Why do my hands swell?
Physiological reasons
Unilateral swelling can occur when the lymphatic and blood vessels of the arm are pressed by the body or clothing during sleep.
Small symmetrical swelling of the fingers and distal parts of the hands, especially noticeable when wearing a wedding ring, is observed after drinking alcohol, consuming salty foods and large amounts of liquid in the evening. In women, swelling of the hands, caused by hormonal changes, is often expressed during gestation. As pregnancy progresses, the symptom increases from mild pastiness to a significant increase in volume. Some patients note morning swelling of the fingers before the onset of menstruation, especially against the background of premenstrual syndrome.
Traumatic injuries
Local swelling while maintaining limb function is characteristic of bruises. Accompanied by minor or moderate pain, hyperemia, and sometimes abrasions and bruises. With hematomas, the symptom is more pronounced, and fluctuation can be detected. With sprains, tears, and ruptures of ligaments, swelling is usually more noticeable than with bruises. The pain intensifies when attempting to move or deviate the arm in the direction opposite to the injured ligament. With a complete rupture, some of the functions of the limb are lost.
Fractures are manifested by rapidly increasing swelling, deformation, loss or significant limitation of function, pathological mobility, and severe pain. In case of injuries without displacement of fragments, epiphysiolysis in children, pathological fractures, some of the listed symptoms are absent or weakly expressed, the swelling is insignificant. Dislocations are characterized by clearly visible, rapidly progressing swelling, which is complemented by severe deformation in the joint area, pain, and springy resistance when trying to move.
With frostbite, swelling affects the fingers and spreads to the hands. It can reach a significant volume, which is why the hands resemble pillows. Against the background of increasing swelling, a tingling sensation occurs, turning into a burning pain. The formation of blisters and areas of necrosis is possible, and in severe cases, some of the fingers are torn away. In patients with burns, swelling is combined with sharp pain, redness, and blistering.
Local infectious processes
Swelling, rapidly increasing twitching pain, cyanosis, hyperemia are the main symptoms of all forms of panaritium. In patients with superficial forms of the disease, swelling of the finger is local, minor or moderate. In deep forms of felon, the swelling is significant and extends beyond the finger to the hand. A more rare lesion of the fingers is chinga, a disease that occurs in people who cut up the carcasses of marine animals. Most often the proximal joint of the finger swells.
Boils and carbuncles appear on the shoulder, forearm, and less often on the back of the hand - where there are hair follicles. The swelling in these pathologies is limited; a dense bluish-purple formation with one or several yellowish areas in the follicle zone is detected. With abscesses, the purulent focus is larger in size, and the edema covers a significant part of the segment. Cellulitis does not have clear boundaries; following pus, swelling spreads along the limb.
With infected wounds, the edges and nearby tissues swell, serous and then purulent discharge appears. Erysipelas is characterized by pronounced swelling and the presence of a clearly defined red spot, reminiscent of a geographical map. The appearance of swelling and other symptoms is preceded by fever; in severe cases, disturbances of consciousness and delirium are possible.
Severe swelling is accompanied by purulent lesions of bones and joints - purulent arthritis, osteomyelitis. Pathologies are characterized by intense twisting, tearing, twitching pain, local hyperemia and hyperthermia, and a sharp limitation of movements. Fever and severe intoxication are noted.
Swelling of the hand
Joint diseases
Local swelling is observed in all forms of arthritis. The severity of edema, as a rule, correlates with the severity of the process and intensifies during periods of exacerbation.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
There is symmetrical damage to the joints of the fingers and hands. The swelling is combined with transient or permanent stiffness, redness, and limitation of movement. - Gouty arthritis.
Manifestation of the disease with symptoms of polyarthritis in the fingers is more common in women. In young people, damage to the elbow, wrist, and shoulder joints is possible. The rheumatoid-like form occurs as oligo- or monoarthritis of the fingers. Typically a rapid increase in edema, sharp pain, dysfunction, general hyperthermia. - Psoriatic arthritis.
The shoulder joints, small joints of the hands and fingers suffer. The onset may be acute or gradual. Patients complain of swelling and pain in the affected joints. The pain syndrome intensifies at rest, at night, weakens with movement, throughout the day. Local swelling and purple-bluish skin color are visually determined. - Infectious arthritis.
It is provoked by viral and bacterial infections. With a viral infection, volatile arthralgia and transient edema are observed. Gonorrheal arthritis typically involves the elbow joint and hands. In the syphilitic form of the disease, the fingers are affected. - Occupational arthritis
. Pain and swelling are detected in the most loaded joints; the location of the lesion depends on the profession. Typists, pianists, and office workers experience swelling in their finger joints. Builders and loaders are often concerned about pain, swelling, and limited movement in the shoulder joint.
Deforming arthrosis is chronic. Swelling of the hand occurs some time after a decrease in resistance to stress, discomfort and pain. In the post-traumatic form of the disease, a connection with a previous injury (dislocation, fracture-dislocation, periarticular fracture) is revealed. In idiopathic arthrosis, there are no obvious causes; a history of joint overload is possible.
Vascular lesions
Swelling of the arm due to thrombosis of the vessels of the upper limb occurs below the location of the thrombus. Accompanied by a feeling of fullness and painful heaviness, intensifying with palpation and lowering the hand. Upon examination, tissue compaction and a purplish-bluish tint of the skin are revealed. Numbness, crawling, and decreased sensitivity are possible.
Lymphatic edema of the arm can be detected in patients who have undergone a mastectomy with removal of regional lymph nodes. Sometimes swelling develops against the background of defects of the lymphatic system, scars after burns, postthrombophlebitic syndrome, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis. At the initial stage, swelling appears in the evening and disappears on its own during the night. Then the swelling becomes permanent, combined with tissue compaction. A distinctive feature of edema due to lymphedema is a dimple that does not disappear for a long time after pressure.
Other reasons
Other conditions that cause swelling of the hands include:
- Erythromelalgia.
Attacks occur suddenly, are provoked by compression or overheating of the limb, and are accompanied by severe pain, swelling, intense hyperemia, and an increase in the local temperature of the fingers and toes. All symptoms disappear within a few minutes, sometimes several hours. - Heart failure.
At first, the swelling is hidden and manifests itself as an increase in body weight. In the final stages, swelling of the legs, arms, and face is observed in combination with ascites, hydropericardium, and hydrothorax. - Kidney diseases.
Swelling is observed in the morning, with prolonged hanging of the arms downwards. At first they are hardly noticeable, identified by the difficulties when trying to remove the wedding ring from the finger. Subsequently they become more obvious. They are distinguished by their softness, wateriness, combined with a yellowish coloration of the skin.
We save ourselves from alcoholic edema with medicines
It is advisable to use pharmacological drugs with a diuretic effect in case of severe edema and as an emergency aid . For example, when an important event is coming up, and there are obvious traces of yesterday's drinking on the face, swollen feet do not fit into shoes.
The most severe swelling does not appear from strong drinks - vodka, tequila, whiskey. Beer retains fluid in the body best. There is little ethyl alcohol in it, but it is dissolved in a large volume of water. A certain amount of it is excreted in the urine, but most of it penetrates into the soft tissues . Especially if salted fish or chips are used as a snack for beer. Since you can relieve swelling after alcohol using medication, what pills to take:
- Veroshpiron;
- Trigrim;
- Diacarb;
- Hypothiazide.
It is strictly forbidden to take the popular and cheap diuretic Furosemide (Lasix). The above diuretics are potassium-sparing, that is, they do not remove potassium, which is vital for the cardiovascular system. And Furosemide flushes it out of the body, which often leads to cramps in the leg muscles.
The optimal single dose of potassium-sparing diuretics for swelling on the face and body is 1/2 tablet. If you take more, there is a high likelihood of even more severe and dangerous dehydration . Combining diuretics with Hydrovit or Regidron will help avoid loss of electrolytes. One packet of drugs contains all the minerals and glucose necessary to improve physical and mental performance.
Diagnostics
Orthopedic traumatologists are often involved in determining the cause of hand swelling. If indicated, patients are referred to surgeons, rheumatologists, vascular surgeons, and other specialists. The diagnosis is made based on the results of the following procedures:
- Questioning, physical examination
. The specialist determines the circumstances and time of swelling, identifies other symptoms, and monitors the dynamics of the disease. Evaluates the localization, prevalence, severity of edema, range of motion in joints, color, density, tissue temperature. - Radiography
. Prescribed for injuries, joint diseases, and some purulent processes. Allows you to confirm the presence of fragments or displacement of the articular ends of the bone, inflammatory and degenerative changes. - Ultrasonography.
It is carried out to confirm thrombosis, determine the condition of venous and lymphatic vessels, and assess the prevalence of purulent processes. - Other imaging techniques
. In doubtful cases, MRI is performed for a detailed study of soft tissues, and for the study of hard structures. - Laboratory research
. Tests help detect signs of inflammation, markers of rheumatic diseases, and renal dysfunction.
Pressotherapy of hands
Getting rid of edema effectively and safely
Excellent blood thinner, hot wet or dry steam removes excess water from soft tissues. Therefore, if there are no problems with the hearts and blood vessels, it is worth visiting a bathhouse or sauna. Under light blows of a birch or oak broom, blood begins to circulate faster . The body is cleansed of toxic breakdown products of ethyl alcohol, and the restoration of tissues damaged by it begins.
If the bathhouse is prohibited, or it is not possible to visit it, it is advisable to take a contrast shower . And then prepare a healthy tea with a mild diuretic effect. How to remove swelling after alcohol using herbal infusion:
- pour 5 rose hips and juniper berries into a thermos, a tablespoon of corn silk, pour in 2 cups of boiling water. After a couple of hours, cool, strain, drink throughout the day;
- pour 0.5 teaspoons of bearberry, oregano and milk thistle into a ceramic teapot, pour in 1.5 cups of water. Filter after an hour, drink in small sips in two doses.
Such home remedies perfectly calm and at the same time tone, normalize sleep, and improve digestion . It is also useful to do light exercises, take a walk in the nearest park, visit a swimming pool, and, with the proper skills, perform several yoga asanas.
to avoid eating foods rich in salt and spices during the day This is fast food, semi-finished products, smoked meats. You need to eat cereal porridges, clear soups, fresh vegetable salads, sweet and sour fruits and berries.
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
General recommendations include placing the limb in an elevated position. In case of traumatic injuries, the arm should be fixed with a splint or bandage, cold should be applied, and the victim should be given an anesthetic. For joint diseases, local medications with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects can be used. The presence of rapidly growing swelling and intense pain is grounds for immediate contact with a specialist.
Conservative therapy
In case of injuries, the injury site is anesthetized, the arm is straightened or reduced, and a plaster cast is applied. For burns and frostbite, dressings are performed. The treatment regimen for diseases accompanied by hand swelling may include the following methods:
- Protective mode
. The patient is advised to limit the load on the arm. Orthopedic devices are used according to indications. - NSAIDs
. They are used for joint diseases in the form of topical agents, tablets or injections. Reduce the severity of pain. Eliminate inflammation and, as a result, swelling of the hands. - Glucocorticoids
. Blockades with hormonal drugs are performed for joint damage. Indications are intense pain, active inflammatory process, which is not relieved by other medications. - Vascular agents
. Angioprotectors, phlebotonics and antispasmodics are recommended for diseases of the veins and lymphatic vessels. - Physiotherapy
. To reduce pain, relieve inflammation, and improve blood circulation, medicinal electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, UHF, mud therapy, and lymphatic drainage massage are prescribed. - Physiotherapy
. Special exercise therapy complexes are used during the rehabilitation period after injuries, and for diseases of blood vessels and joints. Therapeutic exercise is supplemented with massage and manual therapy.
Surgery
Taking into account the characteristics of the pathology that causes swelling of the hands, the following surgical interventions can be performed:
- Injuries
: osteosynthesis of the humerus or forearm bones, open reduction of dislocations of the shoulder and elbow joint, opening of hematomas, excision of areas of necrosis during frostbite, plastic surgery for burns. - Infectious processes
: opening of felon, boil, carbuncle, abscess or phlegmon, arthrotomy, sequestrectomy. - Joint diseases
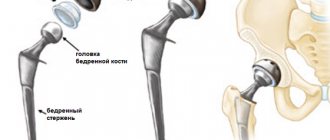
: arthroplasty, arthrodesis, endoprosthetics. - Vascular pathologies
: regional thrombolysis for venous thrombosis, tunneling for lymphedema, lymphovenous shunting.
After operations, painkillers are prescribed, antibiotic therapy is carried out, and rehabilitation measures are carried out using physiotherapeutic techniques.
How to remove swelling after alcohol without medications?
The morning after a party or family feast with alcohol, a person’s blood is thickened and circulates poorly through the veins and arteries. The heart has difficulty pumping it, while at the same time experiencing an acute deficiency of minerals, especially magnesium and potassium. It is required to thin the blood and at the same time provide the body with microelements . The organs of all vital systems will work at full capacity, blood circulation and metabolism will accelerate, and soon the swelling of the eyelids, ankles, and fingers will disappear. How to relieve swelling after alcohol:
- use home canning . The brine after fermentation (not pickling!) of cucumbers and tomatoes is saturated with useful minerals and other bioactive substances. Just one glass is enough to restore water and electrolyte balance in the body;
- drink mineral or table waters . Not all of them are equally useful. For example, in the pharmacy assortment there are 3 types of Essentuki water - No. 2, No. 4 and No. 17. The latter contains excess salts, so after consuming it the swelling will become even more intense. But Essentuki No. 2 and No. 4, like Narzan, Nagutskaya, Smirnovskaya, Slavyanovskaya, are very useful in a hangover state - they will replenish the reserves of microelements and reduce blood viscosity.
Such methods of restoring water and electrolytes will help not only eliminate edema, but also other symptoms of alcohol abuse. Excessive fluid accumulation often provokes compression of nerve endings and increased intracranial and blood pressure. Redistributing fluid using brine or mineral waters will quickly get rid of headaches, muscle pain, and attacks of nausea. After eliminating the mineral deficiency, the hands stop trembling finely, and objects no longer appear double before the eyes.
What are the causes?
Identifying the onset of development of elephantiasis in the hands allows you to prescribe the most effective treatment. This mechanism can be triggered by various factors, which are often interrelated. Among the most common factors leading to the progression of arm lymphostasis are the following:
- surgery to remove lymph nodes;
- negative effects of radioactive radiation in the treatment of oncology;
- serious injuries accompanied by damage to lymph nodes and blood vessels;
- fractures with a violation of the integrity of bone tissue in the form of comminuted fractures;
- infectious diseases and pathological neoplasms in the lymphatic system.