A fracture is a bone injury that disrupts its integrity. Traumatic fractures are divided into open (there is damage to the skin in the fracture area) and closed (the skin is not broken).
With an open fracture, the injury is beyond doubt. A closed fracture is not so obvious, especially if it is incomplete, when part of the diameter of the bone is broken, often in the form of a crack.
All fractures are characterized by:
- sharp pain with any movements and loads;
- change in the position and shape of the limb, its shortening;
- dysfunction of a limb (impossibility of usual actions or abnormal mobility);
- swelling and bruising in the fracture area.
Providing first aid for fractures of the extremities largely determines the outcome of the injury: the speed of healing, the prevention of a number of complications (bleeding, displacement of fragments, shock) and has three goals:
- creating immobility of bones in the fracture area (which prevents displacement of fragments and damage to them by the edges of blood vessels, nerves and muscles);
- prevention of shock;
- prompt delivery of the victim to a medical facility.
First aid for a closed fracture
When providing first aid for a closed fracture, you should immediately contact an ambulance. After this, it is necessary to immobilize the broken limb and, if possible, apply ice or a cold object to the injury site. The person may be given a painkiller. When transporting independently, a splint is applied using available items: board, stick, ski, etc.
In the absence of available means, the injured limb is bandaged to the uninjured one. During transportation, the victim must lie down - the broken limb should be slightly raised.
MedGlav.com
A fracture is a break in the integrity of a bone. traumatic and pathological fractures The occurrence of the latter is due to the presence of pathological processes in the bone (tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, tumors), in which the usual load at a certain stage in the course of these diseases leads to a fracture.
Traumatic fractures are divided into:
- closed (no bone damage) and
- open , in which there is bone damage in the fracture zone. Open fractures are more dangerous than closed ones, since the possibility of infection of fragments and the development of osteomyelitis is very high, which significantly complicates the healing of bone fragments.
A fracture can be:
- complete and
- incomplete . With an incomplete fracture, some part of the diameter of the bone is broken, most often in the form of a longitudinal gap - a bone crack.
Fractures come in a wide variety of forms:
- Transverse,
- Oblique,
- Spiral,
- Longitudinal.
- Comminuted are often observed when the bone is broken into separate fragments. This type is more common in gunshot wounds.
- A fracture caused by compression or flattening is called a compression fracture.
Most fractures are accompanied by displacement of fragments, which is caused, on the one hand, by the direction of the mechanical force that caused the fracture, and on the other hand, by the traction of the muscles attached to the bone due to their contraction after injury. Depending on the nature of the injury, the location of the fracture, the strength of the attached muscles, etc., displacement of bone fragments can be of various types: displacement at an angle, displacement along the length, lateral displacement. Impacted fractures often occur, when one of the fragments is embedded in another.
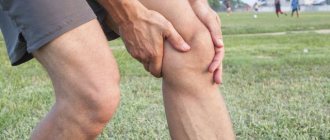
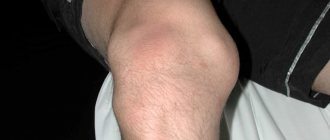
A fracture is characterized by: sharp pain that intensifies with any movement and load on the limb, changes in the position and shape of the limb, disruption of its function (inability to use the limb), the appearance of swelling and bruising in the fracture area, shortening of the limb, pathological (abnormal) bone mobility. When palpating the fracture site, the patient feels a sharp pain; in this case, it is possible to determine the unevenness of the bone, the sharp edges of fragments and crunching (crepitus) with light pressure. Feeling a limb, especially determining pathological mobility, must be done carefully, with both hands, trying not to cause pain, and in such a way as not to cause complications (damage to blood vessels, nerves, muscles, skin and mucous membranes from bone fragments).
With an open fracture, a bone fragment often protrudes into the wound, which directly indicates a fracture. In this case, palpating and examining the fracture area is prohibited.
Correct and timely first aid for fractures is one of the most important aspects of their treatment. Quickly provided first aid largely determines the healing of fractures and can often prevent the development of a number of complications (bleeding, displacement of fragments, shock, etc.).
The main first aid measures for bone fractures are:
- creating bone immobility in the fracture area;
- carrying out measures aimed at combating shock or preventing it;
- organizing the fastest delivery of the victim to a medical facility.
Rapid creation of bone immobility in the fracture area - immobilization - reduces pain and is the main point in preventing shock.
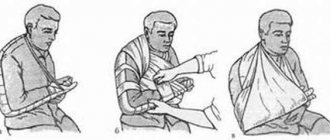
The bulk of fractures are fractures of the limbs. Correctly carried out immobilization of the limb prevents the displacement of fragments, reduces the threat of possible injury to the great vessels, nerves and muscles by sharp edges of the bone and eliminates the possibility of damage to the skin by fragments (translation of a closed fracture into an open one) during transferring and transporting the patient. Immobilization of the limb is achieved by applying transport splints or splints made from available hard material.
The splint must be applied directly at the scene of the incident, and only after this can the patient be transported. Splints must be applied carefully so as not to displace the fragments and cause pain to the victim. It is not recommended to carry out any corrections or comparisons of fragments. The patient must be carried very carefully; the limb and torso should be raised at the same time, always kept at the same level.
In case of an open fracture, before immobilizing the limb, the skin around the wound must be treated with an alcohol solution of iodine or another antiseptic and an aseptic bandage applied. If sterile material is not available, the wound should be covered with any cotton cloth. You should not try to remove or set protruding bone fragments into the wound - this can cause bleeding and additional infection of the bone and soft tissue. When bleeding from a wound, methods of temporarily stopping bleeding should be used (pressure bandage, application of a tourniquet, twisting, etc.).
It is most convenient to immobilize the lower limb using a Dieterichs transport splint, the upper limb using a Kramer ladder splint or a pneumatic splint. If there are no transport tires, then immobilization should be carried out using improvised tires from any available materials (boards, skis, guns, sticks, rods, bundles of reeds, straw, cardboard, etc.). To firmly immobilize the bones of the limb, it is necessary to have at least two solid objects or transport splints, which are applied to the limb from two opposite sides. In the absence of auxiliary material, immobilization should be carried out by bandaging the injured limb to a healthy part of the body: the upper limb - to the torso using a bandage or scarf, the lower - to the healthy leg.
When carrying out transport immobilization, the following rules must be observed:
- the splints must be securely fastened and well fix the fracture area;
- the splint cannot be applied directly to a naked limb; the latter must first be covered with cotton wool or some kind of cloth;
- creating immobility in the fracture zone, it is necessary to fix two joints above and below the fracture site (for example, in case of a tibia fracture, the ankle and knee joints are fixed) in a position convenient for the patient and for transportation;
- In case of hip fractures, all joints of the lower limb (knee, ankle, hip) should be fixed.
Prevention of traumatic shock and other general phenomena is largely ensured by correctly fixing the damaged organ, i.e. fixing it in a position in which the least amount of pain occurs. Excessive fussiness, loud and harsh conversation, and discussion of the existing injury and his condition in front of the victim have an extremely unfavorable effect on the patient. Cooling predisposes to the development of shock, so the patient must be covered warmly. Giving small amounts of ethyl alcohol, vodka, wine, hot coffee and tea has a beneficial effect. Pain can be reduced by prescribing 0.5-1 g of amidopyrine or analgin. If possible, painkillers should be administered.
It is better to transport the patient to a medical facility in a special ambulance; if this is not available, any type of transport can be used. Patients with fractures of the upper limbs can be transported in a sitting position. Victims with fractures of the lower extremities should be transported on a stretcher in a supine position. The limb should be placed on something soft in a slightly elevated position. Transportation and especially repositioning of the patient should be extremely gentle. It must be taken into account that the slightest displacement of fragments causes severe pain. In addition, bone fragments can move, damage soft tissues and thereby lead to new serious complications.
Transportation of the wounded with jaw damage is carried out in a sitting position, with a slight tilt of the head forward. An unconscious victim should be transported in a prone position with cushions of clothing, blankets and other things placed under the forehead and chest. This is necessary to prevent asphyxia by blood, saliva or sunken tongue. Before transportation, the jaws should be immobilized: for fractures of the lower jaw - by applying a sling-like bandage, for fractures of the upper jaw - by inserting a strip of plywood or a ruler between the jaws and fixing it to the head.
A fracture of the nasal bones is often accompanied by nosebleeds. Patients with this injury should also be transported on a stretcher, but in a semi-sitting position, i.e. with their head raised.
This damage usually occurs when falling from a height, falling over with heavy objects, or a direct and strong blow to the back (automobile injury); A fracture of the cervical spine is often observed when hitting the bottom while diving. A spinal fracture is an extremely serious injury. Its sign is severe pain in the back at the slightest movement.
If the spine is fractured, spinal cord injury (rupture, compression) is possible, which is manifested by the development of paralysis of the limbs (lack of movement and sensitivity).
In case of spinal fractures, even small displacements of the vertebrae can cause a rupture of the spinal cord, therefore it is strictly forbidden to sit down a victim with a suspected spinal fracture or put him on his feet. First of all, the victim needs to create peace by laying him on a flat, hard surface - a wooden board, boards. The same items are used for transport immobilization. In the absence of a board and the victim is unconscious, transportation is least dangerous on a stretcher in a prone position with pillows placed under the shoulders and head. In case of a fracture of the cervical spine, transportation is carried out on the back with immobilization of the head, as in the case of skull injuries. Victims with spinal injuries should be transported with extreme caution. Shifting, loading and transportation should be carried out simultaneously by 3-4 people, keeping the victim’s torso at the same level at all times, avoiding the slightest flexion of the spine; It is better to shift the victim together with the board or shield on which he lies.
A pelvic fracture is one of the most severe bone injuries, often accompanied by damage to internal organs and severe shock. Occurs when falling from a height, compression, or direct strong blows. A sign of injury is severe pain in the pelvic area with the slightest movement of the limbs and a change in the position of the victim.
In case of fractures of the pelvic bones, immobilization with the help of splints is impossible, so the first aid is to give the victim a position in which pain is less likely to occur or intensify and damage to internal organs from bone fragments is least possible. The patient should be laid on a flat, hard surface, legs bent at the knee and hip joints, hips slightly apart (frog position), a tight cushion made of a pillow, blanket, coat, hay, etc., 25-30 cm high, should be placed under the knees.
It is very important to carry out all anti-shock measures. Transport the victim on a stretcher or a hard board on his back, giving him the position described above (To prevent the thighs from slipping off the roller, they are fixed with something soft (towel, bandage, etc.).
Fractured ribs occur with strong direct blows to the chest, compression, falling from a height, and even with severe coughing or sneezing. A rib fracture is characterized by sharp pain in the area of the fracture, which intensifies with breathing, coughing, and changing body position. Multiple rib fractures are dangerous due to increasing respiratory failure. The sharp edges of the fragments may damage the lung with the subsequent development of pneumothorax and intrapleural bleeding.
First aid consists of immobilizing the ribs - applying a tight circular bandage to the chest. If there is no bandage, you can use a towel, sheet, or pieces of fabric for this. To reduce pain and suppress cough, the victim can be given a tablet of analgin, codeine, amidopyrine. The most painless transportation to the hospital is in a sitting position. In severe conditions, when the victim cannot sit, transportation is carried out on a stretcher, giving him a semi-sitting position. First aid and transportation to a medical facility for complicated rib fractures (pneumothorax, hemothorax) are the same as for penetrating wounds of the chest.
A clavicle fracture is characterized by pain in the area of injury and dysfunction of the arm on the affected side. The sharp edges of the fragments can be easily felt through the skin. First aid consists of immobilizing the fracture area. This is achieved by fixing the arm with a scarf, Deso bandage or cotton-gauze rings.
First aid for an open fracture
Such an injury is extremely dangerous, as the wound can become infected. First aid for an open fracture begins with stopping bleeding using a pressure bandage or tourniquet if significant blood loss is observed. Antiseptic preparations are used to treat the skin around the wound. To transport the victim, it is necessary to carefully apply a splint without touching the wound.
Signs of a fracture
The main signs of a fracture are intense pain, swelling and pathological mobility in the injured area. There are additional signs that depend on the type and location of the fracture, but in order to suspect a fracture, three main ones are enough, and sometimes even one - severe pain. The fact is that swelling is not always noticeable to the untrained eye. For example, in people with a dense build it can be difficult to detect, and in some cases it may not be too pronounced. As for pathological mobility, it also cannot always be detected, for example, if the fracture is located close to the joint.
A doctor will be able to accurately determine the presence of a fracture after taking an x-ray, and for first aid, any bone injury that is accompanied by severe pain that intensifies when trying to move will be considered a fracture. If it later turns out that the injury is less serious, for example, a bruise or dislocation, and first aid is provided as for a fracture, this will not cause any harm to the victim, while underestimating the severity of the injury can lead to very serious complications.
Types of fractures
Broken arm
First aid for arm fractures is based on prompt immobilization of the limb, application of a splint and fixation. Severe pain is relieved with painkillers. If pain shock begins to develop, the victim is warmed up and given hot tea. It should be noted that drinking is prohibited if the patient is vomiting or has an abdominal injury. When the symptoms of shock are eliminated, the injured person can be moved.
An open fracture of the arm requires stopping the bleeding using a tourniquet, which is applied above the injury. Antiseptics are used to treat the wound. Having stopped the bleeding and treated the wound, it is necessary to carry out the procedure of fixing the hand.
Attempts to realign bones are strictly prohibited.
Broken leg
First aid for leg fractures involves using a splint to secure the limb. An open injury may bleed, so stop the bleeding using a tourniquet. The wound is treated with antiseptics, and if the victim feels severe pain, anesthetics are used.
Independent attempts to straighten the bone are strictly prohibited.
Spinal fracture
A spinal fracture is a serious injury that threatens the life of the victim. For such a fracture, pain relief must be given very quickly, and the body must be fixed immediately. To move a person, boards, doors, and plywood are used. The head is fixed with a rigid collar made of suitable items.
It is prohibited to sit down, try to stand, pull the limbs, or straighten the spinal column of the victim.
Pelvic fracture
A pelvic fracture can be accompanied by severe complications and internal bleeding, which sometimes result in disability and death. When providing first aid in such cases, you should examine the victim, immobilize him in a supine position (knees should be bent), fix the pelvis, and raise the knees with a roller. In addition, the patient’s condition should be constantly monitored until doctors arrive.
It is forbidden to seat or try to position a patient.
Fractured ribs
When a rib is fractured, internal organs and the cardiovascular system can be damaged, which is very dangerous for the victim. However, a simple fracture of one or two ribs does not require the attention of specialists - the patient recovers on his own. In difficult cases, it is necessary to urgently hospitalize the injured person and provide him with qualified assistance.
This type of fracture requires rest, so it is worth limiting active movements and sports.
Tibia fracture
First aid for lower leg injuries consists of fixing the limb, applying a splint, and administering painkillers to the patient. If there is bleeding, a tourniquet is applied.
Repositioning the bone is strictly prohibited.
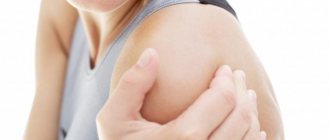
Shoulder fracture
A shoulder injury can be complicated by internal hemorrhage, which is extremely dangerous to health. The patient needs immobilization for a fracture using a splint, and he should also be given painkillers. The victim must be moved in a sitting position.
It is forbidden to straighten the shoulder and carry the patient without fixing the limb.
Immobilization rules
Immobilization is a set of measures aimed at ensuring the immobility of the injured limb. For this, various tires are used, including those made from handy materials - sticks, boards, rods, etc.
Splinting rules
When applying a splint, you must follow a number of rules:
- It needs to be applied as early as possible. The fracture is accompanied by swelling, which will not allow splinting to be carried out correctly.
- The splint is applied after pain relief, and not vice versa.
- The object is applied on both sides of the damaged limb, fixed with a bandage along the entire length, except for the fracture site.
- If the femur is fractured, a splint is applied from the armpit to the foot.
- If the fracture is open, first treat the wound, apply a sterile or clean bandage, and only then begin splinting.
- The bleeding must be stopped before a splint is applied. If a tourniquet was used, a splint is applied so that it can be removed without disturbing immobilization.
- The arm is suspended in a sling; if a leg is broken, something soft is placed under it.
- In the cold season, the injured limb is wrapped in a warm cloth.
- To control blood circulation, the first phalanges of the fingers are left open.
When transporting a victim to a medical facility, it is necessary to ensure the correct position of the body. If the legs are broken, the patient is transported in the “lying” position, placing a soft cushion under the injured limb. If an arm is broken, transportation while sitting is allowed.
Additionally read: