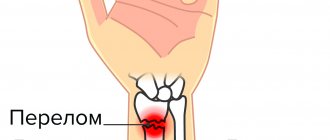
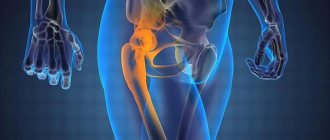
A hip fracture is a dangerous injury, most often found in older people due to increased bone fragility. Although it can also be diagnosed in young and middle-aged people who have been involved in serious accidents, fallen from a height, etc. It accounts for about 6% of all cases of fractures.
When a femoral neck is fractured, the fragments heal poorly, so conservative therapy is ineffective and is used only if it is impossible to perform the desired type of surgery. Moreover, this injury, especially in older people, can cause the development of fatal complications that claim the lives of about 30% of victims. Therefore, it is extremely important to diagnose a fracture of the femoral neck as early as possible, carry out treatment appropriate to the situation and help the patient to properly recover from the injury.
Total information
Most often, this pathology affects elderly and senile people - even if they have not had any disorders throughout their lives that would lead to weakening of bone tissue, one way or another they appear in old age as a result of “wearing out” of bone tissue. But a minimal physical impact on the femur is still necessary for a pathological fracture to occur - often this can even be simply the pressure of one’s own body weight.
Important
The processes of demineralization are of greatest importance for the formation of a pathological fracture of the femur - they can underlie a number of pathologies. This is the most common common cause of the described pathology.
Of all the structures of the femur with the described pathology, the neck most often suffers.
The biggest problem that arises with this type of injury is the difficulty of healing, since it occurs against the background of pathological changes in bone tissue.
For this reason, the periods of bed rest are delayed, which entails the development of complications not directly related to the pathology of bone tissue - these are:
- bedsores;
- congestive pneumonia;
- pronounced contractures.
Conservative treatment
Advertising:
Conservative therapy for a hip fracture is prescribed only if the patient is over 85 years old or has contraindications to surgery.
Also, surgery is not prescribed if the fracture has a horizontal stripe or the injury is localized at the base.
The main methods of conservative treatment are skeletal traction and derotation boot. They are aimed at immobilizing the articular bone, which promotes rapid tissue restoration at the site of damage.
Skeletal traction is used extremely rarely for people over 80 years of age, as it is a rather labor-intensive and painful procedure. The injured bone is connected with a special knitting needle and fixed with a splint with additional weight, the weight of which can reach 2-3 kg. Most often this method is used for horizontal fractures.
A derotation boot is a plaster splint equipped with a transverse bar that prevents movement of the limb.
Thanks to this plaster construction, the leg is slightly retracted to the side - this ensures optimal immobilization and restoration of bone tissue.
When conservative therapy is prescribed, treatment of elderly patients over 80 years of age is carried out on an outpatient basis and takes up to 8-10 weeks.
Causes
The most common causes of a pathological fracture of the femur are the following types of disorders:
- neoplasms;
- osteodystrophy - a group of diseases and secondary pathological conditions that arise due to local metabolic failure;
- dysplasia – diseases in which there is a violation of the development of the femur:
- infectious lesions.
The first two groups of pathologies more often than others lead to a pathological fracture of the femur.
The disorders against which the described pathology usually appears include:
- solitary cysts are single cavity formations with liquid contents inside. According to statistics, a pathological fracture of the femur is observed in 50-60% of diagnosed cases of solitary cysts;
- giant cell tumors;
- Paget's disease is a violation of the process of recycling (reuse) of substances in the body, in which new bone tissue must replace the old, worn one;
- Recklinghausen's disease is a genetic disease that manifests itself in a variety of tumors and in which, among others, bone structures are affected.
With tumors, pathological fracture of the femur occurs in 35-50% of diagnosed cases, with Paget's and Ricklenhausen's diseases - in 40-50%.
Tumors, in particular malignant ones, play a special role in the occurrence of the described pathology. These may be tumors:
- primary – those that appeared during the degeneration of normal tissue;
- metastatic - neoplasia that is formed when cells from malignant tumors of another localization enter through the blood or lymph flow.
Pathological fracture of the femur often develops with metastatic tumors. A characteristic feature of such damage is that not one fracture occurs, but several. The described pathology often appears against the background of such malignant lesions of the femur as:
- myeloma is a malignant blood disease that occurs due to a malfunction of plasma cells in the bone marrow;
- hypernephroma – malignant neoplasm of the kidney;
- kidney cancer is a malignant tumor of the kidney that forms from the epithelium;
- osteoplastic bone carcinosis – tumor pathology in the form of multiple metastases;
- osteoclastic sarcoma is a tumor that develops in the form of bone plates and spines located in an oblique direction or perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the bone.
Benign tumors of the femur can also be complicated by fractures, but not as often as malignant ones. This:
- chondromas - tumors from the tissue of cartilaginous articular surfaces;
- Osteomas are neoplasms from the bone tissue itself.
The group of diseases of a dystrophic nature, against the background of which a pathological fracture of the femur often develops, includes:
- osteomalacia – increased flexibility of bone structures, which occurs against the background of their reduced mineralization;
- osteoporosis – increased bone fragility that appears with reduced mineralization;
- osteochondrosis – a disorder of the structure of bone tissue that develops against the background of a degenerative process;
- osteosclerosis – increased production of connective tissue, which can replace bone;
- Rickets is an abnormal formation of bones due to a lack of calcium salts in the body and their impaired metabolism.
note
Osteoporosis is one of the most common causes of pathological fracture of the femur. Against this background, the described damage most often occurs in postmenopausal women - as a rule, this is damage to the femoral neck.
Diseases of bone tissue of a dystrophic and dysplastic nature, which can provoke the occurrence of a pathological fracture of the femur, can be not only acquired, but also congenital - appearing due to a failure in the intrauterine development of the unborn child. Thus, in some cases, osteopsatirosis is diagnosed - congenital fragility of bone structures. This is often a systemic disease - that is, it affects many bone structures, including the femur.
Among the infectious lesions, the background for the occurrence of the described pathology can be:
echinococcocosis is a disease that is caused by helminths from the cestodiasis group and is characterized by the formation of parasitic cysts (cavities with a thin wall and liquid contents containing many parasites) in various organs;- tuberculosis is a specific infectious pathology caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Koch bacillus). A pathological fracture of the femur often occurs against the background of secondary bone tuberculosis;
- osteomyelitis – the formation of a purulent-necrotic focus in the bone structures with the subsequent formation of fistulas or fistulas (pathological tracts);
- tertiary syphilis - infection with Treponema pallidum.
Pathological fragility of the femur can also be observed with pathologies such as:
- osteogenesis imperfecta is a hereditary systemic skeletal disease in which collagen formation deteriorates;
- osteoarthropathy - chronic non-inflammatory lesions of the joints and articular ends of articulating bones (in this case, involving the femur);
- scurvy is a lack of vitamin C. A pathological fracture of the femur with this disease most often occurs in childhood.
Bone tissue disorders with the subsequent occurrence of a pathological fracture of the femur also occur with the following diseases:
- syringomyelia is a chronic progressive lesion of the central nervous system, in which cavities form in the spinal cord;
- Taste of the spinal cord is a type of late neurosyphilis (tertiary syphilis). It is characterized by damage to the spinal nerve branches and posterior columns of the spinal cord;
- osteosclerosis of various origins.
A pathological fracture of the femur can occur against the background of neurogenic disorders - mainly paresis and paralysis of both traumatic and non-traumatic origin.
The stated reasons play a different role in the occurrence of pathological fractures of the femur. Thus, microfractures, which can be diagnosed with a delay, always form with osteochondropathy; this is somewhat less common with congenital syphilis and childhood scurvy. Even less commonly, a pathological fracture of the femur occurs with osteomalacia and rickets.
This pathology can also occur due to a violation of the integrity of the callus, which forms after a traumatic fracture of the femur.
A special case is a pathological fracture of the femur that occurs due to ankylosis - complete immobility of the joint, resulting from injury, arthrosis or arthritis. In this case, a pathological fracture can occur due to ankylosis of the hip or knee joints, in the formation of which the femur takes part. The mechanism of occurrence of such a violation is as follows. The patient makes some movement with the lower limb, but the load falls not on the motionless joint, but on the weakened part of the bone, which causes it to break.
Recovery Features
After treatment in one way or another and consolidation of bone fragments, patients enter a period of rehabilitation, which is carried out at home or in specialized centers. In the first case, older people and their loved ones will need to strictly follow the recommendations received from their attending physician and take prescribed medications. Also shown during this period:
- exercise therapy;
- massotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- diet.
In general, this stage has much in common with conservative treatment for a femoral neck fracture, but does not require immobilization. The duration of recovery largely depends on the chosen method of treatment and the individual characteristics of the patient.
If rehabilitation takes place at home, the injured elderly person will need to purchase a specialized bed with an anti-decubitus mattress and a special frame. If material resources do not allow this, it is necessary to re-equip the existing bed and replace the usual mattress with a harder and higher one. A rope is installed at the foot of the bed, which will act as reins. With its help, the patient will be able to get up and out of bed independently.
Diet is also given a lot of attention. To fully restore the body, you will need to switch to the most balanced diet, which will contain all the necessary minerals, vitamins, amino acids, etc. in proper quantities. Therefore, it is important to provide the elderly person with a varied diet, which will include fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, meat and offal, cereals, fish and seafood. At the same time, you will need to avoid spicy, fried, fatty, smoked foods, as well as carbonated drinks, alcohol and coffee.
In order for recovery to proceed as successfully as possible and without complications, patients themselves need to avoid deep bending, sitting on low chairs, sleeping on an injured limb, crossing their legs and some other actions.
Since the rehabilitation period is quite difficult from a psychological point of view even for the most cheerful pensioner, it is important to support him and provide him with interesting leisure time.
The patient’s relatives will need to constantly help him even with basic hygiene procedures, make sure that he does not remain in one position for a long time to avoid the formation of bedsores, regularly change his underwear, etc. It is also important to follow the recommendations received from the doctor and help your elderly loved one perform breathing exercises, Exercise therapy.
To facilitate the patient’s movement, it is worth installing handrails or other supporting structures around the perimeter of the room in which he lives. It is also recommended to carry into it all the things that an elderly person may need and place them so that they are at hand.
A very common problem that many older people face when treating and recovering from a femoral neck fracture is constipation. To avoid its occurrence, it is recommended that the patient drink plenty of fluids and, if necessary, use mild laxatives. At the same time, the toilet should also be converted by installing a special lining on it to increase the height. This will protect the hip joint from excessive stress and re-injury.
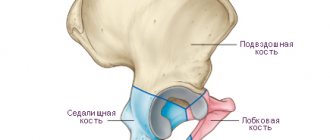
Development of pathology
There are a number of pathological fractures of the femur. Their classification reflects the general classification of such damage. Depending on the location of the fracture line, there are pathological fractures:
- hip joint;
- femoral neck;
- diaphysis;
- condylar.
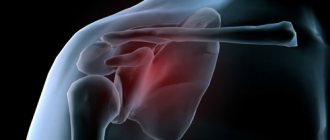
In turn, pathological fractures of the hip joint are divided into:
- major – fracture of the femoral head;
- subcapital – damage below the head of the femur;
- pertrochanteric.
Avulsions of the greater and lesser trochanters due to pathology of the femur are rarely diagnosed.
Pathological fracture of the femoral neck occurs:
- transcervical – the cervix itself is injured;
- basicervical - the fracture line passes at the base of the cervix.
A diaphyseal pathological fracture of the femur is a violation of the integrity of the diaphysis - that part that is located between the two epiphyses (ends of the bone). Such fractures are most often accompanied by displacement of bone fragments. If there is trauma to the upper third of the bone, then under the influence of the gluteal muscles the fragments are displaced in different directions; if there is damage in the lower third of the femur, the gastrocnemius muscle pulls the bone fragments in the posterior direction.
Condylar pathological fractures of the femur are also diagnosed somewhat less frequently. They are detected in the lower segment of the femur, which takes part in the formation of the knee joint.
Significant displacement of bone fragments in a pathological fracture of the femur is observed quite rarely. In this case, the following types of violations may occur:
- compression lesions (indentations);
- large cracks;
- spyglass-shaped fractures. These are specific transverse injuries in which the thinned cortical layer of one bone fragment literally slides onto another bone fragment.
Surgical treatment and prosthetics
Advertising:
Surgical intervention is possible only if there are no contraindications associated with age and chronic diseases. During the operation, punctures and fragments are fixed - this leads to faster rehabilitation and restoration of the damaged bone.
Main types of surgical operations:
- Osteosynthesis is the fastening of damaged bone elements with special metal structures. Most often, this operation is performed on patients under 65-70 years of age.
- Installation of a bipolar prosthesis is prescribed for patients in the age category from 70 to 80 years.
- Unipolar hip replacement is considered the best option for elderly patients.
In the process of unipolar endoprosthetics, the femoral head is removed and replaced with an artificial implant. Surgical intervention takes a minimum of time and is considered the safest and most gentle for elderly patients.
For complex, labor-intensive and multi-level surgical procedures, special fixing screws, three-blade nails, and dynamic hip screws can be additionally used.
Symptoms of a pathological hip fracture
A distinctive feature of a pathological fracture of the femur is the mild severity of symptoms compared to traumatic fractures. Characteristic signs are:
- pain;
- swelling of soft tissues.
Characteristics of pain:
- by location - in the area of the fracture;
- in terms of distribution - without any typical irradiation;
- by nature - aching;
- in terms of intensity - unexpressed, can increase with the physical activity of the victim (in this case, the fragments are displaced and affect the nerve structures);
- by occurrence - they arise at the moment of fracture, but they are often not given importance.
Swelling in the area of the fracture is mild, and in some cases may be absent.
Before the appearance of a pathological fracture, a specific clinical picture may be observed, which should alert you - this is:
- bone deformities;
- strange spontaneous pain;
- soreness in the femur on exertion.
Important
Often, a pathological fracture of the femur is the first manifestation of any bone disease. If a fracture is diagnosed, but there was no trauma as such, then the victim must be examined for systemic pathologies that could lead to a pathological fracture of the femur.
Pathological mobility and crepitus in the described pathology are not determined. Bleeding is mild or not clinically manifest.
Diagnostics
The weak severity of clinical manifestations makes diagnosis difficult for a pathological fracture of the femur. Therefore, it is important to conduct additional research methods.
From the anamnesis, it becomes clear whether the victim suffered from systemic pathologies, whether he had pain in the area of the femur when performing physical activity.
The results of a physical examination are not very informative - the patient’s general condition may be normal, and measurement of the lower extremities will also not always indicate the presence of the described pathology.
Instrumental diagnostic methods are mandatory:
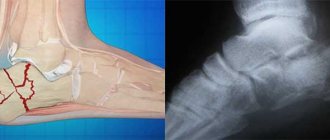
- X-ray examination - it is most important in identifying a pathological fracture of the femur. Pictures are taken in two projections, the fracture line and displacement of fragments (if any) are revealed;
- computed tomography (CT) – used in controversial cases. Computer sections will help assess the condition of bone tissue more than radiography;
- Magnetic resonance examination (MRI) – in addition to assessing the condition of bone tissue, it will help analyze the condition of soft tissue in the area of damage;
- scintigraphy – the patient is intravenously injected with a pharmaceutical drug containing radioactive isotopes, it is distributed in the body and, during a tomographic examination, creates a color image, which is used to evaluate the condition of the bone tissue. This method is the most informative in cases of tumor origin of a pathological fracture of the femur - scintigraphy allows diagnosing metastatic lesions four times more often than conventional radiography;
- Densitometry is a non-invasive method for determining bone mineral density;
- biopsy – removal of bone tissue for examination under a microscope. Allows you to identify pathology that could lead to weakness of bone tissue with subsequent formation of a pathological fracture.
Laboratory testing also plays a role in diagnosing diseases that could lead to the formation of a pathological fracture of the femur. This:
general blood test - an increase in the number of leukocytes (leukocytosis) and ESR indicates an inflammatory process, a sharp increase in ESR signals the presence of a malignant tumor;- biochemical blood test - during osteolytic processes that can provoke the development of pathological fractures, hypercalcemia (increased calcium levels in the blood) is often detected; in osteoplastic disorders, a decrease in the amount of calcium and an increase in the level of alkaline phosphatase in the blood serum are noted;
- urine analysis - a large amount of calcium is detected in it;
- microscopic examination - a biopsy specimen is studied under a microscope, and first of all, the tumor nature of the disease that provoked the appearance of a pathological fracture of the femur is excluded or confirmed.
Rehabilitation after a hip fracture in the elderly
Due to their advanced age, it is more difficult for older patients to choose medications, therapy and rehabilitation methods. If surgery is needed, the issue of tolerability of general anesthesia, as well as other associated ailments, is decided. An operation cannot be performed on an elderly person if he has a diseased heart, lungs, or kidneys.
It is unknown how long treatment and rehabilitation will last for a hip fracture. Sometimes old people don’t recover at all.
When the body is immobilized and constantly remains in a horizontal position, all body functions are disrupted and other diseases develop.
Due to this lifestyle, an elderly person, forced to endure constant pain and dependence on outside help, develops psychological problems. Both physical and emotional states suffer from complete immobility of the body.
However, it must be said that not all situations are hopeless; there are cases of recovery.
Rehabilitation measures include treatment, physical exercise, and therapeutic massage. To restore full blood circulation, massage both legs.
Examples of exercises:
- strengthening muscles with the help of a gymnastic stick suspended above the patient’s bed, which he will reach.
- in the second stage of the recovery period, it is allowed to move the lower limbs, gradually increasing the amplitude.
- Before lifting the patient out of bed, he is taught how to turn from different sides and how to lift the pelvis.
You can use folk remedies to speed up recovery:
- To improve blood circulation, prepare an ointment with linden honey, dry mustard, salt (it’s good if it is obtained from the Dead Sea). Rub the mixture into the injured area.
- Oak bark mixed with butter and black poplar buds (2:7:1) will help cope with bedsores. Place the prepared composition in a dark place overnight. The next morning, keep the mixture in a water bath. Drain everything into a jar. Lubricate bedsores with ointment.
- If a person lies for a long time, he may develop pneumonia. Prepare the following mixture: mix warm cheese with honey. Apply the mixture to the cloth and then to your chest. Cover the top with thin paper and a fine woolen cloth.
- Cough is treated with warm milk and figs.
- Shilajit with the addition of rose oil perfectly restores bone tissue.
- Eating foods high in calcium is helpful for faster bone healing.
The rehabilitation period is more easily tolerated by people who have adhered to a healthy lifestyle all their lives, performed therapeutic physical exercises, and ate foods with calcium. In addition, rapid healing of the fracture is guaranteed with timely treatment and high-quality qualified care.
Restorative measures include regular massage, which should be used in conjunction with physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises. Psychotherapeutic prevention is successfully used to eliminate depressive conditions in older people associated with immobility, helplessness and pain.
The initial set of exercises, prescribed a week after the fracture, includes simple exercises.
- The patient flexes and extends the healthy limb and rotates the foot. The same movements are repeated with the injured leg, reducing the load and making sure that it does not hurt.
- An elderly patient sits on the bed with his feet on the floor. The patient should, slightly straining his muscles, press his feet onto the floor.
- While resting, the patient leans slightly towards the healthy leg. It is necessary to try to straighten and bend the other limb at the knee.
After the cast is removed, the exercises become increasingly more difficult. Exercise includes walking with crutches, a walker, or a cane. A positive result is possible only with desire, perseverance and confidence in success.
We recommend
“How to care for a bedridden elderly person” Read more
Complications
The most common complications of a pathological fracture of the femur are:
- contracture - impaired mobility in the joints in the formation of which the femur takes part;
- ankylosis - complete immobility.
It is also possible to develop complications that arise due to the fact that such patients remain in bed for a long time:
- muscle wasting – weakening;
- bedsores - tissue necrosis in the place where the bone is close to the skin;
- thrombophlebitis - inflammation of the venous wall and the formation of a blood clot in this place;
- trophic ulcers – the formation of soft tissue defects due to a violation of their nutrition;
- congestive pneumonia – inflammation of the lungs due to poor air circulation.
Early mobilization
If surgical intervention is not possible, rehabilitation after a femoral neck fracture is carried out using the method of early mobilization. It is also used if it is not possible to provide long-term immobilization of the joint.
The essence of early mobilization is the use of skeletal straightening for a short period of time - up to 7-10 days.
Immediately after this, the person is allowed to try to lower his legs from the bed and stand up. After 2 weeks, the elderly man or woman is recommended to try to rise from the bed using crutches.
In this case, you need to carefully ensure that the load does not fall on the injured limb - only on the healthy one. A feature of early mobilization is that it does not lead to complete fusion of damaged bone tissue. As a result, it is impossible to achieve full restoration of the functionality and mobility of the leg. Subsequent movement of the patient is possible only in a wheelchair or using crutches.
Treatment of pathological hip fracture
Complex treatment of a pathological fracture of the femur includes therapy for the disease that provoked it.
The fracture itself requires surgical intervention - thanks to it:
- hospital treatment time is reduced;
- makes patient care easier;
- early activation of the victim becomes possible;
- the risk of complications is reduced.
The extent of the operation also depends on the type of pathology that caused the fracture:
for benign neoplasms, resection of the affected area is performed in combination with osteosynthesis (fastening of fragments). If a large tissue defect occurs, replacement is performed with an allo- or homograft in combination with osteosynthesis;- if a joint or periarticular area is damaged, endoprosthetics is performed - replacing the joint with an artificial one;
- if a violation of the integrity of the diaphysis is diagnosed, the damaged area is strengthened with bone cement or the defect is replaced with a graft.
Bone fragments are fixed using nails, plates, pins, screws or an Ilizarov apparatus.
During the rehabilitation period, exercise therapy and sufficient consumption of food enriched with microelements and vitamins are important.
Endoprosthetics
In cases where the tumor is small and localized within clear boundaries, it is removed indented within healthy tissue. The deleted area is recreated.
If the tumor spreads significantly, it is necessary to remove a large fragment of bone or the entire bone. To recreate it, the international clinic Medica24 uses modular prostheses.
Such designs are today recognized as the “gold standard” for prosthetics after operations for bone tumors. The main advantage of modular endoprostheses is that they can be used to recreate a bone of any length with a joint or two joints.
This does not require making an individual prosthesis in each case. The modular design allows them to be perfectly and quickly adjusted on site.
The endoprostheses used in our clinic are distinguished by high reliability, durability, absolute bioinertness, high manufacturability, perfect biomechanics and functionality.
The material was prepared by oncologist, traumatologist-orthopedist of the international clinic Medica24 Andemir Olegovich Akhov.
Prevention
Measures to prevent pathological fracture of the femur are:
- prevention of diseases that lead to weakening of the bone tissue of the femur; if they occur, timely detection and treatment;
- strengthening bone tissue. This is facilitated by a balanced diet with a sufficient amount of vitamins and microelements, giving up bad habits, and exercising;
- creating favorable conditions for the course of pregnancy - this will help reduce the risk of intrauterine disorders, against which a pathological fracture of the femur often occurs.
Forecast
The prognosis for a pathological fracture of the femur is different - it depends on the disease that provoked the described disorder. At a young age, the manifestations of a fracture are not critical; in general, the prognosis is favorable, but one should be prepared for a long recovery. In old age, pathological fractures of the femur (in particular, its neck) often result in death due to severe complications.
If the provoking pathology is not stopped, relapses of fractures may occur.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
9, total, today
( 49 votes, average: 4.43 out of 5)
Post-traumatic arthrosis of the knee joint
Purulent arthritis: what happens and how to treat