Pain in the knees is a common pathology in people of different age groups. The knee has a complex structure, so there can be a large number of reasons that provoke pain.
Night pain in the knee joint does not just complicate life. It indicates the presence of a dangerous process that over time can disrupt motor functions and lead to disability.
Main risk factors and symptoms that cause concern
Knee pain is most often associated with the following risk factors:
- activities that place increased stress on the knee joint;
- lack of physical activity;
- injuries;
- excess weight problems;
- metabolic disorders;
- hereditary factors;
- hormonal abnormalities;
- infectious diseases;
- age.
If your knees hurt at night, you should be alert to the following symptoms:
- swelling;
- redness;
- increase in temperature;
- numbness;
- crunch;
- knee deformity;
- limited mobility.
How is the knee joint structured?
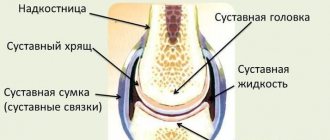
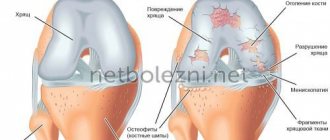
Let's look at this in more detail. The knee has a rather complex structure. This joint is formed from several bones at once: the patella, femur and tibia. The menisci located between them perform a shock-absorbing function. They prevent bones from rubbing against each other and also provide protection during physical activity. The knee joint includes tendons and muscles that are located on the side of the leg and thigh. If any of the above elements are damaged, severe discomfort may occur. It is almost impossible to determine a clear localization of pain in this condition. Why does he twist his knees? The reasons can be completely different. For an accurate diagnosis, you should definitely contact a qualified specialist.
Why does pain occur or worsen at night?
Many people are interested in the question of whether the knee can hurt at night, because the joint is at rest. This pain occurs for many reasons:
- Excessive activity during the day.
- Injury.
- Joint stiffness from a sedentary lifestyle.
- Magnesium and calcium deficiency.
- Increased inclusion of salt, sugar, and fats in the diet.
- Taking medications.
- Dilation of blood vessels during sleep, increasing pressure on nerve endings.
- Weather factors.
Joint dystrophy: causes
If your knee hurts for a long time, and it spins at night, then perhaps it’s due to an incorrect diet. The lifestyle of a modern person does not allow us to pay enough attention to a nutritious meal. Due to the constant lack of time, we are forced to snack on something on the go. This negatively affects the general condition of the body, including metabolism in the joints. A lack of nutrients can cause deformation of cartilage tissue. But it is precisely this that protects the joint from friction and possible destruction.
What is dystrophy of cartilage tissue? The amount of synovial fluid reaching the joints is significantly reduced. But it is precisely this that is a natural lubricant that protects the articular surfaces of the bone from friction. As a result, they are injured from contact with each other.
How should you eat so as not to feel the signs of joint dystrophy? The optimal number of meals per day is 4-5 times. It is with this diet that the blood will be continuously saturated with useful substances. All systems and organs will receive on time the components necessary for proper functioning.
Nature of night knee pain
Knee pain can be acute or chronic. Acute pain often occurs after injury. It is distinguished by suddenness and high intensity.
Chronic – appears gradually. It may begin with mild discomfort, mild pain, gradually increasing.
Night pain in the knee joint has the following characteristics:
- Sharp. It occurs as a result of injury, the appearance of bone formations in the muscles.
- Aching. Signals about chronic pathology, inflammation, the onset of arthrosis, dysfunction of the circulatory system, hypersensitivity to the weather.
- Systematic – for cramps in muscle tissue.
- Pulling – for any disease of the knee.
- Shooting. It happens when pathology affects the nerves. Manifests itself in the form of lumbago.
- Cutting – occurs when a nerve is pinched or a meniscus is torn.
- Pulsating – for inflammation of soft tissues, rheumatoid arthritis, thrombophlebitis.
- Explicitly expressed - characteristic of fractures, acute inflammatory processes, pinched nerve endings.
- Constant – characteristic of reactive synovitis, fibrosis of the joint capsule, muscle spasms.
Localization of night pain:
- in front - speaks of apical patella syndrome, patellofemoral syndrome, Osgood-Schlatter disease;
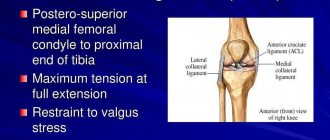
- on the outer part - damage to the external meniscus, collateral ligament, X-shaped deformation of the joint;
- in the internal area - in case of damage to the medial meniscus, collateral ligament, O-shaped deformity of the joint in the knee;
- behind the joint - characterizes Baker's cyst.
Additional symptoms?
Associated symptoms will help determine the approximate mechanism of the lesion and establish a preliminary diagnosis. Their combination may be characteristic of a specific disease or group of diseases:
- inflammatory processes are accompanied by swelling, redness of the joint and an increase in local temperature;
- increased pain when moving, crunching in the joints, limited mobility speak in favor of chronic degenerative diseases;
- impaired mobility with preserved tissue sensitivity is characteristic of tumors, cysts, arthropathy;
- In case of injury, joint deformation, pathological mobility, and accumulation of blood in the joint cavity or soft tissues are observed.
Systemic diseases (osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout) cause pain not only in the knee, but also in other joints. Arthritis that occurs against the background of a general illness is accompanied by malaise, fatigue, weakness and fever.
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, taking into account the symptoms and examination results.
Diseases that cause pain at rest at night
Many diseases can cause knee pain at night. The most minor lesions of the joint cause pain.
Arthritis and arthrosis
One of the ailments that causes knee pain is arthritis in the knee joint. This is inflammation, which can be an independent pathology, as well as a symptom or complication of another disease.
Arthritis pain is associated with inflamed joint tissues. The synovial membrane, where lymphatic, blood vessels, and nerve endings are located, is affected. The nutrition of the joint and the production of synovial fluid are disrupted.
The symptoms are:
- increased sensitivity to touch, poor mobility, swelling;
- aching, sharp pain at rest and movement;
- stiffness in the morning;
- general weakness;
- temperature;
- sweating
Long-term arthritis can develop into arthrosis - joint destruction. Osteoarthritis of the knee deforms the joint and deprives it of mobility. This is caused by a lack of nutrition in the joint tissues. Arthrosis is characterized by the destruction of cartilage located on the bone surface. Next, tissue destruction occurs.
Symptoms of arthrosis:
- Pain during exercise, crunching.
- Short-term pain after rest.
- Dull pain at night.
- Swelling.
- Difficulty in mobility.
- Joint distortion.
Etiology of arthrosis:
- hereditary dysplasia;
- long-term arthritis;
- injuries received;
- increased physical activity;
- hormonal disbalance.
Osteoporosis
The disease is a pathology in which calcium is washed out of the skeletal system. The bone becomes brittle.
Osteoporosis is a progressive chronic pathology of bone tissue that disrupts the architectonics. Bones lose their previous structure and are susceptible to injury.
The cause of the disease is:
- metabolic disorders;
- leaching of beneficial microelements.
In the knee joint, osteoporosis in the initial stage occurs without symptoms, with mild discomfort. The nature of the manifestations changes its intensity gradually.
Symptoms of the disease:
- severe pain syndrome;
- spasms at rest;
- pain due to weather changes;
- deformation;
- swelling;
- limited movement.
Synovitis
It is characterized by the appearance of fluid collected in the joint capsule.
The most common causes of the disease are autoimmune processes, injuries, and poor metabolic processes.
Symptoms of the disease are:
- dull pain;
- increase in joint volume;
- edema;
- difficulty in motor function;
- elevated temperature;
- general weakness.
Bursitis
Damage to the knee leads to inflammation of the synovial bursae (bursae). Such bags are filled with fluid, they reduce friction between the joint and ligaments and tendons.
When the bursa becomes inflamed, swelling, pain, stiffness of movement appears, and the temperature of the affected area increases.
Bursitis can be of the following types:
- Knee – for knee injury, high joint load, infectious diseases.
- Prepatellar - in the patellar bursa after a kneecap injury or other bruises.
- Suprapatellar - in the popliteal bursa with tendon injury.
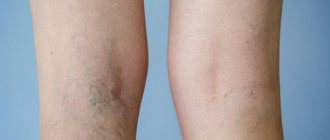
Venous congestion
Pathology manifests itself with a lack of physical activity. Blood stagnates and its circulation is impaired. Venous congestion refers to vascular disorders.
Signs of the disease:
- swelling, heaviness in the legs;
- pale skin;
- burning at night;
- soreness in both knees.
Injuries
A common cause of nighttime knee pain is injury. Among them may be:
- dislocation, bruise of the knee;
- injury to the meniscus - meniscopathy;
- rupture, sprain of ligament, tendon;
- patellar fracture.
In case of injury, symptoms appear:
- strong pain;
- swelling;
- change in skin color;
- painful movements.
Blood clots
Severe pain at night can be caused by thrombosis of the popliteal vein. In people with high blood viscosity, the smallest factor can lead to the formation of a blood clot.
In the presence of thrombosis, symptoms appear:
- Drawing pain.
- Swelling appears at the site of the vein lesion.
- Increased temperature above the knee.
- Bad feeling.
Pinched nerve
The pathology manifests itself as a sharp piercing pain. It covers the knee joint. At night it is difficult to find a comfortable position; it is difficult for the patient to relax in order to fall asleep. There are sharp shootings. The person loses mobility and becomes numb.
The causes of a pinched nerve can be trauma, inflammation, or neoplasms. Burning pain occurs due to pressure on the nerve processes.
Development of osteophytes
Osteophytes are new formations in joints made from bone tissue. Bone pathological growths occur when joint tissues are poorly nourished.
The pathology causes aching pain even in sleep, discomfort, difficulty moving, and crunching.
Inflammatory processes, arthrosis, excess weight and much more contribute to the formation of osteophytes. Bone tissue is destroyed.
The body tries to compensate for the load on the joint. This is accompanied by the proliferation of bone tissue in the form of osteophytes - spines.
Excess weight
The knee joint is constantly under a certain load. If you are overweight, the load increases. Overweight people often experience pain in the knee joint even during rest periods.
Extra pounds help accelerate the development of pathological processes in the knee joint. They wear out faster. Degenerative-dystrophic changes occur, causing pain in the knees.
Obesity negatively affects the lymphatic system and blood flow. This disrupts tissue nutrition and metabolic processes. Joint ailments and excess weight are directly related.
Diagnostics
If you experience knee pain, especially if it happens regularly or is present all the time, you should consult a doctor. If the patient has recently encountered traumatic factors, he should contact an orthopedic traumatologist. In other cases, you can initially make an appointment with a therapist. The doctor will assess the patient’s condition, collect anamnesis and prescribe diagnostic procedures. This will allow him to make a preliminary diagnosis and refer the patient to a specialist whose help will be most effective in a particular case.
But you can immediately contact a neurologist if a person notices the presence of lower back pain, diffuse pain in the leg, a burning sensation along its back surface, or other symptoms described above. This will save time and money, quickly determine the true cause of changes in well-being and begin treatment. If the patient notices changes in the condition of the feet, in addition to pain in the knee, he is concerned about pain in the ankle joints, it is better to immediately make an appointment with an orthopedist.
In any case, the doctor will examine the situation in detail, assess the nature of the complaints and refer the patient for examination, which may include:
- laboratory tests (CBC, biochemical blood test) necessary to identify signs of inflammatory processes occurring in the body;
- X-ray of the knee in two projections (if there is a suspected pathology of the feet or spine, they are also examined using radiography), required to assess the condition of the bone structures, as well as identify indirect signs of a number of diseases;
- CT is used for more accurate diagnosis of joint diseases, as well as the most reliable assessment of the degree of their destruction;
- Ultrasound of the knee joint, used for visual assessment of all structures of the knee, their size, position;
- MRI, which is currently the best method for diagnosing various pathologies of soft tissue structures, including knee joint cartilage and intervertebral discs.
In some cases, patients may be prescribed arthroscopy, which is an invasive method for diagnosing and treating pathologies of the knee joints. As a rule, it is required for severe arthrosis and traumatic injuries to ligaments, menisci, etc.
Preventing nighttime knee pain
Eliminating factors that cause injury and illness will help keep your knee joints healthy. Some rules must be followed:
- When work involves a long static position, you need to take breaks, warm up, and squat.
- When lifting weights, properly distribute the existing load.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Do not carry infectious diseases on your feet.
- Maintain a balanced diet and water balance.
- Watch your weight.
- Wear comfortable shoes.
Troubling knee pain at night should be taken seriously. You should immediately seek help from doctors. The consequences of such pain can be the most unpredictable.
Degenerative joint diseases
What makes them special? A distinctive feature of degenerative diseases is constant continuous deterioration in the structure of the affected organs and tissues. Typically, such processes occur in tissues that participate in the formation of joints. These include articular cartilage, areas of the bone layer that are in constant contact with the fibers of the ligaments, and the ligaments themselves.
Typically, symptoms of degenerative diseases appear gradually. At first, a person feels that he is slightly twisting his legs and knees, then the pain becomes constant and does not go away even at night. This is due to the fact that over time the disease affects a fairly large area of connective tissue.
Patella luxation
Is it dangerous? If, after hitting a hard surface or an injury during sports, your knees twist strongly, then the reason may be a detachment of bone or cartilage tissue. If the pain is accompanied by swelling, unnatural twisting or bending of the leg, then most likely it is a dislocation of the kneecap. In this case, blood vessels and nerve endings may also be damaged. Therefore, along with aching pain, the patient may also feel numbness and tingling in the joint area. At first, the injured area may simply turn red. Blueness appears much later.
Surgery
If destructive processes in the joints have gone far enough and do not respond to standard therapy, surgical intervention may be required. This measure is considered radical and is prescribed only as a last resort. Today, there are several ways to perform joint surgery.
Here are some of them:
- Total joint replacement: performed when the joint and surrounding bones are completely destroyed. During the operation, the patient is fitted with a prosthesis.
- Partial joint replacement: only the damaged elements of the joint are changed.
- Arthroscopy: during surgery, destroyed elements of the joint are removed through 2-3 small incisions.
After any surgical intervention, doctors recommend that patients wear a tight pressure bandage for a long time.
Osteoarthritis
This joint disease is characterized by changes in tissue structure and the formation of growths on the bones. The causes of this disease are still not fully understood.
Only a few factors have been established under the influence of which deforming osteoarthritis can develop:
- genetic predisposition;
- metabolic and circulatory disorders;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- entry of proteoglycans into the joint.
The first stage of the disease occurs without any symptoms. First, it affects cartilage, which does not have nerve endings and nearby blood vessels.