Synonyms: rheumatoid factor, RF, Rheumatoid factor, RF.
One of the main studies in rheumatology is the analysis of rheumatoid factor. RF are proteins (immunoglobulin antibodies) that are produced by the body’s immune system to destroy its own cells that it mistakenly perceives as foreign. In laboratory diagnostics, rheumatoid factor plays the role of an indicator of the inflammatory process and autoimmune disorders.
The RF test is a fairly informative test that allows one to determine the presence of autoimmune pathologies, in particular rheumatoid arthritis and Sjogren's syndrome, as well as a number of other diseases that have a non-immune etiology: chronic bacterial and viral infections, some cancers, pulmonary, urinary and hepatobiliary pathologies systems
Why do women get rheumatoid arthritis more often than men?
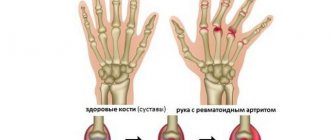
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic connective tissue disease primarily affecting small joints of the hands and feet of an autoimmune inflammatory-erosive nature, followed by destruction (destruction) of bone and cartilage tissue. A systemic form of rheumatoid arthritis affecting internal organs is common.
It has been reliably established that this is a predominantly female disease, but the exact causes and mechanisms of its development have not been established. The main causes of rheumatoid arthritis in women and men are the same; they are complicated heredity and a viral infection. But women, unlike men, have many more additional triggering factors that provoke the development of the disease. These factors include:
- Any hormonal disorders. Determined that:
- a high concentration of female sex hormones estrogen in the blood stimulates the proliferation of connective tissue, which means a tendency to progression of the pathological process and dysfunction of the limb; and yet during pregnancy, with sufficiently high estrogen levels, RA remission often occurs;
- the disease begins mainly at the age of 40 - 45 years and older, when a woman’s hormonal levels decrease and in this case hormonal imbalance is of great importance;
- endocrine diseases - diabetes, obesity, hypothyroidism increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
- Smoking leads to persistent narrowing of blood vessels, increasing the susceptibility to the development of rheumatoid arthritis.
The development of RA is also facilitated by the response of a woman’s immune system to infection:
- the female body more actively produces antibodies (immunoglobulins - Ig) in response to the introduction of infection; why this happens has not been established; at the same time, Ig class M - rheumatoid factor - is especially actively produced;
- the balance of certain types of T-lymphocytes responsible for cellular immunity is disrupted; the number of T-helpers (helper cells, T4 or CD4+, they help other cells destroy the infection) increases, while the number of T-suppressors (cells that suppress the activity of immune cells so that they do not destroy body tissue, T8 or CD8+) remains the same; this leads to the development of autoimmune reactions.
Due to the increased amount of adrenal hormone cortisol in the blood, women also experience increased (compared to men) production of cytokines (messenger molecules) that support inflammation. These are interleukin 1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). At the same time, the amount of anti-inflammatory cytokines does not increase, which helps maintain a long-term inflammatory process.
A woman can get sick at any age. In girls, adolescents and young women, the seronegative form of the disease is more common, when rheumatoid factor is not detected in the blood (RF - IgM antibodies to one's own tissues). In middle and old age, a seropositive form of the disease develops more often, in which high titers of RF are detected in the blood. But with early menopause, starting before age 50, women often experience seronegative rheumatoid arthritis.
Ways to reduce rheumatoid factor
Quit smoking
Smoking is directly associated with an increased risk of elevated rheumatoid factors and the development of rheumatoid arthritis . [R, R, , , , , , ]
If you are a smoker and have high levels of rheumatoid factor (or a family history of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis), it is imperative that you stop smoking, which can help reduce your risk of poor health and the development of autoimmune diseases.
Reduce coffee consumption
If you're an avid coffee drinker, gradually reducing the amount of coffee you drink each day, or avoiding coffee altogether, can help lower your rheumatoid factor levels and reduce your risk of rheumatoid arthritis.
Vegetarian diet
A study of 53 people found that following a vegetarian diet for one year resulted in a greater reduction in rheumatoid factor levels than an omnivorous diet. []
Yoga
One week of yoga practice led to 8% reduction in rheumatoid factor levels in a study of 64 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. []
Fish oil and olive oil
A combination of fish oil and olive oil for 24 weeks reduced rheumatoid factor levels by 30% in a study of 43 people with rheumatoid arthritis. [ ]
Vitamin E
In a study of 50 people who took 600 mg of vitamin E (dl-α-tocopheryl acetate) per day for 6 weeks, rheumatoid factor levels decreased by 44%. []
Vitamin K1
Taking 10 mg per day of vitamin K1 for 8 weeks reduced rheumatoid factor levels by 16% in a study of 64 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. []
Curcumin
In a study of 12 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, taking 1000 mg of curcumin per day reduced rheumatoid factor levels over 90 days. If you choose to supplement with curcumin, then purchase bioactive forms that have better absorption in the intestines. []
Ashwagandha, ginger, boswellia, turmeric
An Ayurvedic combination of ashwagandha, ginger, boswellia and turmeric, when used by 165 patients with rheumatoid arthritis for 16 weeks, helped reduce rheumatoid factor levels along with reduced joint swelling. []
Andrographis
Andrographis is a popular herbal supplement often used in Southeast Asia to reduce pain, inflammation and fever in Traditional Chinese Medicine and Ayurveda. In a study of 60 people with rheumatoid arthritis, taking andrographis for 14 weeks reduced rheumatoid factor levels. []
Annual wormwood (Artemísia annua)
Artemisia annua extract reduced rheumatoid factor levels in 159 people with rheumatoid arthritis (clinical study). []
Thunder God Vine (Tripterygium wilfordii)
Tripterygium wilfordii is a plant used in traditional Chinese medicine as a remedy for various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
In a meta-analysis of 6 studies and a total of 643 participants in people with rheumatoid arthritis, this plant reduced rheumatoid factor levels. []
Some aqueous extracts of this plant can have a negative effect on intestinal function, stimulate the appearance of rashes, and reduce the number of white blood cells. Almost all of these negative effects can be avoided by using safer alcohol extracts and taking them in the correct dosage. [, ]
Pine pollen
Pine pollen extracts reduce rheumatoid factor levels and other markers of inflammation in mice with arthritis. []
Resveratrol
In arthritic rats, resveratrol reduced rheumatoid factor levels by 63%. []
Alginic acid (brown seaweed)
Alginic acid, found in brown, red and green seaweeds, reduced rheumatoid factor levels in rats with rheumatoid arthritis. []
Arisema rhizomatum
Arizema rhizome is a traditional Chinese medicine herb that is used to reduce pain and inflammation. It markedly reduced rheumatoid factor levels in a study of arthritic rats. []
Symptoms
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in women
The more common seropositive form of rheumatoid arthritis (SPRA) develops gradually in women. This is a typical course of RA in middle-aged and elderly women.
The first symptoms of SPRA, when they appear, you should consult a doctor:
- morning stiffness that persists for half an hour or more;
- mild swelling and tenderness in three or more small joints;
- the pathological process begins from the metacarpophalangeal joints of the hands or from the metatarsophalangeal joints of the feet; this is confirmed by a positive transverse compression test - pain when squeezing the hand or foot.
Clear signs of SPRA are a reason to consult a doctor immediately!
Joint inflammatory processes progress, joint pain becomes constant, debilitating, stiffness in the morning increases and lasts at least an hour. New small and even large joints may be involved in the process. The lesion remains symmetrical.
A woman’s body temperature may rise, but more often it is a slight (low-grade) rise, and signs of damage to other organs and systems appear. The risk of developing contractures (reduced joint mobility) and ankylosis (complete immobility of joints) increases.
Extra-articular symptoms (not always found, but require immediate medical attention):
- rheumatoid nodules on the skin in the area of the affected joints;
- enlarged, painless lymph nodes;
- decrease in muscle volume;
- inflammation of blood vessels - vasculitis in the form of the appearance of pinpoint areas of necrosis around the nail bed;
- damage to the heart and lungs, accompanied by shortness of breath;
- kidney damage with impairment of their function;
- enlarged liver and spleen;
- low hemoglobin, anemia.
Possible complications - require hospital treatment:
- necrosis of the cartilage of joint bones - arthritis can cause such complications very often as the process progresses;
- loss of calcium in bone tissue (osteoporosis), bone fragility;
- habitual fractures, dislocations and subluxations in the affected joints;
- compression of peripheral nerves by inflamed tissues - tunnel syndromes;
- amyloidosis – deposition of amyloid in the internal organs, which leads to disruption of their function;
- exhaustion.
All the obvious symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in women
Symptoms of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis in women:
- the onset of this disease is subacute or acute with fever, malaise, weakness, headache, muscle pain;
- swelling and pain in one or two large joints (knees, elbows, etc.);
- at the beginning of the disease, the lesions are asymmetrical, but over time, symmetrical lesions of small joints may occur;
- There is no rheumatoid factor in the blood.
Other causes of elevated rheumatic factor values
The cause of an increase in the concentration of rheumatoid factor in the blood, in addition to the classic version of rheumatoid arthritis, can be many other pathological conditions:
- Acute inflammatory diseases (influenza, syphilis, infectious mononucleosis, bacterial endocarditis, tuberculosis, viral hepatitis);
- A wide range of chronic inflammatory processes localized in the liver, lungs, musculoskeletal system, kidneys;
- Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disease that affects connective tissue and involves the exocrine glands (tear, salivary glands - primarily) into the process. Sjögren's syndrome is also characterized by corresponding symptoms: dryness of the mucous membranes of the eyes, mouth, external genitalia, suffering from the respiratory system, cardiovascular system, and kidneys;
- Felty syndrome, which is a special form of RA, characterized by an acute onset with a decrease in the number of white blood cells in the blood - leukocytes (leukopenia);
- Still syndrome (Still syndrome) is a form of juvenile (childhood) rheumatoid arthritis, the symptoms of which coincide with those of Felty syndrome, but differ in the indicators of a general blood test - the number of leukocytes is increased (leukocytosis);
- Scleroderma;
- Hyperglobulinemia of various origins;
- B-cell lymphoproliferative diseases (myeloma, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, heavy chain diseases);
- SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus);
- Sarcoidosis;
- Dermatomyositis;
- Surgical interventions;
- Oncological processes.
Obviously, the list of conditions that can cause an increase in the concentration of rheumatoid factor is not limited to rheumatoid arthritis alone.
In addition, it should be borne in mind that this indicator naturally increases in older people (60-70 years old), as well as when using certain medications (methyldopa, anticonvulsants and contraceptives), therefore it should be considered specific and especially significant for diagnosis inappropriate.
However, the treating doctor will figure it out, and our article is intended for people trying to independently interpret the results of biochemical studies. After all, it happens that upon hearing information about high numbers of some kind of analysis, especially suspicious citizens fall into panic or (even worse) begin to show initiative and be treated with various dubious means.
Stages
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
There are 4 clinical stages of the development of rheumatoid arthritis in women:
- Initial
– lasts for 6 months, the first signs are somewhat erased, but remain constant; sometimes there is an acute onset; - Early
– the development of pathology in the first year of the disease, the symptoms appear clearly. - Expanded
– the first two years of the disease, the signs are bright, the course is progressive, possible impairment of joint mobility. - Neglected
– more than two years, symptoms of joint deformation and persistent impairment of limb function appear, which becomes a cause of disability.
From stage to stage, there is a clear tendency for arthritis to progress in the absence of treatment. Therefore, it is very important to promptly identify the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in women and immediately begin treatment.
How to prepare for research
Basic rules of preparation:
- Blood is donated from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach; before the test you must refrain from eating for 8-12 hours.
- Do not drink any drinks (coffee, tea, etc.). Before the analysis, you can only drink clean water.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking for 24 hours before blood collection;
- Do not eat fatty, spicy, smoked, or other “heavy” foods the day before the test.
- Be sure to inform your doctor about the drugs you are constantly using, as they may affect the test result.
Diagnostics
The following diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis in women exist:
- Clinical
: characteristic symptoms of RA. - Laboratory
:- general blood test - acceleration of ESR, decrease in hemoglobin;
- biochemical analysis - the appearance of C-reactive protein (CRP) - a sign of inflammation;
- immunological analysis - the presence in the blood of rheumatoid factor, antibodies to peptides containing the amino acid citrulline (ACCP), cytokines IL1 and TNF-alpha. Women's blood is also tested for hormones to rule out diseases that support the autoimmune inflammatory process.
- Instrumental
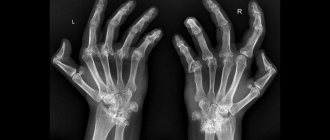
:- X-ray – signs of progressive arthritis and joint damage;
- Ultrasound - signs of damage to articular and periarticular tissues;
- MRI – detection of articular changes in the pre-erosive period, already 4 weeks after the onset of the disease.
Normal rheumatoid factor levels
The normal level for rheumatoid factor varies depending on the reagents used in different laboratories, but generally the normal value should be less than <14 IU/mL (or <20 IU/mL, depending on the laboratory). [,,]
If you believe your rheumatoid factor levels are elevated, tests for certain diseases or conditions may show false readings.
Rheumatoid factor may interfere with the following laboratory tests:
- Malaria (false positive) []
- HIV (false positive) []
- Hepatitis C (false positive) []
- Antibodies to cardiolipin (false positive) []
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (falsely increased) [, , ]
- Cytokines including IL-1-beta, IL-4, IL-6 and IL-8 (falsely elevated). [ ]
Treatment
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women
If signs of rheumatoid arthritis appear in a woman, treatment should be prescribed immediately after diagnosis, taking into account the data of the examination. Prescribed:
- a diet with sufficient animal protein and calcium - dairy products, lean meat and fish, vegetables, fruits, cereals; spicy foods and sweets are excluded;
- correct daily routine with alternating sleep and wakefulness, eliminating stress;
- drug therapy and traditional methods of treating rheumatoid arthritis in women;
- physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy (physical therapy), massage;
- methods of gravitational blood surgery - hemosorption, plasmapheresis;
- orthopedic correction methods;
- surgical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women.
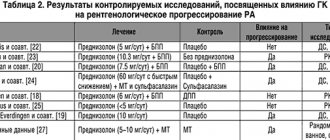
Drug therapy
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women is carried out comprehensively, with the appointment of symptomatic and basic therapy. Drugs of these two groups are prescribed simultaneously:
- symptomatic remedies can quickly alleviate a woman’s condition by eliminating swelling and pain; are prescribed in the shortest possible courses;
- basic drugs suppress the mechanism of disease development; they have been accepted for years.
Symptomatic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women
To reduce the most severe manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis, medications from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are primarily prescribed. Most of them eliminate tissue swelling and associated pain. One of the first and most effective NSAIDs is Diclofenac. It is prescribed in the form of injections, rectal suppositories, oral tablets, ointments and gels. The disadvantage of the drug is side effects: gastric ulcers and decreased blood clotting.
More modern drugs of this group - Nimesulide, Meloxicam, with high efficiency, have almost no such side effects.
Symptomatic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women
Medicines from the group of glucocorticoid hormones (Betamethasone, Prednisolone, etc.) relieve swelling and pain in arthritis even better. But their use in women is associated with the risk of stimulating the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1 and TNF-alpha, so drugs of this series are prescribed with caution, only when indicated and in short courses. They also have many serious side effects.
As soon as the pain decreases, symptomatic therapy is removed. In order to reduce the dosage of drugs from these groups, they are often prescribed in combination with folk remedies and homeopathic medicines:
- celery juice
- prescribed 20 ml three times a day 30 minutes before meals as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent; course of treatment 1.5 months; - Goal T
is a homeopathic drug, prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections, lozenges and ointments; relieves joint inflammation and pain.
Only a doctor can prescribe folk and homeopathic remedies. Taking them on your own is absolutely ineffective; moreover, it can accelerate the progression of the disease.
Basic therapy
Basic therapy drugs are also divided into two large groups - synthetic and biological. Synthetic ones include Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine, Lkflunomide. They suppress the increased reactivity of the immune system and have an anti-inflammatory effect. Most often, the time-tested Methotrexate is prescribed, but at the same time the content of folic acid in the body decreases, so it must be prescribed simultaneously with Methotrexate.
Biological basic drugs include drugs that specifically suppress educational cytokines. These drugs are especially effective in the treatment of female forms of rheumatoid arthritis, since cytokines are the main cause of a long-term inflammatory process. The use of Infliximab and Adalimumab, drugs containing antibodies to TNF-alpha, is especially effective in women. If IL-1 cytokines predominate in a woman’s blood, then Anakinra, which contains antibodies to this cytokine, is prescribed.
Additional therapeutic procedures
These methods include:
- physiotherapeutic procedures
– enhance the effectiveness of drug therapy in women suffering from arthritis; - plasmapheresis and hemosorption
- used for severe rheumatoid arthritis in women to cleanse the blood of toxic products; - Exercise therapy and massage
prevent the development of severe ankylosis (immobility of joints); courses are conducted only as prescribed by a doctor and under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor; doing exercises on your own can cause irreparable harm to the body; - orthopedic correction methods
- the use of special devices that hold the limb in the correct position, as a result of which the process of deformation of the limbs is stopped; - surgical operations
- endoprosthetics (in case of a high degree of damage to the joint, replacing it with an artificial one).
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women in our clinic
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women in the clinic
At the Moscow clinic “Paramita” they approach the treatment of female forms of rheumatoid arthritis with special care. To do this, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out, identifying hormonal disorders and concomitant diseases that contribute to the development and maintenance of the autoimmune inflammatory process. Correction of these disorders is necessarily part of the complex therapy of a woman suffering from rheumatoid arthritis.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
The doctors of our clinic have at their disposal a wide range of the latest European and traditional oriental healing methods. In our practice we use:
- drug therapy, combining the administration of the most effective modern drugs, medicinal herbs and homeopathic remedies; this allows you to quickly relieve pain and significantly reduce the drug load on the patient’s body;
- physiotherapeutic procedures - their skillful combination with drug therapy according to modern regimens leads to a rapid improvement in a woman’s condition;
- kinesitherapy, taping, exercise therapy and massage courses are selected strictly individually, preventing the development of ankylosis and joint deformities;
- PRP therapy is a unique modern method of stimulating the regenerative abilities of tissues by introducing the patient’s own platelets, processed using a special technique;
- reflexology (RT) - influence on acupuncture points (AP) on the human body, reflexively connected with various organs and systems; our specialists have been trained in RT in China and Tibet, they are proficient in all methods of RT - acupuncture, cauterization with wormwood cigarettes, acupressure, etc.; in skillful hands, the effectiveness of RT can be equal to the effectiveness of drug therapy;
- pharmacopuncture – introduction of modern medicines into AT; one of the most effective ways to treat RA.
This approach to the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women allows patients to constantly be in a state of remission. They regularly undergo courses of maintenance therapy in our clinic, lead an active lifestyle, forgetting about painful exacerbations and the prospect of disability.
How to achieve lasting remission
In order to forget about exacerbations of rheumatoid arthritis, you need to:
- Healthy food;
- move more, do exercise therapy, swim, walk;
- get rid of stress, overload at work and at home, heavy physical work;
- no smoking;
- promptly identify and treat hormonal disorders;
- regularly carry out courses of maintenance treatment prescribed by your doctor.
Rheumatoid arthritis in women is treated at any stage. The specialists of the Moscow Paramita clinic know this well.
Literature:
- Nasonov EL, Karateev DE, Balabanova RM. Rheumatoid arthritis. In the book: Rheumatology. National leadership. Ed. E. L. Nasonova, V. A. Nasonova. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media; 2008. pp. 290–331.
- Folomeeva O. M., Galushko E. A., Erdes Sh. F. Prevalence of rheumatic diseases in adult populations of Russia and the USA. Scientific and practical rheumatology. 2008;46(4):4-13. DOI:10.14412/1995-4484-2008-529.
- Leandro G, Mangia A, Hui J, et al. Relationship between steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gastroenterology 2006;130(6):1636-42.
- Rubbia-Brandt L, Quadri R, Abid K, et al. Hepatocyte steatosis is a cytopathic effect of hepatitis C virus genotype 3. J Hepatol 2000;33(1):106-15.
- Hezode C, Roudot-Thoraval F, et al. Different mechanisms of steatosis in hepatitis C virus genotypes 1 and 3 infections. J Viral Hepat 2004;11(5):455-8.
Themes
Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 04/14/2020 Date of update: 03/12/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 4.67 / 5 (3)