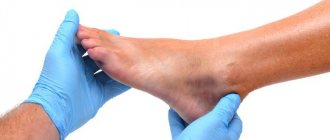
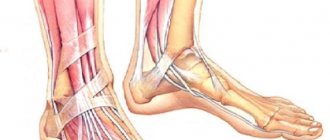
A lump on the foot near the little toe, due to the prevalence of the pathology in recent times, represents not only a medical, but also a social problem. This is associated with a decrease in the quality of life: when a bone appears near the little finger, not only the leg suffers, when the patient cannot fully walk, but the general condition worsens. The patient develops irritability, increased fatigue, and disturbed sleep. Due to late consultation with a doctor, the pathology progresses. If there is no effect from the use of any prescribed medication, the only treatment option left is surgery.
Causes of a lump near the little finger
When a bone near the little toe forms and grows on the leg, increasing in size, in order to carry out successful treatment it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. Numerous observations show that the lump on the side of the little finger in etiology and pathogenesis, as well as in clinical manifestations, is a mirror image of Hallux valgus.
Therefore, the risk factors for both pathologies are similar. A person begins to fall ill when there is one or simultaneous influence of several causes. These include:
- genetic predisposition (bumps on the legs of close relatives);
- female gender due to the predominant wearing of narrow shoes with thin soles and high thin heels and the development of transverse flat feet with hallux valgus. This is an orthopedic disease, common mainly in women due to the fact that they have softer cartilage than men;
- elderly age;
- excess weight, which creates increased stress on the legs;
- endocrine pathology (pregnancy, menopause, diabetes, hypothyroidism);
- features of the profession (long stay on your feet);
- injuries (dislocations, sprains, bruises, fractures, when post-traumatic deformity develops after an improperly healed fracture of the metatarsal hand of the little finger);
- gout with excess urea in the bloodstream (this situation is not uncommon among novice athletes for whom weight indicators are important - by taking diuretics, they get rid of extra hundreds of grams, causing irreparable damage to health);
- unbalanced diet (constant consumption of large quantities of meat, sugar and salt);
- bursitis (infectious inflammation of the synovial bursa);
- arthrosis (a degenerative disease of the skeletal system that affects all joints);
- Taylor's deformity;
- osteoporosis with a lack of calcium in the bones;
- congenital instability of the joint.
Genetic predisposition explains the appearance of this pathology in girls who do not yet wear high-heeled shoes.
Taylor deformity
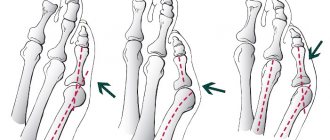
Taylor's deformity, or tailor's foot, is a varus deformity of the 5th toe (as opposed to a vagal deformity of the big toe). Taylor's deformity is a pathological condition in which the little toe begins to protrude inward and the metatarsal bone protrudes outward, resulting in a lump at the base of the fifth toe.
The name originated hundreds of years ago when tailors worked all day long with their legs crossed, resting on the outer edges of their feet. Pressure on the bones of the foot caused a growth to appear in the area of the little toe, which began to swell, become inflamed and accompanied by pain. As a result, the tailor's foot was a convexity outward at the base of the little toe with the toe itself deviating inward.
With this pathology, the finger can sometimes move upward. The changes are congenital or acquired. With congenital Taylor deformity, a large angle of deviation of the 5th metatarsal bone is expressed, or in the distal part the bone has the appearance of a rocker arm. A combination of both factors is possible. At the same time, there is hallux valgus, which is explained by congenital weakness of the foot ligaments.
The symptoms are standard; with different etiologies of the lump, the clinical picture is similar:
- pain;
- hyperemia;
- edema.
A harbinger of Taylor's varus deformity is the appearance of a callus near the little finger. In some cases, the callus forms in the later stages, with severe deformation, when the metatarsal bone can move out of articulation. And then the pain becomes constant, even in loose shoes.
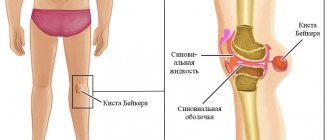
Hygroma
A lump developing on the little finger may be a hygroma. This formation is a benign tumor (its cells differ from normal ones):
- with gelatinous serous-fibrinous or serous-mucous colorless liquid inside;
- ranging in size from 3-4 mm to 7 cm;
- round shape;
- elastic consistency;
- practically motionless, since it develops on a ligament, but the skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue located above the hygroma retain their mobility.
What to do if your ankle bone hurts
What to do if a bone in your foot hurts? There are many pain relief methods that can be used as symptomatic therapy at home before going to the doctor.
Among them are:
- tablet preparations;
- ointments for external use;
- herbal baths;
- compresses;
- massage.
Please note: Each method is good individually, but you can also use an integrated approach - apply several methods simultaneously
Massage
If there are no medicines in the house, and the bones in your feet hurt, you can use improvised remedies. Massage will numb the affected area.
Movements should be soft, circular. You need to massage your thumb, as if rubbing ointment into the skin.
Pills
This is the most common method of pain relief. If the bones of the big toes hurt, people always turn to the first aid kit.
In this case, 2 groups of tablets will help:
- narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve swelling of the joint and surrounding tissues, block the release of inflammatory mediators, and improve blood flow to the organ due to the manifestation of antiplatelet properties. The local temperature decreases and erythema (redness) disappears. By relieving the symptoms of inflammation, NSAIDs relieve pain.
The following types of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used as such therapy:
Among general painkillers, narcotic analgesics are used extremely rarely. This is possible only in the early postoperative period. The human body quickly gets used to exogenous opium, so dependence develops. To avoid such a syndrome, in case of severe pain in the bunions on the big toe, they are used with caution.
Non-narcotic analgesics act on pain receptors. The medicine blocks them, preventing the impulse from reaching the cerebral cortex. Therefore, a person under the influence of drugs does not feel pain at all.
If a bump on your leg hurts, ointments from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and non-narcotic analgesics will quickly help:
Relieve pain and ointments aimed at restoring cartilage tissue. These drugs are used for a long time and do not help immediately. The medicine works for a long-term effect, its goal is not to anesthetize and relieve inflammation, but to help damaged cells recover. Examples:
Baths and compresses
At home, you can use folk wisdom. Many herbs have analgesic and sedative effects with anti-inflammatory effects.
You can use both baths and compresses.
Compresses are done mainly at night. You need to have a warming bandage. It can be replaced with a double layer of gauze with cotton wool and a plastic bag.
Clinical picture of the pathology
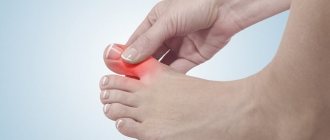
Symptoms accompanying a bunion in the area of the little toe include:
- pain;
- edema;
- expansion of the transverse arch of the foot;
- hyperemia;
- thickening of the soft tissues of the joint;
- callus on the side or from the plantar surface in the projection of the head of the fifth metatarsal bone.
To carry out differential diagnosis with diseases accompanied by severe joint pathology, it is necessary to accurately describe the complaints at the doctor’s appointment. Prescribing correct and adequate treatment depends on this. In addition to the above symptoms, the manifestations of a lump, unlike other growths on the leg, are:
- constant pain or burning sensation in the feet;
- leg cramps, mainly at night;
- corns and calluses;
- lump near the little finger.
Symptoms worsen after prolonged standing. By evening, literally, it becomes impossible to stand.
Why does the bone on the foot near the big toe hurt?
Pain in the bunions near the big toes occurs for several main reasons:
- Inflammatory process in the joint cavity;
- Changes in the physiological structure of the foot with curvature of the main axis;
Bursitis
Inflammation of the joint capsule does not occur immediately. The reason for the development of the process is constant trauma to the joint.
Treatment
The goals of treating a pathological process on the foot:
- elimination of inflammation in the area of cones;
- pain relief;
- process stabilization;
- restoration of functions;
- prevention of further deformation.
Treatment for a bump on the little finger depends on the cause of its appearance and the precise diagnosis. Most often this is the result of progression of transverse flatfoot. Therefore, the therapy is similar to the treatment of valgus: wearing insoles, arch supports and inserts. Orthoses prevent the development of further deformation. Regular massage and therapeutic exercises are considered a prerequisite for treatment. The exercises prescribed by the attending physician will have to be done regularly so as not to disrupt the rehabilitation process.
In most cases, with existing Hallux valgus, treatment of the formation that appears on the little finger using conservative methods is ineffective.
Surgical intervention is indicated:
- removal of developed cones;
- reconstruction of the arch of the foot.
In the postoperative period, an 8-week immobilization of the foot is performed. In the future, wearing orthoses that support the arch of the foot is prescribed.
If the bone is a manifestation of gout or bursitis, treat the underlying disease.
If you suspect a fracture, you must immediately apply cold to the sore spot, drink painkillers if necessary, immobilize your finger and consult a traumatologist.
In any case, if there is no effect from conservative therapy, surgical treatment is recommended.
Conservative therapy
For any etiology of stone formation, at the first signs of inflammation, NSAIDs are prescribed - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Movalis;
- Diclofenac;
- Nimesil;
- Ibuprofen and others.
For severe pain and swelling, local injections of GCS (glucocorticosteroids) are used:
- Prednisolone;
- Dexamethasone.
During a gout attack:
- stabilization of uric acid levels (Allopurinol);
- using NSAIDs to relieve inflammation, pain and swelling;
- strict diet (exclusion of spicy dishes, rich broths, jellied meats, fatty meats, fish, switching to boiled and steamed foods).
Massage and physiotherapy can help remove small tophi in the future:
- mud therapy;
- ultraphoresis;
- phonophoresis with hormonal drugs;
- dry heat.
To reduce the risk of tophi formation, drugs are prescribed that improve microcirculation in tissues:
- Pentoxifylline;
- Actovegin.
Treatment of bursitis includes methods:
- local;
- general conservative.
Appointed:
- antibacterial drugs;
- painkillers;
- GCS;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
If the disease continues to progress, surgery is indicated. If there is significant deformation of the foot, orthopedic shoes are made from a cast of the foot.
Surgery
Indications for radical treatment include:
- in the absence of effect from conservative treatment methods;
- with the second or third degree of severity of the pathology;
- with sharp progression of pathology;
- with poorly corrected disorders of the musculoskeletal function of the foot;
- with pronounced aesthetic defects (desire to get rid of deformation and wear more elegant shoes).
Surgical interventions are not indicated:
- elderly and weakened patients;
- with severe concomitant diseases;
- with severe circulatory disorders in the lower extremities (diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis).
When treating hygroma, the most reliable method is surgical removal of the formation. There are 3 ways to surgically treat a bunion on the little toe:
- by excision;
- endoscopically;
- using a laser.
The hygroma is removed along with the capsule, the cavity is washed with an aseptic solution and the incision is sutured. With the endoscopic method, special instruments are used that are inserted into a small incision. During laser surgery, minimal blood loss is observed. The laser beam causes heating and destruction of the changed tissues.
A safer method is puncture. A puncture needle is inserted into the cyst and fluid is removed from it. Sclerosing drugs (Doxycycline, 96% alcohol) are injected into the cleaned cavity. After the procedure for removing the contents of the hygroma, a tightening bandage is applied. The patient is prescribed rest for 1 week. Immobilizing the foot helps slow down the formation of synovial (joint) fluid and minimize the risk of relapse. After puncture, the cyst can grow again, since its shell remains inside.
Gout
A bunion on the little toe may appear due to gout, a disease characterized by the deposition of uric acid salts in the joint of the foot. Gouty deformity occurs due to a person’s poor nutrition, excess weight, frequent consumption of alcohol, and kidney disease.
The finger may hurt even with slight palpation, as well as swell and turn red. A gouty nodule occurs in the joint, and if not removed in a timely manner, deformation of the joint may occur. In these cases, you should consult a specialist, as dangerous consequences can occur, including impaired kidney function.
Treatment of a lump near the little finger due to gout consists of eliminating the original disease. First of all, they normalize the level of uric acid in the human body. The use of non-steroidal drugs is also prescribed.
But diet is of great importance in the treatment of gout. Thus, it is recommended to consume boiled and steamed dishes and limit salt. Hot spices and sauces, broth, jellied meat are contraindicated. It is allowed to include butter, vegetables, especially white cabbage, as well as berries and fruits.
Consequences of neglecting treatment
If, when a bunion develops on the foot, you do not promptly consult a doctor and find out the cause, you may miss a serious pathology, which can subsequently cause disability. Progression of changes in the foot will lead to the following consequences:
- further deformation;
- increase in transverse flatfoot;
- increased pain;
- limitation of physical activity;
- will significantly reduce the quality of life.
In later stages, due to the impossibility of conservative treatment, complex surgical intervention is necessary, followed by long-term rehabilitation.
Alternative medicine
If it seems that professional drug treatment does not help enough in getting rid of the defect, try turning to traditional methods of traditional medicine that have been proven over the years. You don’t even need to go into the forest to collect various herbs. Most methods are publicly available.
For example, this applies to drugs created on the basis of bile of birds and animals. Detailed instructions can be read on the packaging of the drug purchased at the pharmacy; the general recommendation is simple: if pain occurs, you need to wipe the area near the growth or lump with bile and secure it with a compress. As a rule, the pain goes away quickly.
Prevention
Prevention is the elimination of all risk factors leading to foot deformation. Recommended:
- refuse tight high-heeled shoes and thin soles made of artificial materials with a narrow toe (the heel must be stable, no higher than 4-5 cm, so that the correct distribution of the load on the foot is observed, there are no obstacles to the movement of the toes, squeezing them, and blood circulation in the feet);
- regular gymnastics, daily physical education - for this it is enough to allocate 10 minutes at home;
- walking barefoot on uneven surfaces;
- proper nutrition with the exception of fatty foods, abuse of spices, seasonings, coffee, alcohol;
- observe the rules of hygiene.
At the first signs of foot problems, you should consult a doctor in order to begin treatment in a timely manner and prevent the development of serious consequences.
Bursitis
Bursitis that appears near the little finger is an inflammatory disease that occurs in the joint capsule. Most bunions are observed around the big toe, but the little toe is no exception.
There are many reasons for the development of inflammation:
- bruise, as well as other injury to the little finger;
- systematic load on the little finger;
- congenital foot deformities, valgus foot placement;
- presence of flat feet;
- deposits of calcium salts in tendons;
- infection of the joint capsule;
- impaired metabolism in the body;
- any autoimmune disease;
- arthritis;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes.
The acute form of bursitis is characterized by the following symptoms: pain; swelling of the joint; skin redness; limited mobility; increase in local temperature.
Sometimes it is possible to diagnose a deterioration in a person’s general condition and an increase in body temperature. The initial stage of the inflammatory process is accompanied by the appearance of a small lump, which upon palpation resembles a lump or a bag of liquid. As it develops, this lump increases in size and turns red. Along with the tumor, pain also occurs, which also intensifies with the progression of the disease and is observed even at rest. In this case, the mobility of the joint is limited.
If not treated in a timely manner, bursitis progresses to a chronic stage, which has periods of exacerbation and remission.
The treatment complex includes local and general conservative methods. If they are ineffective, they resort to surgical intervention. What to do at home:
- to eliminate inflammation, cold compresses are recommended;
- provide rest to the leg;
- apply a fixing bandage to the foot;
- treatment with folk remedies is used: compresses, lotions;
- ointments are used locally.
When diagnosing the disease at a moderate or severe stage, the use of antibiotics, painkillers, and corticosteroids is prescribed. Physiotherapy procedures are also used.