.
Important: physical therapy exercises should not cause pain!
When performing exercises through force, without listening to acute or sharp pain,
you can only harm your joints!
Occupational therapy is also used as exercise for rheumatoid arthritis. In the remission stage, patients with damage to the interphalangeal and wrist joints are shown activities that develop fine motor skills of the fingers and strengthen the muscles of the wrist and hand - for example, modeling from dough, clay or plasticine, exercises with an expander, fingering rosaries. If the pathological process has affected the elbow and knee joints, you should think about purchasing specialized special expanders
.
Surgical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Surgical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis is indicated only when persistent contractures develop that interfere with the patient’s daily life, as well as when neoplasms (for example, Baker’s cyst) appear that require surgical intervention. The basis for surgery is severe deformation of the joints
which interferes with the patient’s daily self-care—in this case,
endoprosthetics
.
In case of severe inflammatory damage to the synovial cartilage, a partial synovectomy
(excision of the affected area) is performed.
There are different types of treatment for arthritis