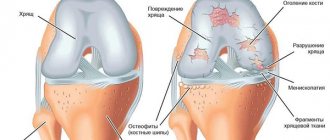
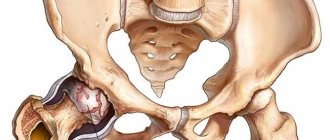
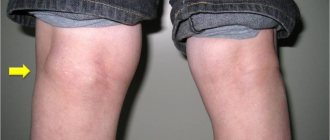
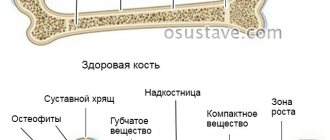
Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee is a disease that leads to degenerative-dystrophic changes in the knee joint.
To support the entire body weight during movement, the knee joint is subjected to constant loads. With age and the thinning of hyaline cartilage, which provides mobility to the joint, the bone is exposed, growths (spikes) form, and the knee becomes deformed. The opinion is erroneous when, with pain in the knee, people think that the joint is filled with salt deposits.
The disease deforming osteoarthritis has nothing to do with calcium salts. Rather, it can be called age-related, developing in people after 40 years of age (more often in women).
The disease is common, diagnosed in 1/5 of the entire population of the planet.
Reasons for appearance
Ostearthrosis can be primary or secondary in form.
The primary form of the disease usually develops with age due to constant heavy loads on the joint. The secondary form of development of the disease is preceded by joint injuries and various diseases.
The development of deforming osteoarthritis in the knee is promoted by:
- Excess everything human
- Low physical activity, inactivity, sedentary lifestyle
- Constant intense stress on the legs
- Age-related changes
- Meniscus tear, ligament
Diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, gout.
Symptoms and degrees
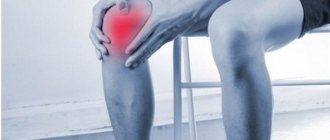
The main symptom of this disease is pain in the knee, severity, strength, intensity of which depends on the stage of the disease.
As the pain develops, it becomes more intense, mobility is limited, and movements in the knee become stiff and painful. At an advanced stage of the disease, the joint is completely blocked, and complete immobility occurs.
At first, the symptoms are minor and often the patient simply does not pay attention to it.
Over time, signs of deforming osteoarthritis begin to appear more actively; the knee begins to hurt even at rest.
The disease at a late stage is much more difficult to treat; sometimes surgery is the only way to alleviate the patient’s condition.
There can be no talk of a complete cure for this disease at stage 3, when at stages 1 and 2 patients rarely see a doctor.
Let us consider the signs of deforming osteoarthritis separately at stages 1, 2, 3 of its development.
1st degree
The manifestation of the disease is insignificant, at times it tightens under the knee, it hurts when stretching the leg, or after a long stay in a sitting position.
The pain is short-lived and goes away quickly when changing position. slight discomfort occurs in the knee , but in general it does not cause inconvenience to the person.
At the first stage of the disease, few people go to the doctor. The mobility of the joint is normal, there is no deformation yet.
2nd degree
replaces the first with more pronounced symptoms. The pain becomes more severe, prolonged, often intensifies in the evening, torments at night, and hurts in the calves.
The joint begins to deform, causes discomfort when flexing and extending, becomes limited in free movement, swells and crunches abnormally when walking.
At stage 2, treatment is quite successful and effective. It is still possible to return the patient to full movement and return the joint to full functionality, but not everyone goes to the doctor.
3rd degree
Advanced, the pain is constant and prolonged , and does not subside even at rest.
Worse at night, while sitting, standing or walking. The knee begins to ache when weather conditions change and becomes sensitive and vulnerable.
The joint becomes deformed, and over time this becomes visually noticeable, and the person begins to limp. The mobility of the joint is limited, sometimes it is simply impossible to bend it, and severe, burning pain begins.
Drug therapy
Since the pain that occurs is not severe, analgesics in the form of tablets or injection solutions are rarely used. To eliminate mild discomfort, patients are prescribed ointments, gels, creams, and balms for local application to the knee joint. Therapeutic regimens may include drugs from the following groups:
- means to improve blood circulation - Pentoxifylline, Xanthinol nicotinate;
- preparations with a complex of B vitamins - Milgamma, Combilipen, Neuromultivit;
- balanced complexes of vitamins and microelements - Supradin, Complivit, Vitrum, Centrum, Multitabs.
Systemic chondroprotectors Teraflex, Structum, Artra, Dona, Chondroxide are mandatory for long-term course use (from 3 months). The active ingredients of these products stimulate partial restoration of damaged cartilage.
| External agents for the treatment of grade 1 osteoarthritis of the knee | Therapeutic effect |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Voltaren, Fastum, Artrosilene, Nise, Ketorol, Diclofenac, Indomethacin) | Stop inflammatory processes, reduce the severity of pain, stimulate the resorption of edema |
| Ointments with a warming effect (Viprosal, Finalgon, Apizartron, Nayatox) | Eliminate morning swelling and stiffness of movement, eliminate pain |
Surgery
For grade 1 osteoarthritis, surgery is not required. Arthroplasty, aimed at restoring the size, shape and conformity of the surfaces of the knee joint to each other, is carried out with multiple bone growths (osteophytes). Such changes are not typical for this stage of the disease.
Exercise therapy
Dosed physical activity is the most effective method of treating osteoarthritis at the initial stage of development. The main objectives of exercise therapy are to strengthen the muscles of the knee and improve the blood supply to its structures with nutrients. A set of exercises is compiled by a physical therapy doctor immediately after making a diagnosis. The patient’s age, physical fitness, and general health must be taken into account.
Physical education for grade 1 knee osteoarthritis.
The following exercises are most often recommended for patients:
- flexion and extension of the legs at the knee joints while lying on the back;
- imitation of cycling in a lying or sitting position with emphasis on arms extended back;
- in a standing position, swing your legs back and forth, from side to side;
- shallow squats;
- walking around the room with your knees raised high.
The appearance of even a slight painful sensation is a signal to stop exercising. You can start training only after an hour break. During exercises, movements should be smooth, slightly slow, without jerking.
Massage
At the beginning of treatment, about 5 sessions of classical massage are performed. When performing them, all traditional massage movements are used - kneading, rubbing, clapping, vibration. To improve the patient’s well-being, vacuum massage, including hardware massage, is also used. Before installing plastic or glass jars, air is removed from them to ensure better contact with the skin. This stimulates blood flow to the knee and the production of bioactive substances with an analgesic effect. The therapeutic effect of the procedure is enhanced when the massage therapist begins to smoothly move the cups and perform kneading and rubbing with them.
Manual therapy
The help of a chiropractor is used for osteoarthritis accompanied by increased muscle tension. The doctor acts on the spasmodic skeletal muscles with his fingers. The muscles relax, which improves blood circulation and lymph flow.
In addition to common massage movements, the chiropractor uses superficial and deep palpation techniques.
Nutrition
Since the development of osteoarthritis is associated with a deterioration in the blood supply to tissues, the goal of the diet is to restore optimal blood circulation. To do this, you should exclude from your diet foods high in fat, which is deposited as cholesterol blocks on the walls of blood vessels. You need to give up semi-finished products and fast food, and use vegetable oils when cooking, not margarine or cooking oil. The daily menu must include fresh vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products, and cereal porridges.
Traditional methods of treatment
After the main treatment, during the rehabilitation period, patients are allowed to use folk remedies. These are ointments, rubs, infusions, decoctions that accelerate the cleansing of the joint from tissue breakdown products and mineral salts, and have a mild warming effect. What folk remedies are advisable to use for grade 1 osteoarthritis:
- Herb tea. Pour a teaspoon of corn silk, St. John's wort, sage, elecampane into a ceramic teapot, and pour 2 cups of boiling water. After an hour, strain, drink 100 ml three times a day;
- compress. Mash a fresh leaf of horseradish well, grease with honey, and apply to the sore knee for an hour.
Herbal collection.
In spring you can start preparing a healthy tincture. You need to collect, put in a jar and pour vodka over young leaves or flowers of calendula, dandelion, plantain, clover, shepherd's purse, chamomile, coltsfoot. By the end of autumn, the tincture for rubbing on the knee is ready.
All methods of treatment of deforming ostearthrosis of the knee
The treatment is prescribed by a traumatologist-orthopedist.
Treatment methods are conservative or surgical.
It all depends on the degree of the disease, clinically expressed symptoms, the general condition of the patient, and individual indications. Treatment is purely individual.
Drug therapy
To relieve inflammation and joint pain, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Diclofenac, Meloxicam, Nimesulide.
Medicines or ointments will alleviate the situation during exacerbation of the disease.
To dilate blood vessels, Nicospan, Trental, Teonicol, Betamethasone, Hydrocortisol in injections, and hyaluronic acid are prescribed.
For synovitis and cartilage depletion, corticosteroids are prescribed by injection into the affected joint.
To increase blood circulation, vasodilators : Hyaluronic acid, Corticosteroids in the form of injections to relieve inflammation and swelling.
Chondroprotectors will help maintain joint function . They are necessarily included in the course of treatment, regardless of the choice of method and the degree of damage to the joint.
The knee is treated by intramuscular or intra-articular administration of Glucosamine, Chondrotin sulfate. Chondroitin contains some biopressures, which are also recommended in the treatment of the disease.
In case of severe pain, the doctor will prescribe analgesics, but every patient should understand that taking medications cannot cure the disease. This is just a relief of symptoms, a short-term effect to alleviate the patient’s condition.
A daily menu with the consumption of fresh greens, fruits, green vegetables, salmon, seafood, lean turkey meat is recommended.
Spicy, salty, fatty, carbohydrate-rich foods are contraindicated.
Cartilage tissue does not absorb amino acids well, and a person quickly gains extra pounds. There is a lot of essential chondroitin in crabs and shrimp, and collagen in lean meat.
Surgical method of treatment
Surgery is necessary at the 3rd, advanced stage of the disease.
Arthroscopy is prescribed - an endoscopic operation to remove destroyed elements of the meniscus, cartilage, and nearby damaged structures.
method has proven itself well for removing pieces of destroyed cartilage. The surgeon has the opportunity to assess the condition of the joint from the inside.
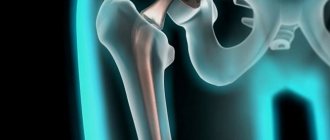
It is also possible to perform joint replacement, replacing it with an artificial implant - an endoprosthesis, the material for which is steel, titanium, or polyethylene. These materials are strong, durable and will last up to 25 years.
Read also: Osteoarthritis of the knee joint treatment drugs
other methods
Administration of orthokine obtained from the patient's cells. Blood taken from a vein is processed to produce a protein that can stop the breakdown of cartilage. But, treatment with this method is effective at stages 1-2 of the disease, as soon as the first symptoms appear; with complete destruction of the cartilage, more radical methods of treatment are needed.
The Bubnovsky method can improve the nutrition of cartilage and eliminate dysfunction in the knee muscles. According to the Bubnovsky method, the patient undergoes treatment on a special simulator to improve the nutrition of joint tissues, work out each muscle group separately, and restore blood microcirculation.
Using table cages . The cells are taken from the patient by inserting a thin needle into the pelvic bone. After their activation, they are reintroduced into the joint cavity. The method is effective for grade 2 deforming osteoarthritis; stem cells are able to restore destroyed cartilage in full.
A normal life for the patient, unhindered movement is guaranteed.
Nutrition
A balanced diet for arthrosis of the knee joints ensures the prevention of excess weight gain and the intake of minerals and vitamins.
Nutrition Features:
- The plant component should predominate in the diet.
- Reduced salt content in the daily amount of food consumed.
- Daily water consumption is at least 2 liters.
Recommended Products:
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- cold pressed vegetable oils;
- vegetables, fruits, herbs;
- low fat dairy products.
Traditional methods
They are harmless in the early stages of the disease and are quite effective when treated in combination.
a) Celandine oil, infusion of vegetable oil (2-3 tbsp) of crushed leaves, rubbed into sore spots.
b) Place burdock (several leaves) in a saucepan, put on fire, steam, then lubricate the knee with vegetable oil and apply the burdock to the knee, secure with a warm bandage.
c) Mumiyo is ground into powder and diluted with water. The mixture is applied to relieve pain and warm the joint.
d) Blue clay. Grind into powder, dilute with water to the consistency of thick sour cream, apply as a compress, wrap in woolen cloth, leave for 2-3 hours.
e) Dandelions, prepare a tincture. Place the yellow flowers in a dark glass container, pour in the usual triple cologne, leave for 2 weeks in a dark place, shaking the container periodically, rub the composition into the sore joint 2-3 times a day.
f) Mix apple cider vinegar (3 tbsp) with honey (1 tbsp), rub into sore spots, cover with a cabbage leaf and a bag on top, securing with an elastic bandage. Carry out procedures daily for 1 month.
Paraffin compresses reduce pain.
It is useful to drink tomato juice, apple cider vinegar 1-2 tsp, 2-3 times a day.
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the joints is detected using the following studies:
- X-ray diagnostics;
- Ultrasound of joints;
- MRI of joints;
- blood tests: general and biochemical;
- diagnosis of synovial fluid.
1 MRI of joints
2 Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
3 Consultation with a rheumatologist
Therapeutic gymnastics and its role
Gymnastics is an excellent addition to drug treatment in combination with compresses and proper nutrition. Exercises should be performed regularly, and the load on the joint should be completely eliminated.
The goal of gymnastics is to reduce pain and strengthen the muscle ligaments around the sore joint. You cannot perform exercises without the prescription and supervision of a doctor or trainer.
If performed incorrectly, you can cause irreparable harm to the joint. First, you need to consult with a physiotherapist; perhaps there are contraindications to the behavior of gymnastics, or you need to take into account certain features when performing it.
a) Lie on the floor on your back, straighten the sore leg, lift it slowly from the floor to a height of 20 cm, keep it raised as long as possible.
b) Lie on the floor on your back, lift your sore leg off the floor to 20 cm in height, lower it down, repeat the movements 10-15 times.
It is useful to sit on the edge of the table and dangle your legs, or do the bicycle exercise while lying on your back.
This will strengthen the leg muscles, increase the range of motion, and nourish the cartilage tissue.
Therapy and procedures
Physiotherapeutic methods are aimed at improving blood supply to the knee joints, eliminating soft swelling, and improving overall well-being. Each procedure relaxes the muscles, which subsequently makes it possible to walk normally without additional means of support.
Physiotherapy
A course of physiotherapeutic procedures is carried out every 6 months to prevent arthrosis of the knee joint. The best therapeutic effect is obtained in combination with exercise therapy and massage.
Types of physiotherapy used for arthrosis of the knee joint:
- pressotherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- UHF therapy;
- ultrasound therapy.
Physiotherapeutic treatment has a number of contraindications:
- oncological diseases;
- acute phase of the disease;
- skin damage and diseases;
- infectious diseases.
Prevention
1) Watch your weight, obesity leads to increased stress on the joint, which then leads to its destruction.
2) Give up bad habits.
Smoking and alcohol are harmful to joints.
3) Wear special knee pads.
If deforming osteoarthritis could not be avoided, the joint needs to be fixed, so there will be less pain.
4) Wear shoes with insoles and arch supports.
They will support the foot in the desired position.
Deforming osteoarthritis is incurable, but it is still possible to reduce pain in the joint and stop the progress of the disease.
What complications can there be?
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly but persistently. Its course is complicated by secondary reactive synovitis, spontaneous hemorrhages into the joint cavity (hemarthrosis), osteonecrosis of the femoral condyle, and external subluxations of the patella. At the 4th radiographic stage, the joint space fuses, which leads to complete or partial immobilization.
Prognosis and complications
Deforming osteoarthritis in the knee is a common disease, but it is sometimes difficult to determine the causes of its occurrence. However, the destruction of a joint inevitably leads to a limitation of its mobility, up to immobilization, and therefore to disability and the inability to move independently.
The appearance of pain is a symptom, a signal that not everything is okay with the joint.
Complications with dystrophic lesions of the knee joint are inevitable:
- Nearby tissues are injured
- Muscle contracture develops
- A patient with immobility develops hypostatic pneumonia.
Do not hesitate to go to the doctor; it is easier to treat the disease at an early stage. With connivance, sometimes there can be no talk of cure. It is possible to replace a destroyed joint with an artificial one, but this is troublesome, expensive and, of course, painful.
Diagnostics
To improve the quality of life and identify the early stages of arthrosis of the knee joint, a comprehensive diagnosis is necessary. Initially, an examination by an orthopedist is required, who will prescribe the necessary diagnostic measures.
Instrumental
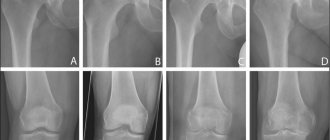
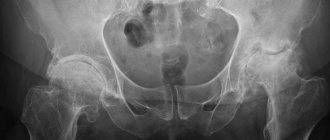
- The gold standard for diagnosis is radiography of both knee joints in two projections - anterior and lateral.
- MRI diagnostics, in addition to bone structures, makes it possible to identify changes of an inflammatory or destructive nature in the soft tissues of the knee joint.
- Computed tomography is most often used in addition to the x-ray method when planning surgical treatment.
- Diagnostic arthroscopy of the knee joint has gained wide popularity, allowing to visually assess the intra-articular picture and make the final decision in choosing a treatment method.
Laboratory (Analysis)
- clinical blood test;
- blood chemistry;
- blood test for C-reactive protein;
- clinical urine analysis;
- blood test for rheumatoid factor (if necessary).
Causes and treatment of deforming osteoarthritis (DOA) of the knee joint
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the knee joint lead to deforming osteoarthritis. Arthrosis reaches this stage due to neglect of the disease, ineffective treatment, the body’s reactivity to basic drugs and due to chronic concomitant pathologies.
Acute forms of osteoarthritis alternate with remissions, and during subsidence, wear and tear of the articular joint and the muscular-ligamentous corset continues. During an exacerbation, this process accelerates, plus a microbial infection joins inflammation, pain, swelling and motor dysfunction. It plays a major role in deformation of the knee (or knee joints) leading to ankylosis of the locomotor organ.
Forecast
The last stage of arthrosis is an incurable condition. Patients lose their ability to work and become disabled. It is possible to restore limb function only after joint replacement.
Arthrosis of the joints of the 3rd degree is the final stage of the disease, characterized by irreversible changes. Patients become disabled if left untreated. The only effective way to maintain a healthy lifestyle is endoprosthetics.
Arthrosis of the knee joint 3rd degree (also known as gonarthrosis, osteoarthrosis) is a chronic dystrophic, degenerative condition accompanied by pain, limitation of movement, deformation, change in the axis of the lower limb, leading to a decrease in the quality of life.
There are ways to solve the problem - surgical (operative) and therapeutic (conservative) methods. Each of them has a number of advantages. Most people are afraid of surgical interventions and wonder how to treat grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint without surgery at home?
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the main symptoms of gonarthrosis.
Etiology of the disease
The sources of diseases of the musculoskeletal system are a number of external and internal factors. Certain conditions contribute to the rapid development of osteoarthritis of all joint groups of the human skeleton. The largest joints that suffer first are the knees, which are constantly exposed to physical stress. They bear the bulk of physical activity and all body weight.
Read also: How to cure osteoarthritis
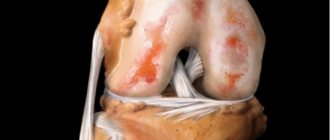
The mechanism of development of osteoarthritis is based on the principle of gradual wear and tear of the joint, namely the abrasion of the cartilaginous “covers” of the articular bones, atrophy of the synovial capsules and inhibition of the production of lubricating fluid. Calcium and phosphorus are washed out in the bones, due to this the bones thicken and the ligamentous apparatus atrophies. The process of regeneration and reproduction of collagen and elastin is completely disrupted. Cartilage tissue is not renewed by new cells, so the old cartilage covering wears away, and bone spines grow in its place.
Excessive work of the knee joints, prolonged vertical positioning, carrying heavy objects or being in an uncomfortable position for a long time causes wear and tear of the joints of the lower extremities with a complete picture of inflammation, swelling and pain. Under certain circumstances, pathology leads to deformation of the organ, that is, to anchorage of the joints. The process may involve one knee or both, depending on the underlying cause. The ligamentous-muscular system also changes, experiencing degeneration of the fibrinous type, leading to rigidity. Subsequently, the entire structure is subject to sprains, ruptures, dislocations, subluxations and fractures.
Important causes of inflammatory-destructive pathology of the knees:
- Infectious agents + inflammatory reaction + joint swelling.
- Traumatization of the knees of a mechanical, chemical, physical nature.
- Degeneration of the articulation of the knees due to degenerative-dystrophic processes.
This pathology often affects older people due to metabolic disorders and a lack of sex hormones, which regulate almost the entire chain of hormonal substances. Plus, elderly patients have many chronic diseases of organs and systems. It is these diseases that are the pushing mechanism for the development of deforming osteoarthritis of the knees. Poor vision and pathological processes in the central nervous system lead to loss of balance, so old people often lose control and fall, damaging their knees. But this pathology can affect all people, regardless of age, since injuries and purulent infections can lead to destruction and deformation of the joints.
Causes of deforming osteoarthritis of the knees:
- Hereditary pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
- Collagenoses.
- Increased load on the knee joints due to body weight.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Kidney pathologies (urolithiasis, glomerulonephritis, gout, renal failure).
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Injuries of any etiology.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Pathologies of the central nervous system.
- Liver dystrophy.
- Rheumatism.
- Allergic diseases.
- Infectious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Cancer of bones, organs and blood.
Deforming osteoarthritis of the knees appears in people who work on their legs with constant vertical load, which wears out the joints to the point of complete deformation. Builders, athletes, bakers, turners, loaders - they are at risk.
Attention! All patients suffering from arthritis or arthrosis, as well as people at risk, are recommended to be examined by an arthrologist or rheumatologist twice a year. Timely examination and treatment will help stop the pathology at an early stage and prevent irreversible processes in the form of deformation and ankylosis.
Causes of the disease
Primary osteoarthritis is called osteoarthritis, which develops due to a decrease in the functional endurance of hyaline cartilage. As the body ages, regeneration processes occur more slowly. Even with minor microtrauma, tissues do not have time to recover in a timely manner. The situation is aggravated by a decrease in the production of collagen in the body - the building material of ligaments and tendons.
Secondary osteoarthritis occurs against the background of existing cartilage damage. They appear due to damage to the knee joint by gout, rheumatoid, reactive, and psoriatic arthritis. The development of osteoarthritis is provoked by injuries, endocrine and hormonal pathologies, a sedentary lifestyle, and excessive physical activity.
Symptoms
Signs of manifestation of deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joints depend on the degree of destruction and involvement of soft tissues and connective ligaments in the process. The depth of the lesion, the state of the immune system, the degree of reactivity of the body, plus chronic diseases also affect the symptoms. The symptomatic picture of osteoarthritis at different degrees of pathology is completely different, but at all stages there is pain, inflammation, swelling and limitation of motor ability.
Inflammation covers the circumferential area of the knee: all ligaments, muscles, and the joint structure as a whole. Redness of the skin around the articulatio genus, local temperature, is a reaction of inflammation and infection.
The inflammatory reaction is accompanied by edema ; it is the result of the effusion of synovial fluid into the muscle tissue. Exudate leaks through the muscle fibers and tendons of the second order. The whole range of inflammatory reactions is accompanied by pain , which manifests itself differently depending on the degree of destruction. The pain of the first degree of destruction is acute after a long walk, but goes away after a night's rest. Other degrees are characterized by constant pain even during sleep.
Limitation of the motor ability of the knee begins in the second degree of destruction of the joint. Changes in the anatomical parameters and axis of the lower extremities plus lameness appear after metabolic disorders and erosion of all articular elements of the knee. Innervation and blood supply are impaired, atrophy of muscles and ligaments appears. The knee undergoes changes in its anatomical shape. A thick, immobile and painful joint gradually becomes ankylosed, ankylosis is the last stage in the development of deforming gonarthrosis.
Important! Muscle cramps are the beginning of complete ankylosis, that is, complete immobilization of the locomotor organ without the right to rehabilitation through medications. This situation is fraught with lifelong disability. In this case, it is impossible to do without surgical intervention. After surgical restoration of the joint, the cramps stop.
Symptoms of pathology
At the initial stage, the disease may not manifest itself clinically at all. As it progresses, the first discomfort appears when going up or down stairs, after running, intense sports training or long walks.
When visiting a doctor, patients complain of some stiffness of movement immediately after waking up, a feeling of “tightening” on the outside of the knee. These sensations disappear quickly and are rarely accompanied by pain.
No external changes in the joint are observed. Only occasionally does the knee look a little swollen. Swelling of the skin may indicate synovitis, an inflammation of the synovium. Others with its specific symptoms are a feeling of heaviness and limited mobility.
The essence of pathology
Gonarthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the knee joint. This is a chronic pathology. With it, the hyaline cartilage is deformed. It becomes thinner and can practically disappear as the disease progresses. In such advanced cases, the bone becomes exposed and grows.
Read also: Polyosteoarthrosis treatment with folk remedies
Among all patients suffering from rheumatic diseases, most of them are diagnosed with gonarthrosis. Its share reaches 60 percent. If adequate therapy is not carried out in time, the disease can lead to disability.
Types and degrees of illness
According to one of the classifications, DOA is distinguished between the right knee joint, the left one, or both. The disease is also divided into primary and secondary.
Here is their brief description:
- primary gonarthrosis occurs regardless of other diseases, becoming a consequence of congenital weakness of the joint or its age-related wear and tear;
- the secondary form develops against the background of other pathologies of the joint and its injuries.
There are 3 stages of the disease:
- DOA 1st degree . It is practically asymptomatic. There may be slight discomfort in the limbs after physical activity. Occasionally, the disease makes itself felt with mild pain in the knee. They go away after rest. The mobility of the joint is not impaired. Its deformation has not yet begun.
- DOA 2nd degree. The signs are already quite pronounced. Often troubling is pain of a pulsating nature, which occurs even after slight physical activity and is not always relieved with medications. Deformation of the articular cartilage begins.
- DOA 3 degrees. It is considered an advanced stage. The pain is constant. A person becomes weather dependent. His condition worsens significantly when the weather changes. The deformation of the joint is clearly visible visually. The knee practically does not bend.
Since grade 1 DOA hardly manifests itself at all, the disease is usually detected already in advanced stages. Treatment here requires serious and long-term treatment. The prognosis is correspondingly worse.
Clinical manifestations
Arthrosis of the joints of the 3rd degree has a pronounced clinical picture. The main complaint of patients is pain. Unlike arthrosis of previous degrees, pain occurs not only at the moment of movement, but also at rest. This is due to the constant inflammatory process in the joint. The pain is aching in nature and reaches significant intensity.
Motor function is almost completely limited, not only due to pain, but also due to the fusion of bone surfaces with each other. When the hip joints are affected, a person acquires a duck's gait - he walks, waddling from one foot to the other. When the knees are affected, a person walks with his legs constantly straightened, and there are difficulties when climbing stairs.
Externally, the joints look deformed and enlarged compared to healthy ones. With the development of the inflammatory process, swelling of the soft tissues is noted. When performing movements, a crunching sound is clearly audible due to the contact of bones. Due to the lack of cushioning by cartilage, movements are no longer smooth.
Causes of gonarthrosis
The knee joint is the largest joint in the human body. But it can also withstand a greater load than the others. With age, the joint “gets tired” and often malfunctions, especially if a person has not taken care of himself throughout his life. This is what causes the development of gonarthrosis.
In addition, the disease can be triggered by:
- obesity;
- dysplasia and other pathologies of the joint, congenital or acquired;
- endocrine diseases;
- metabolic disease;
- injuries (see Common knee injuries);
- low or too high physical activity.
Heredity also plays an important role. According to statistics, a person whose close relatives suffered from DOA of the left knee joint, the right one, or both, is at risk of developing it seven times faster than others. Therefore, it is necessary to take this into account and take preventive measures.
Today gonarthrosis is getting younger. This is explained by the fact that many people lead an unhealthy lifestyle, abuse fast foods, fatty foods, etc., and exercise little. The price of this behavior is knee problems at a relatively early age.
Disease prevention
The substantiation and development of a differentiated approach to the selection of methods for the prevention and treatment of grade 3 arthrosis of the knee joint is very relevant. Among diseases leading to disability, arthrosis occupies one of the leading positions.
According to statistics, of all chronic diseases leading to permanent loss of working capacity, patients with arthrosis of the knee joints often receive the 3rd degree of disability.
Measures to prevent arthrosis of the knee joint:
- Daily physical activity (at least 6000 steps per day).
- Swimming is the optimal type of physical activity for gonarthrosis. Visiting the pool 2-3 times a week for 40 minutes;
- See an orthopedist once every six months;
- Perform joint x-rays annually;
- Once every six months, undergo a course of physiotherapeutic treatment.
Symptomatic picture
The clinical picture of horarthrosis is usually quite pronounced at the second stage of the disease. And by the third, the situation worsens even more.
The most common symptoms of the pathology are:
- pain in the knees during movements;
- crunch in the joint;
- stiffness;
- discomfort in the limbs, especially painful with the onset of cold weather or rainy weather;
- swelling of the affected area of the leg;
- heaviness, pulsation in the limb.
The symptoms of gonarthrosis are similar to those of some other diseases. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. It is necessary to contact a rheumatologist or orthopedist after the first alarm signals.
Diagnosis of the disease
The main diagnostic method for gonarthrosis remains radiography. It is prescribed to all patients after a visual examination, collection of anamnesis and clarification of symptoms. Photos taken during the procedure make it possible to understand how advanced the situation is and how severely the joint and bone are deformed.
Additional methods include: blood tests, histology of external joint tissues, cartilage biopsy, study of interarticular fluid. They are used in cases of doubt or suspicion of complications of gonarthrosis.
Diagnostic methods
The basis for making a diagnosis are patient complaints, results of external examination and radiography. This instrumental study is the most informative, but with grade 1 osteoarthritis, characteristic signs may be absent. At the final stage of the disease, radiological stage 1 reveals single osteophytes, narrowing of the joint space and compaction of the subchondral zone.
If radiographic images are uninformative, MRI, CT, and ultrasound may be prescribed. The resulting images clearly visualize cartilage tissue, ligamentous-tendon apparatus, blood vessels, and nerve trunks.
Differential diagnosis is carried out to exclude damage to the knee joint by arthritis, synovitis, bursitis, tendonitis, and tendovaginitis.
Features of treatment
Treatment of the knee joint with DOA can be traditional medicinal, non-medicinal and surgical. The choice of tactics depends on the stage of the disease and the general condition of the human body. With gonarthrosis of the 1st and 2nd degrees, it is quite possible to manage with conservative methods.
The purpose of taking medications is to relieve pain, stop inflammation and support cartilage. For this purpose, analgesics, non-steroids, and chondoprotectors are prescribed. The use of corticosteroids is sometimes practiced. The drugs are taken orally, by injection and externally (if we are talking about ointments, gels, creams). Each medicine comes with instructions, which must be followed strictly.
Physiotherapeutic methods play an important role in gonarthrosis: treatment with ultrasound, high frequencies, laser beams, radon, hydrogen sulfide, healing mud. Such methods are not indicated only at the last stage of the disease. They are not used during exacerbations.
But exercise therapy is practiced for any degree of disease. In the first two stages, it helps speed up the healing process. On the third (meaning after surgery) – it contributes to faster and better rehabilitation.
Surgical intervention for gonarthrosis is indicated if conservative methods fail. In almost all cases, it is impossible to do without it at the third stage of the disease. Most often, patients undergo endoprosthetics, which restores lost joint functions for the next twenty years.
Latarjet operation as a method of treating osteoarthritis
This type of surgery is used to treat instability of the shoulder joint. The essence of the method is to move the coracoid process of the scapula and its attachment to the defective area of the glenoid cavity.
Many specialists have carried out such interventions in different ways. The most modern one is using an arthroscope. An arthroscope is a device that will help not only to perform surgery on the shoulder joint, but also to see the joint from the inside due to the built-in camera.
The advantages of this method of treating osteoarthritis include rapid recovery and minimal intervention in the body. Also a low rate of complications and eliminating the possibility of dislocations in the future.
Experienced doctors at the Elena Malysheva Medical Center use only the latest and proven methods in their methods of diagnosing and treating osteoarthritis. Sign up for a consultation!