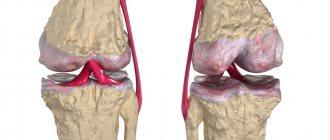
Joint health and mobility are related to a person’s diet. If you feel pain, stiffness or tightness, or hear cracking joints when moving, it means that the body lacks the building components of cartilage tissue. But a lack of glucosamine and chondroitin in foods is not always accompanied by severe symptoms. We may not know that there is anything wrong with our joints.
Why do we need glucosamine in food?
what to replace it with and how will it help in the fight against arthritis, arthrosis and osteochondrosis?
Glucosamine and chondroitin in foods: what are they?
Glucosamine
– a natural aminosaccharide, a supplier of substances for the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans in chondrocytes.
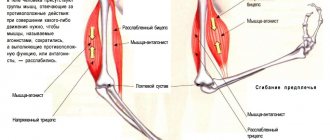
It is involved in the construction of tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. Chondroitin
is a connective tissue polysaccharide that normalizes the structure of articular cartilage. Both chondroitin and glucosamine are found in foods and in the human body.
At a young age, enough of these substances are produced to meet all the body’s needs, but after 30-35 years their production decreases. We are experiencing an acute shortage, which peaks at 50-60 years of age.
Glucosamine and chondroitin are found both in foods and in the human body.
Cartilage diseases and what does glucosamine have to do with products?
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, 97% of patients aged 60 years complain of acute pain in the joints when walking
. However, not only the elderly are susceptible to joint diseases - even young people face the problem. This occurs due to an acute lack of glucosamine in food.
Who is at risk?
- Overweight people.
- People with a sedentary lifestyle. For example, programmers who work at the computer all day.
- Athletes or people who engage in intense physical activity. This includes those whose work involves stress on the joints (miners, builders, loaders).
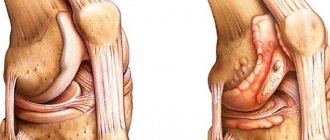
Due to the deficiency of glucosamine and chondroitin in foods, cartilage tissue is not restored, metabolism in the joint capsule slows down and worsens. This is the main reason for the development of arthritis, arthrosis and osteochondrosis.
. A person is bothered by clicking or crunching sounds when bending the limbs, pain, stiffness, and a reduction in the range of motion. These symptoms may appear and disappear after a short rest, but the joint continues to degrade - the cartilage is slowly and imperceptibly destroyed, its structure changes, and bone growths appear. As a result, the pain becomes chronic; just getting up from the couch is already difficult and painful.
By consuming products containing glucosamine, a person can slow down degenerative changes in cartilage tissue, and therefore save joints
.
Why are glucosamine and chondroitin needed in foods?
Glucosamine in foods and supplements has anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties. It relieves pain and swelling in the joints, relieves inflammatory processes, and eliminates pain in all parts of the spine. In addition, glucosamine in food regenerates damaged areas, stimulates the synthesis of chondroitin, and improves the lubricating properties of synovial fluid.
Scientists have found that both chondroitin and glucosamine in products have a positive effect on the cardiovascular, endocrine, reproductive and other systems of the body. An adult needs 800-1200 mg of chondroitin and 1500 mg of glucosamine per day.
In general, products containing glucosamine can increase cartilage density and prevent wear and tear in all joints.
Other sources of vitamins and nutrients
If a person is unable to include enough of certain vitamins and nutrients in their food, then supplements may be taken to correct the deficiency. But changing your diet or taking nutritional supplements or vitamin complexes must be agreed with your doctor. A healthy diet requires a wide range of nutrients and vitamins and provides the opportunity to achieve and maintain a normal body weight and provides sufficient energy and vitality to perform daily physical activities. In addition to eating a balanced diet, there are several other aspects of self-care that can help you maintain and maintain a healthy diet in the long term.
Drink plenty of water
It is vital to drink plenty of water and is part of a healthy diet for the whole body, which consists of approximately 60% - 70% water. Drinking water allows nutrients to reach vital organs, eliminate waste products, and helps protect joints and organs.
Water is also important for the spine and back. For example, intervertebral discs are composed primarily of water (at birth, the discs contain about eighty percent water, but as we age, the water content of the discs decreases). Therefore, sufficient regular hydration of the body with water also plays a role in keeping the intervertebral discs healthy. As a general rule, drinking at least 8 large glasses of water every day is recommended as part of a healthy diet. It's also important to drink water every day, not just when you're thirsty.
Drinking enough water also helps in maintaining an optimal weight or achieving weight loss when needed.
Exercise regularly
Getting enough exercise is important for many reasons. When it comes to your back, exercise provides double the benefits, helping you recover faster and preventing pain from recurring. Movement through carefully selected exercises stimulates the flow of nutrients into the spinal structures, which helps the regeneration process. For example, physical activity causes the intervertebral discs to swell with water and then squeeze out water, a process that is necessary to facilitate the exchange of nutrients between the discs and other structures of the spine.
If there is little physical activity and light exercises are not performed, then the intervertebral discs are deprived of the nutrients necessary for full functioning. Targeted selection of an exercise program must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist (physical therapy doctor) - and this is an important part of almost any method of treating back pain. Most exercise programs include a combination of stretching, muscle strengthening, and low-intensity aerobic exercise. For people who do not have back problems, exercise is also important to reduce the risk of developing back problems in the future.
Avoid smoking
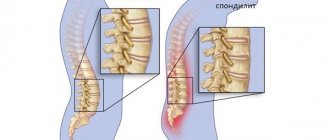
There are certain substances that are harmful to the body, and it is necessary to minimize the risk of exposure to these substances in the body. Smoking, in particular, is harmful in many ways. There is now good evidence that smoking damages the vascular structures of the discs and joints of the spine, leading to lower back pain. There are even studies that have shown a clear cause-and-effect relationship between smoking and the development of spondylosis and lower back pain.
In addition, nicotine disrupts the process of bone tissue consolidation after spinal fusion surgery by inhibiting bone tissue regeneration. Therefore, if an operation such as spinal fusion is planned, the patient must quit smoking so that regeneration is sufficient.
Avoid excessive alcohol consumption
Alcohol acts as a sedative, but can cause feelings of depression in chronic pain. In addition, chronic pain and depression are interrelated and can reinforce each other.
Alcohol has little nutritional value and only adds extra calories, which can contribute to weight gain and obesity.
Calcium is essential for strong bones
Calcium is necessary to maintain the body's required bone mass and bone density, which significantly affects supporting structures. In addition, the body constantly uses calcium for the functioning of the cardiovascular system, muscles and nerves. Calcium is also lost as a result of normal processes in the body, such as hair growth, nail growth, sweating, and skin growth. If a person's diet does not contain enough calcium to replace natural losses, the body will pull calcium from the bones, which weakens them and makes them more susceptible to fractures. Surprisingly, experts estimate that 70% of people do not get enough calcium from food.
Calcium helps prevent osteoporosis
Calcium is very important for children and adolescents, since the growth of the body requires a large amount of nutrients, including calcium, which is vital for the formation and growth of bone tissue. It has been noted that in the long term, lack of sufficient calcium in the diet during childhood significantly increases the risk of developing osteoporosis with age.
Osteoporosis can lead to cracks in the bone tissue of the vertebrae, which in turn can lead to chronic pain and possibly spinal deformity. The risk of developing osteoporosis is higher for older women.
The process of maintaining bone density includes the following steps:
- Getting enough calcium in your diet by eating enough calcium-rich foods.
- Consumption of foods that allow maximum absorption of calcium from the intestines
The recommended amounts of calcium for adults are as follows:
- For people over 50 (and postmenopausal women): 1500 mg calcium per day with 400-800 IU vitamin D.
- For people 25-50 years old (and women of reproductive age): 1000 mg calcium per day with 400 IU vitamin D.
But it must be taken into account that consuming more than 2000 mg of calcium per day can be harmful to the kidneys and lead to the formation of kidney stones. This does not happen when calcium is consumed in recommended doses. If a person already has kidney disease, they should consult a doctor before taking supplemental calcium.
Dietary sources of calcium:
- Dairy products (such as yogurt, cheese and especially milk)
- Dark green leafy vegetables (such as spinach, broccoli and kale)
- Beans and peas (such as tofu, peanuts, peas, black beans)
- Certain types of fish (eg salmon, sardines)
- Some other foods that contain calcium (eg, oranges, molasses, almonds).
How are glucosamine and chondroitin absorbed?
Glucosamine is contained in products, and therefore is well and easily absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract. Then it is transported to cartilage and tissues, where it is synthesized into necessary substances, including chondroitin.
What microelements help glucosamine be absorbed?
Vitamins A, B and C, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, selenium, manganese salts, copper collagen enhance the absorption of active substances
.
Also, food sulfur plays an important role as a connecting link, which increases the permeability of the cell membrane. Sulfur
is necessary for the fastest and most complete absorption
of glucosamine
and
chondroitin
. There is a lot of it in beef, chicken, cod, sea bass, as well as radishes, onions and all types of cabbage.
Vitamins A, B and C, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, selenium, manganese salts, copper collagen help absorb glucosamine.
Vitamins
Vitamin A is an antioxidant that helps the immune system fight various diseases. This vitamin is also important for the spine because it helps restore tissue well and is involved in the formation of bones. This vitamin also helps the body use proteins more efficiently.
The human body can convert beta-carotene into vitamin A. Beta-carotene is found in dark green leafy vegetables and most orange vegetables and fruits. It is very important not to over-intake vitamin A beyond the recommended daily value, as excess vitamin A can contribute to bone fractures. But excess beta-carotene does not increase the risk of fractures. Vitamin A is found in foods such as: beef, veal and chicken liver, eggs; dairy products such as milk, butter, cheese; orange fruits such as apricots, nectarines and melons; orange or green vegetables such as carrots, sweet potatoes and spinach.
Vitamin B12 is vital for healthy bone marrow and the entire body, including the spine. Vitamin B12 is found in: meat products such as liver, fish, red meat, poultry and eggs; dairy products such as milk and cheese; and green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale and broccoli.
Vitamin C is necessary for the production of collagen, which is an important element in tissue formation, which is extremely important for the healing of damaged tendons, ligaments and spinal discs, as well as maintaining the strength of bones and other tissues. Vitamin C is found in fruits such as strawberries, kiwis and citrus fruits (eg oranges, guavas, grapefruits) and tomatoes; many vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, red and green peppers, sweet potatoes and white potatoes.
Vitamin D helps with the absorption of calcium, which is very important for the development of strong, healthy bones. Adequate calcium absorption is especially important to prevent the development of osteoporosis, a disease characterized by weak and brittle bones, primarily in the spine, which can lead to the development of vertebral compression fractures.
Vitamin D is a natural component of foods such as egg yolks and fish oil. In addition, vitamin D is produced in the human body after exposure to sunlight.
Vitamin K is essential for bones and allows calcium to be absorbed. The combination of vitamin K and calcium helps bone tissue throughout the body remain strong and healthy. Vitamin K is found in liver, pork, green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale and broccoli, and dairy products.
Iron is necessary for the body, as it allows you to receive oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide. Iron is also necessary for the formation of myoglobin, an important element of healthy muscles that provide support for the spine. Iron is found in meat products such as liver, pork, fish, shellfish, red meat and poultry; lentils, beans, soybeans, eggs, grains, and green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale and broccoli.
Magnesium is an important factor necessary for muscle contraction and relaxation. Magnesium also helps maintain muscle tone and bone density, which in turn can help prevent spinal problems. In addition, magnesium is involved in the body's absorption of protein. Magnesium is found in whole grains and whole grain breads, beans, seeds, nuts, potatoes, avocados, bananas, kiwi, shrimp, and green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale and broccoli.
Calcium is essential for bone health and helps maintain adequate levels of bone mass throughout life and especially in old age. Adequate calcium intake is especially important as it can help prevent the development of osteoporosis, which causes the bones in the spine to become brittle and can lead to painful vertebral fractures. Calcium is found in dairy products such as yogurt, cheese and milk; dark green leafy vegetables such as spinach, broccoli and kale; tofu, peanuts, peas, black beans and baked beans; some types of fish (salmon and sardines); a variety of other foods such as sesame seeds, molasses, corn tortillas, almonds and brown sugar.
What foods contain glucosamine?
Glucosamine
It is often found in food, but it is easily destroyed under the influence of various factors even before it enters our body.
The reason is the instability of glucosamine and chondroitin - destruction occurs during cooking, frying or stewing
. It is mainly present in food in the form of polymers - proteoglycans, collagen, proteins and other components.
Once you find out which foods contain glucosamine, do not rush to eat them - first check to see if you are allergic to them. Better yet, consult your doctor!
Healthy foods containing glucosamine
What do doctors focus on?
- Poultry and beef
. Due to the fact that most of the glucosamine in food is destroyed, it is recommended to simmer the meat broth over low heat without overcooking it. - Pig ears, beef tails, chicken feet
. You can make jellied meat from these ingredients. However, such a dish contains not only benefits, but also harm - excess cholesterol in the composition can accumulate on the walls of blood vessels. - Cheeses
in their pure form without heat treatment. - Sea and river fish
. Especially salmon and salmon. Patients who have been diagnosed with stage 1 arthrosis are advised to use glucosamine in foods - prepare fish aspic with the addition of gelatin at least once a week! - Seafood
. Mussels, shrimp. - Marmalade and pastille
. Carefully! People with diabetes are better off abstaining. - Eggs
(soft-boiled, not overcooked). - Wheat sprouts, mushrooms, nuts, broccoli, seaweed
. They contain a high concentration of collagen-like compounds.
Be careful!
Even regular consumption of products containing glucosamine does not guarantee the health of cartilage under heavy household and professional stress on the joints, metabolic disorders, and age-related changes.
There are many products containing glucosamine.
Harmful products
Some dishes and foods can harm your joints. Among them:
- Smoked products
due to the increased content of carcinogens. Even if products containing glucosamine were used for their preparation, smoked meats can cause pathological changes in the joints. - Oxalic acid
. It can be found in sorrel and pitted fruits. - Plenty of coffee and tea
.
And although there is a lot of glucosamine in food products, such as the shells and shells of crustaceans (shrimp, lobsters, crayfish), eating them in their pure form is strongly not recommended!
How to create a menu to strengthen the spine and joints correctly?
In order for bone and cartilage tissue, as well as the muscular and ligamentous apparatus of a person to be healthy, the body needs certain vitamins and microelements.
Of course, a person should mainly “take” these substances from the food he eats daily. Therefore, it is necessary to pay very close attention to the preparation of your daily diet.
Most often, the following products should be found in a healthy menu for the spine:
- Milk, a number of fermented milk products, and other milk products. This is the best source of calcium. To replenish the norm of this substance in the body, a person needs to drink at least a liter of milk or kefir per day. The same amount of calcium is contained in 200 grams of cottage cheese or 120 grams of hard cheese.
- Greens and all leafy vegetables This group includes spinach, cabbage, green lettuce, parsley, celery, etc. These foods are rich in calcium. In addition, they also contain many vitamins and microelements that are beneficial for bones - iron, zinc, potassium and magnesium.
- Fatty fish, fish liver, caviar. Attention should be paid to salmon, trout, sardines, tuna. Vitamin D, which is contained in these products, is very useful and necessary for bones. It is worth noting that only fresh fish prepared by baking or steaming will benefit. Do not eat overcooked, salted, smoked fish or canned fish. It is enough to consume 50 grams of fish daily to replenish the daily reserve of vitamin D in the body; cod caviar and liver - 20 grams each.
- Other varieties of fish and seafood This group of products includes flounder, squid, seaweed, capelin, mackerel, cuttlefish, mussels, pollock, herring, and shrimp. All of them contain a lot of phosphorus of organic origin, which makes it easy to absorb in the human body and enrich the diet aimed at strengthening bones and joints.
- Animal liver It is better to choose beef or lamb liver. This product is rich in copper, vitamins A and D3. The latter vitamin significantly improves the absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the body, which is simply necessary for a person of any age.
- Seeds, cereals, nuts In this group, peanuts, pumpkin seeds, and buckwheat are especially useful for the spine. All of these foods contain large amounts of zinc, which helps the body absorb vitamin D and bone-healthy calcium.
- Apricot Contains potassium, which contributes to the normal functioning of the muscular system, which should form a strong corset around the bones and support the spine. Apricots can be consumed in the form of apricots - 7-10 pieces daily are enough.
- Beetroot, porcini mushroom, spinach These foods are rich in manganese, which promotes normal growth and regeneration of bones and cartilage tissue in the body.
- Pumpkin, persimmon, tomatoes, bell peppers This group of products contains beta-carotene, which is very important for bone and muscle tissue.
- All citrus fruits are an inexhaustible source of vitamin C, which is very beneficial for bones.
- Vegetable oils All vegetable oils contain unsaturated fatty acids, which have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Gelatin, agar-agar, lean meats and chicken. All these products are a source of protein, which is a “building material” for cartilage tissue, bones, and muscle fibers. It is known that aspic, strong broths and jellies are very useful for fractures and bone pathologies.
An approximate diagram of a healthy nutrition menu to strengthen the spine and joints:
It is divided into 5 meals:
Breakfast (first)
- Freshly squeezed carrot juice (can be apple or citrus).
- Curd pudding with candied dried fruits (on other days you can prepare an omelet from 1 egg, boiled chicken breast (150-200 grams), lazy dumplings, oatmeal with milk (it is better to take cereal, not rolled oats)).
Breakfast (second)
- “Greek” salad (On other days - a sandwich with black bread and cheese without butter, a baked apple with pumpkin seeds or nuts, a boiled egg, kozinak from various grains with candied fruits and honey, cottage cheese soufflé, protein pancakes with fresh berries).
- Green tea with a spoon of honey.
Dinner
- Puree soup with grated vegetables in meat broth (on other days - soup with lentils and spinach, borscht, cabbage soup with carrots, cabbage and spinach, fish soup with egg dumplings).
- A slice of black bread (or grain bread).
- Pieces of boiled chicken fillet in creamy sauce (or lean beef, chicken or beef jellied meat, vegetable stew).
- Tea with herbs.
Afternoon snack
- Light yogurt (cottage cheese with nuts).
- 150 gr. protein biscuit (curd mousse, baked cheesecakes, cheese cookies, jelly with fresh berries and fruits).
- Herbal tea or green tea with honey and lemon.
Dinner
- Boiled or baked fish with vegetables (brown rice porridge with nuts and dried fruits, buckwheat porridge with a piece of chicken, vegetable stew with lean beef).
- Kefir (green tea with honey).
What to do if there is not enough glucosamine in food?
Even though glucosamine is contained in foods, many people, for health reasons, cannot constantly eat aspic or fatty broths. In addition, there is little pure glucosamine in food. If the joints are affected or you notice the first signs of degradation - pain, crunching, limited mobility, you need a full course of chondroprotectors.
Artracam is a domestic drug from the group of chondroprotectors
. You don’t need to think about what products contain glucosamine; 1 sachet of Artracam contains its daily requirement. It is enough to dissolve 1 sachet (packet of powder) in 200 ml of water. The resulting solution is odorless and colorless. The course is 6 weeks. Noticeable improvement occurs within 3-4 weeks. It acts slowly, accumulates in the body, reduces the need for NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and analgesics. The drug can be taken for prevention if you are in a risk group.
Advantages of Artracam
before glucosamine in food:
- 1 package = daily requirement.
- Effectively and in 1 course, it strengthens joints, relieves swelling and inflammation, and eliminates pain. Especially in the first stages.
- Easy to digest. The drug in liquid form is safer for the stomach.
- High bioavailability (a large amount of the active substance reaches the “site of action”).
Officially
: Today, most glucosamine is found in pharmaceutical products - chondroprotectors.
Healthy joints to you and your loved ones!
Images designed by Freepik
Diet for rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in the treatment of which diet is auxiliary. However, a proper diet for rheumatoid arthritis can significantly alleviate the patient’s condition during drug therapy and significantly prolong the state of remission. Diet therapy is aimed at reducing inflammation and increasing the body's immune defense.
A diet for rheumatoid arthritis should include a normal or moderately high protein content, a normal carbohydrate content while limiting sugar and foods containing it, a limited amount of animal fats and replacing them with vegetable fats (olive and flaxseed oil are especially recommended), and a limited amount of salt. The diet should contain sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals. Meals should be divided (meals 5-6 times a day). Dishes are prepared boiled or baked. The diet for rheumatoid arthritis excludes meat, fish, mushroom broths and sauces, fatty meat and dairy products, beef, lamb, pork, cooking fats, smoked meats, canned food, pickles, marinades, savory snacks, spices and seasonings, butter dough, ice cream, strong tea and coffee, very cold or hot food. The diet can be built on the basis of diet No. 10, taking into account the considered nutritional features.