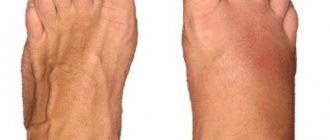
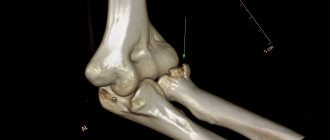
A huge number of people who lead an active lifestyle, are fans of yoga, running, girls in high heels, etc. can get such a fracture.
The foot fracture is localized in the place shown in the photo:
The marching fracture got its name from the marching military. This pathology is most often found in this category of citizens, especially after active training or forced marches.
A marching fracture is a structural deformation of the metatarsal bone due to uneven loads on the foot.
Like many other pathologies, Deichlander's disease brings a huge amount of inconvenience to human life. There are many methods for treating a fracture, but each of them uses the following rule:
Remove all factors that cause foot overload. That is, a rest mode is assigned to the foot. At first, you should try not to step on your sore leg.
Mechanism of development of the marching foot
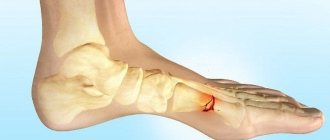
Marching foot fracture is also called Deichlander's disease. Pathological changes occur in the middle part of the metatarsal bone. Bone tissue begins to recover as a result of the action of mechanical and static-dynamic factors.
In most cases, fractures occur in only one bone. Several bones can be captured simultaneously or sequentially. In a varus foot, pathological transformation of bone tissue occurs. This process is not associated with an inflammatory or neoplastic process.
General overview
The term marching fracture most accurately characterizes the etiology of its occurrence. This is a stress fracture of the tarsal bones, resulting from excessive walking, which is most often experienced by military personnel during forced marches, or by athletes.
A stress fracture itself can form not only in this area, but also in any other, for example, in the bones of the lower leg, especially in the tibia, causing many problems for professional athletes or lovers of an active lifestyle.
The principle of formation is the discrepancy between the tension on the muscles of the lower extremities and their ability to withstand such an impact. More often occurs with repeated exercise resulting in overexposure.
Important! Each bone has its own endurance limit - a level of stress that, if repeated, will not cause tissue damage. Exceeding it is dangerous due to the formation of a stress fracture, at a minimum.
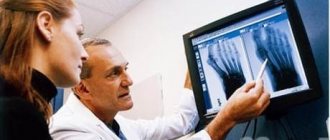
A targeted radiograph of the tarsal bones indicating a stress fracture.
Interestingly, there is a fairly broad spectrum of severity of stress fractures, each of which requires different principles of treatment and has different prognoses for recovery. Clinical manifestations largely depend on the location of the fracture and the activity that caused the injury.
It was previously thought that a stress fracture itself could only occur in the bone that bears the most weight, such as the tibia. Hence, running and jumping were considered to the point of banality as standard causative factors of injury. Recently, the increasingly common diagnosis of stress fracture of the upper limb has amended the previously known diagnosis.
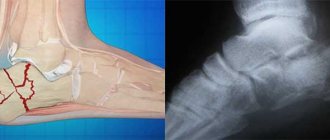
Schematic representation indicating the location of the march fracture.
A marching bone fracture, in turn, cannot be called simply a stress fracture, since it necessarily requires clarification of its location. First described in the mid-19th century among soldiers of the Prussian army, the injury began to be considered as a consequence of repeated actions, as a result of which an incomplete, but still fracture of the tarsal bones is formed.
Who is at risk
Fractures of the walking foot or lower leg occur in people of different professions. The occurrence of this disease is influenced by various factors. The risk group includes:
- Young conscripts. This person is in special conditions where uncomfortable shoes may be necessary. Conscripts have to deal with excessive physical stress. These factors contribute to the formation of single or multiple fractures of thin bones.
- Professional tourists and outdoor enthusiasts. In this case, the person faces a fatigue fracture march. He must walk for a long time on uneven terrain, such as mountains. His legs bear all the weight - the weight of his body, backpack and additional equipment.
- Athletes. When a man prepares for a competition, he strains himself with grueling training. Accordingly, there is a high risk of injury.
- People who need to spend most of their time on their feet. These could be hairdressers, sellers, movers, healthcare workers, couriers.
Young conscripts are in danger
Pathology occurs as a result of functional overload of the foot. It is not associated with inflammation or cancer.
Features and diagnosis of a fracture.
There are two types of such injuries - the “Deuchlander” and “Jones” marching fractures (the latter is localized over a wide area of the base of the fifth metatarsal bone). First of all, radiography is used as a diagnostic method, which makes it possible to establish the clinical picture characteristic of a given pathology.
The main symptoms of the disease are:
- Pain of varying strength in the front side of the foot (especially when walking while rolling);
- Painful lesions on the back of the upper foot (may be accompanied by small tumors about two centimeters in diameter);
- The edematous area resembles bone upon palpation in density;
- In some cases, the swelling is larger and may spread to the entire back of the ankle;
- Sharp pain in the metatarsal bone, arising due to its restructuring and changes in load;
- Painful syndrome when standing on half toes (in the final stages – inability to stand on them).
Diagnosis can be difficult because the problem is not easily identified on an x-ray. Often patients are treated for other diseases - tendonitis, bruises, and so on. In repeated photographs, the march fracture is easier to see - over time, the bone becomes deformed, and the fracture lines become more obvious. In general, the ability to recognize such fractures depends on how long ago the pathology began.
If the diagnostic situation is difficult, the doctor will:
- X-ray ¾ projection;
- Tomography.
At-risk groups.
The following are susceptible to the disease:
- Gymnasts;
- Ballerinas;
- Active tourists and travelers;
- Women who wear high heels;
- Athletes performing exercises after a long break;
- Sellers, waiters, nurses, hairdressers and representatives of other “standing” professions.
The procedure for reconstruction of the second metatarsal bone often has relapses, as well as complications in the form of a fracture with the presence of displacement of detached pieces, a slight dislocation of the proximal Lisfranc articular part.
Symptoms and stages
Many people want to know what the feeling characteristics and symptoms of a march fracture are. When fractures do occur, severe pain occurs. There are several stages in the development of pathology.
Marching fracture: acute
An acute bone fracture in March is manifested by acute pain. There is severe tension and slight swelling. The feeling of pain is constant and gradually subsides 2-3 days after the injury.
Subacute
With a subacute fracture of the walking bone, the pain increases and goes away regularly. The person experiences periods of relief and severe pain.
Marching fracture: chronic
The pain begins to gradually increase. After some time, the person cannot walk independently as he experiences severe pain. The foot is very swollen, making it difficult to wear shoes.
There is thick swelling on the affected area. The skin becomes more sensitive. Changes in skin tone are rare.
March fracture: first aid
In the event of a bone marrow fracture, it is necessary to place the foot on a hard surface and provide the patient with proper rest. It is important to inspect the injured area for other damage or injury. You can call an ambulance and examine the patient in a clinical setting.
First aid:
- Remove your shoes from your feet;
- Painkillers can be given for relief;
- It is advisable to lift the broken limb and place a cushion under it (this can improve blood flow from the damaged area).
The first thing to do in case of a walking fracture is to free the foot from shoes.
You can use cooling agents to reduce discomfort and prevent swelling. Pharmacies sell special ice packs. Wrap them in a towel to prevent frostbite.
Stress fractures of the scaphoid
Until recently, such fractures were considered rare, but in recent years there have been reports indicating an increase in this pathology among athletes professionally involved in athletics and team sports. These fractures are also common in gymnasts. As a rule, the course of the restructuring process in the navicular bone of the foot can last from 1 year to 1.5 years.
This can be explained primarily by incorrect and untimely diagnosis, and hence the early start of exercise after treatment.
In the clinical picture of a stress fracture of the scaphoid, the leading symptom is pain, which appears gradually and intensifies with increasing load, prolonged standing and walking. Pain appears when performing exercises involving rolling the foot from heel to toe or during jolting movements. At rest, as well as with reduced load, the pain may disappear or significantly decrease. However, this period usually does not last long and with an “awkward” movement, acute pain appears again. Usually there is moderate swelling on the inside of the foot, and there is also pain on palpation.
If the diagnosis is established in a timely manner, then treatment of patients should be aimed at ensuring rest and immobility in the joints of the midfoot. For this purpose, patients are given a “boot” type plaster cast with a well-modeled internal arch. The period of immobilization should be 7-8 weeks. In cases where diastasis and displacement of the scaphoid bone are detected by X-ray, surgical treatment is indicated - removal of pathologically altered bone tissue, bone autoplasty.
Marching fracture: treatment
Most hiking fractures do not require first aid or radical measures. Treatment is based on the use of conservative techniques. Treatment methods and recommendations for a speedy recovery are listed below:
- It is important to exclude the negative influence of adverse factors that led to the occurrence of walking sickness. It is necessary to ensure complete rest for the foot and to eliminate physical activity associated with prolonged pressure on the foot.
- We install a plaster strip. Thanks to this, you can significantly relieve the metatarsal bone and protect yourself from unnecessary movements in the limb.
- Wearing special shoes and orthopedic insoles. They help redistribute the load so that the bone heals faster.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. After consultation and diagnosis, the doctor can prescribe the patient a course of magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, or ozokerite. These are effective procedures that promote rapid limb regeneration and reduce pain.
- Additionally, ointments and gels are prescribed that have local anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
- Taking medications to replenish calcium in the body. This is an important element that is a building material for the body. Calcium helps in the rapid restoration of bones.
Plaster splinting is part of the treatment of marching fractures.
If treatment is not started in time, the bone structure is gradually restored. If you suspect a fracture, see your doctor and get an x-ray. A CT scan may be performed to pinpoint the damaged area.
How did this happen?
Repeated mechanical actions over long periods of time, such as walking long distances, place significant stress on the bone, causing the bone to undergo enough microdamage to cause a clinically significant stress fracture.
Like any self-respecting disease, this pathology has its own stages of formation:
- Base of a crack in the bone . The location is the place in the tarsal bone that is most susceptible to repeated stress. Most often this happens at the junction of bone tissues of different densities, for example, lacunae and other histological bone units surrounding them. The initiation of crack formation in itself is not enough for the development of its clinical manifestations. Despite the common assumption about the negative result of the formation of a crack in the bone, there are also positive aspects, namely bone remodeling. Microtraumas to bone tissue stimulate it to strengthen and increase density, which cannot but have a positive effect.
- Crack propagation. If mechanical impacts are repeated at regular intervals, this disrupts the healing process of microdamages and leads to their spread. The most common place where microtrauma tends to increase in size is the joints between osteons - the structural units of tubular bones. Continuation of damaging loads on the tarsal bones stimulates not only an increase in the size of the cracks that appear, but also their merging into a single and clinically significant stress fracture for the patient.
- A complete fracture . Such a final stage becomes a kind of apogee of the entire story with the formation of a stress fracture. The clinic, indicating pathology, and thereby stimulating the owner of this fracture to change activity and reduce the load on the bones of the foot, significantly worsens when the interconnected cracks develop into a complete bone fracture. In this case, it immediately becomes clear to a person what a march fracture is.
Localization of damage in marching foot.
Do not forget that load is different from load. This means that not every crack can develop into a fracture, which is familiar to every third person since childhood. This is influenced not only by the initial state of the skeletal bones, but also by the type of traumatic impact.
Thus, a soldier who frequently experiences forced marches with a bag weighing more than ten kilograms is more susceptible to developing a complete bone fracture than an athlete suffering from a stress fracture, but continues to run several times a week, despite warning pain in the leg.
Healthy bone tissue is always in balance between the appearance of microdamages and their healing. These two processes, which are opposite in nature, create homeostasis in the musculoskeletal system and allow you not to be afraid of any blow or fall that threatens the crutches for at least three weeks. This process is described in more detail in the video in this article.
Stress fractures are a common pathology among soldiers, runners and loaders.
Important! Any excessive load leads to microdamage in the bone, but not every injury risks becoming a fracture.
Risk factors or am I susceptible?
The ability of bone tissue to self-heal is limited by a number of mechanical and biological factors
- age;
- floor;
- neuromuscular junction;
- hormonal status;
- nutrition;
- genetic factors.
Other factors that no less influence the process of stress fracture formation are the blood supply to the bones of the foot, initial sports training, unsuitable shoes for a certain activity, incorrect exercise technique, etc.
Shoes that are not appropriate for the activity often cause injuries.
Important! Correctly selected individual sports training is the price of whole bones and pleasure from sports.
An interesting fact is that muscle contractions can be both a provoking factor for the formation of a stress fracture and a preventive factor for it. An example of a damaging effect would be the act of throwing a ball with the hand, in which the muscles that are part of the so-called rotator cuff group result in a rotator load directly on the humerus.
Among the professions most likely to become “happy” owners of marching feet are soldiers, especially recruits who are not physically prepared enough to carry out the entire load, people whose daily work involves walking with additional weight, such as loaders, as well as athletes who have not yet learned to accurately calculate the strengths and capabilities of their musculoskeletal system.
Marching foot is a common pathology among recruits.
Attention! Instructions for performing exercises are a reasonably designed plan, following which will protect a person from unnecessary and, especially, unwanted injuries.
March fracture: consequences
If the patient refuses treatment and does not follow all the recommendations of the attending physician, he may face the following unpleasant consequences:
- Severe foot deformity;
- development of osteoarthritis;
- If the bone does not heal properly, it becomes painful with prolonged use;
- foot movement becomes limited.
With proper treatment, the prognosis for full recovery is favorable. After therapy, the person will be able to return to their normal lifestyle.
Diagnostic methods
A marching foot fracture is diagnosed like other types of fractures. The difference is that the patient's condition allows him to independently arrive at the point of care. Next, the attending physician conducts a survey, where he clarifies the patient’s type of professional activity, recent changes in physical activity and the presence of chronic diseases. After this, an x-ray and general tests are prescribed to assess the current condition of the body. The image visualizes cracks at different stages of their development.
If damage to structures such as blood vessels, tendons, and nerve endings is detected, then an additional examination of the foot is prescribed using CT (computed tomography) or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). Based on a complete examination, doctors make a diagnosis and determine treatment tactics.
Prevention measures
To prevent serious metatarsal injury from occurring, precautions should be taken. The following recommendations can be highlighted:
- You should not independently diagnose a fracture or the occurrence of a fracture (in this case, it is important to seek help from a doctor);
- wear comfortable shoes that are exactly the right size;
- avoid long hikes;
- regular visits to the doctor for preventive examinations in order to identify the problem in time;
- compliance with all recommendations and rules of the orthopedic surgeon.
The doctor must take into account the condition of the body and bone tissue. A marching fracture is not fatal for a person, since a person experiences various bone changes in the skeleton and limbs throughout his life.