Advantages of treatment in our clinic:
|
Coxoarthrosis - another name for degenerative-dystrophic disease of the hip joint - is caused by the destruction of cartilage. The disease develops slowly, but you should not have any illusions in the hope of being able to cure the disease later. Arthrosis continuously progresses and causes serious limitation of joint mobility . However, it is possible to stop and even reverse the disease! Doctors at the clinic of Professor Oleg Savyak achieve success in more than 90% of cases without joint replacement.
Causes of the disease
It is not always possible to establish the causes and identify the prerequisites for the development of premature deformation of hyaline cartilage. In this case, we are talking about primary (ideopathic) coxarthrosis, which appears and progresses on its own, without visible reasons. Destructive-degenerative joint damage, formed under the influence of various external and internal factors, is called secondary coxarthrosis.
Pathology develops due to various reasons:
• Diseases of the spine and joints. These include hip dysplasia, congenital hip dislocation, flat feet, Perthes disease, curvature of the spinal column, injury due to a fall or severe bruise.
• Genetic predisposition. Coxarthrosis is not inherited, but through kinship, a child can inherit the structural features of the musculoskeletal system and cartilage tissue, as well as the specifics of metabolism.
• Violation of metabolic processes.
• Changes in hormonal levels.
• Inflammatory processes in the joint capsule (reactive and rheumatoid arthritis, salt deposition, synovitis, bursitis, tendonitis).
• Loss of bone tissue (osteoporosis).
• Diabetes.
• Irreversible age-related changes in the osteochondral structure of the joint.
• Exhaustive physical work.
• Significant overload of the joint due to professional activities or training in heavy sports.
Too little physical activity, excess weight, bad habits, prolonged stress - all this negatively affects the condition of the bone and cartilage tissue in the hip joint.
Treatment at the Savyak Clinic
The high effectiveness of treatment of hip arthrosis by our specialists is observed due to an integrated approach and an impact on the cause, not the symptoms. Therapy is divided into several stages:
- diagnosis and relief of acute pain;
- restoration of cartilage tissue using traditional and proprietary techniques;
- recovery period and prevention of exacerbations.
For treatment , manual therapy, physiotherapy, arthrotherapy, traction using special devices, and massage are used. Gentle stretching relieves joints and improves mobility. Massaging stimulates blood flow and metabolism. With the help of physiotherapy, pain is relieved and recovery processes are launched.
Give yourself the gift of health, contact Oleg Savyak’s clinic!
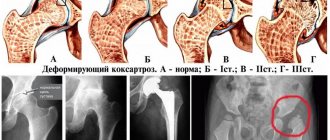
Stages of progression of coxarthrosis
There are three stages in the development of the pathology, the common symptom of which is pain in the hip joint with gradually increasing intensity. Other signs of the disease appear as the condition worsens, so over time it becomes much easier to determine the advanced state of coxarthrosis. Stages of disease development:
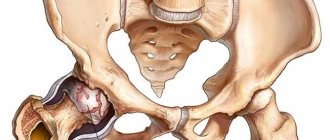
• First degree. It is characterized by an uneven narrowing of the gap between the articular surfaces and the formation of single osteophytes at the acetabulum. In this case, the neck and head of the femur are in normal condition.
• Second degree. There is a narrowing of the joint space by approximately 2 times the norm, upward displacement of the deformed and enlarged femoral head, and proliferation of osteophytes on the edges of the acetabulum outside the cartilaginous disc.
• Third degree. There is partial or complete fusion of the joint space, an enlarged femoral head, and a large number of bone growths
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint, 2nd degree
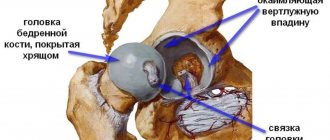
Definition of coxarthrosis of the hip joint Arthrosis is a pathology characterized by degenerative and deformational changes in the structure of tissues. Coxarthrosis, as one of the types of arthrosis, is diagnosed most often, especially in women. There are more cases of joint damage in the hip area, even if we do not take into account professional athletes who consulted a doctor. Due to the fact that coxarthrosis develops slowly, doctors’ forecasts are positive. The mechanism of the disease is the thickening of the fluid located in the joint capsule, which is why it cannot perform its job efficiently.
Symptoms The main symptom is pain. Its location may include both the groin and hip areas, as well as the knee area. The nature of the pain is ambiguous, since it depends on the stage of development of the disease. At first, discomfort occurs only during physical activity, and then becomes permanent, not going away even at rest. In this case, the location of the pain symptom becomes wider.
Classification of degrees of development
First degree The joint space becomes narrower, the neck and head of the femur are in a normal state, but growths are visible in the area of the acetabulum. Second degree On an x-ray, a narrowing of the gap becomes noticeable, the femoral head is deformed, moves upward, and increases in size. Bone growths are visible along the edges of the acetabulum. Third degree The gap narrows significantly, while the femoral head is expanded. The pain becomes constant, the muscles atrophy as blood circulation to the joint is disrupted. Shortening of the limb becomes noticeable. The goal of the therapy prescribed by the doctor is to influence the cause that led to the onset of the disease. Therapy includes:
treatment with medications (injection, local, oral); physiotherapy that affects the damaged joint. This will improve blood circulation and relieve vascular spasms. It is important to note that without the use of medications, this type of therapy is practically useless. It is also worth paying attention to shock wave therapy (the effect of waves on bone growths), magnetic therapy (impulse and constant impact on the joint); Exercise therapy to maintain mobility of the hip joint). You should not engage in heavy physical activity, as this will only aggravate the situation due to the load on the joint. However, activity cannot be completely ruled out. To compile a high-quality set of exercises, you must consult a doctor (it is important to note that the compiled set of exercises should not contain an axial load); diet. Of course, it is not capable of treating coxarthrosis, however, with this pathology, a person must monitor his weight so as not to overload the joint. It is necessary to count calories, consume more clean water, eat foods containing calcium (focus on dairy products), increase protein consumption (fish, lean meat), and also need to consume gelatin-based dishes (jelly and jellied meat) more often, since this a natural source of collagen, essential for cartilage; massage; treatment with medications. Includes both ointments and injections, which are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician. The doctor may also prescribe medications made from hyaluronic acid (they are necessary for the restoration and protection of cartilage tissue). Injections performed intramuscularly may contain chondroprotectors and anti-inflammatory drugs: “Diclofenac” (relieves pain, eliminates swelling, but the period of use should not be more than two weeks), “Artradol” (made on the basis of chondroitin sulfate. Can stop the development of the inflammatory process, restore and prepare the joint for loading. Prevents the destruction of cartilage).
Interesting
pain under the right shoulder blade from the back
lumbodynia of the lumbar region
physical therapy of the hand for Sudeck syndrome
Primary doctor: Klyuev Kirill Evgenievich
Symptoms of the disease
The presence of coxarthrosis of the hip joint can be suspected if characteristic signs and pronounced localization are present. The intensity of discomfort depends on the stage of the disease.
At first, the pathology is asymptomatic or has mild symptoms such as barely noticeable pain and slight restrictions in movement. Symptoms appear after significant physical activity, prolonged walking or prolonged standing. Localization of pain is noted in the hip joint, sometimes moving from the thigh to the knee. Unpleasant sensations disappear after rest. Occasionally there is stiffness in the joint in the morning, but in general the range of motion is completely preserved. There is no muscle atrophy or changes in gait.
Lack of treatment for a disease such as coxarthrosis of the hip joint threatens to move into the second stage. Symptoms at this stage become more pronounced: the intensity of pain increases, discomfort is disturbing even in complete rest. After physical activity, lameness may occur. In addition to the joint, pain is felt in the groin and thigh. The range of motion decreases, the person experiences discomfort during abduction and internal rotation of the hip. As a result of displacement of the head of the bone and a forced decrease in motor activity, atrophy of the muscles responsible for adduction/abduction of the hip, as well as extension/flexion, is observed. On the part of the affected joint, a decrease in the volume of the femoral and gluteal muscles becomes noticeable.
The third degree of coxarthrosis is characterized by constant severe pain that does not go away day or night. It becomes more and more difficult to move; a person is forced to use a cane or walker for support while walking. There is a sharp limitation in the range of motion, drying out of the muscles of the lower leg, thigh and buttock. Due to the weakness of the femoral abductor muscles, there is a shortening of the leg and a skew of the body towards the affected limb. A shift in the center of gravity leads to an increase in the load on the affected joint.
When extending or flexing the hip joint, while walking, you can hear crackling, crunching, or clicking sounds in it. This happens due to friction between bone growths and surfaces. Normally, this also happens, but in the case of coxarthrosis, such sounds are combined with painful sensations.
Prices
| Services list | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a traumatologist-orthopedist, kinesiotherapist, primary | 1 600 |
| Ultrasound diagnostics of 1 joint | 1 300 |
| Individual lesson with a kinesiotherapist instructor | 2 700 |
| Acupuncture | 2 700 |
| Khivamat - therapy | 2 200 |
| Shock wave therapy, 1 procedure | 2 000 |
| Manual therapy 1 department (15 min.) | 2 700 |
| Osteopathic correction | 7 500 |
| Massage of the lumbosacral spine + one lower limb (leg) (30 min.) | 3 000 |
| Kinesio taping | 1100 |
Contact us
Call now
8 (495) 803-27-45
Make an appointment through our service
Make an appointment
Depending on the stage of the disease, we choose one or more treatment methods:
Osteopathy
Soft technique of working with the spine, joints, muscles, ligaments, internal organs. Eliminates pain and starts the self-healing process.
Therapeutic massage, osteopathy, manual therapy
Helps bones and joints take the correct physiological position, relieves pain and spasms, relaxes muscles.
Acupuncture
Work on biologically active points. It affects the affected area and the body as a whole. Eliminates the cause of the disease and removes the symptoms.
In addition, according to indications, the following are used: taping, pharmacopuncture, FormTotix insoles, exercise therapy with an instructor and other methods. The choice of procedures depends on the current condition; taken together, they act faster and give a more lasting result.
osteopath services in Moscow
Complications of the disease
The progression of the disease leads to serious complications, which result in limited mobility, deterioration in quality of life, and disability. The lack of effective treatment for coxarthrosis of the hip joint or neglect of the doctor’s recommendations entails the development of the following pathologies:
• Protrusion of the acetabulum. Due to the thinning of the cartilage tissue on the articular surface, the pressure under load is distributed unevenly, and over time, bone deformation occurs. Mobility is reduced and pain is felt when moving.
• Gonarthrosis of the knee joints. Deformation of the pelvic joints and dysfunction entails an increase in the load on the joints located below, as a result, an inflammatory-deforming process occurs in them.
• Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. As a result of deterioration of local blood circulation, bone tissue begins to receive much less nutrients, which leads to its gradual death.
• Arthritis. Inflammation develops in the joint cavity, damaging the synovial membrane, joint capsule and ligaments.
• Ankylosis. With coxarthrosis, cartilage is gradually replaced by connective tissue, which is why the joint space disappears and movement in the joint becomes impossible.
• Bursitis. At the point of attachment of the tendons to the femur, calcium salts begin to be deposited, as a result of which the joint membranes become inflamed, causing severe pain on the outer surface of the thigh.
• Curvature of the spine (kyphosis and scoliosis). Forced gentle body positioning in order to reduce the load on the hip joint leads to poor posture, deformation and back pain.
• Deformation of the pelvic bones.
What is offered to patients at stage 3 of coxarthrosis?
Traditionally, in advanced forms of coxarthrosis, patients are recommended to undergo hip replacement. This is a radical way to relieve a person from pain - expensive, lengthy, and requiring long rehabilitation. One of the surgical options is arthrodesis. The articular bones are fixed with metal staples to completely immobilize the supporting anatomical structure.
After total endoprosthetics, the patient undergoes long-term rehabilitation. During this period, it is very important to follow all recommendations, otherwise there will be a need for repeated intervention. If prosthetics are contraindicated, surgeons may recommend osteotomy - temporary fusion in the desired position of artificially broken hip bones. However, there are other, more gentle options.
Even at stage 3 of coxarthrosis, it makes sense to take a course of Noltrex intra-articular injections, which will help avoid complex surgery. The drug is injected into the joint, it expands the rubbing surfaces and restores the viscosity of the joint fluid. The hip joint is again able to absorb the load, so the pain during movement goes away. After 12-18 months, the course is repeated.
Noltrex is a good alternative to joint surgery in old age