Causes of pain
Pain and swelling in the knee are always a sign of trouble. However, the nature, localization and intensity of the pain syndrome may be different. These indicators are an important diagnostic sign for recognizing the type of disorder. The main causes of discomfort in the joint can be injuries , overload (microtraumas) and diseases of various origins.
Joint trauma is a common cause of severe and acute pain in the knee. The consequences of an impact or an unsuccessful jump are clearly visible, but it is not always possible to understand which part of the connection is damaged. Therefore, correct diagnosis is important for choosing a treatment method. Possible types of traumatic injuries to the knee joint:
- Fractures of the patella, tibia, or femur almost always cause severe pain, deformity, abnormal positioning, or excessive mobility of the limb. Such a lesion is often accompanied by soft tissue injuries with hemorrhages in the joint, swelling, pain when moving the limb;
- If the meniscus is damaged, immediately after the injury, severe sharp pain occurs in the knee, which goes away after a few seconds. After a few tens of minutes, when the state of local shock passes, the discomfort in the joint becomes aching due to vascular damage and bursting due to synovitis. Often, when a cartilage ruptures, a blockade occurs: the torn part of the meniscus is pinched between the bones, causing immobility of the joint and sharp pain with any movement;
- rupture or sprain of the ligaments is accompanied by sudden severe pain, a feeling of dislocation of the limb and a characteristic cracking sound due to damage to the fibers. Severe trauma may cause joint instability. Later, with the addition of hemarthrosis and edema, the aching pain in the knee becomes dominant.
Inflammatory diseases
The inflammatory process in the knee joint can be acute or chronic. It can be primary (infectious, septic, rheumatoid, metabolic), post-traumatic, and also accompanying degenerative diseases of the joints. The main diseases of the knee joints of inflammatory origin:
- arthritis is a general name for a group of inflammatory diseases of various origins, but with similar symptoms (osteoarthritis, gout, lipoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis). A characteristic symptom is pain in the knees, aggravated by movements, an increase in the size of the joint, an increase in local temperature, and sometimes redness;
- bursitis (damage to the joint or tendon capsule) is usually accompanied by pronounced constant pain, independent of movement. They arise due to overstretching of the capsule with pus or fluid and effects on the nerve endings;
- Tendinitis (inflammation of ligaments and tendons) is characterized by swelling and discomfort in a specific area. It intensifies with flexion and extension of the knees and contraction of the muscles associated with the tendon affected by inflammation, and radiates to the neighboring muscles of the leg and thigh;
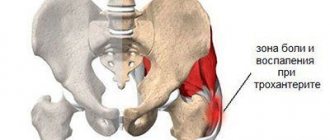
- Becker's cyst (popliteal hernia) in its active stage causes pain of varying intensity in the popliteal region. It extends along the calf muscle into the sole and interferes with flexion of the joint.
Non-inflammatory diseases (chondropathy, meniscopathy, tendinopathy)
With such dystrophic diseases of the knee joint, as a rule, only one type of connective tissue is affected - cartilage, meniscus, tendons or ligaments. These pathologies are accompanied by pain in the knees when walking, flexion-extension of the limb, crunching in the joint, and sometimes involuntary buckling of the leg when stepping on it.
Degenerative diseases
This kind of irreversible destruction of articular tissues, in particular cartilage, usually has a long-term nature. Therefore, symptoms also form gradually, in stages, involving increasingly larger areas of connections in the destructive process.
Unpleasant sensations in the knees can occur with arthrosis of both the knee joint and the spine. The main causes of knee pain are:
- gonarthrosis (knee joint - KS) and coxarthrosis (hip joint - HJ). Severe discomfort at the very beginning occurs only after exercise and subsides at rest. As it progresses, it first becomes periodic and, in the final stages, permanent. Ankylosis or abnormal mobility in the joint is formed;
- if the pain radiates to the knees, but there is no problem in the joint itself, you need to examine the spine for the presence of radicular lesions;
- neuropathy in the joint or nearby structures.
Read also: Pus in the knee joint
Vascular diseases
Poor circulation in the extremities can also cause discomfort in the knee joint. However, the main difference between pain of vascular origin and other pathologies is that the mobility of this organ does not suffer. This disorder sometimes occurs in adolescence with uneven growth of bones and blood vessels, but most often goes away by the age of 18–20.
Such problems sometimes accompany people throughout their lives. They are not always described as pain, but rather the term “twisting of the knees” is more suitable for them when the weather changes, colds and physical activity. Vascular disorders are not characterized only by pain in the right knee or pain in the left knee, but there is always a symmetrical nature of sensations.
Aseptic necrosis (or infarction) of the bone of the knee joint occurs when there is a sudden disruption of blood circulation. The death of part of the hard tissue usually occurs within a few days and is accompanied by very severe, sometimes unbearable pain.
Pain in the knee joint occurs when soft and connective tissues are damaged. This most often occurs as a result of injury, its complications or chronic diseases.
Discomfort becomes noticeable when excess intra-articular, inflammatory fluid or blood during hemarthrosis compresses the nerve endings of the joint. When diagnosing, the following features of the pain syndrome are taken into account:
- sudden pain in the knee is a clear sign of a recent injury, joint blockade due to damage to the meniscus, as well as the introduction of acute bone growth into soft tissues;
- aching pain in the knees indicates chronic processes in the joint: inflammation, the initial stage of arthrosis, or the manifestation of weather dependence due to vascular disorders;
- shooting pain in the knee occurs during inflammatory processes when nerve endings are affected, as well as during the advanced stage of arthrosis;
- severe pain in the knee is characteristic of a pinched nerve, blockade due to a meniscus tear and other acute injuries to this part of the leg, soft tissue damage, fractures, acute inflammatory processes and the last stages of osteoarthritis;
- constant pain in the knee joint is most often associated with spasms of nearby muscles, fibrosis of the capsule, reactive synovitis and neuropathies;
- throbbing pain in the knee occurs with acute inflammation of the soft tissues of the joint, rheumatoid arthritis at the initial stage, with thrombophlebitis and other vascular disorders;
- severe, cutting pain in the knee when trying to move suggests a meniscus tear and blockade of the joint or a pinched nerve, including in the spinal region;
- nagging pain in the knee can be observed in most pathologies of the knee joint at different stages of development.
Read also
Elbow pain
Clinical manifestation of elbow pain This symptom can occur in the segments controlled by the ulnar nerve.
If this is due to Guyon's stock, which is being pressed by a tubercle, rupture or damage in ... Read more
Patellar tendinopathy
Patellar tendinopathy is pain in the knee joints and patella. This painful condition often occurs in young people involved in sports. Tendinopathy occurs due to excessive stress...
More details
Shoulder blade pain
Symptoms of Scapula Pain Symptoms include pain and paresthesia on the inside of the scapula, pain on the outside of the rib cage, limited scapular function, and pain radiating from the shoulder to the arm. These symptoms...
More details
Heel spur
Have you been bothered by pain in your heel when walking for some time (or maybe quite a long time)? The feeling of stepping on a sharp nail or pebble, constant discomfort and unpleasant sensations during…
More details
Periarthrosis or periarthritis?
Let's imagine that you are driving a luxury car along our wonderful roads and suddenly notice that something persistently creaks in the area of the front wheel on the right. Moreover, this creaking intensifies periodically...
More details
Diagnosis based on characteristic pain manifestations
Based on typical symptoms, some pathologies can be questioned. Some types of pain may be unique to certain knee diseases.
However, such signs are given only for self-familiarization before a mandatory visit to the doctor. Nature of pain:
- increased pain at night is important for diagnosis, as it is typical for few diseases. It occurs in rheumatoid arthritis and diseases of vascular origin and, conversely, is not typical for arthritis and meniscopathy;
- pain that occurs only with certain positions or movements indicates stretching of the capsule during periarthritis;
- “starting pain” in the morning occurs with developing osteoarthritis of the knee joint, if it lasts no more than 20 minutes after the start of walking;
- morning stiffness of the joint, when it is difficult to make amplitude movements, is very informative for inflammation of the soft tissues or capsule with arthrosis, if it goes away after half an hour;
- pain below the knee is associated with injury to the menisci, tendons and ligaments, fracture of the patella, as well as detachment of the periosteum;
- pain above the knee can provoke coxarthrosis, problems with the spine and vascular disorders;
- spreading pain, moving from one joint to another, is characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis. Even if it recedes, the joint becomes sensitive to any weather factors, causing aches and pains inside the joint.
Any pain in the knee joint should always alert you and force you to take action. Until a final diagnosis is made after examination, self-medication can be dangerous, since therapy must be individualized. Sometimes healing methods for one type of lesion may be completely unacceptable for another pathology of the joint.
Read also: Restoration of cartilage tissue of joints
Causes of jerking knee pain
Jerking, throbbing pain in the knee joint indicates the development of one of the diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, disease of the deep venous vessels, or periarthritis of the knee joint. This article will discuss one of the reasons - periarthritis of the knee joint.
The root of the jerking pain at rest is latent or acute tendonitis, the growth of “crow’s feet” without involving the knee joint itself. The localization of inflammation is the inner surface of the knee at the site of attachment of tendon fibers, semimembranous and internal lateral ligaments of the knee joint.
1.Knee pain, causes of knee pain
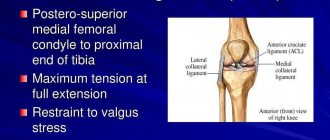
Knee
is one of the large, complex and vulnerable joints.
It is located between the two longest bones of the skeleton and serves as a hinge. The knee joint is exposed to enormous stress every day. Any movement of the leg when running or walking is not complete without its use. And knee pain and swelling are the most common symptoms of diseases or injuries of the knee joint that cannot be ignored. As a rule, the cause of knee pain is an active lifestyle and playing sports, since in this case the knee joints are subject to significant stress and wear.
Even unpleasant sensations or discomfort in the knee when moving indicate a possible problem, so if such symptoms appear, you should definitely consult a doctor. Knee-joint
is a joint connecting the patella, tibia, fibula and femur. In other words, the knee is a complex anatomical structure consisting of four main bones, as well as many interconnected tendons and muscles. Knee pain manifests itself in different ways. The intensity and frequency of pain depend on whether the pain is caused by knee disease or injury, and on the extent of damage to the joint. In some cases, patients complain of slight discomfort in the knee after intense sports training. Such pain can bother a person even at night, gradually developing into a severe and painful pain syndrome. This speaks to the importance of identifying the causes of pain at an early stage. Let's look at the most common causes of knee pain:
- Circulatory disorders.
Symmetrical knee pain can occur as a result of poor circulation. They are called vascular pain and in most cases first appear during the period of active growth, since the vessels “do not keep up” with the accelerated growth of bones in adolescents. After 18–20 years, the intensity of vascular pain in the knee, as a rule, decreases. - Injuries.
Mechanical damage is the most common cause of knee pain. A knee joint injury can be caused by a sudden fall, a blow to the kneecap, or twisting of the leg. Some of the most serious injuries to the knee joints include damage to the meniscus - a rounded cartilage, sprained ligaments and tendons, fractures of the kneecap and dislocation of the patella. - Arthrosis.
This chronic disease is accompanied by a feeling of stiffness in the joints, crunching in the knees when moving, and limited mobility. If left untreated, arthrosis progresses, causing knee deformation and other dangerous consequences. - Osgood-Schlatter disease.
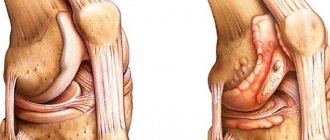
This disease is associated with the destruction of the tibia, which occurs against the background of numerous injuries to the knee joints. Osgood-Schlatter disease is common among athletes and is typical for boys whose age ranges from 11 to 15 years. - Baker's cyst.
A Baker's cyst is a soft, dense, elastic tumor-like formation that develops in the popliteal fossa - on the back surface of the knee joint. - Arthritis.
This inflammatory disease accompanies pathologies such as gout, rheumatism, and ankylosing spondylitis. Distinctive features of arthritis are stiffness in the joints, severe pain, limited mobility, swelling, and increased body temperature in the affected area. - Osteoporosis.
In osteoporosis, the level of calcium in the bones decreases. Most often it occurs in women after menopause, as well as in people suffering from calcium metabolism disorders in the body. - Infectious diseases.
Infectious diseases: dysentery, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and others that occur latently in the human body can provoke the occurrence of pathologies of the knee joints. Most often, infections contribute to the development of reactive arthritis, which affects not only the joint, but also the tendons around it. - Sciatic nerve neuropathy.
Pinched nerves in some cases cause pain in the knee joints in addition to pain in the hip area and inability to bend the leg.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Causes of jerking pain
The cause of the tugging and throbbing pain is microtrauma of the knee joint. Traumatic exposure does not have to be a consequence of a sports injury; it can occur at both the domestic and professional level. Daily heavy lifting, carrying a tall child, similar, repetitive movements of the knee joint, for example, a seamstress, a cyclist, a runner.
When walking while flexing the knee joint, tension occurs in the tendons of the “sartorius” muscle, which contributes to the development of inflammatory processes that spread to the serous bursa of the joint. During night sleep, a twitching pain is felt on the inner surface of the knee. On palpation, sharp painful points are felt with light pressure. Sometimes pain points can be felt from the outer surface of the popliteal fossa.
Diagnosis of periarthritis is difficult due to many similar clinical pictures of the course of traumatic and post-traumatic injuries. But first of all, it is necessary to differentiate periarthritis from infectious arthritis. The treatment plan is different for different diseases!
Treatment for jerky knee pain
Therapy is aimed at reducing microtrauma to the tendons of the knee joint. Rest of the affected tendon is the key to successful recovery. It is necessary to stop activities associated with excessive mechanical stress on the knee joint. For this purpose, splints are applied to reduce the mobility of the knee joint.
- Analgesics - reopirin, butazolidine, analgin, amidopyrine.
- Water aerobics class.
- Anti-inflammatory drug therapy - corticosteroid hormones: prednisolone, hydrocortisone. Treatment is carried out by giving injections or taking tablet forms.
- X-ray therapy. Low-dose X-ray rays pass through cartilage tissue and trigger repair and regenerative processes. X-rays have a pronounced analgesic effect. When exposed to low-frequency rays, a blockade of nerve endings occurs. There is a dullness of painful sensations and the joint regains mobility.
- Balneotherapy of the knee joints. Balone therapy procedures are aimed at reducing pain through the effect of hydrogen sulfide and radion substances on cartilage tissue.
Therapeutic liquid resolves inflammatory synovial fluid in the knee joint, improves the trophism of cartilage tissue and reduces the sensitivity threshold.
We invite you to watch a video about periarthritis:
If you are reading this article, then most likely you are looking for the cause and treatment of jerking pain in the knee, we suggest that you choose a suitable orthopedist from the catalog and, without leaving this site, make an appointment right now.
3.Treatment of knee pain
Depending on the cause, your doctor will prescribe an individual treatment regimen for your knee pain. Although there is no universal solution to this problem, doctors recommend the following:
- See your doctor if you experience spontaneous, severe knee pain.
- Try to minimize the load on the knee joint. The immobility of a sore knee is the key to its fastest recovery.
- Use special bandages or a bandage to stabilize the joint.
- Take anti-inflammatory and pain medications if necessary.
- Remember that if pain in the knee joint bothers you for a long time, you should definitely consult a doctor. Avoid self-medication and do not ignore knee pain, as the progression of the disease can result in joint deformation and regular and painful pain when walking. Timely treatment of knee pain is the key to health and well-being.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Causes of vein pulsation in the leg
Many people experience periodic pain and a feeling of heaviness in their legs throughout their lives. For some, problems persist for a long time, which causes discomfort. Why does a person have a condition when he feels like a vein in his leg is pulsating?
Fluttering veins can be due to a problem in the bones and muscles, or to the nerves.
Factors that provoke the appearance of pulsation of the veins of the lower limb:
- Leg injury (new or long forgotten). If the integrity of tissues and nerve fibers has been compromised, then it reminds of itself with pain in the legs.
- Varicose veins Vascular disorders lead to blood accumulation and stagnation, as a result of which the limbs begin to ache.
- Obesity. Due to heavy loads on the legs, throbbing pain appears.
- Pinched nerve. With this problem, the sensation of fluttering is mistakenly mistaken for pulsation due to the fact that the pain radiates to the lower extremities.
- Radiculitis. Due to compression of the spinal cord roots, painful sensations radiate to the leg.
- Deep vein thrombosis, atherosclerosis. Circulation problems lead to poor blood flow and leg pain.
If numbness is added to the fluttering of the veins, then this condition indicates developing neuropathy (a problem with the nerve) or the occurrence of tissue ischemia (lack of blood flow to the affected area).
Read also: Fluid in the knee how to treat
Clinical manifestation of pain on the inside of the knee and sphenoid neuralgia
Sphenoid neuralgia usually occurs when the nerve passes through Gunther's canal, or, more often, due to its friction with the sartorius, adductor, and gracilis muscles. This compression neuropathy causes pain, paresthesia, and sensory disturbances in the areas through which the nerve passes. These symptoms lead to the patient most often complaining of pain on the inside of the knee. Pain caused by sphenoid neuralgia may be worse when the patient sits or squats. An objective examination can reveal pain in the area under which the sphenoid nerve passes, on the inside of the femur in its middle part, exactly along the midline. Flexibility is not lost. Sitting or squatting places additional pressure on the sphenoid nerve, which worsens the symptoms of sphenoid neuralgia. Sphenoid neuralgia is often misdiagnosed as lumbar spinal nerve radiculopathy or knee problems.
Muscle contractions
Pulsation in the legs sometimes masks muscle contractions (fasciculation) rather than problems with the veins.
The symptoms are similar to a pulsating vein. Usually the twitching goes away on its own. Despite the fact that muscle fluttering may appear for several years, fasciculation does not threaten health. If the patient observes weakness in the muscles and changes in motor function in the legs, then there is a reason to consult a doctor.
Benign muscle contractions may be a consequence of a lack of magnesium in the body. Constant stress, playing sports with increased stress, alcohol abuse, and hypothermia can also cause twitching in the legs.
Such pain can occur at any time of the day.
Treatment, doctor's choice
If the causes of venous pulsation are not known and there are doubts about which specialist physician to contact, then you need to consult with your local doctor.
After the examination, the specialist will establish an accurate diagnosis and advise further actions. The choice of equipment in modern medicine is quite large (ultrasound, MRI, CT, ultrasound).
If you suspect pinching of the sciatic nerve or nerve roots of the spinal cord, you must take an x-ray of the lumbar spine. You should not delay treatment of the disease, as this is a direct path to lameness, pain when moving and muscle atrophy. Weakness in the limbs and impaired joint mobility can also cause pinched nerves.
If you have varicose veins, you need to consult a phlebologist.
A neurologist treats diseases such as pinched nerves.
If you suspect a neurological abnormality rather than muscle fasciculation, you should consult a neurologist. A specialist will help you understand this problem and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
When the pulsation radiates into the knee along the outer or front surface, the problem may be related to the nerves. If you have the same sensations in the popliteal fossa, then you cannot do without a vascular surgeon.