The hip joint (HJ) is one of the largest and most important joints in the body. It supports the body and allows you to maintain mobility. Unfortunately, problems with it are not always recognized in time. Very often the pain radiates to the groin, lower back, knees and other areas, which is why people do not associate the discomfort with joint diseases. But not only the elderly are at risk, but all young people who are overweight, lead a sedentary or overly active lifestyle. As a rule, osteochondrosis of the hip joint occurs in 7% of the population under 30 years of age. After 40 years, the indicator triples, and after 55 – 7 times!
Ignoring the pain signal may result in disability, but osteochondrosis of the hip joint is not a death sentence. The sooner you start treatment, the easier and faster the rehabilitation will be. So how to prevent the disease and cure it if the first pain sensations are already making themselves felt?
What is osteochondrosis of the hip joint?
Osteochondrosis of the hip joint (HJ) is a degenerative-dystrophic disease, the pathological processes of which are localized in bone and cartilage tissues and cause limited mobility of the lower extremities.
Depending on the etiology of origin, osteochondrosis of the hip joint is classified into several types:
- primary – develops mainly in old age (after 45 years), is characterized by symmetry of the lesion and an extremely unfavorable prognosis;
- secondary – occurs against the background of diseases and a number of external factors.
Degenerative changes are most often diagnosed in women, mainly after 40 years.
The main causes of noise in the head in older people
The question “What causes noise in the head in the elderly” is extremely relevant - every day it is asked to doctors by both the elderly themselves and their caring relatives. This symptom can be caused by both physiological, age-related changes in the human body, and a number of pathologies that he may suffer from. Many people over 60 years of age have a whole bunch of diseases, some of which may be accompanied by discomfort and unpleasant sounds in the head.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels (cerebral atherosclerosis)
Atherosclerosis is a chronic, steadily progressing disease, which is based on a violation of lipid metabolism in the body. It is characterized by the formation of fat deposits on the walls of arteries - lipid plaques. This process leads to a narrowing of the blood vessel, which means that the tissues to which blood flows through it do not receive enough nutrients and oxygen - they experience hypoxia.
If the arteries of the heart are affected, angina pectoris develops. In cases where the pathological process affects the vessels of the brain, the patient develops the corresponding symptoms:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- tinnitus (at first transient, occurring only during intense mental activity; as the disease progresses, it becomes constant and disturbing even at rest and when trying to sleep);
- memory impairment (the patient remembers perfectly well what happened many years ago, but tries unsuccessfully to remember the events of recent minutes, hours, days);
- speech impairment (it becomes unclear, blurred, the patient forgets words), handwriting;
- sleep disturbance (difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings at night, early awakenings in the morning) and so on.
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels is the main cause of ischemic stroke, a disease with a high mortality rate. Therefore, when the first signs of this pathology appear, the patient should consult a doctor for examination and receive treatment recommendations.
Blood pressure (hypertension, hypertension, increased blood pressure)
Persistently elevated blood pressure (hypertension) and cerebral atherosclerosis, against which it arose, lead to insufficient blood supply to the brain tissue, structures of the inner and middle ear. This is what provokes the appearance of a buzzing, ringing noise in the head, the intensity of which increases with a sharp increase in pressure - a hypertensive crisis.
In addition to this symptom, hypertension can manifest itself in others, such as:
- dyspnea;
- feeling of heartbeat;
- pain in the heart area;
- headache;
- weakness.
However, in some cases, pressure increases almost asymptomatically and unpleasant sounds in the head become almost its only manifestation.
Thyroid problems
In some cases, the underlying cause of tinnitus is an endocrine problem - decreased thyroid function, or hypothyroidism. It is a frequent companion to a disease called autoimmune thyroiditis (more common in women), and also develops in people who receive insufficient amounts of iodine in their diet. Elderly people, especially those living independently, often eat an unbalanced diet, not consuming, among other things, the required amount of iodine-containing foods.
Ringing in the ears is not the only manifestation of hypothyroidism; it can also be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- weakness, fatigue;
- sleep disorders;
- hair loss;
- decreased appetite;
- stool disorders (tendency to constipation);
- low mood, reluctance to do anything;
- convulsions;
- hearing impairment;
- imbalance.
Cervical osteochondrosis
Previously, it was believed that noise in the head - constant, monotonous, both low and high frequency - most often indicates osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, pathology of the intervertebral discs, and a violation of the normal, physiological position of the vertebrae. It was indicated that with these pathologies, the blood vessels carrying blood to the brain are compressed, which is why the blood supply to the brain deteriorates and a number of problems arise, including the symptom we are describing.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
According to the latest scientific data, the spine is an extremely stable structure, and the vertebral arteries are well protected in the spinal canal and are not easily damaged. It has been proven that osteochondrosis and most other diseases of the spinal column and neck cannot cause noise in the head. Therefore, if you have such a symptom, you should not blame osteochondrosis, but should start looking for the real cause of the deterioration of the condition in order to rid yourself of it.
Stress
In contrast to the previous point, psycho-emotional stress is a very common cause of noise in the head in older people, the treatment of which in some patients simply consists of proper rest, while in others it requires consultation with a psychiatrist and medication.
Thus, anxiety-depressive disorders, somatoform autonomic dysfunction are often accompanied by ringing and other noises in the head, as well as:
- various complaints of pain in the heart, stomach, intestines (provided that during an examination by a somatic doctor no organic pathology was identified that could cause such symptoms);
- weakness, fatigue;
- sleep disturbance;
- decreased appetite;
- feelings of anxiety, inner restlessness, inexplicable excitement, fear;
- low mood, reluctance to do anything;
- irritability, tearfulness;
- lack of initiative.
If such symptoms, including noises in the head in old age, arose after emotional stress, an acute or chronic stressful situation and do not go away within several weeks, do not be shy and wait, but should seek help from a psychiatrist.
Injuries
Open and closed head injuries often lead to tinnitus. As one of the symptoms, it will occur when:
- skull fracture at the level of the temporal bone, middle and inner ear;
- hemorrhage into brain tissue;
- damage to the central auditory pathway;
- traumatic injury to the midbrain.
The most common mechanism for such an injury is a blow to the back of the head, as in a fall on the back, which is not uncommon among older people. And in this situation, the victim notes the presence of other complaints:
- nausea;
- headache, dizziness;
- decreased or complete loss of hearing;
- unsteadiness, imbalance.
Relatives who were present at the time of injury will report the fact of a short-term loss of consciousness (but this is not a mandatory sign), and may also detect bleeding from the external auditory canal of the victim.
The noise as a consequence of a traumatic brain injury is usually intense, monotonous, and, together with other symptoms, significantly worsens the condition of an old person.
If the injury was serious, it can manifest itself even decades later, causing headaches, dizziness, and chronic buzzing in the ears and head.
Other reasons
These for old people are:
- infectious diseases of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis);
- inflammatory processes in the ear (otitis, mastoiditis and others);
- hearing loss of any etiology;
- cerumen plug in the external auditory canal;
- foreign bodies stuck in the ear canal;
- benign and malignant tumors of the ear, brain;
- acoustic trauma (from a loud explosion or listening to very loud music);
- work in conditions of increased noise (in production facilities where devices are installed that produce a constant monotonous sound);
- taking certain medications that have a toxic effect on the organ of hearing (antibiotics, cytostatics, etc.);
- dental problems (pathology of the temporomandibular joint);
- anemia.
Factors that aggravate the situation are non-compliance with work and rest schedules, smoking, alcohol consumption, and unbalanced diet.
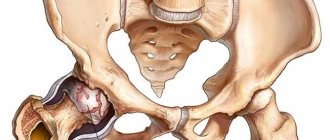
Osteochondrosis of the hip joint: causes
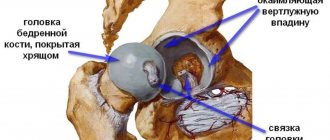
The head of the femur and the pelvic bone are connected to each other by cartilaginous structures, the destruction of which can cause a complete loss of human mobility.
Osteochondrosis of the hip joint is a complex pathological disease that involves the development of degenerative processes in the articular tissues. The probable causes of the development of this type of pathology are usually identified as:
- genetic predisposition – a diagnosed disease in close relatives increases the risk of its manifestation;
- excess body weight - obesity negatively affects not only a person’s appearance, but also the functionality of the musculoskeletal system;
- metabolic disorder – metabolic failure provokes stability of nutrition of tissues of various types;
- incorrect shoes - the inconvenience experienced when wearing shoes every day causes excessive stress on the parts of the musculoskeletal system;
- infectious diseases – the presence of an infection in the body can provoke inflammation of various types of tissues;
- congenital pathologies - dysplasia is usually classified as such;
- previous injuries - any violation (bruise, fracture, dislocation, etc.) causes weakening of the joint and increases the risk of their deformation.
Types and causes of coxarthrosis development
The reasons for the formation of primary coxarthrosis have not been reliably established. This form of the disease is most often accompanied by concomitant lesions of the spine and knee joint, osteochondrosis and gonarthrosis.
Secondary coxarthrosis of the hip joint is a direct consequence of the following diseases:
- Congenital hip dislocation;
- Necrosis of the femoral head;
- Hip dysplasia;
- Perthes disease;
- Inflammation and infections in the joints;
- Injuries or fractures.
Degrees of osteochondrosis of the hip joint
Today, it is customary to distinguish three degrees of development of osteochondrosis of the hip joint. Each of them has its own characteristics and requires a specific treatment plan, which can only be determined by the attending physician, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the clinical picture of the disease.
Osteochondrosis of the hip joint 1st degree
Osteochondrosis of the hip joint of the 1st degree is quite difficult to diagnose due to mild or absent symptoms.
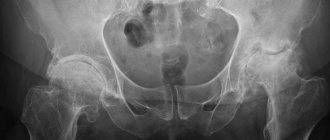
During this period, dystrophic changes begin, which can be determined using x-ray examination (visually noticeable minor growths along the edge of the pelvic cavity).
Osteochondrosis of the hip joint 2nd degree
With osteochondrosis of the hip joint of 2nd degree, dystrophic changes expand in area and affect bone tissue.
The head of the femur undergoes deformation, the cartilage tissue becomes thinner, bone growths form, and the area of inflammation expands its boundaries.
The patient experiences a change in gait and lameness.
Osteochondrosis of the hip joint, grade 3
With osteochondrosis of the hip joint of the 3rd degree, degenerative-dystrophic changes lead to the complete destruction of the cartilage tissue of the joint; individual cartilaginous remains are observed between the tibia and pelvic bone.
During the examination, replacement of cartilaginous tissue with bone growths is noted. Inflammation and visually noticeable swelling are diagnosed.
When to see a doctor
If after minor exercise you feel pain in the hip joint, this is a reason to consult a doctor. Remember that the disease is gradually progressive; in the initial stages, the pain syndrome disappears after rest, so patients often do not pay attention to it.
At the same time, untimely contact with a specialist will lead not only to the development of a new degree, but also to increased pain and stiffness of movement. The sooner you see a doctor, the easier the treatment will be, the better the result will be. In some cases, in the later stages, conservative treatment does not help, so the patient is prescribed surgery.
At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) you can make an appointment with qualified doctors with extensive experience.
The clinic is located at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane 10.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the hip joint
The symptoms of the pathology are directly related to the degree of development of the disease.
With osteochondrosis of the hip joint of 1 degree, the following symptoms are observed:
- pain after physical activity of varying intensity, dull or aching;
- pain disappears after a short rest.
With osteochondrosis of the hip joint of the 2nd degree, it is customary to distinguish the following symptoms:
- increased pain, even at rest;
- the occurrence of lameness after lifting heavy objects;
- difficulties in flexion/abduction of the lower limb;
- discomfort after a long stay in the same position;
- slight shortening of the limb.
Osteochondrosis of the hip joint grade 3 has pronounced symptoms and involves:
- regular pain of severe intensity;
- the need to use a cane for walking;
- insomnia;
- depression;
- increased irritability;
- atrophy of the muscles of the lower extremities.
Noise in the head during a stroke
Stroke is an acute disorder of blood circulation in the brain. It can be hemorrhagic and ischemic.
- In the first case, a brain vessel ruptures and blood flows into the brain tissue. The patient feels as if there was a strong blow to the head, a sharp headache, loses consciousness and falls. Other symptoms depend on which part of the brain is affected.
- The second option, ischemic stroke, is based on blockage of the lumen of a blood vessel by a thrombus. As a result, the brain tissue that this vessel supplies with blood does not receive nutrition and experiences oxygen starvation. The symptoms of this condition are very diverse - from mild speech impairment, dizziness and some tinnitus to severe weakness in the limbs and their paralysis.
A stroke is an acute condition, and the sooner the patient receives quality medical care, the greater the chance that he will quickly recover. However, long-term consequences of this pathology occur in the majority of people who have suffered it. They are:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- noise in one or both ears of varying nature (humming, pulsation, shooting, clicking) and intensity.
One of the leading methods of combating stroke and its consequences is the prevention of these diseases. Reducing the risk of their development is much easier and more effective than treating them later.
Features of diagnostic measures
Anyone can seek qualified medical help if one or more symptoms of the disease develop.
To make a diagnosis, you must first consult a therapist. Who will give a referral to a highly specialized specialist (rheumatologist/orthopedist/surgeon).
The first stage of diagnosis is the collection of anamnesis and medical history of the patient. After this, instrumental research methods are prescribed, which include such medical procedures as:
- radiography;
- ultrasonography;
- computed/magnetic resonance imaging.
In order to exclude the possibility of concomitant diseases, the patient is also prescribed laboratory tests of blood and urine.
In addition, it is worth noting that to determine the existing degree of development of pathological processes, diagnostic methods such as an immunogram and a test for rheumatoid factor are used.
Diagnostics
As part of the diagnosis of osteochondrosis, a survey, examination of the patient, collection of anamnesis are carried out, and other methods are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
Instrumental
When carrying out diagnostics, the following methods are used:
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- CT;
- Ultrasound;
- arthroscopy.
X-ray of the hip joint is one of the diagnostic methods
Laboratory (Analysis)
When carrying out diagnostics, general and biochemical blood tests are used; if inflammatory processes are suspected, an analysis of synovial fluid is performed.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the hip joint
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the hip joint involves complex therapy, the key purpose of which is to restore mobility, as well as relieve symptoms while simultaneously preventing the development of complications.
Regardless of the diagnosed degree of development of a degenerative-dystrophic disease, treatment necessarily includes the following areas:
- use of medications;
- physiotherapeutic treatment;
- massage;
- use of therapeutic physical training techniques;
- nutrition correction.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapy helps reduce swelling and also triggers regeneration, accelerating blood circulation in the tissues.
For osteochondrosis of the hip joint, the following types of physiotherapeutic treatment can be prescribed:
- myostimulation - the use of electric current pulses;
- magnetotherapy - heating tissues using magnetic field;
- phonophoresis – a combination of ultrasound and medicinal effects;
- shock wave therapy – tissue stimulation using sound waves.
The list of procedures is selected taking into account the degree of osteochondrosis and the general health of the patient.
Massage
The purpose of massage can improve blood circulation in the affected tissues and stimulate acceleration and increase in the volume of fluid released, which improves joint mobility.
The procedure is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician. The implementation of procedures should only be entrusted to an experienced specialist.
The course is determined by individual indicators.
Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy)
Exercise therapy plays a special role, because it helps restore joint stability and relieve muscle tension.
If the hip joint is affected, it is recommended to regularly engage in gymnastic exercises. The complex is determined individually by a physical therapy instructor based on the recommendations of the attending physician.
All movements when performing exercises should be smooth and performed with caution. After completing a set of exercises, self-massage of the muscles of the buttocks and thighs is allowed.
Drugs for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the hip joint
The use of drugs of various groups involves achieving such goals as:
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- normalization of providing tissues with an optimal amount of nutrients;
- launch of regenerative processes;
- improved blood flow;
- reducing the load on the affected joint.
When treating with drugs, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- muscle relaxants;
- vasodilators;
- painkillers;
- chondroprotectors;
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Particularly important in treatment are considered to be drugs from the NSAID group, one of the most effective of which is Artradol.
Surgical intervention
A radical treatment method is indicated in a situation where the patient has:
- high intensity pain syndrome;
- significant destruction of articular tissues;
- low rates of effectiveness of conservative techniques.
Pathogenesis
Bones and joints have a complex structure, and the patient’s motor activity directly depends on their condition. Cartilage tissue absorbs all bone movements, the process is accompanied by the release of joint fluid, which is used as a lubricant.
The main reason for the development of osteochondrosis of the hip bone is considered to be constant sitting and lack of physical activity. The impetus for the development of destruction of joints can be constant loads on them, microtraumas, etc. As a result, aerobic/anaerobic oxidation reactions develop in the tissues.
At the next stage, a decrease in the number of protein-polysaccharide complexes in the cartilage is observed; against the background of the pathological process, their elasticity decreases, desiccation, and cracking occur. As a result, the load on the subchondral region increases and the integrity of bone tissue is disrupted.
Against the background of these changes, bone production is activated, which leads to the formation of osteophytes in the least loaded areas.
Bone growths help reduce the load on joint tissues, but have an irritating effect on the synovial membrane. The development of stagnant processes leads to muscle atrophy, as a result, even a slight load leads to the formation of an inflamed hip joint. Further development of osteochondrosis threatens a decrease in motor activity.
Nutritional Features
Compliance with the basics of dietary nutrition during complex treatment helps to reduce the load on the affected lower limb and relieve inflammation, improving the nutrition of the affected tissues.
It is recommended to expand the daily diet and enrich it with such foods as:
- nuts and seeds;
- Fish and seafood;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- citrus;
- whole grain food products.
If you want to achieve the most positive result in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the hip joint, you should limit the consumption of strong tea/coffee, as well as instant foods and bakery products. Bad habits (drinking alcohol and smoking) should be abandoned altogether.
Treatment of head noises in old age
The principles of treating noise in the head in older people directly depend on what disease caused it. For partial or complete hearing loss accompanied by tinnitus, the only effective method is to wear a hearing aid. In case of pathology of the temporomandibular joint - surgical intervention to correct the existing problem. If the disease is iatrogenic (drug-induced), abolition of noise-provoking drugs or reduction of their dosages is required, and if it is neurotic, relief of the person’s condition may be observed after psychotherapy.
Sometimes the treatment is complex – it includes the patient taking medications, physiotherapy, and folk remedies.
Drugs
The patient may be prescribed drugs from the following groups:
- antibacterial;
- vascular;
- antidepressants;
- anti-anxiety.
Physiotherapy
It is not an independent treatment method, since the effectiveness of none of the methods has been proven by large-scale studies. However, as part of complex therapy for a number of diseases, the manifestation of which is tinnitus, physical therapy has shown its effectiveness. The patient may be prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy.
Traditional methods
Head noise in older people can be alleviated by using traditional medicine methods as part of a comprehensive treatment. It is important to understand that they should complement drug and other types of therapy, and not replace them - this is the only way you can achieve a positive effect and not trigger the disease.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Recipes:
- Fill a 500 ml jar with washed clover heads, add vodka, leave for two weeks in a dark place. Take 1 tbsp. l. a day after meals;
- 1 tbsp. l. Grind viburnum berries with honey, consume in the morning on an empty stomach;
- Mix honey and onion juice in a 1:1 ratio. Take 3 times a day an hour after meals.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of the disease or reduce the likelihood of its complications include:
- balanced diet;
- systematic performance of gymnastic exercises;
- rejection of bad habits;
- eliminating the possibility of hypothermia;
- control of optimal body weight indicators;
- timely treatment of various types of diseases;
- systematic preventive medical examinations.
A long course of degenerative-dystrophic processes without proper treatment can lead to the development of lameness and disability of the patient.
Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, adjusting your daily diet and systematically visiting your doctor is the key to effective prevention of the development of the disease.