A clavicle fracture is a fairly common injury that can occur at any age. Since the collarbone is a long and thin bone, a fracture most often occurs in the middle. Rehabilitation after a clavicle fracture consists of a set of exercises and physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at restoring the function of the injured arm.
Causes of fracture and symptoms that indicate it
The cause of a collarbone fracture can be a direct blow to the shoulder, for example, during a car accident, or a fall from a height onto the arm.
Symptoms of this type of damage include:
- pain in the area of injury;
- inability to raise your hand;
- the shoulder on the side of the fracture is lowered and moved slightly forward;
- Possible swelling and bruising around the collarbone.
Most often, a collarbone fracture occurs as a result of a fall on an arm or shoulder. Also, clavicle injury occurs in newborns directly during childbirth.
Symptoms of injury
When bone fragments shift during a clavicular bone fracture, the following clinical picture develops:
- Sharp painful sensations that intensify during movements of the limb;
- Swelling in the area of injury;
- Bruising if displaced bone fragments injured blood vessels;
- Changing the position of the shoulder (it lowers and moves forward);
- Hand drooping and numbness due to damage to the nerve processes;
- Impaired motor activity of the limb;
- Protrusion of the scapula on the side of the injury;
- Crepitus during palpation and pathological bone mobility;
- Bleeding and fragments visible from the wound with an open fracture.
If the bone is displaced in such a way that it damages the dome of the pleura, this leads to increased pain and breathing problems.
Recovery in case of a displaced fracture
If the injury occurs with displacement of the fragments, then surgical intervention is required. During surgery, the fragments are connected and secured with internal plates, bone implants or screws. Rehabilitation after a displaced clavicle fracture consists of three stages:
- immobilization;
- restoration of function of the shoulder joint;
- development of the damaged limb until its functions are fully restored.
First stage of rehabilitation
The first stage of recovery after a collarbone fracture lasts approximately three weeks. It begins on the second day after the injury and ends with the removal of the fixing bandage.
At this stage the following set of exercises is shown:
- The patient spreads and closes the fingers of the injured hand.
- Flexion and extension of the hand into a fist.
- The tips of each finger should touch the thumb. Repeat 10 times.
- Click each finger in turn 6-8 times.
- Move each finger in a circle in different directions.
- Flexion of the phalanges of the fingers.
- Lowering and raising the injured arm 4 times.
- Rotate the brush in a circle.
Seven days after the fracture, you can begin exercises to restore the elbow joint. The patient performs flexion and extension of the injured arm at the elbow
Second stage of rehabilitation
The second period of rehabilitation after a clavicle fracture begins after the bandage is removed. Its duration depends on the patient’s age, physical fitness, and characteristics of the fracture. This period usually takes about 15 days until the basic movements of the injured arm in different directions are restored.
Exercises for rehabilitation after a clavicle fracture at this stage aim to restore the function of the shoulder joint. Therapeutic exercise is performed simultaneously with the injured and healthy hands. Each action is repeated 8-10 times.
Set of exercises:
- The patient holds his palms on his shoulders and raises and lowers his elbows.
- The patient makes circular rotations with his elbows in different directions.
- Hands are lowered along the body. Raising and lowering straight arms with slow movements is performed.
- The patient raises his arms straight, then takes them back and lowers them.
- The patient, with straight arms, performs swing movements with one arm back, and the other forward, and then vice versa.
- The patient raises his arms up and then lowers them, holding a gymnastic stick in his hands.
- With a stick in bent arms, movements of the arms are performed in a circle in different directions.
- The patient alternately raises his hands up, holding the stick by its ends.
- The patient raises the stick above his head, then lowers it alternately on his head and behind his head.
- The victim leans forward and makes swinging cross movements with straight arms.
Third stage of rehabilitation
The main task of the third and final period of rehabilitation is the complete restoration of the function of the injured limb. The duration of this period is not limited.
A set of exercises at the third stage (movements must be repeated 8-10 times):
- The patient holds a ball weighing 3 kg with straight arms above his head, then he leans forward and, lowering his arms, pushes the ball between his legs.
- The patient makes movements in a circle in different directions with his arms extended upward with the ball.
- The patient throws and catches the ball.
- Raising your arms up and down with dumbbells of 2-3 kg.
- The patient performs circular movements in different directions, holding dumbbells in his hands.
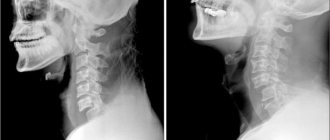
Diagnostics
In case of a displaced clavicle fracture and planning an operation, an X-ray examination, sometimes in different projections, is necessary to confirm the preliminary diagnosis. The pictures will clearly show:
- bone condition,
- shifting broken parts,
- presence and location of bone fragments.
If necessary, an additional computed tomography is performed. Having made a diagnosis based on research results, doctors decide on methods of treating the fracture.
Physiotherapeutic procedures during the recovery period
A week after a collarbone fracture, the doctor prescribes physiotherapeutic procedures. The damaged limb is exposed to a magnetic field, electrophoresis or ultraviolet irradiation.
These methods increase blood circulation in the injured area, which promotes faster bone healing. Physiotherapeutic procedures will be more effective if they are combined with exercises and massage.
Massage after a clavicle fracture
The doctor prescribes a course of massage depending on the degree of complexity of the injury. The early course begins ten days after the fracture. First, the undamaged areas near the fracture site are massaged.
After removing the fixing bandage, the massage becomes more intense, which restores the sensitivity of the skin in the area of the fracture and improves blood circulation.
Progress of the operation
For osteosynthesis, plates, knitting needles, pins, Bogdanov nails and other orthopedic structures are used. Doctors choose a specific type based on the nature of the injury. Titanium plates are most often used for clavicle osteosynthesis.
Reconstructive surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The patient lies on his back. Rollers are placed under the shoulder blade on the side of the damaged collarbone. Next, an incision is made in the skin, exposing the fracture site. Surgeons remove blood clots, apply a plate, and secure it with screws. The wound is drained and sutured, and a sterile bandage is applied on top.
Possible complications after a collarbone injury
- If the fixation bandage is not worn correctly, the pearl may be complicated by the displacement of fragments of the broken bone. To prevent this from happening, the patient must strictly follow the recommendations for wearing a fixing bandage and visit a doctor from time to time to check the condition of the injured collarbone.
- A large lump may form at the site of the fracture. Over time it decreases, but a small bump may remain.
- After surgery, you may experience numbness in the skin just below the surgical incision. After some time, this numbness goes away completely or decreases.
- Infection of the surgical incision.
- Bleeding from the wound.
- Severe pain after surgery.
- Formation of blood clots in the legs.
- Damage to blood vessels or nerves near the broken collarbone.
- Lung injury.
- Nausea after anesthesia.
- Implant rejection.
Preparation
Emergency surgical treatment is initiated when there are clear signs of damage to the neurovascular bundle (rapidly growing hematoma, disruption of innervation), or the threat of perforation of the skin or nearby vessels with nerves.
In other cases, the operation is performed as planned, mainly in the first five days from the moment of injury. The need for surgery must be confirmed. To do this, the patient takes an x-ray to determine the type of fracture, the number of fragments and their position. To assess the extent of damage to soft tissues and blood vessels with nerves, he is prescribed an MRI.
During a planned operation, the patient undergoes a standard examination, including:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- blood biochemistry;
- determination of blood group and its Rh factor;
- coagulogram;
- ECG;
- therapist appointment.
Since the operation in most cases is performed under general anesthesia, the patient must be consulted by an anesthesiologist before the operation, selecting medications and their dosage.
Features of a clavicle fracture in children
A clavicle fracture in children is one of the most common injuries. Children can get injured during active play or falls.
At two to three years of age, children often experience incomplete greenstick fractures. In this case, the periosteum remains intact and holds the bone fragments together. Parents may think that this is an ordinary bruise, since there is no displacement and the pain is minimal.
A non-displaced fracture of the clavicle in children two to three years old requires only an ordinary bandage made from wide bandages to fix the shoulder. For displaced fractures, a Deso bandage can be used for children over the age of one year. For older children who have several displaced bone fragments, a figure-eight plaster cast is recommended.
Rehabilitation of a child after a collarbone fracture in a sanatorium is carried out under the supervision of rehabilitation specialists. There they undergo physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, and children perform special health-improving exercises.
First aid
Read also: Symptoms and treatment of ankle arthrosis
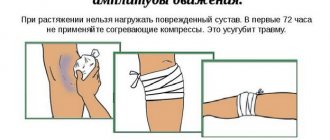
When providing first aid for a clavicle fracture, it is important to immobilize the limb as quickly as possible, thereby preventing further movement of the broken bone elements. To do this, it is necessary to bend the injured arm at the elbow and fix it in this position, hanging it with a wide bandage around the neck or tying it to the body. An improvised cushion must be placed under the victim’s armpit. After fixing the limb, the patient should be taken to the emergency room as soon as possible.
When providing first aid to a person with such a diagnosis, you cannot:
- try to set the protruding bone fragments,
- try to straighten the injured limb,
- tie it with a narrow bandage,
- pull on the sore arm.
Such a victim can only be hospitalized in a sitting position.
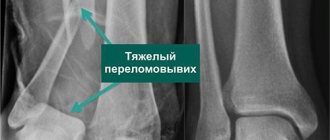
The essence of extraction
Dismantling the plates is necessary even if it is not a classic fracture, but a dislocation of the clavicle. In this case, it is most productive to use the strategy of applying a hook-shaped plate to the acromioclavicular joint.
If it is not removed in time, then the victim faces a not-so-great scenario:
- development of arthrosis in the articular area;
- formation of bone growths called osteophytes;
- damage to muscle fibers by bone growths.
All of the above provokes a pronounced pain syndrome. Treating it with analgesics without leveling the original source of the problem is an ineffective solution. The pain will return and intensify over time.
Surgeons pay special attention to patients whose professional activities are closely related to sports achievements. Such people are representatives of a group at increased risk of getting a relapse in the same place. To reduce the percentage chance of recurrence of an identical injury, doctors insist on the need to remove the metal structure immediately after confirming successful fusion. If you leave everything as it is, then if there is a second fracture, the presence of a metal fixator on or inside the bone will significantly complicate subsequent assistance. Not to mention the slowdown in new healing after surgery.
Often, metal retainers that are not removed after the scheduled period become the reason for denying a person permission to perform military service. The same implants may be a contraindication to a number of other professional activities. To solve this problem, you will have to remove previously installed parts, even if they are small in size.
For several decades, the indication for reoperation was the discovery of a fragment of a needle or drill, which was localized in the lesion.
This happened due to inaccurately carried out intervention, as well as the use of homemade devices. They were often not adapted for these purposes, being made from completely weak alloys, which were not adapted for high loads by default. When they were deformed, small particles fell between the bones, which were supposed to grow together, and injured the surrounding soft tissue, muscle fibers and even blood vessels. Damage to the latter threatens extensive internal bleeding, which is quite difficult to diagnose with the naked eye.
Those patients who seemed to have had a successful operation to install clavicular plates, but after a while it turned out that the foreign body causes significant pain, should not endure pain. Discomfort is often caused by the head of the screw or staple interacting closely with the tendons.
As soon as the tendons begin to move, even with a small action, the muscle begins to rub against the protruding part of the supporting mechanism. Most often, people with a thin physique have to deal with such inconveniences.
Also, all ladies who are planning a pregnancy and have already successfully undergone fusion thanks to the plates should have them removed before conception. This will avoid latent negative effects on the fetus.
When is removal necessary?
Treatment of clavicular fractures has long advanced, eliminating the need to wear bulky plaster casts or even uncomfortable wooden splints for a long period.
Today, surgeons around the world prefer to use lighter structures for identical purposes, be it wires, full metal plates or single high-strength screws. All of them are designed to speed up the recovery process after serious damage to the collarbone.
Some innovative techniques provide the ability to introduce stable metal structures directly into damaged bone structures. This allows you to reliably fix their position in one position, which has a beneficial effect on the speed of fusion.
But classic plates, which are sometimes installed together with adjacent screws for strength, are usually fixed over the bones. The effect from them is approximately the same. The only difference is the type of initial injury. For the convenience of traumatologists, the developers of the method have provided a separate classification for all metal fixators supplied to the medical market. They differ in size, purpose, and types of fractures of the clavicular region.
Instead of suffering with uncomfortable plaster casts that severely limit normal activities and are difficult to even wash with, patients now enjoy the benefits of high-strength plates. They have a number of advantages over outdated methods of helping victims of fractures:
- increasing the mobility of the victim;
- reduction of the rehabilitation period;
- the opportunity to return to sports activities much earlier.
But for a successful return to normal activity, even after a relatively simple clavicular fracture, you will first need to get rid of the metal assistant. Reverse intervention is especially important if, during the examination, the doctor discovers signs of a purulent process in the victim. This situation indicates the body’s inability to accept a foreign body even for good purposes, or a carelessly performed surgical intervention.
Another important reason for the need to get rid of the plate even before the time recommended by the doctor is often osteosynthesis. This is what professional terminology refers to as unsatisfactory fixation of bones, which indicates strong compression or too little pressure.
Clinical cases stand apart when the victim has an individual intolerance to the implant or an allergic reaction to its components. Here it will not be possible to conduct a full allergy test, since the body’s response may not manifest itself immediately. Because of this, neutralizing a potentially dangerous device is an emergency indication.
If we are talking about an extensive fracture, which often entails additional damage to the ligaments of the acromioclavicular joint, then here too one cannot do without installing a special plate. But usually the operation is accompanied by additional installation of screws necessary to enhance the fusion effect.
Damaged ligaments usually heal, regaining their former functionality, after about three months. It is also worth making allowance for the fact that bone structures with fragmentation versions of damage can take much longer to heal.
Once the restoration of all structures has been successfully completed, it will be necessary to get rid of the previously installed metal structure. If you ignore such a doctor’s order, the patient is likely to experience plate failure in the near future.
The outcome is explained by the fact that certain devices are designed for a strictly specified operational period. Although they can continue to perform their assigned duties longer, this will not lead to any good.
Fracture treatment
If damage occurs in which bone fragments are displaced, then treatment can be carried out conservatively or, most often, surgically. Conservative treatment is only applicable if manual reduction of the fragments can be performed. After comparing the bones, the doctor places a cushion in the armpit area and fixes the arm with a scarf or Delbe rings that pull the shoulder back. In some cases, a cast is applied.
If a large displacement occurs, then surgery is performed to fracture the clavicle, during which an osteosynthesis procedure is performed. This surgical intervention is used if there is an unstable fracture of a tubular bone or a joint is damaged. In this case, a plate can be applied to the collarbone, or the fragments can be connected using pins, screws, knitting needles, nails, screws, for the manufacture of which biologically inert materials are used. The attachment can be located inside or outside the bone.
Contraindications to exercise therapy classes
Exercise therapy after a clavicle fracture has a number of contraindications:
- Acute infectious diseases;
- General serious condition of the patient due to blood loss, shock;
- Malignant tumors;
- Foreign bodies near large neurovascular trunks;
- Severe disorders of the heart and lungs;
- Lung injury due to a broken collarbone;
- High risk of bleeding;
- Intense pain syndrome.
Planned and emergency removal
The decision on the date of the dismantling operation should be made only by the orthopedist after studying the examination results. X-rays and the patient’s current state of health are taken into account. If visualization methods of the lesion demonstrate complete and correct fusion, then the only matter left is to remove the plates with screws.
If metal structures are located in the area of important nerve endings or large vessels, it is necessary to take into account the increased risk of re-fracture in the same place after removal of the mechanism.
Medical practice has also recorded cases where victims were denied removal due to a number of serious chronic diseases. If the benefits of neutralizing the metal fixator do not outweigh the risks in chronic diseases, then surgeons will not undertake such a dangerous task. Traditionally, such manipulations are carried out as planned after a person has completed all preoperative stages with preliminary examinations. But there are a number of exceptions that require early extraction without a preparatory stage.
This concerns the migration of the retainer due to unreliable fastening. When it moves towards vital organs or large vessels, the likelihood of damage increases. Not to mention the accompanying perforation of the skin. To protect the patient from the worst-case scenario, one has to take extreme measures, carrying out radical intervention urgently.
The same can happen if the victim is found to have:
- deep suppuration;
- rejection of alloy material;
- formation of a false joint;
- absence of callus, despite all the deadlines that have passed for this.
Despite the apparent simplicity, removing the rods is a labor-intensive process that requires special skill of medical personnel.
During manipulation, the doctor must always be prepared for unforeseen situations, because the story when, when unscrewing the mechanism, the head is deformed and the splines are damaged is not such a rarity.
Due to the poor quality of medical “assistants,” a quite simple task often turns into an almost impossible one. In addition to the surgeon’s skills, special tools specifically for non-standard situations can help resolve the issue.
Rehabilitation methods
Surgical recovery is impossible without special procedures. The most effective methods of rehabilitation are exercise therapy, massage and physiotherapy - baths, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, heat therapy with paraffin, sand, steam, ozokerite, therapeutic mud, etc. The procedures prevent stagnation of blood and lymph, restore sensitivity, reduce swelling, and promote rapid healing of injury.
It is equally important to eat right, add foods high in calcium, vitamin D and C to your diet. And if the patient feels helpless and depressed, a psychotherapist talks to him.
Massage
Depending on the complexity of the fracture, massage can begin 3-10 days after the injury. This procedure increases blood supply to the damaged area, accelerating metabolism and tissue regeneration, and also restores sensitivity to the skin in case of damage to the integrity of the nerve fibers.
While the shoulder is under the bandage, only visible parts can be massaged: arm, fingers, chest, back. All movements are soft, gentle, and performed in a sitting position. Kneading, stroking, and pinching techniques are allowed. It is important that the massage is performed by a professional, otherwise the risk of displacement of fragments increases.