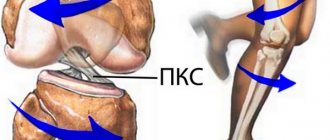
The posterior cruciate ligament or PCL is one of the 4 main ligaments that provide stability to the knee joint. Therefore, its damage is one of the most serious injuries to the knee joint. And the fairly high frequency of their occurrence (3-20% of cases of knee injuries) makes the problem highly relevant in modern orthopedics. Therefore, today there are already ways not only to restore the integrity of the PCL, but also to return it, and therefore the knee joint, to normal functionality as quickly as possible and with the utmost safety for the patient.
Causes of injuries
It's not easy to damage the posterior cruciate ligament. His mechanics are a powerful straight punch just below the knee. When does this happen? This often happens during a car accident, when during a head-on collision the driver’s leg is hit by the dashboard of the passenger compartment or a pedestrian is hit by the car’s bumper. In sports, the posterior ligament is most often injured by skiers when they collide with an obstacle on the descent. Ligament damage is often accompanied by injuries to the menisci and other nearby ligaments and structures. In such cases, treatment is carried out surgically, since the return of function is otherwise difficult. Arthroscopy is usually performed to reconstruct the ligament and restore other structures.
Forecast
Even comprehensive treatment using the best and most expensive medical means does not guarantee complete restoration of the ligaments. Therefore, in some cases, patients are prohibited from playing sports, running, or lifting heavy objects.
If the course is not dangerous, the prognosis is more favorable. You can return to sports immediately after the ligament weakness is resolved. This may take from eight weeks to several months.
For a full recovery after surgery, you need to take a photo of the affected part. If all treatment conditions are met, patients will be able to return to their normal lifestyle.
Types of PCL ruptures
The first degree is characterized by incomplete rupture of the ligament (microtears, sprains). The pain syndrome is relieved in such cases by taking anti-inflammatory drugs. But specialist supervision is necessary; the lower limb is temporarily immobilized.
Second degree - rupture of the ligament without deformation of other structures. Here it is important to assess the consequences of such an injury and how the knee joint functions. The doctor makes the decision on surgical intervention after acute symptoms have resolved.
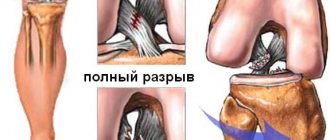
Third degree - complete rupture of the PCL in combination with damage to the anterior ligaments, meniscus and other tissues of the knee almost always causes instability, which becomes the reason for surgery to avoid complications.
Clinic of Dr. Glazkov. Treatment of the knee and shoulder joint.
Clinic of Dr. Glazkov.
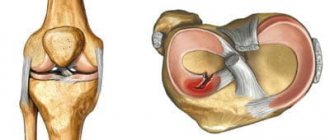
Treatment of the knee and shoulder joint. Knee ligaments are connective tissue bands whose main function is to strengthen the joint. They are quite strong formations, they have little elasticity.
When exposed to excessive mechanical force aimed at increasing their length, the fibers of the connective tissue cord are stretched. With further exposure to force, micro-tears of the fibers or a violation of the integrity of the entire ligament appear.
This condition is accompanied by a violation of the functional state of the knee joint, as well as an inflammatory reaction. The possibility of restoring damaged anatomical structures of the knee depends on the degree of integrity damage. If the ligaments are torn, their independent restoration without adequate treatment is impossible.
Symptoms.
Quite characteristic symptoms for this type of pathology. Immediately after the injury, the patient presents the following complaints:
- Intense pain in the knee.
- Joint instability, loss of knee functionality.
- Feeling of dislocation.
- Instability, loss of knee functionality.
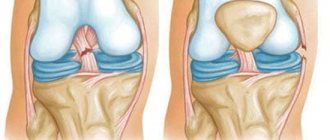
- Swelling of the knee due to hemarthrosis.
- Hemarthrosis (outflow of blood into the joint cavity due to damage to blood vessels).
- Limitation of movements.
- Hemorrhages are visible on the lower leg and in the popliteal region.
- Clicking sound when injured.
Rehabilitation
Regardless of whether the patient needs surgery or not, rehabilitation is mandatory. Exercises help restore joint function:
- Strengthening the rectus femoris muscle: sit on the floor, stretch the injured leg, bend the other. Press your sore knee toward the floor, contracting your quadriceps muscle. Hold the position for 10 seconds. Perform 2 sets of 15 repetitions.
- Isometric contraction: Sitting in a straight-backed chair, bend your knee to 90 degrees. Tighten your quadriceps muscle as you lift your leg off the floor. Hold the tension for 10 seconds. Perform 2 sets of 15 times.
- Leg raises: lying on your back, bend your uninjured knee, place your foot on the floor. Tighten the rectus femoris muscle on the injured limb and lift it 20 cm above the floor. Slowly lower your leg to the floor. Perform 2 sets of 15 repetitions.
- Squats with a ball: stand with your back against a wall, place your feet at a distance of 40 cm from it. Place a soccer or basketball ball behind your back. Leaning on the ball, slowly squat until your knees bend at an angle of 45 degrees. There is no need to try to go deeper. Hold the position for 10 seconds, then slowly return back. Repeat 10 times, perform 2 approaches.
- Steps with an expander: secure the expander loop at ankle level. Place the injured leg into the loop. Move away to slightly stretch the expander. Take a step back, turning your body towards your healthy leg, which remains in place. Try not to turn your pelvis.
Only after a month can you put weight on the operated leg, and after three months can you run and perform active exercises.
You definitely need to take care of a massage, which improves blood supply to the joint. You can visit an osteopath after surgery to remove any adhesions that have formed.
Diagnosis of PCL damage
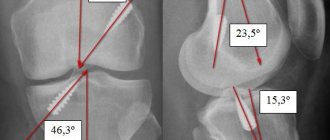
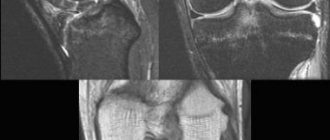
A specialist can already guess the diagnosis based on the mechanism of injury. This is why it is so important not to miss the details when visiting a doctor in a clinic. Swelling and severe hemarthrosis often do not allow for a detailed examination. However, functional tests are indicative of this injury. Imaging methods, namely MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), CT (computed tomography), provide the clearest picture of the process. According to indications, diagnosis is carried out using arthroscopy - a minimally invasive operation that allows you to visualize the pathology from the inside.
Manifestations
When the posterior and anterior cruciate ligaments are damaged, the victim experiences pain. Doctors identify the following clinical symptoms characteristic of this type of injury:
- acute pain with a tendency to intensify with movements, attempts to lean on the injured leg;
- swelling;
- a specific clicking sound at the moment of damage;
- impairment of motor activity;
- joint instability;
- hemarthrosis – accumulation of blood localized in the area of the joint capsule;
- subcutaneous hemorrhages, hematomas.
Patients complain of pain, unsteady gait, and the inability to step on the injured limb.
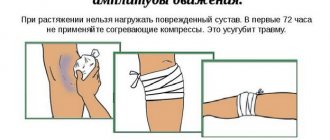
In such situations, it is necessary to competently provide first aid. Ice or a cold compress can be applied to the injured area to reduce swelling, pain, and prevent further development of hemarthrosis.
After this, the knee joint area is immobilized using a tightly applied bandage. Having completed this part of the therapeutic measures, the patient should be taken to the emergency room as soon as possible and transferred to the hands of traumatologists.
Treatment of posterior cruciate ligament rupture.
Patient management tactics are individually selected by a specialist depending on the general picture of the disease, lifestyle and age characteristics:
Conservative technique
It is suitable when the position of the lower leg remains stable after injury. At first, you need to apply cold to the damaged area and take medications to reduce pain and swelling. During the treatment period, it is necessary to limit the movement of the knee by using orthoses and braces. The doctor eliminates hemarthrosis by puncturing the joint with a syringe. Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma and hyaluronic acid help speed up the healing process and reduce inflammation. Gradually, when the swelling decreases, therapeutic exercises are prescribed to strengthen the muscles. Physiotherapeutic procedures help speed up the healing process.
Surgery
Arthroscopy is used as the most gentle method that promotes a speedy recovery, as well as the most effective. The reason for surgery is instability in its work, pathological movements, which additionally cause microtrauma to the articular cartilage and meniscus, which provokes the development of arthrosis. If there are indications, the patient is prepared for surgical treatment. The operation then provides access to the joint by making small incisions in the skin - just enough to insert the arthroscope and surgical instruments into the cavity. Due to the fact that the image of the joint structures is transmitted from the arthroscope camera to the monitor, visualization of the joint structures is provided at multiple magnification. The specialist determines the area of damage, then decides what manipulations need to be performed and immediately performs them.
If the PCL is ruptured, its repair is performed arthroscopically using an autograft. Typically, the semitendinosus tendon is used. This method of treatment helps to restore lost functions. If deformation of other tissues is detected, their integrity is restored if possible. After arthroscopy, the patient is discharged on the day of surgery. Subsequently, to ensure better results after surgery, it is recommended to visit a doctor and undergo a rehabilitation course.
You can read more about knee arthroscopy on our website:
Rehabilitation after PCL injury
Rehabilitation activities include a whole course of exercises, procedures and the use of auxiliary devices, which are developed individually for each person. First of all, fixation of the joint is necessary. Then a gradual increase in loads is carried out by prescribing physical therapy and mechanotherapy. Physiotherapy is needed to speed up healing. Sometimes, for the same purposes, a course of intra-articular injections of PRP or hyarulonates is carried out. Initially, the patient performs the exercises in the clinic, then they are allowed to perform them at home. The minimum rehabilitation period is 3 months.
Forecast
Most often, the prognosis for this type of injury is favorable. Even with conservative treatment, a return to sports activities is possible, since knee stabilization is achieved by training the anterior thigh muscles. After plastic surgery of the ligament and completion of a course of postoperative rehabilitation, as a rule, the function of the joint, its stability, is completely restored, and it becomes possible to return to sports activities.
Our specialists are always ready to help you! Call us by phone or.
Basic treatment methods
For minor ruptures, treatment is conservative. Patients are advised to wear an orthosis, take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nise, Nurofen, Ketoprofen) if pain occurs, 5-10 sessions of physiotherapeutic procedures (UHF therapy, electrical stimulation, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy).
In case of serious injury, minimally invasive surgery is performed. After applying a pneumatic tourniquet to the thigh to prevent bleeding, the surgeon makes two small incisions of 0.5 cm each. After introducing an arthroscope and medical instruments (shaver, scissors, nippers), the connective tissue structures are examined and the dimensions of the surgical field are determined. The device is equipped with a miniature video camera, so all joint elements are clearly visualized on the monitor screen. The surgeon removes the detached elements of the PCL, clearing the area for graft placement. Another mini-incision is made through which a small tendon of the femoral muscle is harvested. If this manipulation is impossible, the graft is taken from the patellar ligament. The removed tendon is sutured, then channels are formed in the tibia and femur to remove the graft and fix it in tension position.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/NBsNqGy5WeM
For 4-5 weeks after surgery, patients are advised to use crutches when moving. Regular lymphatic drainage of the operated area is carried out, and analgesics are used to eliminate pain. The load on the knee is gradually increased to stimulate blood circulation and prevent post-traumatic osteoarthritis. During the entire rehabilitation period (2-3 months), the patient performs special exercises daily to help increase the functional activity of the joint.
In the absence of medical intervention, 5 years are enough for the complete destruction of hyaline cartilage after a ligament rupture. When the lower leg slips, the patellofemoral joint experiences excessive loads, causing rapid wear of the cartilage tissue of the patella. Therefore, even with a minor injury, you should seek medical help.
Knee
Knee The knee has a complex structure.
The joint includes the surfaces of the femoral condyles, the tibia, and the patella. For better stabilization, shock absorption and load reduction, paired cartilaginous formations called medial (internal) and lateral (external) menisci are localized in the joint space. They have the shape of a crescent, the narrowed edges of which are directed forward and backward - the front and rear horns. The external meniscus is a more mobile formation, therefore, with excessive mechanical stress, it moves slightly, which prevents its traumatic damage. The medial meniscus is secured by ligaments more rigidly; when exposed to mechanical force, it does not shift, as a result of which damage more often occurs in various parts, in particular in the area of the posterior horn.
degree of meniscus damage
degree of meniscus damage
Depending on the main causative factor that led to the development of the pathological condition of the cartilaginous structures of the knee, traumatic and pathological degenerative damage to the posterior horn of the medial meniscus is distinguished.
According to the criterion of the duration of the injury or pathological violation of the integrity of this cartilaginous structure, fresh and old damage to the posterior horn of the medial meniscus is distinguished. Combined damage to the body and posterior horn of the medial meniscus was also identified separately.