- Causes and course of the disease
- When is surgery necessary for a torn cruciate ligament?
- What happens before surgery?
- How is the operation performed at the Gelenk Clinic?
- What type of doctor performs surgical treatment of a cruciate ligament rupture?
- Probability of success after cruciate ligament rupture surgery
- What type of anesthesia is used during surgery?
- Postoperative observation, rehabilitation and aids after surgery for cruciate ligament rupture
- Will I feel pain after surgery?
- Conditions of stay at the Gelenk Clinic
- What should you pay attention to after surgical treatment of a torn cruciate ligament?
- Cost of knee surgery
- How can a foreign patient make an appointment and the operation itself?
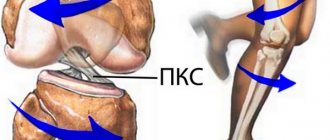
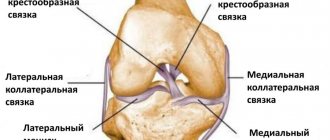
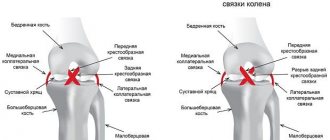
Clear, centered view of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments in the knee joint. The cartilaginous surfaces and menisci on the tibial side are indicated in purple. A sprain or injury to the cruciate ligament can occur as a result of a dislocation or blow. The complete destruction of this component of the knee is called a torn cruciate ligament. © Istockphoto.com/MedicalArtInc In the center of the knee joint, two ligaments intersect, which connect the femur (Femur) and tibia (Tibia) bones and maintain their position. Due to a rupture of one or two cruciate ligaments, the knee joint becomes unstable. A rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament
is observed in patients most often. The causes of injury are injuries sustained after sports training, such as a dislocated knee joint during skiing or a collision during ball sports.
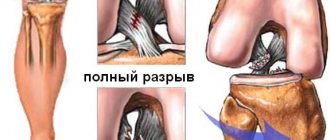
When the cruciate ligament ruptures, the knee swells greatly and the victim experiences severe pain. In most cases, the disease is accompanied by a clicking or crackling sound, during which you feel a jerk in the knee joint. After this, the patient's knee mobility is limited. To re-stabilize the knee and prevent knee osteoarthritis, the orthopedist may repair the cruciate ligament or replace it with a tendon graft.
medical request
Causes and course of the disease
A torn anterior cruciate ligament usually occurs after playing sports. Often, the outward deviation of the tibia puts stress on the anterior cruciate ligament, causing it to tear more easily. The following situations are typical for this injury:
- violent side collision with an opponent during a game of football
- hyperextension of the knee joint
- sudden braking at full speed
- sudden change of direction at full speed
- unsuccessful landing after a jump or spin
A typical accident circumstance involves hitting an opponent's knee while playing soccer. In addition, rupture of the cruciate ligament occurs when skiing, after a fall, followed by dislocation and hyperextension of the lower leg.
As a rule, the patient feels the rupture already during the fall. The injury is often accompanied by the characteristic clicking sound of a stretched and damaged cruciate ligament. Rupture occurs only under significant force. The cruciate ligament typically supports 2400 kg. loads. However, its strength may vary: in women, the diameter of the cruciate ligament is much smaller. Therefore, they suffer from this disease much more often. In children, a more common Segond fracture is an avulsion fracture of the tibial condyle.
A posterior cruciate ligament rupture requires more force than an anterior cruciate ligament rupture. Injuries of this magnitude are usually observed during road traffic accidents, for example, when the knee joint hits the passenger compartment of a car. Therefore, injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament are much less common, namely in only 7-10% of all cases.
Possible treatments
For sprains, only conservative treatment methods are used. Treatment for injuries depends on the severity of the injury and the profession of the victim. For example, athletes or dancers immediately undergo surgery to repair the ligament. Its severe rupture or complete separation from the bone is also the basis for surgical intervention.
Drug treatment
Pharmacological drugs are used only to eliminate pain, swelling, and bruises. Acute pain syndrome is usually relieved by intramuscular administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Ortofen, Movalis. Drug blockades with anesthetics and glucocorticosteroids are also practiced. To reduce the intensity of mild or moderate pain, patients are prescribed NSAIDs in tablets or ointments (Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen).
You can get rid of swelling and bruising by applying gels with troxerutin or heparin (Troxevasin, Lyoton, Trombless).
Surgery
Indications for suturing or plasty of the ligament are fresh complete ruptures and instability of the knee joint after conservative therapy.
Delayed reconstruction (after 1-1.5 months) is carried out for knee laxity and impaired foot function. In such cases, it is useless to stitch the ligaments; a part of the patellar ligament or artificial materials are taken as a graft.
Orthopedic correction
To reduce the load on the joint, patients are advised to wear orthopedic devices - elastic bandages, rigid or semi-rigid orthoses. A plaster splint can also be applied to reliably immobilize the knee. By fixing the joint, displacement of its structures is eliminated, and the restoration of the connective tissue cord occurs much faster.
Therapeutic exercise and massage
After complete fusion of the anterior ligament of the knee, patients are recommended daily exercise therapy and gymnastics, classical, acupressure or vacuum massage. Health-improving activities help strengthen muscles, improve blood circulation, and microcirculation.
ethnoscience
Products made according to traditional medicine recipes are not used in the treatment of ligament rupture. Their use can distort the clinical picture and even provoke the development of an inflammatory process. The weak analgesic effect of folk remedies often led to improper fusion of fibers due to the lack of medical intervention.
When is surgery necessary for a torn cruciate ligament?
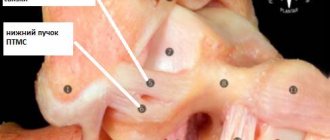
The course of the healthy posterior cruciate ligament from the facial aspect of the femur to the posterior articular surface of the tibia.
© Radiopedia.org Same patient: The anterior cruciate ligament is not visible due to its rupture.© Radiopedia.org If conservative treatment is unsuccessful or does not produce the desired result, and if the patient is young and leads an active lifestyle, surgical reconstruction is the optimal solution for in order to maintain the patient’s quality of life and sports activity. In addition, surgery must be performed if more than 75% of the cruciate ligament is torn or if the ligament is torn off with a bone fragment.
A torn cruciate ligament must be treated promptly. Otherwise, you will develop other injuries in your knee joint within a few years. Excessive stress will be placed on the articular surfaces and menisci, which can lead to premature wear, damage to the articular cartilage, and after 10-15 years to arthrosis of the knee joint. Often, due to existing instability of the cruciate ligament, the meniscus also tears.
In 80% of cases, cruciate ligament rupture causes damage to other structures of the knee joint:
- Internal meniscus tear (69% chance)
- External meniscus tear (49% chance)
- Articular cartilage injuries (20-50% chance)
- Secondary arthrosis of the knee joint due to limited functionality of the meniscus
- Internal ligament injuries (common)
- Damage to external ligaments (less common)
- Rupture of the joint capsule of the knee joint
How to repair a torn knee ligament?
In most cases, the separation of the knee ligament is a reason for performing endoscopic plastic surgery. For reconstruction, synthetic materials or parts of ligaments taken from the ankle joint are used. They are installed using bone screws. After surgery, active rehabilitation is required.
There are techniques for restoring ligament dislocation using manual therapy methods. This can only be done in the early stages, when the risk of ligament rupture is not high. By increasing microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid, the scarring process can be accelerated. Reflexology allows you to start the process of natural tissue regeneration. And physical therapy in combination with kinesiotherapy allows you to enhance diffuse nutrition and strengthen the ligamentous apparatus of the knee.
What happens before surgery?
Before the operation, the doctor conducts a comprehensive clinical examination. First, all the circumstances of the injury and the degree of instability of the knee are clarified. Thus, the specialist receives information about the extent of the gap. Unfortunately, the diagnosis is often made several years after the injury, since patients do not attach much importance to it and consider the injury to be a simple sprain.
In the presence of strong thigh muscles, the diagnosis is usually not made as part of a clinical examination and surgery is not considered. However, over time, the patient feels discomfort in the knee joint. Arthrosis can be caused by trauma that damages the cartilage. Very often, problems of the knee joint appear only after several years, and only then does the patient notice some instability while climbing stairs or during rotational movements, after which he feels severe pain in the knee.
In addition to diagnosing the degree of instability of the knee joint, a cruciate ligament tear is determined using special techniques such as the anterior drawer test (ADT), the Lachman test, or the lateral slip test (McIntosh test).
The Lachman test helps determine the stability of the cruciate ligaments. The test is performed using the anterior drawer principle (ADD), but also involves bending the knee to 30°. © joint-surgeon
In addition, the condition of the cruciate ligaments is determined by MRI. X-rays are required to rule out osseous associated injuries to the knee joint. Also, joint puncture—aspiration of synovial fluid from the joint capsule—helps make the diagnosis. Cruciate ligaments have a good blood supply. Therefore, their rupture causes hemorrhage into the joint. The presence of blood in the joint fluid indicates a cruciate ligament rupture.
AAfter diagnosing and checking the patient’s health status, the attending physician conducts an explanatory conversation with the patient, during which he talks in detail about the progress of the surgical intervention, as well as possible complications. After this, you will be referred to an appointment with an anesthesiologist, who will once again check whether your health condition allows the administration of anesthetic drugs. As a rule, surgery for cruciate ligament rupture is performed the next day after a conversation with the surgeon and anesthesiologist.
Types of ACL damage
The anterior cruciate ligament has a limited stretch limit, since it is formed by fairly rigid collagen fibers. Therefore, it can only stretch 4-5% of its original length. This determines the fact that when greater force is applied, damage to the anterior cruciate ligament of varying severity can occur. Therefore they distinguish:
- Grade 1 ACL injuries or microtears are minor sprains of the anterior cruciate ligament that occur due to the rupture of individual fibers that form it. They cause moderate pain, swelling, and limited movement in the knee joint. But at the same time they do not lead to violations of its stability.
- Grade 2 ACL injuries or partial tears are moderate sprains or tears of the anterior cruciate ligament that are more dangerous than grade 1 injuries because they reduce the strength of the ligament. Therefore, after a partial rupture, repeated injuries often occur even under the influence of less pronounced traumatic factors. At the same time, the symptoms of 2nd degree ACL injuries are almost identical to the signs of 1st degree injuries.
- Grade 3 ACL injuries or complete ruptures are a severe type of anterior cruciate ligament injury, accompanied by severe pain, swelling, severe limitations in movement, impaired support function of the leg, and instability of the knee joint.
Complete ruptures practically never occur in children and the elderly.
It is also possible that one of the anterior cruciate ligament bundles may be torn off. This can lead to the fact that the torn part creates a mechanical obstacle to the full movement of the joint with the development of a clinical picture similar to a block or meniscus tear.
ACL injuries can be either isolated or combined with other injuries of the knee joints, for example, meniscus injuries, etc.
Also, injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament are divided according to the degree of limitation:
- Fresh – diagnosed when no more than a few days have passed since the injury. In such situations, hemarthrosis is usually observed, i.e. the presence of blood in the joint cavity, and severe pain.
- Stale – diagnosed when less than 3-5 weeks have passed since the injury. In such cases, the swelling decreases, but the damaged ligament has not yet healed.
When more than 3-5 weeks have passed since the ACL injury, a period begins when it is possible to accurately assess the degree of impairment of the knee joint due to injury to the anterior cruciate ligament. At this time, pain and swelling are completely absent, which makes it possible to judge as accurately as possible the quality of knee restoration, the degree of damage to the ACL and the need to undergo surgery or continue conservative treatment.
How is the operation performed at the Gelenk Clinic?
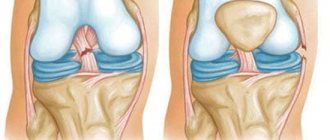
The lateral or medial ligaments of the knee may suddenly fuse.
This self-healing process does not apply to the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. © ttsz, iStock As a result of acute injuries, surgery can only be performed after the concomitant diseases have been cured and the wound has completely healed. For this reason, cruciate ligament reconstruction is performed approximately 2-3 months after the injury itself. During this period, the mobility of the knee joint is severely limited. Physical therapy helps prepare the knee for surgery.
Cruciate ligaments differ in structure from other ligaments of the knee joint: with ruptures of the external and internal collateral ligaments, immobilization of the joint using a special orthosis can promote sudden healing of the injury. Cruciate ligaments do not have this self-healing effect. As a rule, operations on the cruciate ligaments are performed to restore their functionality.
Surgical intervention usually lasts 1.5 - 2 hours. During the operation, surgeons perform a tendon transplant or perform a suture. Which method is right for you should be discussed with your doctor.
Cruciate ligament replacement and tendon transfer
The most common surgical technique is cruciate ligament replacement surgery. During this procedure, the surgeon first completely removes the damaged ligament in order to prepare the patient for transplantation. To obtain a graft, the doctor takes parts of autogenous tendons from other areas of the knee joint. As a rule, the operating doctor uses the patellar ligament, located between the kneecap and the tibia, for this purpose.
The advantage of autologous tendon transplantation is certainly the absence of body rejection, since the graft is obtained from the patient’s own body, namely from the patellar tendon and Achilles tendon. After completing the transplantation process in the femur and tibia using special bone screws, after some time the tendon graft is well absorbed by the body and begins to be supplied with blood vessels.
The only drawback of this intervention is the feeling of pain in the leg, namely at the site of graft collection. The patient may feel discomfort for several months. Tendon removal also slows down the development of physical strength. However, this fact only matters for athletes. After surgery, the patient will undergo long periods of physical therapy and specialized training.
In addition, the operation does not help restore the innervation process, which is of great importance for coordination of movements. In elite sports this is considered a disadvantage, but for most patients this fact is not of great importance.
Stitching of the cruciate ligaments by refixation of damaged structures
Modern procedures make it possible to preserve endogenous cruciate ligaments even after their rupture. The purpose of plastic surgery using the Ligamis method, offered by our clinic since the beginning of 2014, is to restore the stability of the knee joint in accordance with its natural functions. Using this system, the surgeon replaces the torn ligament with an artificial implant, which, during the recovery period, is responsible for mechanical stabilization of the damaged cruciate ligament in the very center of the knee joint. In this case, the torn parts grow together again and heal under the influence of the implant. If this technique is successful, the patient will not require cruciate ligament reconstruction using endogenous tendons.
The result after surgery using the Ligamis technique is much better than after autologous tendon transplantation, since after refixation all nerves are preserved and, thus, the process of controlling the movements of the knee joint remains normal. Athletes should pay attention to the choice of surgical method.
Since refixation of a tendon graft does not require donor material, there is no need for material collection, which is accompanied by pain and muscle weakness in the area of graft extraction. Already a few days after re-fixation, the patient can fully load the knee.
Before referring a patient for surgical refixation of the cruciate ligament, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive MRI examination. After this, the decision should be made as quickly as possible, since more than 3 weeks after the injury, the self-healing ability of the cruciate ligament decreases. Thus, this surgical intervention is recommended during an exacerbation of the rupture, namely within three weeks after the injury. Otherwise, only transplantation can help the patient.
Our highly qualified specialists usually remove the Ligamis implant 6-9 months after successful healing of the cruciate ligament. During the removal of the implant, the process of its healing is also checked.
Definition of symptoms
When most of the fibers break, a sharp sound is heard, reminiscent of the crunch of a thick dry stick being broken. The intensity of the pain directly depends on the severity of the injury. With sprains, clinical manifestations quickly disappear. And with tears and severe tears, after about a day, inflammatory edema forms in the area of damage. It puts pressure on sensitive nerve endings, which leads to increased pain.
The swelling may spread to the lower leg and sometimes even the ankle. After its resorption, a hematoma of a bright blue-violet color is formed. Gradually, the blood cells break down, so the skin color turns greenish-yellow.
What type of doctor performs surgical treatment of a cruciate ligament rupture?
At the orthopedic medical center Gelenk-Klinik in Germany, a trusting relationship between the patient and the medical staff is highly valued. Your attending orthopedic surgeon will accompany you from your first meeting with him until the postoperative period. He also provides follow-up care for the patient. This way, you will have a responsible person whom you can contact at any time. The specialists in the treatment of knee diseases and cruciate ligament ruptures at the Gelenk Clinic are Dr. Baum, Prof. Dr. Ostemaer Privatdozent Dr. med. Dr. Markwas.
Diagnostics
If pain or swelling of the knee occurs after exposure to a traumatic factor, you must immediately contact an orthopedic traumatologist. The doctor will initially find out under what circumstances the injury was sustained, and then proceed directly to the examination. At the same time, he examines not only the affected knee joint, but also the healthy knee. A test for the presence of a drawer sign is mandatory, and if its results are doubtful, the mobility of the lower leg can be assessed with millimeter accuracy using a special atrometer device.
The Lachman test, which involves bending the knee at an angle of 20-30°, can also be performed. In this case, the doctor evaluates how much the lower leg moves forward and what sensations arise in the victim at the moment the movement stops.
But if you do not consult a doctor immediately after receiving an injury, and a few hours later the developing swelling and hemarthrosis will make diagnosis impossible. In such situations, fluid from the knee joint is initially removed.
As a rule, the data obtained after the examination is sufficient to establish the degree of damage to the ACL. But since injuries of the anterior cruciate ligament can be combined with condylar fractures, damage to the menisci and other structures, instrumental research methods are indicated to detect them:
- X-ray of the knee joint - performed to diagnose bone fractures;
- MRI of the knee joint is the most informative method for diagnosing damage to soft tissue structures, including menisci and ligaments, and hematomas;
- Diagnostic arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure performed using special endoscopic equipment, which is inserted into the knee joint and visually assesses the condition of the structures that form it in real time.
What type of anesthesia is used during surgery?
As a rule, cruciate ligament surgeries are performed under general anesthesia. However, doctors sometimes consider administering a spinal anesthetic to avoid the risk of general anesthesia. To do this, the anesthesiologist injects an anesthetic into the spinal canal of the lumbar spine. In this case, the patient is fully conscious. Anesthesiologists at the Gelenk Clinic have many years of experience in performing such operations. Which of the above methods corresponds to your indicators is decided during an explanatory conversation.
Rehabilitation
In the first month after surgery, the patient walks on crutches; any load on the injured leg is excluded. Afterwards, therapeutic exercises are included, and then there are exercises on simulators. Massage and physiotherapy help restore the functionality of the joint and normalize the outflow of lymph.
Consolidation of the positive effect after surgery and further prognosis depends on the patient’s responsible approach to the rehabilitation period.
Will I feel pain after surgery?
Every surgical procedure may involve pain. Surgery to treat a ruptured cruciate ligament of the knee joint is no exception. Thanks to the high professionalism and long-term experience of our surgeons, we are able to reduce the patient’s pain to a minimum. Before the operation, the anesthesiologist gives a special injection that numbs the knee joint for approx. for 30 hours. After this, the pain decreases and the patient’s treatment continues with conventional medications. The goal of the medical staff of the Gelenk Clinic is to ensure a painless postoperative period for the patient
General recommendations
The procedure for treating degenerative changes in the knee crosses is a fairly lengthy complex event, which sometimes takes from 2 months to six months.
If you suspect a pathology, you should definitely contact a specialized traumatologist, orthopedist or surgeon.
Undergo a comprehensive examination and receive a final diagnosis, on the basis of which an individual treatment regimen will be prescribed.
In the vast majority of cases, the problem can be dealt with conservatively, also by following a number of necessary recommendations, carefully adhering to all the doctor’s prescriptions for physical therapy and exercise therapy.
However, in case of severe pathology and complete rupture of the ligaments, the only effective mechanism to combat potential complications in the short term is surgical intervention and restoration of the corresponding structures using implants.
Conditions of stay at the Gelenk Clinic
Single ward at the Gelenk Clinic in Gundelfingen, Germany.
© joint-surgeon During your inpatient stay at the clinic, you are in a single room, which has a shower and toilet. Towels, bathrobe and slippers are provided in each room. In addition, you can use the safe, minibar and watch TV. You must bring your own medications, comfortable clothes and nightwear. After surgery, your condition is monitored around the clock by medical staff and professional physiotherapists. As a rule, you stay in the clinic for no more than three days. Your relatives can stay at a hotel located near the medical center. We will gladly take care of your hotel room reservation.
What should you pay attention to after surgical treatment of a torn cruciate ligament?
Immediately after surgery for a torn cruciate ligament, the knee should be elevated. In addition, a cooling compress should be applied to the knee. Approximately 10 days after surgery, the stitches will be removed and you will be able to shower.
To avoid possible complications, the knee should be at rest for approximately 6 weeks. During this time, you will be issued sick leave and given elbow crutches. Prevention of thrombosis when it is impossible to carry out full loads on the knee is a necessary procedure. To prevent loss of muscle mass and preserve the natural functions of the knee joint, a course of physical therapy is carried out.
You can plan your return flight home no sooner than 10 days later. However, we recommend leaving the clinic after at least two weeks.
- Inpatient treatment: 3–4 days
- Recommended length of stay in the clinic: 10–14 days
- When to book a return ticket: 10 days after surgery
- When is it recommended to leave the clinic: after 2 weeks
- When can you shower: after 10 days
- How long sick leave is issued: 6–8 weeks (depending on professional activity)
- When the stitches are removed: after 10 days
- Outpatient physical therapy: 2 weeks
- When can you drive again: after 6 weeks
- Light sports activity: 3-6 months after surgery
- Habitual sports activities: after 9 months
Collateral ligaments
Collateral ligaments
As soon as the patient is admitted to the hospital, he undergoes a puncture of the joint. The doctor's task is to eliminate hemarthrosis (accumulation of blood inside the knee) and also relieve pain. To reduce pain, after washing the joint, local anesthetics (for example, 0.5% procaine) are administered orally.
A plaster splint is placed on the knee. The patient wears it for about 1 week. The plaster is removed after the swelling of the joint is eliminated. Then it is changed to a circular bandage. It goes from the groin to the toes. The limb is fixed in a state of excessive deviation of the tibia towards the affected ligament.
Limb immobilization is carried out for up to 2 months. After eliminating acute inflammatory phenomena, the doctor prescribes physiotherapy. They improve blood circulation in the joint and normalize regenerative processes. Physical therapy is used. It is aimed at strengthening the thigh muscles. In addition, physical activity also stimulates blood flow, improving the trophism of knee tissue.
Cost of knee surgery
In addition to the cost of surgery for cruciate ligament rupture, it is necessary to take into account the additional costs of diagnostics, doctor's appointments and aids (eg elbow crutches), which range from approximately 1,500 to 2,000 euros. If you plan to undergo physical therapy after surgery, we will provide you with a cost estimate and email it to you.
You can obtain information about the cost of staying at the hotel, as well as possible additional treatment, on the service provider’s website.
physiotherapy
physiotherapy
- NSAIDs;
- analgesics;
- multivitamin preparations;
- chondroitin sulfate;
Non-drug measures are prescribed, mainly physiotherapy (electromagnetic fields, mud, ultraphonophoresis with non-steroidal analgesics).
The nature of the injury and its location influence how long a knee sprain takes to heal. Typically, the average duration of conservative therapy is about a month. If a severe knee sprain has been diagnosed, treatment includes surgery. The operation is performed with an open approach or using arthroscopy.
How can a foreign patient make an appointment and the operation itself?
You will first be asked to provide current MRI scans as well as X-ray results. This way the doctor can assess the condition of the knee joint. After we receive all the necessary documents through our website, within 1-2 days we will send you a preliminary treatment plan and cost estimate.
The Orthopedic Medical Center Gelenk-Klink provides foreign patients with the opportunity to make an appointment within a short time. We will be happy to help you with obtaining a visa after the advance payment specified in the preliminary cost estimate has been received into our account. In case of refusal to issue a visa, the advance payment is refunded in full.
For patients from abroad, we try to reduce the time between the preliminary examination and the operation itself. This way you will not need to come to the clinic several times. During both outpatient and inpatient treatment, you will be accompanied by qualified medical personnel who speak several foreign languages (English, Russian, Spanish, Portuguese). We also provide assistance in finding a translator (for example, into Arabic), which is paid for by the patient separately. We will be happy to help you organize a transfer, find a hotel and tell you how to spend your free time in Germany interestingly for you and your family members.
medical request
Warning
The effectiveness of non-operative treatment in active patients is controversial, for the simple reason that there is currently insufficient hard evidence. Key findings come from one randomized trial.
Future work should confirm whether there really is a group of “copers” and what complications may arise when ACL repair is abandoned. It is known that Monk et al. consider the available evidence for the absence of a difference between conservative treatment and ACL reconstruction to be weak. Currently, the ability to identify people as “coping” and “not coping” is quite small.