Causes of arthritis (knees, shoulders and fingers)
There are three main groups of arthritis: independent forms of arthritis, traumatic arthritis and arthritis associated with other diseases. Arthritis can develop slowly and gradually (chronic forms) or suddenly and suddenly (acute forms). The exact causes of the independent disease arthritis can be difficult to establish.
The cause of the development of the inflammatory process in the joint can be local or general infection, trauma, allergies, autoimmune disorders, metabolic disorders, hormonal disorders, etc. However, the cause of some severe inflammatory joint diseases is still not clear enough. Factors contributing to the development of arthritis are hypothermia, physical overload of the joint, and hereditary predisposition:
Each type of arthritis has its own cause, the primary treatment should be aimed at eliminating it. Symptoms of arthritis can also vary depending on the form of the disease and its type, but joint pain is an inevitable accompaniment of any arthritis. Arthritis is often accompanied by fever, swelling and redness in the joint area, impaired motor function of the joint, weakness and weight loss, and morning stiffness. As the disease progresses, the pain becomes more intense and greatly exhausts the patient. At the same time, pain in arthritis is spontaneous, most intense in the second half of the night and in the morning, and decreases after movement.
Up to contents
Arthritis of the fingers: symptoms and treatment
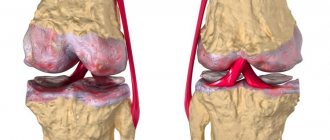
Hundreds of thousands of people on Earth suffer from arthritis, a painful disease of the musculoskeletal system, which dates back to the 5th century BC. described by Hippocrates. Under the name “arthritis,” experts traditionally understand a whole group of diseases that affect the joints and are inflammatory in nature. Moreover, the inflammatory process sooner or later covers all elements of the joint: hyaline cartilage, internal synovial membrane, joint capsule (bursa) and other parts.
What is finger arthritis
There are several types of arthritis, differing in cause:
- rheumatoid (autoimmune disease caused by a malfunction in the immune system);
- infectious-allergic (reactive, etc.);
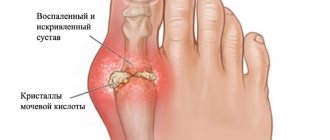
- gouty arthritis (associated with general metabolic disorders);
- traumatic (developing due to mechanical damage);
- osteoarthritis (a very common degenerative disease with an inflammatory component).
All types of arthritis are dangerous due to their destructive effect directly on the musculoskeletal system, as well as the involvement of other, sometimes vital, organs in the disease process: heart, kidneys, eyes.
In addition to etiology, arthritis is divided according to the location of inflammation. A common disease is arthritis of the fingers. This is a peripheral type of arthritis because it affects small joints - metacarpophalangeal and metatarsophalangeal.
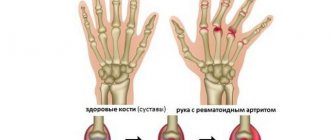
Arthritis of the finger joints is typical, for example, of rheumatoid arthritis. In this case, the joints are affected symmetrically - this is considered one of the brightest, diagnostically significant signs.
It has been noted that women suffer from arthritis of the fingers much more often than men, according to various sources - 2-4 times. This is probably to some extent due to the fact that the fairer sex devotes much more time and effort to small, monotonous work, leading to abrasion and inflammation of the joints of the fingers: sewing, embroidery, cleaning and cutting food when cooking, typing on the keyboard.
Another significant factor that increases the incidence of hand arthrosis is a woman’s hormonal background. Thus, the development of arthritis is influenced by a deficiency of estrogen, which plays an important role in bone and joint balance. This happens during menopause (menopause).
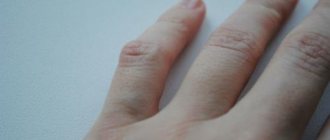
As a rule, finger arthritis begins with inflammation of the inner lining of the joint. Then the arthropathy expands and captures more and more new “territories”: the joint capsule, cartilage tissue. It reaches tendons, ligaments and muscles, then leads to bone damage. The patient suffers from pain and stiffness (glove symptom), and the finger joints become swollen and deformed, turning into ugly bumps.
Untreated arthritis progresses steadily and can become chronic. Inflammation can spread to more and more areas, depriving a person of everyday skills, the ability to perform everyday activities, as well as professional duties. The inevitable outcome may be loss of ability to work. Therefore, it is important to begin prevention and comprehensive treatment of hand joints as early as possible.
Symptoms of arthritis in the fingers
The symptomatic picture of arthritis of the joints of the hands consists of the following signs:
- pain, and if at first it occurs during movements, then later it torments the patient even at rest;
- discomfort and stiffness in the affected joints of the hand;
- limited mobility, stiffness in the hands, as if they were wearing a narrow glove, especially in the morning;
- reaction to changes in atmospheric pressure, weather changes, dampness;
- local increase in temperature (an indicator of inflammation);
- redness of the skin;
- swelling;
- crepitus – characteristic sounds (creaking, crunching);
- deformation of fingers (curvature, lumps, knots)
In addition to general symptoms, additional ones may be noted: weakness, fever, rash, damage to other organs.
Symmetrical deformations of the joints – “walrus flippers” – are considered specific to rheumatoid arthritis of the hands. The hands become like a spindle. There is dizziness, pain in the eyes, chest pain, a feeling of numbness in the fingers, and body weight drops.
If arthritis has a gouty basis, salt deposits form near the joints in the form of nodes - tophi. Attacks most often occur at night, after a heavy dinner or drinking alcohol.
Osteoarthritis is characterized by specific Heberden nodes.
With arthritis caused by psoriasis, nails peel, fingers swell, and become thick. The pain is usually not too severe and only torments the patient in the morning.
Infectious arthritis involves the presence of symptoms of intoxication of the body - nausea, vomiting (more often in children), chills.
Reactive arthritis is a very common pathology of the finger joints with uneven tissue damage. The first signs are similar to a common cold, which is expressed by malaise, high fever, and headaches. Pain in the fingers themselves is usually tolerable. Often accompanied by inflammation of the genitourinary system, frequent urges, and pain when urinating. Affects the eyes and often provokes conjunctivitis.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of “arthritis of the finger joints” is made based on the patient’s complaints, medical examination, and the results of laboratory and hardware tests.
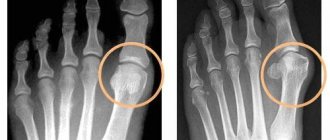
The mandatory method is radiography. It's still an informative and accessible way to get the data you need. The x-ray is taken in two projections and shows the varying degrees of destruction of the finger joints due to arthritis.
X-rays show porosity of bones and joints (osteoporosis), a decrease in the joint space, defects (erosions) on the articular surfaces, and the intercartilaginous space becoming overgrown with fibrous or bone tissue (ankylosis), leading to loss of motor function.
In addition, x-rays allow you to see dislocations and subluxations of the joints, which may indicate chronic arthritis.
In addition to radiology, the doctor may prescribe arthroscopy, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, as well as ultrasound of the joint.
Blood tests make it possible to evaluate the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), the level of leukocytes (white blood cells indicating the presence of inflammation), and hemoglobin. In addition, it may be necessary to identify acute phase indicators, and if rheumatoid arthritis is suspected, rheumatoid factor.
If gouty arthritis is diagnosed, tests for uric acid in the urine and blood are ordered.
Treatment for finger arthritis
If your fingers hurt, you should first contact your local physician, who will conduct an initial examination and prescribe basic tests.
Then you may need to visit a rheumatologist, phthisiatrician, infectious disease specialist, as well as additional studies. Complete information about the pathology in the joints of the fingers will allow the specialist to select a treatment complex that will help avoid the irreparable consequences of arthritis. The doctor must take into account the etiological factor.
You will have to undergo treatment for a long time. First, you need to adjust your diet and nutrition system (read about the diet for arthritis of the fingers below). It is necessary to protect against hypothermia of the hands, to exclude labor associated with constant microtrauma to the fingers (chemical agents, work with a vibrating tool).
The bulk of treatment consists of medications
purposeful action.
- To eliminate pain, swelling, and inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used, in the form of tablets, injections, as well as external preparations - ointments, gels, creams.
- Since treatment is usually long-term, histamine receptor blockers and proton pump inhibitors may be prescribed simultaneously with NSAIDs to protect the stomach.
- Vasodilator drugs in courses - to improve blood supply and nutrition of organs.
- Chondroprotective agents containing chondroitin and glucosamine are designed to help restore damaged cartilage tissue. Long-term course admission is required.
- Corticosteroids, including intra-articular - in severe conditions and ineffectiveness of NSAIDs.
- Antibiotics (penicillins and macrolides) - to destroy pathogenic bacteria in the case of infectious arthritis or purulent form of arthritis.
- Vitamins, restorative medications, dietary supplements with brewer's yeast and calcium.
Physiotherapy for arthritis of the fingers is an integral part of the treatment complex and involves the use of methods based on natural physical factors.
Physiotherapy for arthritis of the hands allows you to obtain the maximum therapeutic effect with minimal, gentle stress on the body. Its significant advantages are accessibility and compatibility with various therapeutic agents as part of complex treatment, gentle effect on the body, long-lasting effect, absence of side effects.
The main goal of physiotherapy for arthritis of the fingers is to increase the functional activity of the joint and relieve pain.
Physiotherapy can significantly improve the quality of life and well-being of arthritis of the fingers. It must be taken into account that not all methods are applicable in the acute stage, so consultation with a doctor is necessary.
The following physiotherapeutic methods are popular and effective:
- Pulsed magnetic field therapy (magnetotherapy). Activates microcirculation and blood supply to joints with nutrients. Helps remove inflammation and decay products. Suppresses autoimmune reactions. Reduces pain, swelling, inhibits the processes of cartilage degeneration. Increases vascular permeability and drug absorption - procedures can be carried out after applying the ointment (magnetophoresis). Improves mobility. It is convenient because you can take courses right at home, using portable magnetic therapy devices.
- Ultraviolet irradiation (UVR). Reduces sensitivity in the affected area, eliminates pain. Promotes the synthesis of vitamin D3 in the body, which is necessary for the absorption of calcium, which is important for the musculoskeletal system. Stimulates metabolic processes in the joints of the fingers.
- Electrophoresis is the introduction of drugs into the thickness of the muscles through the skin using an electric current. Accelerates blood flow in the joints of the fingers, relieves inflammation, swelling and pain. Eliminates cramps and spasms. Usually has a prolonged therapeutic effect.
- Phonophoresis is an analogue of electrophoresis, only the therapeutic agent is administered using a sound wave. Enhances the effect of pharmaceuticals, stimulates joint restoration.
- Laser treatment. Aimed at relieving inflammation and pain, improves tissue restoration of the fingers. Not used for severe arthritis.
- UHF is the effect on joints of ultra-high frequency waves. The method helps get rid of pain, inflammation and swelling. Contraindicated in hypertension.
- Acupuncture (reflexotherapy). The method is based on reactions to a stimulus - inhibition and excitation. Needles are inserted into bioactive points on the fingers. The procedure makes it possible to relieve pain and improve muscle tone. As a rule, it is not prescribed to children and very elderly patients.
- Ultrasound. Increases the absorption of hormonal ointments and other external agents. Contraindicated for angina pectoris and ankylosing spondylitis.
- Balneotherapy - water procedures, therapeutic baths and baths (radon, salt, naphthalan, herbal, hydrogen sulfide, iodine-bromine). They improve blood circulation, metabolic processes, tissue trophism, stimulate regeneration, reduce inflammation and pain. Particularly effective in the early stages of arthritis. Often prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis, recommended as part of spa treatment in Sochi, Evpatoria, Pyatigorsk.
- Mud therapy. Wraps, applications, baths have a thermal and mechanical effect. Nourishes tissues with beneficial minerals and bioactive substances, helps eliminate inflammation and persistent pain. The method is well suited for gouty and infectious arthritis of the hands.
- Paraffin wraps. Usually used as auxiliary methods. The paraffin is melted in a water bath and cooled to a tolerable temperature. The joints of the fingers are coated with paraffin mass or paraffin “cakes” are placed on them, and the top is wrapped with polyethylene and soft cloth. Blood circulation improves and pain decreases. Not used for osteoarthritis.
- Massage and manual therapy. Recognized, popular and very effective methods of the treatment complex. For arthritis of the joints of the hands, local massage is necessary - it increases muscle strength, strengthens muscles, relieves spasms, and accelerates the blood. Pain sensations become weaker.
Exercise therapy and arthritis
Exercise therapy for arthritis, as well as for its prevention, can be very effective in strengthening muscles and joints and preventing the development of arthritis of the hands.
It is necessary to do exercises during the remission phase, when there is no pain or swelling. The maximum benefit comes from a specially designed exercise system recommended by the attending physician. Physical education helps improve blood circulation and innervation of joints, improve motor skills, and prevent adhesions and ankylosis.
Each exercise must be performed 4-5 times; you cannot act “through pain.” Rotations in the wrist joints, squeezing and unclenching of the fingers, and flexion of the wrists can be the most universal and useful.
It is useful to “knock out a fraction” with your fingers on a flat table surface, roll a ball in your palms, and finger a rosary.
You can clasp your hands and lift them up, turning the back of your hand towards the ceiling. If you have mastered light exercises, it’s time to start moderate strength loads, adding exercises with a wrist expander.
Please take into account that therapeutic exercises for the fingers should be carried out systematically and should not be abandoned even if the condition improves.
Diet and arthritis
The correct diet for any type of arthritis, including arthritis of the fingers, involves minimal salt intake, even elimination. In addition, you should forget about fried, salty, fatty, smoked, pickled and spicy foods, sweets and baked goods, carbonated drinks, alcohol and coffee. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of baked goods and sweets, replace red meat with poultry. For gouty arthritis, table No. 6 is prescribed, excluding beans, chocolate products, red wine and some other foods.
But whole grain cereals, fruits and vegetables, baked lean fish and meat, cheeses, cottage cheese, other protein dairy products, foods rich in calcium and omega acids are welcome and will be very useful for joints with arthritis of the fingers.
A balanced diet helps normalize weight, which is important for joint diseases.
To help a professional treatment complex for arthritis of the joints of the hand and fingers, proven folk recipes may come in handy.
An alcohol tincture of bird cherry bark, white acacia, and lily flowers applied to the affected areas helps relieve pain.
Compresses made from onions, ground into a paste, warm up and increase local blood flow. You can mix honey with vodka, soak a cloth and apply it to your fingers.
Many arthritis patients respond well to a homemade cream made from honey and egg yolks, which should be rubbed into sore fingers and hands.
Tea drinks made from chamomile, lemon balm, lingonberries, rose hips, and currant leaves have a beneficial general strengthening effect.
Treatment of arthritis pain
Treatment for arthritis is long-term, takes more than one month and requires compliance with all medical prescriptions. The sooner you contact a competent specialist, the higher the likelihood of recovery or a significant reduction in relapses. In the acute period, when the pain is severe, it is necessary to avoid direct stress on the joints of the arms and legs. But with your doctor’s permission, you can engage in swimming and light warm-up so as not to lose shape and skills.
To get rid of joint pain, your doctor may recommend taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as part of complex therapy for the treatment of arthritis. After the acute period of the disease and reduction of signs of inflammation, physiotherapy is used: ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, massage, exercise therapy.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery or endoprosthetics are recommended.
Up to contents
Treatment of arthritis of the finger joints
Treatment can be carried out therapeutically or surgically. In the initial stages of the development of the disease, complex conservative treatment of the disease can achieve high effectiveness. All medications and additional treatments must be prescribed after a thorough examination to completely eliminate the possibility of an incorrect diagnosis. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, since the symptoms of arthritis in the joints of the fingers can be confused with the clinical picture of other diseases. Medications are also prescribed based on the individual characteristics of the patient, the stage of development of the disease, and the degree of joint damage.
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints, so antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are necessarily prescribed for its treatment. During an exacerbation, it is imperative to relieve the inflammatory process and pain. To restore cartilage tissue, chondroprotectors are prescribed. These medications are very effective, but their use must be long-term and consistent.
Massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, mud therapy, traditional medicine can be used as additional methods that increase the effectiveness of the main course of treatment. They are always assigned individually.
Prevention of arthritis
Prevention of arthritis comes down to avoiding and eliminating all possible triggering factors. A healthy lifestyle, weight control, a balanced diet, avoidance of excessive alcohol consumption and regular preventive examinations with a doctor will significantly reduce the likelihood of developing arthritis, and following all the doctor’s recommendations in the early stages of the disease will significantly increase the likelihood of recovery or significantly reduce the likelihood of relapses.
Up to contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.