The knee joint is one of the large joints of the human skeletal system, formed by the articular surfaces of the tibia and femur, ligaments, patella and articular capsule. A dislocation of the knee joint is an injury to it, most often due to trauma, characterized by displacement of the joint formations and requiring mandatory treatment.
Symptoms of a luxated patella
Vivid clinical manifestations of patellar dislocation appear immediately after traumatic mechanical impact. The first symptom is sudden pain in the knee. The victim notes a sharp limitation of active mobility in the knee joint. Performing passive motor acts is not possible in full. Any passive movement or attempt to stand on the injured leg is accompanied by acute pain and palpable clicks.
When examining the patient, the fact of displacement of the patella relative to the knee joint is determined. The knee area is swollen and hyperemic. During palpation, a crunching sound (crepitus) may be detected in the area of displacement. In case of soft tissue damage, subcutaneous hemorrhage is possible.
Features of the structure of the knee
The patella is a rounded bone that covers the articular apparatus of the knee in front (located in a small depression). Fixation of the patella is possible thanks to the internal and external supporting ligaments, the quadriceps femoris muscle, and powerful cruciate ligaments.
The patella plays the role of a protective mechanism that prevents lateral displacement, thereby ensuring the safety of the joint, ligaments, and other tissues. The bone is the first to suffer from any mechanical impact, so patellar dislocation is considered a fairly common injury.
Types of patellar dislocations
The classification of patellar dislocations is based on the cause of occurrence - congenital or acquired. In addition, patellar displacements are divided into types depending on the direction:
- lateral;
- rotary;
- vertical.
Depending on the severity of the damage, dislocations can be:
- mild to moderate degree – insignificant displacement, which is not accompanied by damage to the ligaments;
- acute - dislocations that occurred for the first time, without complete displacement and damage to surrounding tissues;
- habitual - dislocations of the patella, repeated systematically, caused by pathological changes in the surrounding muscular-ligamentous apparatus.
Determining the type of patellar dislocation largely determines medical tactics and a program of restorative measures.
Preventive recommendations
First, work on improving the strength and tone of your leg muscles. As practice shows, people with well-developed muscles are much less likely to be diagnosed with dislocations. You don't have to do weightlifting: walk, swim and cycle more.
Second, minimize the risk of injury of any kind. Be careful during sports training.
Third, respond promptly to any damage. If these occur, be sure to consult your doctor.
Be healthy! Study the following link for treatment of laryngitis in children.
Congenital dislocation of the patella
Congenital dislocation of the patella is considered a fairly rare developmental anomaly. The pathology is diagnosed in one out of two hundred children. Among boys, congenital dislocation is observed twice as often as in girls.
According to traumatologists, a congenital anomaly occurs against the background of pathological formation of the hip bone. In this case, the quadriceps femoris muscle acts on the lateral condyle of the femur and prevents its normal development. As a result, the tibia deviates in an outward direction, and the patellar plate is fixed in a pathological position. The combination of these mechanisms leads to dislocation of the patella.
In some cases, pathological transformations begin with disturbances in the development of the lateral epicondyle. Muscle abnormalities are secondary. Experts believe that patellar displacement occurs when the condyle develops incorrectly. This same feature does not allow the knee joint to develop physiologically.
Typically, congenital luxation of the patella is detected in children with other genetic diseases. In healthy children, this condition occurs extremely rarely. The diagnosis is first made before the age of three. If the disease develops slowly and there are no provoking factors, congenital dislocation of the patella can be diagnosed at 7-8 years of age or later.
Anatomical features of the kneecap
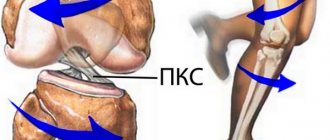
The knee joint is one of the largest and most important in the human body. It consists of the femur and tibia, as well as the patella.
The latter (better known as the patella) is a small bone located in front and at the top of the knee. Its main task is to protect the knee joint from injury and subsequent damage.
The knee joint has many important functions. At a minimum, without it a person would not be able to fully stand, walk and bend and unbend his legs.
As noted, a patella dislocation is considered an injury in which the relationship of the bones changes in an uncharacteristic way. Such unfavorable disturbances appear as a result of strong impacts and other reasons. More about them later.
Traumatic dislocation of the patella
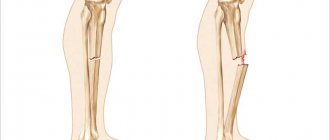
In traumatology, complete and incomplete dislocations of the patella are distinguished. In the first case, the patella plate shifts in the outer direction with localization on the lateral condyle of the femur.
If the dislocation is incomplete, then an incomplete displacement relative to the midline of the knee joint is recorded. In this case, there is a possibility of self-reduction of the patella when the leg is extended at the knee. Patients complain of rapid fatigue during walking, active movements, and unsteady gait. As a result, a psychological problem may develop in the form of fear of moving on uneven roads or surfaces.
When examining the patient, the presence of fluid, hemorrhages in the knee joint, and pathological mobility caused by instability of the ligamentous apparatus are detected.
Causes.
Those most susceptible to injury are those who lead an active lifestyle, play sports, and undergo severe physical activity. The most common mechanisms are a fall on the knees, a side blow to the joint area and a sharp extension of the lower leg.
Possible causes of this type of injury include:
- Meniscus tear.
- Anomalies in the development of the patella.
- Weak ligaments and muscles in this area.
- Patella position too high.
- Dysplasia.
- Arthrosis of the articular part of the knee.
- Valgus deformity.
- Injuries suffered.
- Hemorrhage into the joint cavity.
Recurrent patellar dislocation
Recurrent (repeated) dislocation of the patella appears in childhood. Up to 20% of all children suffer from this type of pathology, and the disease is more common in girls. Displacement of the patella occurs without any apparent traumatic cause, even with minor loads on the knee joint. In most cases, recurrent patellar dislocation occurs on both sides.
Patellar displacement occurs after contraction of the quadriceps femoris muscle during flexion of the joint. Dislocation always occurs outward, which is a distinctive feature of the injury. Repeated displacements lead to chronic damage to the articular surfaces of the knee plate and femoral condyle. As a result, flattening of the surfaces is formed, which subsequently leads to the development of deforming arthrosis and curvature of the lower leg bones.
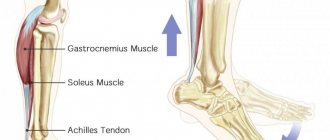
Structure and functions of the patella.
The patella is a large sesamoid (located in the thickness of the tendon) bone, which is located in the anterior part of the knee joint. Otherwise it is called “patella”. It is covered with cartilage tissue on the inside, facing the articular cavity. Muscle tendons, patellar ligaments are attached to it, and also a ligament extends inward from it, which is attached to the femur. The main function is protective (covers the structures of the joint from the front surface), as well as stabilizing (prevents displacement of the tibia and femur relative to each other).
Treatment of patellar luxation
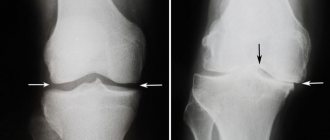
To confirm patellar dislocation, hardware diagnostic methods are used - radiography, CT or MRI. This is necessary in order to assess the condition of the patella plate, osteochondral structures of the joint, femur and tibia bones. The treatment method is selected only after a thorough examination.
In most cases, patellar luxation is treated conservatively. First of all, its reduction is carried out. All manipulations are performed by a traumatologist or orthopedist under local anesthesia. After anesthesia, the specialist bends the injured leg at the hip joint to relax the tendons of the quadriceps femoris muscle. Then, the knee joint is carefully extended and the patella is shifted in the required direction. The correctness of the actions performed is controlled by radiographs.
After reducing the dislocation, it is necessary to apply a plaster cast. In some cases, it is allowed to use a special orthopedic orthosis. Fixation of the knee joint takes from 4 to 6 weeks. The patient is prescribed painkillers or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,
Old, recurrent patellar dislocations and acute traumatic dislocations may require surgical intervention. After surgery, it is necessary to plaster the knee joint for a period of 4 to 8 weeks (depending on the underlying cause and type of surgical treatment). Immediately after immobilization, rehabilitation of the joint begins, which continues for at least a month from the moment of injury until complete restoration of mobility. Unfortunately, the operation does not always maintain a lasting effect - in 15-40% of cases, patients experience an exacerbation of the disease.
Rehabilitation after kneecap dislocations
Recovery after arthroscopic surgery, due to its minimally invasive nature, occurs quite quickly. However, in this case, strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations is necessary. The use of orthoses or braces may be recommended for the first time after surgery. A course of intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid may be recommended. Physiotherapy promotes rapid restoration of joint tissue and muscles. As the swelling of the joint decreases, its motor activity is gradually increased. Kinesiotherapy and mechanotherapy are prescribed. After a course of rehabilitation measures, patients quickly return to their normal lives, and athletes return to training.
For diagnosis and effective treatment of dislocations and other injuries, contact our clinic!
Fixing splints for an injured shin
The lower leg is the most commonly injured leg. A closed fracture occurs without damage to the skin; we see an abnormal displacement of the damaged part of the leg. When a fracture occurs, the victim feels severe pain, and swelling quickly appears at the site of injury. To avoid moving the bones further, it is absolutely forbidden to lean on a limb, even if the injured person can do so. With closed bone injuries, internal bleeding occurs, which can lead to the death of nerves, so the victim must be taken to a medical facility as soon as possible for surgery.
A fracture of the leg requires immediate immobilization of the damaged organ. It is more convenient to make a Kramer splint from scrap materials, which is modeled in accordance with the shape of the leg, placing fabric folded in several layers inside to cushion movement. The splint must be applied over the entire back surface of the leg, starting from the subgluteal fold, ending with the heel, then bent and ensure the immobility of the entire foot. For stronger fixation, it is advisable to use additional side splints made of plywood on both sides of the injured leg. They must be carefully bandaged to the limb.
Of course, you don’t always have the necessary equipment at hand, so you can improvise. If it is possible to find an easily bendable plastic material, it is placed on the sides of the leg, covering the heel and placing a board of a suitable size on the foot. This improvised splint should be bandaged from the knee to the toes.
An umbrella, a cane, a ski pole, branches - all this can serve as improvised tires in a difficult situation when nothing else is at hand. The most important thing is to immobilize and fix the ankle joint and foot.
If you could not find anything at all that would serve as a splint, then, as a last resort, you can fix the broken leg by tightly bandaging it to the healthy one using any fabric - a towel, scarf, piece of clothing.
If an open fracture occurs with damage to the skin and bleeding, then you must first stop the bleeding by pressing your finger on the artery above the fracture site. Then you need to apply a hemostatic tourniquet and be sure to record the time when it was applied. Broken bones that are visible from the wound should not be touched with hands, so as not to cause infection. You should carefully apply a sterile cloth over the wound surface and go to the emergency room.
The spiral upward method of laying the bandage is simple - it is a few circular wraps of the bandage on the ankle, then rise up, covering the underlying bandage by about two-thirds with each subsequent stroke. To model the shape of the leg, it is necessary to make bends along the front part of it. The bandage should be secured under the knee with several circular turns. Another dressing option is a scarf. It is done using a scarf, which is placed with the long side below the injury site, and the triangular side above.
If there is a special medical bandage with rubber fibers, it can also be used with the leg elevated, so as not to provoke stagnation of lymph, moving from bottom to top, since lymphatic vessels can be damaged. It is important to ensure that no folds form and that the bandage is not pulled too tight.
Treatment methods for gonarthrosis
Damage to cartilage is irreversible. This means that gonarthrosis, unfortunately, cannot be cured, so treatment is aimed primarily at relieving pain and slowing the progression of the disease.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment may include medications, physical therapy, a weight loss program, habit changes to reduce stress on the knees, and the use of orthotics. Anti-inflammatory and painkillers are used to prevent inflammation and reduce pain. The use of elastic orthopedic bandages can reduce pressure on the joint, and special exercises and physical therapy methods can improve its mobility and strengthen the muscles.
Surgery
Surgical intervention becomes necessary if conservative treatment does not give the desired result. There are procedures to create secondary cartilage tissue in the knee. This can reduce discomfort and, in some cases, eliminate pain altogether. However, the load-bearing capacity of the new cartilage is not as great as the old one. In difficult cases, knee replacement is recommended.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Classification of patellar injuries
Existing types of dislocations:
- lateral dislocation;
- vertical (the joint space is blocked);
- rotational (the patella is rotated around its axis vertically).
Damage occurs:
- spontaneously appearing (occurs after a period of normal bone alignment);
- permanently existing (not eliminated after bone reposition);
- habitual (after each movement of the joint the bone moves away from its normal position).
Medical statistics confirm that more often patients turn to a traumatologist with an external dislocation, less often with an internal dislocation. Vertical and rotational types of dislocations are too rare.
The same applies to traumatic dislocations, however, they are dangerous due to the occurrence of relapses, which means a transition to a more serious stage (the dislocation becomes habitual).
Prices
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for diagnosing childhood arthritis | 2 000 — 3 000 |
| Prices for diagnosing childhood epilepsy | 3 100 — 4 900 |
| Prices for pediatric neurosurgery | 30 000 |
| Prices for treatment of childhood epilepsy | 3 750 — 5 450 |
| Prices for treatment of umbilical hernia in children | 9 710 |
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for hip replacement | 23 100 |
| Prices for clubfoot treatment | 25 300 |
| Prices for Hallux Valgus treatment | 7 980 |
| Prices for knee joint restoration | 13 580 — 27 710 |
| Prices for scoliosis treatment | 9 190 — 66 910 |
| Prices for knee replacement | 28 200 |
| Prices for treatment of intervertebral hernia | 35 320 — 47 370 |
swelling on the knee
swelling on the knee
If, after a fall or other injury, a person notices one or several symptoms of a dislocation, you should immediately contact a specialized clinic for help. The sooner therapeutic measures are taken, the higher the chance of a positive treatment outcome. You can also determine a dislocation yourself due to the loss of sensitivity in the foot area and its pallor. Such symptoms manifest themselves as a result of impaired blood flow.