Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease of unknown etiology that affects the joints and internal organs. It usually affects people over 40 years of age, and women are three times more likely to develop the disease. The main danger of arthritis is that as a result a person may partially lose mobility and even remain disabled. That is why it is very important to promptly recognize the symptoms of this disease, which usually begins with the joints of the fingers.
Why does rheumatoid arthritis develop?
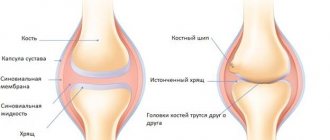
The disease belongs to the category of autoimmune disorders, which are associated with the improper functioning of the immune system, when it perceives the cells of its own body as foreign and begins to attack them.
The exact causes that trigger the pathological process are still unknown; the disease usually occurs suddenly, but there are a number of factors that can trigger its development.
- Age.
In older people, arthritis develops more often, since over time the cartilage wears out, metabolism and blood circulation deteriorate, and hormonal changes occur in the female body, which negatively affect the condition of bones and joints. - Mechanical damage.
One of the causes of the disease is previously received bruises, cracks, fractures and other injuries. Over time, the tissues heal, but the strength of the joints decreases, which can eventually lead to rheumatoid arthritis. - Image of activity.
The disease is considered occupational for athletes, seamstresses, artists and other people whose hands are constantly under tension. - Genetic factors.
According to research, people whose relatives suffered from joint diseases are more likely to develop similar ailments. - History of infectious diseases.
Rheumatoid arthritis often develops as a complication of infection with staphylococci or streptococci, as well as a number of other diseases: sore throat, ARVI, lupus erythematosus, gout, tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus. - Allergic reactions.
Allergy sufferers are more prone to joint disease than people who do not suffer from all kinds of allergies.
In addition, rheumatoid arthritis can be triggered by excess weight, smoking, decreased immunity, frequent colds and even regular psycho-emotional stress.
Video - Rheumatoid arthritis: symptoms, signs, treatment
Causes
The impetus for the development of this disease may be:
- Genetic predisposition. If blood relatives have rheumatoid arthritis, the risk of its occurrence increases up to 4 times.
- Infectious agents. The trigger for arthritis can be rubella, herpes, cytomegalovirus, influenza, or exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
- Injuries. Intense sports, wearing uncomfortable shoes - all this leads to an imbalance of loads on the arches.
Arthritis symptoms
The disease is characterized by several functional classes, each of which is characterized by varying degrees of loss of joint function. In this case, certain changes occur in the joint, on which the clinical picture of the disease depends.
| Function class | Signs |
| I | In the first functional class, self-service, non-professional and professional activities are completely preserved. The person feels virtually no discomfort. The only sign by which the development of rheumatoid arthritis can be determined is stiffness of movement, which manifests itself in the morning (for example, a person cannot perform simple actions: turn the door handle, etc.). It goes away very quickly, so almost none of the patients turn to specialists. |
| II | Retained: self-service, professional activities, limited: non-professional activities. At the second stage, the signs of the disease become more pronounced. There is pain and swelling in small joints, and stiffness becomes more prolonged. |
| III | Saved: self-service, limited: non-professional and professional activities. If the patient has not been prescribed appropriate treatment, subluxations occur in the joints, as a result of joint deformation, as well as the formation of multiple erosions against the background of progressive osteoporosis. The pain intensifies, the skin turns red and becomes hot. Movements are constrained, and the symptoms do not go away until the person takes the appropriate medications. |
| IV | Restricted: self-service, non-professional and professional activities. In advanced forms of arthritis, the joints begin to fuse together (bone ankylosis), and the fingers lose motor function. The patient is unable to perform simple activities. After the fingers, the pathological process affects other, larger joints. |
In addition to the above symptoms, there are so-called systemic manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis, which distinguish it from other joint diseases (for example, arthrosis).
- Rheumatoid nodules. Dense formations in the tissues under the skin, usually located in the elbow, outer forearm and other places that are often subject to injury (occurring in 20-50% of patients).
- Sjögren's syndrome. Drying of the mucous membranes (eyes, mouth, nasopharynx).
- Cutaneous vasculitis (ulcerative necrotizing vasculitis, nail bed infarctions, digital arteritis, livedoangiitis)
- Vasculitis of other organs
- Neuropathy (mononeuritis, polyneuropathy)
- Pleurisy (dry, effusion), pericarditis (dry, effusion)
- Eye damage (scleritis, episcleritis, retinal vasculitis)
In any case, you should not engage in self-diagnosis or self-medication - only a specialist can determine the presence of rheumatoid arthritis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of arthritis
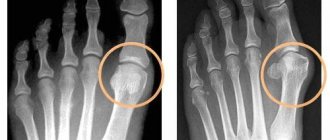
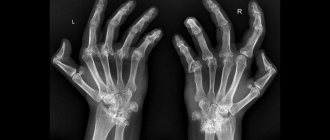
Diagnosis of arthritis includes a series of tests and studies. In a general urine test for this disease, protein is detected, in a general and biochemical blood test - signs of anemia, increased ESR and C-reactive protein content. One of the most accurate markers of the disease is positive rheumatoid factor (detected in 70-90% of cases). In addition, patients undergo radiography of the affected joints, which makes it possible to determine the location and specificity of the pathological process.
Prognosis for patients
According to statistics, an average of 9 months pass from the development of arthritis to the moment of diagnosis and prescription of therapy (this is due to the absence of pronounced symptoms in the first stages). But even in such cases, strict adherence to doctors’ recommendations allows us to achieve, if not complete recovery, then stable remission.
Even in old age, patients who have received appropriate treatment can take care of themselves and even engage in work.
Causes of hip arthritis
Purulent arthritis of the hip and other joints can be a complication of injuries, wounds, diagnostic punctures of the joint, and operations that result in direct infection of the joint cavity. In other cases, septic coxitis can develop when a purulent focus breaks through from adjacent tissues (perphlegmon, osteomyelitis, etc.) or metastatic infection of the joint cavity from distant inflammatory foci (furunculosis, tonsillitis, otitis, pneumonia, etc.). In addition to infectious arthritis caused by nonspecific pyogenic flora, there are specific coxitis associated with tuberculosis, brucellosis, gonorrhea, and syphilis.
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Treatment of joint diseases is a complex process that includes taking medications, proper nutrition, physical therapy, performing appropriate exercises, etc.
Medications used to treat rheumatoid arthritis include the following:
- To reduce joint pain, NSAIDs are used, which have a good symptomatic (analgesic) effect, but do not affect the progression of joint destruction, the prognosis of the disease and can cause severe adverse reactions (AR) from the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system. To reduce the risk of ADR the use of NSAIDs in RA should be limited as much as possible.
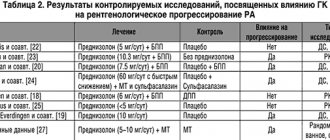
- Treatment with glucocorticoids (GC). Recommended in combination with synthetic disease-modifying anti-inflammatory drugs (DMARDs). Methotrexate (MTX) is the first-line drug for the treatment of RA with proven efficacy and safety. The use of GCs in RA should be limited to strict indications and carried out by rheumatologists. DMARD therapy should be administered to all patients with RA without exception and prescribed as early as possible (within 3-6 months from the onset of symptoms of the disease).
- Genetically engineered biological products (GEBP). These include TNF-a inhibitors (infliximab - INF, adalimumab - ADA, etanercept - ETC, certolizumab pegol - CTZ, golimumab - GLM), anti-B cell drug - rituximab (RTM), costimulation blocker of T - lymphocytes - abatacept (ABC) and interleukin 6 receptor blocker – tocilizumab (TCZ).
- During treatment, the effectiveness of therapy should be carefully monitored (every 1-3 months), and a treatment regimen should be “selected” depending on the activity of the disease ;
The effect of DMARDs and biologically active drugs on the progression of joint destruction should be assessed every 6-12 months in early RA and every 12 months in advanced RA and taken into account when choosing therapy, regardless of its clinical effectiveness
. - When choosing therapy with DMARDs and GEBD, it is necessary to take into account the duration of the disease (< 6 months - early stage; > 6 months - advanced stage) and the presence of unfavorable prognosis factors (rheumatoid nodules, vasculitis, Felty's syndrome, positive results of determining RF and ACCP, as well as increase in ESR and CRP) .
Systemic antibiotics. If the disease is the result of a bacterial infection, treatment uses systemic antibiotics, usually from a number of penicillins and macrolides. In addition, when treating rheumatoid arthritis, the following recommendations should be followed:
- during the period of remission, perform exercises prescribed by your doctor daily;
- minimize the load on affected joints, do not lift heavy objects;
- sleep at least eight hours a day;
- adhere to the recommended diet without taking breaks;
- drink enough fluid (1.5-2 l) per day;
- if there is no temperature and on the recommendation of a doctor, treatment with electrophoresis, ultrasound, quartz treatment, as well as massage can be used.
In difficult cases, when conservative treatment does not produce results, patients are advised to undergo endoprosthetics. This operation involves replacing joints with prostheses that are developed taking into account the physiological characteristics of a particular person.
After surgery and a course of rehabilitation, the patient can return to a full life, restore motor function and forget about the severe pain that characterizes the last stage of arthritis. Disadvantages of endoprosthetics: a fairly large number of contraindications, some restrictions on activity (in particular, a decrease in arm span).
Treatment of hip arthritis.
Pharmacotherapy is carried out taking into account the etiology of coxitis and may include the use of NSAIDs, specific chemotherapy (for tuberculous arthritis), antibiotic therapy (for infectious arthritis), etc. Intra-articular injections of corticosteroids are performed according to indications.
For purulent coxitis, a series of therapeutic punctures, lavage of the joint with antiseptic solutions, and flow-through drainage of the joint are performed. After relief of acute manifestations of arthritis of the hip joint, massage, therapeutic exercises and swimming, and physical therapy are prescribed). To facilitate movement, it is recommended to use canes, crutches, walkers and other devices.
If attempts at conservative treatment of arthritis are unsuccessful, in case of chronic pain and persistent limitation of joint function, the issue of surgical intervention is decided. Forecast and prevention of arthritis of the hip joint
The outcome of arthritis can be either mild stiffness or complete ankylosis of the hip joint. A complication of purulent arthritis can be infectious-toxic shock or sepsis. Timely and complete treatment allows you to minimize dysfunction of the hip joint and prevent the development of osteoarthritis.
Folk recipes
Traditional recipes for the fight against rheumatoid arthritis can be used in combination with conservative therapy and taking into account the characteristics of the body (allergic reactions to individual ingredients, etc.).
Potato
Raw potatoes have an anti-inflammatory effect, so they are often used in the treatment of various diseases, including joint diseases. Potatoes can be used to prepare both means for internal use (infusion) and for external use, that is, compresses and rubbing.
1. To prepare the infusion, you need to take a raw potato, grate it and pour a glass of kefir. Take according to the following regimen:
- the first ten days every day;
- the second ten days every other day;
- the next ten days - every two days.
The entire course lasts two months, after which the pain syndrome disappears, but over time a relapse may occur, so preventive therapy is sometimes recommended.
2. In order to make a compress, you should chop a potato, put the resulting pulp in a gauze bag and place it in boiling water for a few seconds. Transfer it, without wringing it out, into a piece of natural fabric, wrap it and apply it to the sore joints at night, wrapping it in polyethylene and insulating it well. Apply the compress every day for a week.
Apple vinegar
One common alternative recipe for treating arthritis is apple cider vinegar. Drink a teaspoon diluted in a glass of water three to five times a day before meals. If you have stomach problems, the dose should be reduced by half. The course lasts from two to four weeks.
You can make compresses from the vinegar solution to reduce pain. Take a tablespoon of 6% vinegar and dilute it in half a liter of hot water. Soak a piece of cloth in the solution, wrap it around the affected areas, wrap it well and hold until the compress has cooled.
Bay leaf
Take half a pack of bay leaves, place in a suitable saucepan, pour in 300 ml of boiling water and boil for five minutes. After this, close the lid tightly and leave for three hours. Filter well, drink the entire broth at night, repeat the procedure for three days in a row, and you need to constantly prepare a new portion. After a week, repeat the course again, after which the pain and other symptoms of arthritis should disappear. Repeat the preventive course after a year.
Pine decoction
Remedies made from pine needles have no side effects and are not addictive, so they can be used for a long time. Such remedies effectively relieve symptoms of the disease, reduce pain and inflammation. For preparation you will need the following components:
- 40 g pine branches;
- 1 tbsp. onion peel;
- 2 tbsp. rose hips;
- chopped garlic clove.
Pour all the ingredients into 2 liters of water, boil for half an hour, leave in a warm place for 24 hours. Strain well and drink throughout the day, but not more than one liter per day. For severe pain, it is also recommended to take baths with a decoction of pine needles.
One of the most important conditions for the normal functioning of joints is proper nutrition. The menu for patients with arthritis should include fermented milk products, protein (boiled or steamed lean meat and fish), fresh fruits, cereal dishes, fresh vegetables, and herbs.
Fresh or frozen berries (lingonberries, black currants, sea buckthorn), freshly squeezed juices from vegetables and fruits: carrots, beets, cabbage, etc. are considered healthy. To improve the taste and healing effect, you can add honey to them.
Today, rheumatoid arthritis is not at all a death sentence for patients. With appropriate treatment and following the recommendations of doctors, even people with advanced forms of arthritis can lead a full and even quite active life for many years. How to test for worm eggs, see the link.
Using orthopedic shoes
To find out what you can do to get relief from rheumatoid arthritis, talk to your doctor. Perhaps, in addition to complex therapy, he will recommend wearing orthopedic shoes. The latter performs a number of useful functions, namely:
- reduces pressure on inflamed joints;
- relieves stiffness of movements;
- normalizes blood circulation;
- prevents swelling in the affected joints.
Orthopedic shoes used for rheumatoid arthritis have a wide toe box and do not squeeze the toes. It is made to order, taking into account the characteristics of a particular person’s feet. Natural materials are used (leather, suede, nubuck).
To buy a special pair in Krasnodar, contact TD “Standard”. You can also get a free consultation with an orthopedist here. To make an appointment with a doctor, leave a request on our website or call the numbers indicated on the main page.