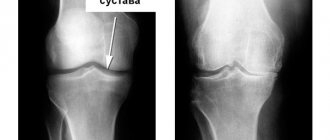
Anterior knee pain Anterior knee pain refers to pain that is localized in the anterior or central portion of the knee joint. The following conditions can be considered as causes:
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease.
- Sinding-Larsen-Johanson syndrome.
- Synovial fold syndrome.
- Hoff's disease.
- Damage to articular cartilage.
- Oncology. Most patients will experience pain in the area where the tumor is located. The pain can intensify during physical activity and often makes itself felt at night. The bone mass around the tumor becomes weaker, and bone fracture may result.
- Osteochondritis dissecans.
- Patellofemoral instability/subluxation.
- Stress fracture of the patella. A stress fracture of the patella is caused either by fatigue from submaximal stress loads or by failure where the bone has previously been weakened due to physiological stress. Decreased shock-absorbing capacity due to repeated loads leads to stress fractures.
- Patellar tendonitis.
- Patellofemoral osteoarthritis.
- Anserine bursitis of the knee joint. The anserine bursa is one of many bursae surrounding the knee joint and is located under the pes anserine. Patients with anserine bursitis often complain of spontaneous pain and tenderness on palpation of the inferomedial surface of the knee joint.
- Quadriceps tendinopathy.
- Prepatellar bursitis.
- Iliotibial tract syndrome.
Epidemiology/Etiology
The etiology of anterior knee pain (AKP) is multifactorial and not well defined due to the variety of symptoms, location of pain, and level of pain experienced by the patient. The underlying factors may be patellar abnormalities, muscle imbalances, or weakness that cause the patella to malalign when the knee joint flexes and extends. This also includes overuse and related conditions: tendinopathy, insertional tendinopathy, patellar instability, chondral and osteochondral damage.
Where can I find a clinic for MRI and CT scanning?
Use the portal tools, where dozens of offers from private and public medical centers are presented. The resource contains a brief description of each of them, information about doctors, technical characteristics of equipment, data on work schedules, the use of contrast, admission of children, as well as blocks with price lists and reviews from visitors.
To select a clinic, enter the name of the prescribed examination and the metro station or city district where it is closest to reach. Use the built-in filter to sort establishments based on different criteria, as well as the online map to help you navigate local locations.
Characteristics/Clinical picture
Knee pain!
What to do? Diagnostics. Yuri Sdobnikov There is no clear definition of pain in the anterior knee joint, since patients may present with various symptoms. Functional deficits, crepitus and/or instability may occur. In daily activities, pain often occurs or worsens when walking down stairs, squatting, pressing the clutch pedal in a car, wearing high-heeled shoes, or sitting for long periods with bent knees. Patients may also experience instability, especially when walking up and down stairs or across ramps. People with overuse injuries may report a feeling of instability or giveness, likely due to neuromuscular inhibition due to pain, muscle weakness, or patellar or joint instability.
How to get rid of nagging pain?
Such discomfort in the knee during flexion is considered to be a consequence of the progression of contracture. In this case, the first thing you will need to do is seek help from a chiropractor or orthopedist. Your healthcare provider will be able to tailor a rehabilitation program based on your personal symptoms. The complex includes the following procedures:
- therapeutic exercises;
- massage;
- osteopathic measures and so on.
The types of programs presented are always selected by the doctor individually for each patient. This is due to the following factors:
- during an initial visual examination, the area of the ligament where scarring has appeared is determined;
- the physician identifies potential dysfunction of the muscles of both the thigh and lower leg;
- the doctor excludes disorders in the circulatory system;
- the causative disease is established.
If there is a lack of information, a number of studies are prescribed. The knee is checked during an MRI or based on indications. Only after the doctor has studied all the data, the patient begins rehabilitation with complete or partial restriction of movements of the knee joint. For osteoarthritis, therapy is carried out by a chiropractor exclusively at the initial stage. Therefore, if discomfort occurs, you should not delay visiting a medical specialist.
Diagnostic methods
Knee Testing (Photo from Knee Treatment Workshop)
Assessing anterior knee pain is challenging because the pain can be nonspecific and the differential diagnosis is broad. This requires a thorough examination, analysis of symptoms, in-depth knowledge of the associated structures and typical injuries. Assessing the growth and development of young people is also important for making a diagnosis.
Diseases of the hip joint and lumbar spine can provoke knee pain and should be excluded.
Some key factors to consider when making a diagnosis:
- localization of pain, its nature, onset and duration, how it manifests itself during movement and at rest (at night), factors that increase and decrease pain;
- trauma (acute macrotrauma, repetitive microtrauma, recent/remote);
- mechanical symptoms (blocking, instability, worsening during or after physical activity);
- symptoms of inflammation such as morning stiffness, swelling;
- the effectiveness of previous treatment and the patient’s current level of functional activity: is there a history of gout, pseudogout, rheumatoid arthritis or other degenerative joint diseases.
The use of instrumental diagnostic methods, such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance therapy, are excellent ways of differential diagnosis and identification of intra-articular pathologies.
Thus, diagnosis and choice of treatment tactics are quite labor-intensive procedures. The European College of Rehabilitation has developed guidelines that should lead to simplified choice of therapy and, ultimately, improved treatment outcomes.
They offer the following evaluation options:
- Symptoms: (1) pain (location and type) or (2) instability problems.
- Lower extremity configuration: (1) asymmetrical patella, (2) high Q angle, (3) genu valgus, (4) knee recurvation, (5) subtalar joint pronation.
- Patellar position: (1) patellar high, (2) patellar low, (3) patellar displacement, (4) patellar inclination, (5) patellar rotation.
- Muscles and soft tissues: (1) wasting of the vastus medialis, (2) imbalance between the vastus medialis and vastus lateralis, (3) weakness of the knee extensors and hip flexors and abductors, (4) tightness of the medial patellar retinaculum, ( 5) tension in the lateral muscle structures, hamstrings and/or rectus femoris.
- Knee function (pain and/or changes in the trajectory of the patella): during various types of physical activity, such as walking up stairs, exercises on a step platform, and single-leg squats.
The Kujala Anterior Knee Pain Scale (AKPS), which was developed for patients with anterior knee pain, can be used to screen for patellofemoral pain in adolescents and young adults. Ittenbach et al suggest that this questionnaire is highly reliable ( it has shown good test-retest reliability), but it is not without limitations and further research is needed into its use outside the clinical environment and in the general population.
The Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS) is an additional self-assessment test to assess the patient's difficulty in physical activity. This scale is less specific for patients with BPACS than the AKPS questionnaire described above, however, it also has high test-retest reliability.
How to sign up for diagnostics?
To apply for an appointment with a radiologist, just use the capabilities of the mrt-v-spb.ru portal:
- fill out a short form on the website so that the manager will contact you using the specified contact information;
- Call the support service yourself.
The company's operators receive calls and provide consultations daily from 8:00 to 00:00. With their help, you can find a clinic near your home or work, find out about hot promotional offers and book an appointment with a doctor at a convenient time. Call now and receive a diagnostic bonus of up to 1000 rubles!
Choice of treatment tactics
In the presence of a bony abnormality or dysfunction of the patellar retinaculum, conservative treatment may be less successful. However, surgical treatment should only be considered when individuals with correctable anatomical abnormalities have failed conservative therapy.
Physical therapy
Knee Mobilization Technique
To achieve long-term results, you must first correct postural imbalances and altered movement patterns before moving on to a strengthening program. When assessing functional impairment and compensatory patterns, the entire lower extremity should be tested. Significant discrepancies in leg length should be corrected as this is a precipitating factor. Eng et al. believe that for patients with BPACS, orthosis along with exercises gives better results compared to exercises alone. However, any exercise and/or stretching program should be individualized depending on the symptoms and movement dysfunctions present.
If the patellar retinaculum is tight and negatively affecting the patellofemoral joint, manual techniques and McConnell knee taping can be used. There is evidence that knee taping combined with exercise provides superior pain reduction compared to exercise alone. Treatments such as proprioceptive training, taping and orthotics are best used as an adjunct to traditional physical therapy—research shows they are not as effective when used alone.
Improving eccentric muscle control is more effective than concentric exercises. Moreover, exercises in a closed kinematic chain are more functional and minimize the load on the patellofemoral joint. Patients with BPACS show decreased knee extensor strength as well as vastus medialis strength, although Witvrouw et al. came to the conclusion that the vastus medialis muscle cannot work in isolation. Vastus medialis weakness is thought to be caused by neuromuscular dysfunction.
The length of the hamstrings, the gastrocnemius and rectus femoris, influences patellofemoral mechanics. Tight hamstrings lead to increased reaction force at the patellofemoral joint level, since in this case the quadriceps muscle works with greater force. Therefore, regular stretching of hamstrings is recommended.
However, according to Mason et al, who compared the effectiveness of stretching exercises, quadriceps strengthening exercises, and taping (isolated and in combination), isolated stretching and quadriceps strengthening resulted in better results than taping. They also concluded that a combination of these techniques is recommended as an initial approach to treating patellofemoral pain, but that further individualized treatment is more functional. Global treatment is also important.
Conclusion
Anterior knee pain is a symptom, not a diagnosis. Making a diagnosis requires taking into account many pathologies that may be suspected during the analysis of the clinical picture and testing of the patient. There is also a high correlation between BPACS and hip biomechanical impairment, so any assessment must include the entire kinetic chain. Treatment is highly individualized and the European Rehabilitation College guidelines are a useful tool for choosing a non-operative treatment protocol.
Treatment method for knee pain
It is difficult to immediately determine what problem a person has with his knee. For a correct diagnosis, sometimes a simple x-ray in several projections is enough, especially in the later stages of development, when damage and bone growths are visible to the naked eye. However, at first, when the pain is minor, x-rays may not reveal microscopic damage. Therefore, the best examination option is considered to be an MRI of the knee joint, thanks to which (without irradiating the patient) high-quality images of the required area of the musculoskeletal system are obtained from all angles. If you want to be absolutely sure of your diagnosis, discuss the need for such an examination with your doctor. In addition to a visual examination, in most cases, doctors can take tests or, in some cases, perform arthroscopy - an operation designed to closely examine the bone and cartilage and correct changes in the condition of the elements of the knee joint. This surgery is performed if the images do not provide all the information needed. Each course is prescribed individually, depending on the causes of pain, the stage of development of a particular disease and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Most often, the course includes: Medicines.
Depending on the nature of the problem, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and other metabolic drugs are included.
Massage and physiotherapy.
Such effects have a beneficial effect on blood flow and improve metabolic processes in the affected area, due to which the vitamins and minerals entering the body are better absorbed.
Therapeutic gymnastics classes.
They are prescribed from the very first day, and, like physical therapy, promote good blood flow.
In addition, in the final stages of recovery, it is training that allows you to develop the joint well. Diet.
A very important factor influencing the speedy correction.
Proper nutrition, following a diet, excluding harmful foods from it and including healthy ones will always have a beneficial effect on the body, and sometimes will allow you to lose weight, which is very important for arthrosis and arthritis. Attention! To protect yourself from knee problems in the future, take care of yourself - maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat right, and stop smoking and alcohol. If you have had similar unpleasant situations in your family, monitor the level of calcium and other elements in the blood. Eat more proteins, vegetables and cereals, as well as various fruit jellies.