Coccydynia is called pain in the coccyx - this is a rather rare and not entirely studied pain syndrome, which manifests itself as constant pain in the very lower part of the spine. The pain is usually clearly localized and worsens when sitting or when putting pressure on the lower spine. This syndrome is much more common in women than in men. Typically, the cause is injury (fall) or childbirth. In rare cases, infection or tumors may be the cause. The term coccydynia has a long history as a poorly understood syndrome. At the beginning of the 20th century, this diagnosis was very popular and designated all pain syndromes in the lumbosacral spine. And, Alas, surgical treatment methods (removal of the coccyx - coccygectomy) were quite often used to treat pain syndromes in the lumbosacral region.
The results of surgical treatment were different. Then the pendulum of medical opinion swung in the other direction and, as was mainly observed in women, it began to be considered a neurosis. Due to the fact that the operation often had no effect, it was decided that the pain was psychogenic in nature and operations were stopped for a long period of time. Currently, these two extreme points of view do not exist in the medical community. It is generally accepted that coccydynia exists as a real syndrome.
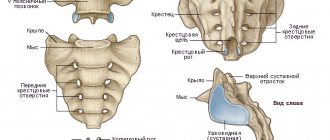
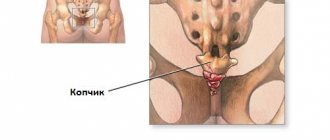
The tailbone is the lowest part of the spine. It is a vestigial tail and consists of 3-5 small bones. Essentially these are underdeveloped vertebrae connected to each other. It was initially assumed that the components of the coccyx were completely fused and devoid of any mobility in relation to each other. It turned out that the coccyx is not a single bone formation and there is a very small range of motion between its component parts due to fibrous joints and ligaments. The coccyx is connected to the sacrum by a rudimentary disc and ligaments. There is also a limited range of movement between the sacrum and coccyx. The more frequent presence of coccygodenia in women is explained by several factors: greater rotation of the pelvis and a wider pelvis, which increases the risk of injury to the coccyx.
Causes
The cause of displacement can be any injury:
- during delivery (this refers to the passage of the fetus through the birth canal, improper straining, as well as the consequence of incorrect actions of health workers);
- during a fall (in case of injury to the coccygeal area);
- impact, violation during sports activities;
- during pregnancy (depending on individual characteristics).
Sometimes a curved tailbone occurs as a congenital disorder. There are also frequent cases of such deformation after certain diseases in the pelvic organs, which are usually chronic. Even sitting on a hard chair for a long time can cause the tailbone to bend.
Types of coccyx displacement
Depending on the nature of the injury, coccyx displacement can be of different types. It happens:
- posterior (segments curve backward);
- right-handed (the bend goes to the right);
- left-sided (vertebral displacement is observed to the left);
- forward and deviated to the side.
Angular shifts usually occur after delivery. Such changes cause displacement of other vertebrae. After this, the person can no longer perform his usual work or play sports or dance as before. Some will have to give up their favorite job, others will have to give up their hobby.
Complications and consequences of a coccyx fracture
The symptoms and consequences of a tailbone fracture can vary. Among the main complications:
- inflammation due to the occurrence of a large hematoma;
- improper fusion and the appearance of severe pain;
- chronic headaches and other consequences of spinal cord displacement;
- inflammation of the nerve plexus.
If an injury is not properly treated, it will one way or another lead to far-reaching consequences.
Therefore, the doctor’s main task is to identify these likely consequences, deal with them and prescribe the correct course of rehabilitation. This article described the symptoms and consequences of a coccyx fracture in women and men. To avoid such an injury, at the first sign of a severe injury, seek diagnostics. Even if the pain and inflammation gradually recede, this may indicate that the damage will manifest itself in the future with renewed vigor. Remember this and treat your condition carefully, do not neglect contacting doctors and getting diagnosed.
Symptoms and signs
The main symptom of a displaced coccyx is severe pain at the site of deformation. It appears when:
- sitting on a hard surface;
- sudden climbs and bends.
At the initial stage, these are paroxysmal pains, which later become progressive and constant. There may be kickback to the hip and groin.
Constipation and problems with emptying the bladder also occur. When bowel movements occur, the patient also suffers from pain. This occurs due to the fact that the nerve fibers and muscle tissue, which are responsible for the functioning of the pelvic organs, are located in the tailbone area.
All existing discomfort becomes the cause of depression and anxiety. The person is often in a moodless, dejected mood.
Sometimes, the tailbone is shifted to the right or left, but the pathology does not make itself felt. It can be detected accidentally during radiography. This feature can have a negative impact during childbirth, so it is advisable to resort to treatment.
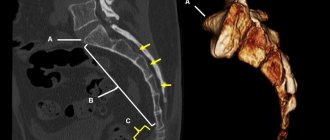
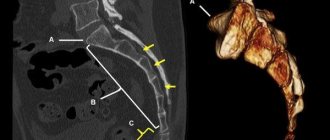
What does displacement in the coccyx and sacrum look like? This can be seen in the photo below:
Tailbone injury: basic concepts
Most often, a serious injury to the tailbone is caused by a sharp fall - in winter or during training - or by strong blows, accidents, when other injuries are superimposed on the bruise. Riding on a hard seat over potholes and rocks can also damage the integral structure of the coccyx, but this happens gradually.
Women damage their tailbone during difficult childbirth, especially if the child is large. Pregnancy itself is a factor that thins bones, so the risk of fracture or crack increases. A deformed coccyx also occurs in infants.
Coccyx injuries are classified depending on the type of violation:
- bruise of himself and nearby soft tissues, internal and external;
- dislocation and subluxation, there are anterior and posterior;
- displacement with a bend - forward, to the side, with displacement of the vertebrae in different directions;
- fractures, like any other bone structure, are divided into closed, open, displaced, fragmentation;
- damage, sprains, ruptures of the ligaments of the sacrococcygeal structure.
If there is a bruise in the lower back, hematomas, vascular hemorrhages, excision of the muscles and fat layer, and deformation of the vertebrae are possible in this area. And the symptoms of even a simple bruise are very painful. Some of them are direct pain in the area of the damaged area, while others relate to the work of various organs and systems.
- pain, even unbearable, on a constant basis, when walking or trying to change position, also during moments of laughter, sneezing, coughing;
- changes in gait, limited mobility of the hip joints;
- pain radiating to the lower extremities and unclear localization;
- hematomas, bruises and swelling.
If the coccygeal region is injured, the general condition may deteriorate, headaches, and nausea may appear as a sign of a concussion. As a rule, victims are in no hurry to go to medical institutions, hoping for self-healing.
The tailbone injuries themselves are not life-threatening, but the long-term consequences and symptoms are very frightening:
- Tumor neoplasms, fistulas, cysts, abscesses, complicated hematoma at the site of injury;
- Pain during the natural process of defecation, constipation;
- Disorder in the functioning of internal organs due to disruption of their connection with the spinal cord;
- Post-traumatic chronic pain in the area of the sacral plexus, called coccydynia, and often accompanying glutalgia - a muscular-tonic complex;
- Loss of sensitivity in the intimate area;
- Disturbance of the birth process in the female half of humanity;
- Migraines and neurological diseases as a result of pressure on the spinal cord, which, in turn, can be wedged into the brain space from a blow;
- callus, immobility of legs.
Diagnostics
Having learned about the symptoms and examined the patient, the doctor cannot clearly say that the patient has a bent tailbone. To establish a clear diagnosis, you need to undergo an examination. A specialist can refer you for instrumental diagnostics, namely:
- computer scanning;
- X-ray of the affected area from different sides;
- MRI.
The coccygeal area must first be palpated.
If the photographs show anterior angulation of the coccyx or other types of deformation that bother the patient, treatment must be resorted to.
How to Diagnose an Injury
To understand whether a patient has damage, a doctor can use several simple diagnostic methods:
- Visual inspection. There will be severe swelling at the site of injury, and some will develop a hematoma. Upon palpation, a person feels a twinge of pain.
- Radiography. It is done in frontal and lateral projections. Finding signs of a coccyx fracture using this technique is quite difficult.
- CT scan. Helps to accurately determine the current condition of bones, find confusion and cracks.
- MRI. The magnetic resonance imaging method shows not only the condition of the bones, but also the space surrounding them - blood vessels and muscles. It is this kind of examination that helps to “look” into a person’s tissues and understand whether everything is in order with his nerve fibers.
Previously, when assessing the condition of patients, the method of rectal or vaginal examination was also used. Now it is not used unless absolutely necessary, because it is associated with great discomfort for the patient.
Treatment
Only a specialist can treat a displaced tailbone; it is not recommended to take any action on your own, as you can harm yourself even more. Before prescribing therapy, the doctor studies the symptoms, causes of the disease and stage. Medicines and radical methods can be used.
Drug treatment of a bent tailbone
The doctor can prescribe a group of medications in the form of:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- vitamins (group B);
- muscle relaxants;
- antidepressants;
- other painkillers (novocaine blockades, very rarely narcotics).
In parallel with the above, the following sessions will help eliminate pain:
- massage therapy;
- osteopathy;
- manual therapy;
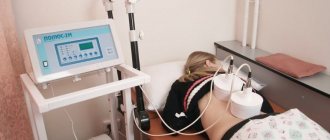
- electrophoresis.
Physical therapy is advisable, and sitting on special softening pads is mandatory.
Radical method
If the patient comes in too late, the pain is too severe and it is not possible to do anything with conservative therapy, the doctor suggests surgery. In this case, two options are implied - rhizotomy and coccygetomy.
Rhizotomy means destruction of nerve endings, after which acute pain goes away and the patient’s quality of life improves. Coccygetomy is the so-called removal of segments of the coccyx. Both the first and second options are considered very traumatic. It will take a long time to fully recover. Complications cannot be ruled out. Before deciding on any operation, you need to make sure it is appropriate. Surgical intervention can be complicated by:
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs;
- thrombophlebitis;
- addition of infection (development of phlegmon, abscess, osteomyelitis);
- impaired motor activity of the legs;
- lack of sensitivity in the groin and legs.
It is also not a fact that the operation will improve the patient’s condition.
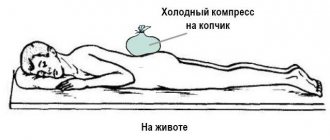
Keep in mind that in the acute phase you need to completely abandon any (even minor) physical activity, compresses, massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, exercise therapy, and taking hot baths. You should also not lie on your back. Apply ointments that warm the affected area. All corrective procedures are indicated at the time of remission. It is important that everything that happens is controlled by a specialist.
Treatment methods for the coccyx in osteopathy
Returning to a normal lifestyle after a tailbone injury, the patient hopes that the pain has gone away without a trace. But over time, he may find that some familiar movements are difficult for him. If you turn or bend over a little, the unpleasant, to put it mildly, sensation reminds you of age.
Professionals or sports enthusiasts note a decrease in flexibility and mobility of the lumbar region, and an increase in “grabbing” of the back. And my posture doesn't look the best.
Massage and therapeutic exercises bring temporary relief, while osteopathy is aimed not so much at the symptoms of injury, but at the full recovery of a person. And the pain-relieving effects occur as a natural result of treatment - when nothing hurts or bothers you.
Who and when needs the help of an osteopath for a tailbone injury?
- For fresh injuries of the coccyx. First you need to wait for the end of the acute phase of pain, healing of fractures or cracks. The osteologist examines the affected areas and assesses the extent of the disorder. Timely restoration of the coccygeal structure will help avoid further complications.
- For old pain. The patient may not know about the injury, may not remember the bruise or may not attach any importance to it, but the osteopath will certainly check the condition of the sacral area. In addition, he examines the entire body for disorders caused by coccyx pathology.
- Pregnant. A woman's body changes, and the load on the pelvis increases. In the 2nd-3rd trimester, visiting an osteopathy clinic is a wonderful opportunity to alleviate the condition and give birth without complications and interventions. The osteopath will gently and carefully eliminate injuries to the coccyx and prepare the pelvic bones for the birth process. It is especially important to undergo treatment for women with a history of coccyx injuries.
- After childbirth. Bearing and giving birth to a child is not easy for every female body. During childbirth, the tailbone may shift, and then over the years this leads to various health problems, especially if repeated births occur.
- Newborn baby. It happens that the anomalies are congenital. Damage occurs in the womb or at birth.
In his work, the doctor uses all available results of tests and examinations.
If there are doubts about the diagnosis, fear of an inflammatory or malignant process, he will additionally refer you for an x-ray of a certain area.
People are encouraged to undergo osteopathic treatment due to pain and dysfunction in the body, and neurological problems. But few people realize that these are all the consequences of a harmless bruise from a fall!
If a curved tailbone pinches nerve endings, puts pressure on the intestines, or displaces parts of the spine, the doctor must first eliminate the cause of these problems.
In response to a specific complaint, the osteopath looks for underlying damage, the root cause.
According to osteoscience, the lower vertebral process is an important element in a single structure consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The doctor pays enough attention to the sacropelvic region, adjusting its synchronization with the skull.
Important participants in this interaction are the bodily diaphragms:
- pelvic;
- sterno-abdominal;
- subclavian;
- submandibular;
- head
With a sharp bruise, reflex spasms of the whole body occur, and he cannot get out of this state on his own.
The osteologist not only corrects injuries directly in the sacral area, but also eliminates the damage they cause to the general condition of the patient. If something interferes with the free circulation of cerebrospinal fluid between the pelvis and head, stagnation occurs, which provokes:
- decreased immunity;
- pain in the head, neck;
- osteochnodrosis;
- inflammatory processes;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- numbness and cramps in the legs, etc.
Clamps in the spinal and cervical spine disrupt the blood supply to the brain, the consequences of which are oxygen starvation and intracranial pressure.
And the causes of a wide variety of diseases are in the once bruised tailbone! The patient may not notice for years that he is breathing shallowly, and only after osteopathic treatment he understands the difference.
It's like an osteopractor tunes the body's strings. Working through them from one end, he checks the sound, including the neighboring strings, along their entire length.
Complications
The consequences of coccygeal displacement can be both dysfunction of internal organs (problems with urination, defecation) and pain in the localized area, which does not make it possible to lead a full life.
Women have problems during childbirth. If a woman has previously been in an accident or had any trauma to the coccygeal area, then she must undergo an examination before giving birth. If there is a significant bend in the coccyx, the passage of the child through the birth canal may be problematic. In such cases, it is recommended to resort to caesarean section.
Symptoms of a coccyx fracture
A fracture of the coccyx vertebra manifests itself with a variety of symptoms:
- Severe pain in the injured area. It may intensify when trying to bend over or sit down, as well as with any other external mechanical impact on this part.
- Difficulty moving. Any attempt to change position will cause acute pain.
- Difficulty with bowel movements. Any tension in the pelvic area will also cause a response in the form of increasing pain.
It is important to understand that this type of injury is not immediately recognized by some people at the time it occurs. They blame everything on a severe bruise and prefer to lie down rather than see a doctor. In this case, there is a high risk of a fused or chronic fracture of the coccyx.
Prevention
For preventive purposes, you should be more careful to avoid injury.
- Follow traffic rules.
- Choose less traumatic sports, and be extremely careful during exercise.
- Avoid fights.
- Do not wear shoes with heels that are too high or unstable.
- When working at height, strictly follow safety regulations.
- Do not sit on hard surfaces.
- Move more during pregnancy, listen to the advice of your midwife and doctor during childbirth.
- Treat all diseases of the pelvic organs in a timely manner.
Conclusion
Displacement of the coccyx can be either congenital or acquired. Some people live with such an anomaly all their lives and are not aware of its presence, while others are forced to seek the help of doctors, since this defect makes them suffer from pain. At the initial stage, you can get by with painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapeutic treatment. In more advanced cases, we will talk about surgical intervention. You should not delay the pathology, since there is no guarantee that the operation will give a positive result.