One of the most severe injuries to the pelvis is considered to be a fracture of the acetabulum. Incorrectly provided assistance or treatment can cause disability for the victim. According to statistics, from 15 to 20% of all pelvic injuries occur in the acetabulum. After an injury, assistance is often forced to be provided by a person unrelated to medicine, which requires maximum responsibility. Anatomy will help you find out what is special about this part of the pelvis.
The structure of the acetabulum
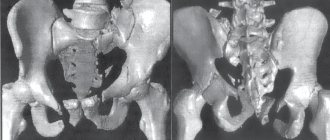
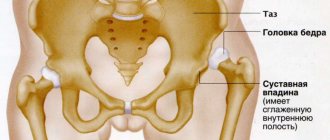
Translated from Latin, the acetabulum is translated as vinegar and has the shape of a hemisphere with a recess inside. The surface is covered with cartilage and resembles a crescent, for which it received the name of the same name. Since the socket is involved in the formation of the hip joint, there is an articular lip to increase its surface. This part of the pelvis is formed by the bodies of the pubic, ilium and ischium bones, which fuse in humans by the age of 16.
There are front and rear walls, as well as columns and a vault of the same name. Together with the head, the socket forms the hip joint, covered with a capsule that secretes synovial fluid. Due to the columns, the joint acquires additional strength.
Drug therapy
Drugs used in first aid:
- Painkillers; in case of severe pain, narcotic analgesics (morphine and analogues) can also be prescribed;
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents;
- Antibiotics (prevention of bacterial complications);
- Blood transfusion according to indications;
- Vitamin therapy;
- Infusion therapy.
Subsequently, to accelerate regeneration, the following is prescribed:
- Vitamins and minerals;
- Physiotherapy;
- A certain diet.
Causes of damage
The factors that result in an acetabular fracture can be very diverse. A strong mechanical force must be applied to the human skeleton, causing the bone to break. The impact can be direct with a direct or lateral impact to the hip joint. The head of the femur hits the bone with force, causing damage. Direct impact occurs as a result of:
- car accidents;
- falling from a height;
- accidents at work;
- falling heavy objects onto the pelvis.
There is also an indirect mechanism of damage, which is rare. The reason is a violation of safety rules when engaging in heavy sports. Separately, it is worth highlighting the dislocation of the femoral head, when a fracture occurs during displacement.
Conservative approach
Do not forget that in the case of a joint, along with a fracture, there may also be a dislocation, which is reduced in the emergency department under general anesthesia.
Next, a traction procedure is prescribed, which lasts 4-8 weeks. Traction is a process in which a knitting needle is attached to the epicondyle or tibial tuberosity, from which weights of a certain mass are hung. Over time, the weights will stretch the bones to restore their correct position.
This procedure is not performed on children and elderly people; it has its own disadvantages and risks. After the end of the treatment period, the following is prescribed:
- Control x-ray;
- exercise therapy;
- UHF.
Classification
For a fracture of the acetabulum, the AO classification is used, which provides alphanumeric designations. The simplest fractures are type “A”, the more severe are “B” and the most complex injuries are designated “C”.
Damage can also be divided into the following groups:
- With simple fractures, the integrity of one part of the acetabulum is compromised. For example, a fracture of the anterior column or part of the posterior arch.
- Compound fractures are characterized by damage to multiple areas. For example, a fracture of the anterior and posterior columns, often there is a violation of the integrity of the femoral neck, dislocation. The fragments may move outside the joint.
- With transverse fractures, the fragments are displaced, which means additional complications.
- A transverse fracture of the posterior column with displacement of fragments that can damage large nerves, which leads to impaired mobility in the future, is considered dangerous.
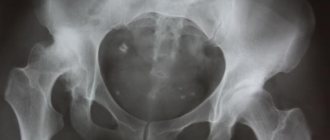
Separately, it is worth highlighting the central dislocation of the hip, in which the bottom of the socket is damaged and the articular head penetrates into the pelvic cavity. The x-ray shows the head of the femur deep in the acetabulum.
Varieties
There is a clear classification developed by a group of traumatologists to simplify the choice of treatment tactics. Using a certain algorithm, a general picture of the injury is compiled based on signs, patient descriptions and laboratory research methods. First of all, complete and incomplete intra-articular fractures are distinguished. Then, depending on this characteristic, other possible signs are considered:
- Comminuted fracture with displacement.
- With displacement of one fragment of the fragment.
- With driving in fragments.
Depending on the location, it is customary to distinguish:
- On the anterior part (ilium, anterior support, anterior wall).
- On the back (obturator foramen, ischium, posterior wall).
Depending on the nature of the injury, there are transverse, direct, bilateral and unilateral, cartilage damage or detachment, with and without displacement, open and closed.
Symptoms of damage
Immediately after an injury, a fracture of the acetabular arch or any part of it can be difficult to suspect. The following symptoms will help guide you to the right idea:
- pain in the groin or hip area;
- limited mobility of the lower limb;
- the pain becomes stronger when you try to move your leg;
- the victim is unable to walk, the same is observed if there is a dislocation.
The appearance of the victim is characteristic.
- On the side of the injury, the lower limb is slightly shorter than the healthy one, and somewhat turned outward. This occurs when the acetabulum is fractured with displacement.
- Active and passive movements are severely limited and painful.
- A person is unable to lift his leg from a horizontal surface.
- With central dislocation, movements are sharply limited, painful and springy in nature.
First aid for a fracture
Emergency assistance to the victim consists of calling the “03” service and monitoring the person’s condition until medical workers arrive.
The list of additional events:
- Limiting physical activity of the injured person.
- Providing access to oxygen.
- Use of oral analgesics (for excruciating pain). You should also notify your doctor about taking pills.
- Applying a hypothermic pack to the fracture area. The cold will minimize possible bleeding and relieve discomfort.
If there are wound surfaces, they should be covered with a sterile napkin.
It is forbidden to move the victim or change the position of the injured leg: this may worsen the patient’s condition.
Early complications of injury
The clinical picture may be supplemented by symptoms of damage to other bones or organs. In such a situation, the victim’s blood pressure drops and shock develops. After a blow or fall or accident, the following is observed:
- violation of the integrity of the pelvic organs (rupture of the intestine or bladder);
- external or internal bleeding develops;
- ruptured or pinched nerves (sciatic, superior gluteal or femoral);
- fracture or dislocation of the femur.
Such injuries only aggravate the victim’s condition and increase the pain shock.
Diagnostics
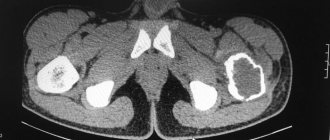
After hospitalization, the doctor needs to resolve the issue related to the diagnosis. This requires an x-ray, if possible in two projections. A plain X-ray of the pelvis is required; however, a fracture of the acetabulum without displacement is not always visible on it.
When in doubt or when there are a large number of fragments, a computed tomogram is indicated. If damage to internal organs is suspected, the doctor will prescribe an MRI. The technique allows you to diagnose a fracture of the posterior wall of the acetabulum from the anterior one. If there is no time to perform a tomogram, and the condition of the victim requires immediate diagnosis, an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs is performed.
In women, internal bleeding is diagnosed using a puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix. When receiving blood from the abdominal cavity, there is no doubt that internal organs are damaged.
What to do before the doctors arrive
With such severe trauma, the patient feels severe pain, cannot move, and may well plunge into a state of shock. There are several important maneuvers that must be done on site to alleviate the patient’s condition and avoid complications:
- Limit the patient from any movement, fix him in a lying position;
- It is necessary to apply a splint to the injured limb. To do this, you need to find something hard under your hands, about the length of your leg; for this you can use a board, a branch, a shovel, an umbrella, a broom, a mop, etc. Improvised splints are installed on both sides of the limb, one ends at the level of the groin area, the second on the other side is slightly higher at the level of the pelvic bones. The leg is wrapped on all sides with a bandage, ropes, and tapes. If there are areas where the splint is causing discomfort or pain, the leg may need to be wrapped or padded over those areas.
- Call emergency medical assistance. Upon arrival, if your splint is ready and done correctly, the patient will be taken to the hospital with it, if not, then the emergency medical team will apply their own.
- In the case of an open fracture, it is necessary to make sure that there is no external bleeding and, if necessary, stop it, remembering the difference between arterial, venous and capillary bleeding.
- Monitor the patient’s indicators, communicate with him, check his pulse and blood pressure.
Treatment
After an injury, there are two ways to deal with damage: conservatively and surgically. It all depends on the type of injury, the degree of displacement and the presence of fragments. Damage to the acetabulum can be treated conservatively, provided there is no displacement or fragments. In other cases, an operation is indicated in which the fragments are fastened with metal.
Conservative approach
Such treatment is indicated when the articular component is not affected and there is no displacement. Plaster immobilization can be used, in which a bandage is applied to the leg and waist. The duration of wearing it is at least three months, after which the rehabilitation period begins.
However, plaster has recently been inferior in treatment effectiveness to external fixation devices. It is mounted using special rods in the pelvic bones, which are fixed using metal slats. Such a device allows you to get the patient out of bed as quickly as possible, allowing him, despite the fracture, to walk. After fusion of the bone tissue of the acetabulum, the device is removed. Traction is rarely used for an acetabulum fracture due to the length of treatment and non-rigid fixation.
Drug therapy
To speed up fusion, medications are used, primarily calcium. The absorption of calcium in the body increases vitamin D, which is produced by skin cells. Doctors use the following drugs: “Calcium D3 Nycomed”, “Structum”, “Kalcemin”, “Osteogenon”. Vitamin D production is increased by ultraviolet irradiation or sunbathing.
Additionally, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are indicated. The choice of such drugs is amazing; the most common drugs are:
- Xefocam;
- Movalis;
- Revmoxicam;
- Almiral;
- Aertal.
Additionally, vascular (Latren, Tivortin, Pentoxifylline) and diuretic (Trifas, Veroshpiron) are used to prevent edema. Immediately after injury, an element of anti-shock therapy is the administration of saline solutions. The infusion volume is up to two liters, since blood loss from pelvic fractures can reach three liters. Among saline solutions, priority is given to the following drugs: Trisol, Ringer's solution, 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
In case of damage to the acetabulum, chondroprotectors and agents that restore articular cartilage become relevant. The following drugs are used: “Protekon”, “Chondroitin complex”, “Hialual”, “Mukosat”. Chondroprotective drugs are prescribed in courses for about three months; the effect should not be expected immediately, but after stopping the drug it lasts for some time.
Operation
When a displaced fracture of the floor of the acetabulum or another part of it is diagnosed, surgical intervention is indicated. The essence of the surgical intervention is to perform metal osteosynthesis. After injury, the intervention should be postponed for about 10 days. During this period, the victim goes through traumatic shock, bleeding stops, tissue swelling decreases, which interferes with the intervention.
But if you delay the procedure for more than three weeks, it will be difficult to achieve a positive result. The reason for this is callus, which prevents the normal alignment of inert tissue. Prescription of antibacterial drugs is indicated per day. Moreover, their appointment lasts two more days after the intervention.
Rehabilitation
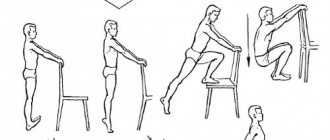
Activities designed to rehabilitate the patient can only begin several weeks after the injury. Typically this period is 7-8 weeks. In order to make sure that the healing of broken bones is proceeding normally, the specialist prescribes another x-ray procedure for the patient. It must show that callus has grown in the place where the integrity of the bones was damaged. This is a good sign indicating that healing is proceeding properly and rehabilitation of the patient can begin.
Even while under skeletal traction, the victim is advised to gradually begin to carry out simple motor movements that will involve the injured part of the body. Those. You can gradually raise the pelvis and move the limb a little. After all the obstacles to preventing normal motor activity are finally removed by specialists who have carefully studied the person’s condition, the latter must make every effort to restore full mobility.
First, for this he needs to use crutches and relearn how to stand on his sore leg. But it is necessary to completely transfer the weight of the entire body onto it very carefully and only after the patient feels that his injury is sufficiently healed and no longer brings severe pain. During the entire period of rehabilitation, the patient must be strictly under the supervision of doctors and not deviate from their recommendations, so as not to aggravate the situation and not to fracture the still weakened bones again.
Consequences of injury
With such an injury, the hip joint and its function are primarily affected. Pathological changes may develop on the surface of the joint. The femoral head or socket tissue may be affected by avascular necrosis. Coxarthrosis often develops, in which the articular cartilage is affected. Large fragments can damage the sciatic nerve. An open fracture is always complicated by infection in the wound.
When the full anatomy of the cavity is restored, the prognosis is favorable. If complications arise, the doctor takes measures aimed at eliminating them. By following all the specialist’s recommendations, complications can be avoided.
Recovery period
Recovery takes place in several stages:
- The first begins at the moment of removal from traction. Light elements of exercise therapy, physiotherapy, breathing exercises, a healthy diet and fresh air.
- The second begins 4 months or six months after the injury. Variable loading on the limbs begins, at this stage the first steps are taken after the fracture.
- The goal of the third stage (9-12 months) is complete recovery and return to the usual rhythm of life.