Arthritis is often the cause of pain and stiffness in the legs. If left untreated, the painful sensations intensify, causing serious discomfort to the patient and limiting his movements. Inflammatory processes that affect the joints can spread to internal organs, which often leads to disability. Therefore, the first priority for anyone experiencing symptoms of leg arthritis is to contact a specialist early.
Deformation on x-ray.
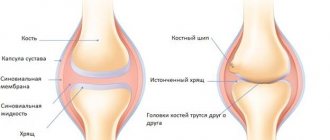
Our daily movements are a miracle of nature. Thanks to the complex interaction of joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles, we can walk. When one of the more than 140 joints becomes inflamed or irritated, the unique locomotor system becomes unbalanced. The word "arthritis" is a general name for conditions of irritation and inflammation of one or more joints.
Why does arthritis develop in the toe joints?
Arthritis of the toe can occur due to:
- injuries;
- improperly healed fractures;
- chronic inflammatory infections in the body;
- when wearing shoes that are too narrow and uncomfortable;
- infections;
- autoimmune diseases;
- diseases of joint and bone tissue;
- chronic stress;
- ingestion of certain groups of medications;
- chronic load on the lower limbs;
- burdened heredity.
If your toes literally don’t fit into your shoes, they burn and swell, this could be a sign of arthritis.
Arthritis can be caused by different reasons for each person. It is believed that the pathology is characteristic of the older age group, because patients are usually elderly. However, currently the disease is getting younger and you can meet young girls and even children at doctor’s appointments.
Only a rheumatologist can say with certainty what triggered the onset of the disease in your case.
Prevention
Specific prevention depends on the etiology of the disease and consists of the following:
- timely anti-inflammatory therapy;
- timely treatment of fractures and injuries;
- timely treatment of the underlying disease (psoriasis).
Otherwise, it is enough to follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle (proper nutrition, exercise).
The prognosis for arthritis is unfavorable (with the exception of post-traumatic). With proper treatment, long-term remission without clinical manifestations can occur.
Symptoms of the disease
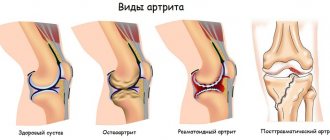
Signs of arthritis vary depending on its type. Doctors distinguish:
- Gouty. Acute gouty arthritis is characterized by severe pain, and every step is difficult for the patient. Most often, the joint of the big toe and the bones of the foot are involved in the inflammatory process.
The main symptoms of this type of pathology:
- aching pain at night or at rest;
- every movement of the thumb or touching it causes severe pain (crystals of deposited salts have sharp edges);
- the joint becomes hot.
The cause of gouty arthritis lies in the excessive accumulation of uric acid salts. A simple blood and urine test, which confirms an excess of uric acid salts, can clarify the diagnosis.
Noticing the signs of arthritis in the legs at the first stage of the disease and taking the necessary measures is a sure way to a quick cure.
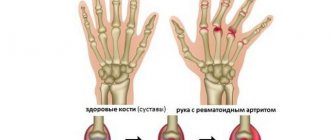
- Rheumatoid. This type of arthritis is caused by the patient's immune system.
Signs of rheumatoid arthritis:
- symmetrically inflamed phalanges of the toes (the disease affects both limbs);
- feeling of stiffness in the joints, especially in the morning;
- deformation of joint tissue and fingers;
- acute pain when putting weight on the foot.
This pathology is chronic, with clearly defined periods of exacerbations and remissions. If left untreated, rheumatoid arthritis can cause complete impairment of walking function. The patient will not be able to move independently. The disease affects the joints not only of the legs and hands, but also the hip and vertebral joints.
- Psoriatic. Psoriatic arthritis is a disease that occurs against the background of psoriasis that the patient already has.
The pathology has characteristic features:
- the joint and tissues around it are very painful;
- the skin in the affected area turns purple, sometimes has a bluish tint;
- fingers can shorten and increase in volume.
- Post-traumatic. This type of arthritis develops as a result of injuries to the joint and periarticular tissues (tendons, fascia, muscles, ligaments). In addition to limited mobility, the patient notices a crunch in the affected joint and pain. In rare cases, body temperature rises and a feeling of loss of strength occurs. The damage to the joint is asymmetrical.
Most often, the pathology occurs in people over 40 years of age.
- Osteoarthritis. The disease is not systemic, but is caused by inflammation and destruction of joint and bone tissue. Pain occurs while walking. The patient may be bothered by a feeling of numbness, especially if the limb has not performed any activity for a long time.
It is important to monitor your health and consult a doctor at the first symptoms. You will need to consult a therapist, rheumatologist, traumatologist, surgeon, and sometimes an oncologist. Under no circumstances should you start such a process, as you may lose the ability to move normally.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is designed to restore joint mobility and restore the normal structure of the joint. A favorable outcome is only in 80% of cases and it will depend on the degree and severity of the disease.
Surgical intervention has a favorable prognosis in 80% of cases
Surgical options:
- Ankylosis is the formation of artificial fusion of articular surfaces. With this tactic, function is completely lost, but no further destruction of the joint and bone structures occurs.
- Puncture is a semi-diagnostic, semi-surgical treatment procedure. Provides relief from tension in the joint.
- Arthroscopy – rarely used on small joints. The method is based on minimally invasive examination of articular surfaces using a special camera.
Previously, methods were used to strengthen joints using titanium plates. At the moment, this is considered an ineffective and outdated tactic.
Diagnosis of arthritis
First of all, the doctor will collect anamnesis, conduct a survey and examine the affected joints.
To make a diagnosis, your doctor may prescribe a number of instrumental and laboratory tests:
Data from biochemical and general blood tests are used
- General and biochemical blood test. Inflammation will be indicated by pronounced leukocytosis, the presence of C-reactive protein in the blood plasma, and high levels of SOE and platelets.
- A urine test may indicate a gouty type of arthritis. In this case, the sample will contain a high content of uric acid.
- X-rays of joints and periarticular tissues will indicate the presence of dystrophic and erosive processes in hard tissues.
- An ultrasound will informatively tell you about the condition of the soft tissues and the joint as a whole.
- MRI and CT. The most informative methods that reveal the degree of tissue damage and the stage of pathology. The joint and tissues can be viewed layer by layer in various projections. But at the same time, MRI and CT are expensive research methods.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, leg arthritis is a hereditary disease that begins to appear in men and women over the age of 50. Its most common types are osteoarthritis (arthrosis), rheumatoid arthritis, and gout. There is also a juvenile type of the disease, which affects children 5-15 years old.
There are more than a hundred varieties of this pathology, among which osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and gout are the most common. Osteoarthritis occurs due to friction between bone heads or thinning of the cartilage structures that would otherwise protect the bones from friction. Rheumatoid arthritis is the result of aggressive attacks by the immune system that affect healthy joints and tissues. Gout is a consequence of metabolic disorders, crystallization of uric acid in the joint cavity, between the bones.
Common causes of the disease:
- heredity;
- natural aging of the body (including joints);
- cartilage degeneration;
- mechanical injuries and bone fractures;
- congenital anomalies of the anatomical structure of the foot;
- infectious agents (bacteria or viruses);
- an overactive immune system;
- metabolic disorders;
- lack of physical exercise in a person's life;
- passive lifestyle;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- unbalanced diet;
- dehydration;
- avitaminosis.
How to relieve inflammation: ointments, injections and other medications
Let's look at the drugs in more detail.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used
NSAIDs
When affected by arthritis at various stages of the disease, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are used:
- "Ibuprofen";
- "Olfen";
- "Has"
- "Dexalgin";
- "Meloxicam";
- "Ketoprofen".
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are available in the form of ointments, injections and tablets. They are used in combination. That is, the patient takes pills, gives injections, and rubs ointment into the affected areas.
Injections are given intramuscularly and relieve pain for 8-12 hours. The course of treatment ranges from 5 to 15 days, depending on the stage and type of arthritis.
Representatives are:
- "Dicloberl";
- "Olfen";
- "Movalis".
Ointments and creams are simply rubbed into the joint and surrounding tissues. They locally relieve inflammation, swelling, and pain. You need to rub them in 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is from 5 to 30 days.
Local medications are also used
Representatives:
- "Fastum gel";
- "DipRelief";
- "Menovazan";
- "Diclofenac gel";
- "Nise."
Glucocorticoids
Hormone-containing drugs are used in the form of tablets or injected into the joint. They relieve swelling, pain, and inflammation well.
Representatives are:
- "Diprospan";
- "Flosteron";
- "Prednisolone";
- "Dexamethasone."
Dosages and course of treatment are prescribed by the doctor individually. This type of therapy is used for any type of arthritis.
Cytostatics
For some types of arthritis, in particular rheumatoid and reactive arthritis, immunosuppressants and cytostatics are prescribed. These drugs inhibit the immune response, as a result, inflammation is relieved and a period of remission occurs. Medicines are the basic treatment for these types of arthritis.
These drugs contain substances that help restore the structure of damaged joint cartilage
Representatives:
- "Methotrexate";
- "Cyclosporine";
- "Arava";
- Remicade.
These drugs are widely used in the treatment of many cancer diseases and have a number of side effects. However, with properly selected therapy for arthritis, they will help the patient avoid complications and forget about pain.
Types of Foot Arthritis
Let's look at the three most common types of arthritis.
- osteoarthritis. Accompanied by the destruction of cartilage tissue, it is a degenerative disease of the joints. This type of foot arthritis develops due to constant pressure on the big toe while walking. Increased stress leads to wear and tear of the cartilage, causing inflammation, redness, swelling, and joint pain. The pain syndrome can spread not only to the joints of the foot, but also to the knees, hips, and back. The development of pathology is facilitated by leg injuries (sprains, fractures), congenital foot abnormalities (flat feet);
- rheumatoid arthritis. This is a systemic disease that affects all the muscles and joints in the leg. It is considered the most serious form of the disease. Often accompanied by prolonged morning stiffness, fatigue, weight loss, and can negatively affect various parts of the body: eyes, lungs, heart, nervous system. Women are 3-4 times more likely to suffer from rheumatoid arthritis than men. This form of the disease is characterized by alternating periods of remission, during which symptoms disappear, and exacerbation, marked by the return of inflammation, stiffness and pain. Severe joint deformities and loss of mobility are common results of acute rheumatoid arthritis. However, there are cases when this disease system lasts for years and then disappears, sometimes forever;
- gouty arthritis. Inflammation caused by the accumulation of uric acid salts (a by-product of diet) in the joints of the toes, which leads to the destruction of hyaline cartilage with periarticular tissues. Attacks of gout are extremely painful, perhaps even more painful than any other form of the disease. Men are more likely to suffer from this disorder than women, indicating a hereditary predisposition. However, a diet that involves consuming large amounts of meat, sauces, seafood, and alcoholic beverages is often associated with gout.
Another type of disease is psoriatic arthritis. This is a chronic inflammatory joint disease that develops in approximately 10% of patients suffering from psoriasis. The severity of the pathology is not related to the degree of damage to the skin. The main dermal symptom is the appearance of well-demarcated, reddened plates on the skin covered with whitish scales. Joint symptoms are common to any type of arthritis (pain, increased local temperature, redness, inability to mobilize the joint, and sometimes its deformation). Psoriatic arthritis damages the distal interphalangeal joints (near the nails), causing joint inflammation of the joints and tendons of the fingers. Inflammation of the Achilles tendon in the heel bone is common in this form of the disease. Sometimes the disease can affect other parts of the body, such as the eyes or bones.
Read the article about ways to treat foot arthritis at home.
When are antibiotics needed?
It is worth remembering that only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment for your arthritis. Antibiotics are indicated in the presence of extensive inflammatory processes, purulent arthritis, and also if the pathology was provoked by infectious diseases.
Antibacterial drugs of many groups are used:
- macrolides;
- penicillins;
- 2nd and 3rd generation cephalosporins.
The course of treatment ranges from 7 to 14 days. Antibiotics can be administered intramuscularly and orally.
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis is different for each form. It will also depend on the age, method of treatment and general condition. In severe forms, the following complications are possible:
- osteomyelitis;
- loss of support function and gait disturbance (disability);
- polyarthritis (involvement of other joints);
- pathological dislocations, fractures.
The disease is fraught with complications.
Complications will not develop with proper and timely treatment.
Therapy for gout and arthritis of the toes
Treatment of arthritis of the toes caused by the accumulation of salts, in addition to NSAIDs and glucocorticoids, includes special medications. They are aimed at removing uric acid and forming soluble sediments.
During treatment for some arthritis, the attending physician may prescribe additional medications.
Representatives are:
- "Allopurinol";
- "Purinol";
- "Remid."
In addition, mud therapy, exercise therapy, lotions and compresses are used.
What is arthritis in the toes?
Arthritis of the big toes is an inflammatory process resulting in deformation. Inflammation is often aseptic (without a pathogen in the affected area) - the primary option. But it does not exclude in rare cases the addition of an infection (staphylococcus) - secondary. In the latter case, arthritis takes on a purulent process with all the corresponding clinical manifestations.
Type of intra-articular fluid:
- serous - poses a danger only due to increased intra-articular pressure;
- hemorrhagic – contents mixed with blood;
- purulent - viscous, viscous, cloudy liquid with a large amount of bacterial component.
Inflammatory process in arthritis
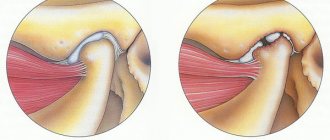
For multiple reasons, gradual wear and tear of the joint occurs. The narrowing of the joint space leads to the fact that the bone structures begin to rub against each other. Aseptic inflammation occurs and gradual replacement of the joint cavity and damaged surfaces.
Connective tissue gives the joint immobility (sharp limitation of range of motion). In addition, with such replacement, the bone structures are joined unevenly, which creates deformations of varying severity.
The process often involves surrounding tissues and structures (vessels, muscles, nerve endings).
Medicinal herbs to treat arthritis
Applications, porridges, compresses and homemade herbal ointments can be applied to the area of the affected joint.
For the treatment of arthritis the following are used:
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- cowberry;
- nettle;
- willow;
- licorice;
- ginger;
- plantain.
Plant materials eliminate swelling and reduce inflammation. But therapy with medicinal herbs should be carried out only in combination with medication or during remissions, as a preventive measure.
As an addition to the main treatment for foot arthritis, you can use folk remedies to combat arthritis of the toes.
Arthritis and traditional medicine
Folk remedies are widely used by doctors and healers. The main ingredients are:
- bee products (honey, propolis);
- livestock products (badger fat, lard, cattle bile);
- plants.
Traditional medicine methods:
- Horseradish rhizomes are grated on a coarse grater and applied to the sore joint. The application is done at night.
- Plantain, calendula flowers, and juniper are taken in equal parts. Make 50 ml of decoction, cool and combine with 50 g of Vaseline. The ointment is rubbed thickly into the inflamed areas.
- Pick 100-200 g of buttercup flowers, only a fresh plant is suitable. Mash the flowers to obtain juice, place them on the bones of the foot, wrap them in polyethylene and wrap them on top with a woolen scarf for 1-2 hours.
- Apple cider vinegar, 1 tbsp. spoon, dilute in a glass of water and take 100 ml 3-5 times a day.
In addition to diet, traditional methods of treating arthritis include juice therapy. Freshly squeezed juices of beets, carrots, cabbage, and spinach are good for it.
Diet
The patient should adhere to the correct principles of nutrition. The diet should contain:
- eggs (no more than 1 per day);
- lean meats – 250-300 g per day;
- fish of fatty and lean varieties - herring, mackerel, hake, salmon, crucian carp, notothenia;
- cereals;
- potato;
- jelly, jellied fish;
- pasta from durum wheat;
- vegetables;
- fruits.
It is worth excluding fatty, smoked and fried foods from your diet as much as possible. It is preferable to steam, boil and stew food.
All foods rich in chemicals and preservatives should be avoided. The list of prohibitions includes alcohol, canned food, chocolate, high-fat dairy products, flour and bakery products.
Nutrition for severe arthritis
The diet for rheumatoid arthritis will depend on the specific form. Below are the nutritional features:
- For gouty arthritis, exclude protein foods (meat) or significantly reduce its amount in the diet.
- For rheumatoid arthritis, reduce the amount of foods that provoke allergic reactions (citrus fruits, chocolate).
- For any form of arthritis, reduce your intake of sugar and salt. Remove alcohol and fast food.
- The diet should consist of 70% plant products.
Nutrition must be correct and balanced.
There are no other features of the diet for arthritis or they do not have a medical basis.